Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prepositions of Time: IN: Native Speakers Use The Preposition IN To Refer To A General, Longer Period of Time
Uploaded by
Marija MicunovicOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prepositions of Time: IN: Native Speakers Use The Preposition IN To Refer To A General, Longer Period of Time
Uploaded by
Marija MicunovicCopyright:
Available Formats
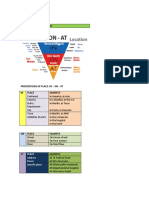
Prepositions of Time: IN
Native speakers use the preposition IN to refer to a general, longer period of time.
In + Parts of the day In + Years In + Periods of time
Examples: Examples: Examples:
In the morning In 1980 In the past
In the afternoon In 1968 In the next century
In the evening In + Decades In the future
In + Months Examples: In the 10 years time
Examples: In the 1960s In the middle ages
In January In the seventies In a few minutes
In February In + Centuries In a moment
In December Examples: In an hour
In + Seasons In the 15th century In 3 hours
Examples: In the 21st century In six months
In (the) spring In + Weeks In a year
In (the) summer Examples: In + Holidays
In (the) fall/autumn In a week Example:
In (the) winter In 2 weeks In the Easter holiday
Prepositions of Time: ON
Moving to more specific periods of time, the preposition ON is used.
On + Days On + Specific days
Examples: Examples:
On Monday On my birthday
On Thursday On holiday
On Sunday On my wedding day
On + Dates On that day
On + Day + Part of day
Examples:
Examples:
On April 3rd
On 1st January 2013 On Sunday morning(s)
On the 10th On Friday afternoon(s)
On the first day On Monday evening(s)
On the last day On + Time
On + Holidays with “day”
Examples: Examples:
On New Year’s day On the weekend (U.S.)
On Christmas day On weekdays
On Easter day On time
On a summer evening
On a cold day
On my lunch break
Prepositions of Time: AT
English speakers use the preposition AT for the most specific times.
At + Hours
Examples:
At 7 am
At 12 o’clock
At 5 pm
At + Parts of the day
Examples:
At night
At noon/ midday
At midnight
At bedtime
At lunch time
At dinner time
At dinner
At lunch
At sunrise/sunset
At dawn
At + Holidays without “day”
Examples:
At Easter
At Christmas
At New Year
At + Time
Examples:
At present
At the weekend (U.K)
At breakfast
At the moment
At this moment
At the same time
At that time
You might also like
- TraderJoes CookbookDocument150 pagesTraderJoes Cookbookjennifer.farris12No ratings yet
- B1+ UNIT 3 Extra Grammar Practice RevisionDocument1 pageB1+ UNIT 3 Extra Grammar Practice RevisionRetox Borukov0% (2)
- Prepositions of TimeDocument19 pagesPrepositions of TimeFelice CardeliaNo ratings yet
- Master IN, ON, AT - Docx1Document15 pagesMaster IN, ON, AT - Docx1A. GHUZZINo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time: By: Rika AnggrainiDocument5 pagesPrepositions of Time: By: Rika AnggrainiPinaSeeYouNo ratings yet
- In, On, at (Time) Unit 120Document5 pagesIn, On, at (Time) Unit 120Phương Trần Thị ThanhNo ratings yet
- Prepositions IN - ON - ATDocument3 pagesPrepositions IN - ON - ATCamilo CordobaNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time !!!Document15 pagesPrepositions of Time !!!Mr PenZoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - This Is What I DoDocument46 pagesUnit 3 - This Is What I Doanthony gNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time - At, In, OnDocument2 pagesPrepositions of Time - At, In, OnpartidalbertoNo ratings yet
- Date and Time: ¿Qué Hora Es? Son Son Aproximadamente ¿A Qué Hora? AlasDocument3 pagesDate and Time: ¿Qué Hora Es? Son Son Aproximadamente ¿A Qué Hora? AlasCarlos GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time In, On, atDocument2 pagesPrepositions of Time In, On, atDennNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of TimeDocument11 pagesPrepositions of TimeDaniel MelloNo ratings yet
- INTERACTIVE ENGLISH Intonation, Adverbs of Frequency & Prepositions of TimeDocument5 pagesINTERACTIVE ENGLISH Intonation, Adverbs of Frequency & Prepositions of TimeRemedios Abiera BianesNo ratings yet
- 15 PrepositionDocument68 pages15 Prepositionayhan.bulentNo ratings yet
- Unidad 16. - at - In.onDocument2 pagesUnidad 16. - at - In.onnorma alicia acevedo ruizNo ratings yet
- General English 5 - PrepositionDocument10 pagesGeneral English 5 - PrepositionMaryam Alimatil AliyahNo ratings yet
- Ketting Formulier, Part 3 (Recovered)Document19 pagesKetting Formulier, Part 3 (Recovered)Yohanan Moraes IsbellNo ratings yet
- Q Skills Level Intro-1-2-3-4 Books RevisionDocument140 pagesQ Skills Level Intro-1-2-3-4 Books Revisionhanaa bin merdah100% (2)
