Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CE 55 Water Resources Engineering Reservoir Building Processes
Uploaded by
Joee Naguio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views16 pagesThis document discusses key concepts in water resources engineering related to reservoir building processes, site selection, zones of storage, safe yield, and reservoir capacity. It outlines investigations like engineering surveys, geological investigations, and hydrological investigations that are conducted. It describes factors considered in site selection like storage capacity, river valley characteristics, and cost. It defines zones of storage such as full reservoir level, minimum pool level, and dead storage. It also covers concepts like safe yield, average yield, design yield, and how reservoir capacity depends on inflow and demand.
Original Description:
Requirements for reservoir building process
Original Title
Reservoir Building Process
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key concepts in water resources engineering related to reservoir building processes, site selection, zones of storage, safe yield, and reservoir capacity. It outlines investigations like engineering surveys, geological investigations, and hydrological investigations that are conducted. It describes factors considered in site selection like storage capacity, river valley characteristics, and cost. It defines zones of storage such as full reservoir level, minimum pool level, and dead storage. It also covers concepts like safe yield, average yield, design yield, and how reservoir capacity depends on inflow and demand.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views16 pagesCE 55 Water Resources Engineering Reservoir Building Processes
Uploaded by
Joee NaguioThis document discusses key concepts in water resources engineering related to reservoir building processes, site selection, zones of storage, safe yield, and reservoir capacity. It outlines investigations like engineering surveys, geological investigations, and hydrological investigations that are conducted. It describes factors considered in site selection like storage capacity, river valley characteristics, and cost. It defines zones of storage such as full reservoir level, minimum pool level, and dead storage. It also covers concepts like safe yield, average yield, design yield, and how reservoir capacity depends on inflow and demand.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
CE 55
Water Resources Engineering
RESERVOIR Building Processes
Investigations
●
Engineering surveys
●
Geological investigations
●
Hydrological investigations
Engineering surveys
●
For dams, reservoirs and other associated work
●
Topographic survey of the area and produce
contour maps
●
Horizontal control provided by triangulation and
vertical control by precise levelling (Currently
done by GIS)
Geological investigation
●
Suitability of foundation for the dam
●
Watertightness of the reservoir basin
●
Quarry sites for construction materials
Hydrological investigation
●
Runoff pattern and storage capacity
●
Determine maximum discharge at the site
Site Selection
●
Large storage capacity
●
River valley should be narrow, for lesser dam
length
●
Watertightness of reservoir
●
Good hydrological conditions
●
Deep reservoir
●
Small submerged area
Site Selection
●
Low silt inflow
●
No objectionable minerals
●
Low cost of real estate
●
Site easily accessible
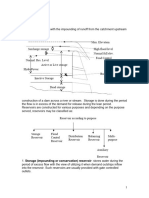
Zones of Storage
Zones of Storage
●
Full Reservoir Level (FRL) – highest water level
during normal operating conditions
●
Maximum Water Level (MWL) – maximum
water level at which surface will rise when the
design flood passes over the spillway
●
Minimum Pool Level (MPL) – lowest level up to
which water is withdrawn from reservoir under
ordinary conditions
Zones of Storage
●
Dead Storage – volume of water held below
minimum pool level; to cater for sediment
deposition; normally equivalent to volume of
sediment expected to be deposited in the
reservoir during its design life
●
Live/Useful Storage – volume of water between
FRL and MPL
Zones of Storage
●
Bank storage – developed in voids of soil cover
in the reservoir area; becomes available as
seepage when water levels drop; increases
reservoir capacity over and above that given by
elevation storage curves
●
Valley storage – volume of water held by natural
river channel before the construction of a
reservoir
Zones of Storage
●
Flood/Surcharge storage – volume between
MRL and FRL; varies with spillway capacity of
dam for given design flood.
Safe Yield
●
Yield – volume of water which can be withdrawn
from a reservoir in a specified period of time
●
Safe Yield – maximum quantity of water which
can be supplied from a reservoir in a specified
period of time during a critical dry year
●
Secondary Yield – volume available during the
period of high flow when yield si more than safe
yield
Safe Yield
●
Average Yield – arithmetic average of firm yield
and secondary yield over a long period of time
●
Design Yield – yield adopted in the design of
the reservoir; usually fixed after considering the
urgency of the water needs and the amount of
risk involved
Reservoir Capacity
●
depends upon the inflow available and demand
●
if inflow in the river is greater than demand,
then there is no storage required
●
if inflow in the river is small but the demand is
high, a large reservoir capacity is required
Reservoir Capacity
●
Required capacity can be determined by
– Graphical method using mass curves
– Analytical method
You might also like
- Principles of Irrigation Engineering – Arid Lands, Water Supply, Storage Works, Dams, Canals, Water Rights and ProductsFrom EverandPrinciples of Irrigation Engineering – Arid Lands, Water Supply, Storage Works, Dams, Canals, Water Rights and ProductsNo ratings yet
- CE 55 Water Resources Engineering: RESERVOIR Building ProcessesDocument16 pagesCE 55 Water Resources Engineering: RESERVOIR Building ProcessesShyn Marie MijaresNo ratings yet
- Hydro - ReservoirDocument25 pagesHydro - ReservoirKristan Rae GaetosNo ratings yet
- Reservoir PlanningDocument28 pagesReservoir PlanningprasitagnihotriNo ratings yet
- 02a - Reservoir CapacityDocument54 pages02a - Reservoir CapacitymowrieNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 18 Batch Part 7 1Document123 pagesHydrology 18 Batch Part 7 1Saèéɖ HaiderNo ratings yet
- Reservoirs and PlanningDocument46 pagesReservoirs and PlanningSAVYA SAACHEINNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ResrevoirDocument35 pagesChapter 2 ResrevoirÅdän Ahmĕd DâkañeNo ratings yet
- ReserviorDocument49 pagesReserviorUJJWALNo ratings yet
- Planning and Analysis of Reservoir StorageDocument56 pagesPlanning and Analysis of Reservoir Storagekamagara100% (2)
- Chapter Three: Sources of Water SupplyDocument22 pagesChapter Three: Sources of Water SupplyBINIAM MEBRATENo ratings yet
- HS Chapter 1Document50 pagesHS Chapter 1alexNo ratings yet
- Reservoirm3 120625050413 Phpapp01Document49 pagesReservoirm3 120625050413 Phpapp01Anonymous 3q9Nkyy92No ratings yet
- 9 Reservoir Planning and Storage AnalysisDocument56 pages9 Reservoir Planning and Storage AnalysisDelina TedrosNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Planning and ComponentsDocument31 pagesReservoir Planning and ComponentsSarah Mae Gonzales100% (1)
- WRE-2 Practical Tutorial-5 Numerical Problem On Reservoir and SedimentationDocument42 pagesWRE-2 Practical Tutorial-5 Numerical Problem On Reservoir and SedimentationRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Our Presentation On Roge Small Scale Irrigation Project: Welcome ToDocument24 pagesOur Presentation On Roge Small Scale Irrigation Project: Welcome ToMisgan engineeringNo ratings yet
- Headwork (Diversion Weir) Design - For AGP SSIP-by AberaChalaDocument49 pagesHeadwork (Diversion Weir) Design - For AGP SSIP-by AberaChalaAbera ChalaNo ratings yet
- Fish PondDocument52 pagesFish PondDominic LuceroNo ratings yet
- ReservoirsDocument11 pagesReservoirsRonit ChariNo ratings yet
- FDDocument74 pagesFDShita AlemieNo ratings yet
- RESERVOIR ENGINEERING TOPICSDocument101 pagesRESERVOIR ENGINEERING TOPICSFarhan KaziNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Reserviour PlanningDocument26 pagesUnit-3 Reserviour Planningsushanth kumarNo ratings yet
- DamsDocument13 pagesDamsQudratullah Ehsan0% (1)
- ReservoirDocument46 pagesReservoirtom stuartNo ratings yet
- Reserviors PlanningDocument49 pagesReserviors PlanningÇhårū KêshNo ratings yet
- Water Resources ReportDocument10 pagesWater Resources ReportChristian BaldoNo ratings yet
- GeologyDocument13 pagesGeologyLimgeeGideonz50% (2)