- IN AT ON: Months, Seasons, Years, Centuries and Long Periods Precise Time Days and DatesDocument2 pagesIN AT ON: Months, Seasons, Years, Centuries and Long Periods Precise Time Days and DatesAnonymous LELyuBoNo ratings yet
- Prepositions: - Are Short Words (At, In, On) Which Are Used To Show Position, Location, Direction, and Time in EnglishDocument24 pagesPrepositions: - Are Short Words (At, In, On) Which Are Used To Show Position, Location, Direction, and Time in EnglishNikko EchegorinNo ratings yet
- English Workshop TIME & DATEDocument28 pagesEnglish Workshop TIME & DATEyezt0826No ratings yet
- March 14 2024Document5 pagesMarch 14 2024Keila OrtizNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time: At, In, OnDocument3 pagesPrepositions of Time: At, In, OnSEPTIANANo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument4 pagesPrepositionsVilnnus BANo ratings yet
- Preposition of Time (Ayuda Mi)Document2 pagesPreposition of Time (Ayuda Mi)Sergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Using Prepositions of TimeDocument4 pagesUsing Prepositions of TimeGabriella Batista Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- 07 UNIDAD Concepto IIIDocument1 page07 UNIDAD Concepto IIIMayerly CalizayaNo ratings yet
- English Club For Beginners W3 OCTDocument4 pagesEnglish Club For Beginners W3 OCTFedrico ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time: In-On - atDocument3 pagesPrepositions of Time: In-On - atFrank Joseph Pacheco GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time MaterialDocument4 pagesPrepositions of Time MaterialPrengki PintubatuNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3B Bahasa InggrisDocument16 pagesKelompok 3B Bahasa InggrisFebrian Bayu NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time - At, In, OnDocument4 pagesPrepositions of Time - At, In, OnMarlon SaÙlNo ratings yet
- English Usage Example: PrepositionDocument6 pagesEnglish Usage Example: PrepositionNishani SharmilaNo ratings yet
- Preposizioni Di TempoDocument2 pagesPreposizioni Di Tempofrancesca.milioto13No ratings yet
- Do You Know How and When To UseDocument3 pagesDo You Know How and When To UseBartłomiej KawulaNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of TimeDocument1 pagePrepositions of TimeKatyuscia AyalaNo ratings yet
- To BeDocument2 pagesTo BeshnamoNo ratings yet
- TimeDocument7 pagesTimeAdith Milena Santos CanoNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time (In, On, At) IntroductionDocument2 pagesPrepositions of Time (In, On, At) IntroductiongbvitaolesiaNo ratings yet
- Prepositions in Time PhraseDocument10 pagesPrepositions in Time Phraseaashish.v.s2004No ratings yet
- English Grammar: Prepositions of TimeDocument3 pagesEnglish Grammar: Prepositions of Timempedraza-1No ratings yet
- Prepositions of TimeDocument2 pagesPrepositions of TimeLingling NGNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time: At-In-On PyramidDocument3 pagesPrepositions of Time: At-In-On PyramidDiana BashinskayaNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of TimeDocument2 pagesPrepositions of TimeLuz Maritza EstradaNo ratings yet
- In, On and at Are The Three Most: Common Time PrepositionsDocument2 pagesIn, On and at Are The Three Most: Common Time PrepositionsLaura GPNo ratings yet
- Sesión 3Document3 pagesSesión 3laprearequipaNo ratings yet
- Eng - B.Tech. Syllabus - TextDocument126 pagesEng - B.Tech. Syllabus - TextManoj ChallaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document5 pagesLesson 6Quang TienNo ratings yet
- Dates: ExampleDocument4 pagesDates: ExampleDm MrkNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time and Time Expressions: Cristina Ortiz SerranoDocument7 pagesPrepositions of Time and Time Expressions: Cristina Ortiz SerranoJuan Carlos SantanderNo ratings yet
- Preposition of TimeDocument13 pagesPreposition of TimeNatahlia BontiaNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of TimeDocument4 pagesPrepositions of Timesmkyapkesbi bjb100% (1)
- Prep With TimeDocument3 pagesPrep With TimeLe Dinh ThinhNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of TimeDocument1 pagePrepositions of TimeAna Claudia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Days, Months, Dates and MoreDocument15 pagesDays, Months, Dates and MoreVictor JoseNo ratings yet
- Trabajos DannaDocument5 pagesTrabajos DannaCesar OrtizNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time: At, In, OnDocument2 pagesPrepositions of Time: At, In, OnPIR oTECNIANo ratings yet
- Master of PrepositionsDocument17 pagesMaster of PrepositionsKarina Kienig-SelwonNo ratings yet