- Reservoir, It's Purposes, Classification of ReservoirDocument19 pagesReservoir, It's Purposes, Classification of ReservoirFaizan PathanNo ratings yet
- Hs-Ii, Lecture On CH-1Document41 pagesHs-Ii, Lecture On CH-1natiz addisNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering NotesDocument7 pagesWater Resources Engineering NotesAlyssa Marie AsuncionNo ratings yet
- RESERVOIR PURPOSEDocument17 pagesRESERVOIR PURPOSEAlyssa Marie AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document39 pagesLecture 2Arsalan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Major Rainwater Harvesting ProjectDocument74 pagesMajor Rainwater Harvesting ProjectGurpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Spillway NOTEDocument74 pagesSpillway NOTEMūssā Mūhābā ZēĒthiopiāNo ratings yet
- Reservoir PlanningDocument5 pagesReservoir PlanningJose GeorgeNo ratings yet
- For Hydrological Design,: I. Roof Harvesting II. Runoff HarvestingDocument42 pagesFor Hydrological Design,: I. Roof Harvesting II. Runoff HarvestingBharathi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Planning TechniquesDocument5 pagesReservoir Planning TechniquesJose George67% (3)
- Irrigation Engg. (CE5G) - Reservior PlanningDocument21 pagesIrrigation Engg. (CE5G) - Reservior PlanningNagendra prajapatiNo ratings yet
- SOMALI REGIONAL PRESENTATION ON INTRODUCTION TO HOW TO CONSTRUCT WOREDA LEVEL SMALL MICRO EARTH FILL DAMSDocument54 pagesSOMALI REGIONAL PRESENTATION ON INTRODUCTION TO HOW TO CONSTRUCT WOREDA LEVEL SMALL MICRO EARTH FILL DAMSSaddam H. MussieNo ratings yet
- Stream Restoration Project Planning and DesignDocument36 pagesStream Restoration Project Planning and DesignPK PhilavongNo ratings yet
- Planning of Water Storage Reservoirs SarahDocument16 pagesPlanning of Water Storage Reservoirs SarahSarah Mae Gonzales0% (1)
- Chapter IDocument109 pagesChapter IephremNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering IIDocument54 pagesWater Resources Engineering IIDIPAK PRASADNo ratings yet
- Resrvoir Storage Design DataDocument11 pagesResrvoir Storage Design DataBabloo JuttNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document72 pagesCH 3Baysa CamadNo ratings yet
- Asmamaw Belay ID 07000694Document37 pagesAsmamaw Belay ID 07000694Zeleke TaimuNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Capacity DeterminationDocument34 pagesReservoir Capacity DeterminationMohamad soltaniNo ratings yet
- ID-710 - Lec 4 PDFDocument18 pagesID-710 - Lec 4 PDFmoazzam mushtaqNo ratings yet
- 01 Design of Hydropower ComponentsDocument212 pages01 Design of Hydropower ComponentsSURAJIT DUTTANo ratings yet
- ECV 502-ResearvoirsDocument22 pagesECV 502-ResearvoirsvediseNo ratings yet
- RESERVOIRSDocument26 pagesRESERVOIRSFelix HabarugiraNo ratings yet
- Layout of Reservoir, Diversion Structures and Other StructuresDocument36 pagesLayout of Reservoir, Diversion Structures and Other StructuresSuman RegmiNo ratings yet
- Construction Features of Hydropower ProjectsDocument36 pagesConstruction Features of Hydropower Projectshamid awelNo ratings yet
- Know Your Dam Failuers R.K.G 01.09Document42 pagesKnow Your Dam Failuers R.K.G 01.09jean-.paulineNo ratings yet
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Deparment Computer Science Information TechnologyDocument18 pagesMirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Deparment Computer Science Information TechnologyMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Nac - Barrages and WeirsDocument91 pagesNac - Barrages and Weirsjonnajon92-1100% (2)
- Reservoir Storage CapacityDocument9 pagesReservoir Storage CapacityPawanKumarNo ratings yet
- Hidrology DAC 20902 Tittle: Wet PondDocument28 pagesHidrology DAC 20902 Tittle: Wet PondPa Alif NunNo ratings yet
- Sheet Wall PilesDocument44 pagesSheet Wall PilesJoee NaguioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Shear Design SP 17-09-07Document37 pagesChapter 2 - Shear Design SP 17-09-07Alex FerrariNo ratings yet
- Joee Urban A3 PDFDocument1 pageJoee Urban A3 PDFJoee NaguioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Shear Design SP 17-09-07Document37 pagesChapter 2 - Shear Design SP 17-09-07Alex FerrariNo ratings yet
- Recycling of Waste WaterDocument14 pagesRecycling of Waste WaterJoee NaguioNo ratings yet
- Gases: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument28 pagesGases: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenAmalia AnggreiniNo ratings yet
- 9A01503 Water Resources Engineering - IDocument4 pages9A01503 Water Resources Engineering - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Module-01 Water Supply Engineering PDFDocument57 pagesModule-01 Water Supply Engineering PDFlalas lalas abdulla100% (1)
- 02 Discharge Relationships Within Drainage BasinsDocument4 pages02 Discharge Relationships Within Drainage BasinsrufaroNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Design, Selecting An EductorDocument3 pagesHydrodynamic Design, Selecting An EductorfifieNo ratings yet
- BSM - Reuse of Water For AgricultureDocument8 pagesBSM - Reuse of Water For AgricultureNidhi Chadda MalikNo ratings yet
- Liquid in Glass Thermometer PrincipleDocument6 pagesLiquid in Glass Thermometer PrincipleInstrumentation ToolsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Avoidance of Vibration Induced Fatigue Failure in Process PDocument5 pagesGuidelines For The Avoidance of Vibration Induced Fatigue Failure in Process PFSAAVEDRAFNo ratings yet
- The First Law of Thermodynamics: Control Volume AnalysisDocument75 pagesThe First Law of Thermodynamics: Control Volume Analysisrizky andrianNo ratings yet
- MIT2 Shapiro 3.05 - SoluDocument4 pagesMIT2 Shapiro 3.05 - SoluDouglas LimaNo ratings yet
- Biogas For Print Model 2Document1 pageBiogas For Print Model 2Berns DulamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Gas and Steam TurbineDocument46 pagesChapter 3-Gas and Steam TurbineHailu FekaduNo ratings yet
- Micro ScaleDocument26 pagesMicro ScaleHager AshrafNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Drive MechanismsDocument36 pagesReservoir Drive MechanismsUsman HasanNo ratings yet
- EASEMENT-OF-AQUEDUCTS Notes PDFDocument16 pagesEASEMENT-OF-AQUEDUCTS Notes PDFJustineNo ratings yet
- Types of Irrigation SystemsDocument10 pagesTypes of Irrigation SystemsDaniel NibotNo ratings yet
- Surface Water Treatment Operator Certification Manual - Tratamiento de Aguas ResidualesDocument311 pagesSurface Water Treatment Operator Certification Manual - Tratamiento de Aguas ResidualesJhon Jairo Mazuera GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Gas Condensate Reservoir Properties and CalculationsDocument14 pagesGas Condensate Reservoir Properties and CalculationsAnonymous nztG1AGvNo ratings yet
- Isentropic Flow - Area VariationDocument11 pagesIsentropic Flow - Area VariationMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet E41001Document6 pagesData Sheet E41001BFEVietnamNo ratings yet
- REVISE- Write only the answers in your rough copyDocument14 pagesREVISE- Write only the answers in your rough copyrituNo ratings yet
- Underground Water PDFDocument16 pagesUnderground Water PDFYuvaraj DNo ratings yet
- Pharaonic Petroleum Company (PHPC) : PHPC Operations Unit SummaryDocument21 pagesPharaonic Petroleum Company (PHPC) : PHPC Operations Unit SummaryramyNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressors For CPI Plants PDFDocument4 pagesCentrifugal Compressors For CPI Plants PDFAmanda Aracely Herreria SalazarNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Sagana National High SchoolDocument17 pagesGas Laws: Sagana National High SchoolHelma Jabello AriolaNo ratings yet
- Water Filtration: MaterialsDocument3 pagesWater Filtration: MaterialsGwyneth Pearl Javier100% (1)
- Everything You Need to Know About PumpsDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About PumpsJireh LoquinarioNo ratings yet
- MATERIAL BALANCES OF A CHLOROBENZENE PLANTDocument4 pagesMATERIAL BALANCES OF A CHLOROBENZENE PLANTMaribel ArcaniNo ratings yet
- 17 Jan Test 1 g112016Document6 pages17 Jan Test 1 g112016Chi NgọcNo ratings yet
- Understanding Production LoggingDocument172 pagesUnderstanding Production LoggingJavier Johnson Lesciur0% (1)