- Topic 18: Location in Time: Temporal Relationships. FrequencyDocument19 pagesTopic 18: Location in Time: Temporal Relationships. FrequencyCarlos JulioNo ratings yet
- Time Prepositions Explanations and Exercises 73402Document12 pagesTime Prepositions Explanations and Exercises 73402hieumatmoi2009No ratings yet
- A Choose The Correct AnswerDocument1 pageA Choose The Correct AnswerMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Coping With A Midlife CrisisDocument3 pagesCoping With A Midlife CrisisMarija Micunovic100% (1)
- A Year in My Country Weather Reading Comprehension Exercises Tests Warmers Cool 20163Document1 pageA Year in My Country Weather Reading Comprehension Exercises Tests Warmers Cool 20163Marija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Complete The Sentences With The Present Perfect Simple Form of The Verbs in BracketsDocument1 pageComplete The Sentences With The Present Perfect Simple Form of The Verbs in BracketsMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Change The Direct Questions Into Indirect QuestionsDocument1 pageChange The Direct Questions Into Indirect QuestionsMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Skin ExercisesDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Skin ExercisesMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Use The Past Simple Form of The Verb in BracketsDocument1 pageUse The Past Simple Form of The Verb in BracketsMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple HandoutDocument1 pageThe Present Simple HandoutMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense and ContinuousDocument6 pagesPresent Simple Tense and ContinuousMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Survival StoryDocument2 pagesSurvival StoryMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Interview With An ActressDocument2 pagesInterview With An ActressMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Example: My / I Name Is JakeDocument6 pagesExample: My / I Name Is JakeMarija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Past Perfect Past SimpleDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect Past Perfect Past SimpleMarija Micunovic0% (1)
- Verb To Be Exercises: Insert The Correct Form of The Verb "To Be" (Present Simple and Present Continuous)Document1 pageVerb To Be Exercises: Insert The Correct Form of The Verb "To Be" (Present Simple and Present Continuous)Marija MicunovicNo ratings yet
- Siemens MCB Price List Wef 15-10-2023Document60 pagesSiemens MCB Price List Wef 15-10-2023M/S.TEJEET ELECTRICAL & ENGG. CORP.No ratings yet
- Blue Green Illustrative Presentation Skills Infographic PosterDocument1 pageBlue Green Illustrative Presentation Skills Infographic Posterpriyaah23No ratings yet
- Angkur BetonDocument36 pagesAngkur BetonmhadihsNo ratings yet
- Bio AdhesiveDocument24 pagesBio AdhesiveNavreet BdaengNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy (Effective From The Session - 2016-17)Document16 pagesPharmacognosy (Effective From The Session - 2016-17)fadli_nugraha6109No ratings yet
- Advanced Training Course On FPGA Design and VHDL For Hardware Simulation and SynthesisDocument17 pagesAdvanced Training Course On FPGA Design and VHDL For Hardware Simulation and SynthesisMD RockyNo ratings yet
- Typical Malfunctions of BWMSDocument2 pagesTypical Malfunctions of BWMSPyaeSoneHtunNo ratings yet
- Soler Han Weston JSE May 2014Document16 pagesSoler Han Weston JSE May 2014missile1124No ratings yet
- Overall Efficiency Evaluation of Commercial Distillation Columns With Valve and Dual Ow TraysDocument8 pagesOverall Efficiency Evaluation of Commercial Distillation Columns With Valve and Dual Ow TraysArioston JúniorNo ratings yet
- 68 - Guideline Handling of Level Crossings With BL3 v1.0 - FinalDocument37 pages68 - Guideline Handling of Level Crossings With BL3 v1.0 - Finalhay902No ratings yet
- Mounting: Operating InstructionsDocument6 pagesMounting: Operating InstructionsstankevichijusNo ratings yet
- Recipe For BPP Ncii UaqteaDocument11 pagesRecipe For BPP Ncii UaqteaPJ ProcoratoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems Instructions Manual Sames DRT6364 UkDocument26 pagesElectrical Systems Instructions Manual Sames DRT6364 UkGermando NUNESNo ratings yet
- Et3491 Esiot LabDocument95 pagesEt3491 Esiot LabfreefireyomaNo ratings yet
- LG 47ld450-Ua Chassis La01bDocument71 pagesLG 47ld450-Ua Chassis La01belrudo11100% (1)
- QP-650 UHF Service Manual-V0.2ADocument42 pagesQP-650 UHF Service Manual-V0.2AAdrian AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Ansi Ies RP-8-21Document547 pagesAnsi Ies RP-8-21cristianbaileyeNo ratings yet
- M T Ch16 Innate Immunity SDocument30 pagesM T Ch16 Innate Immunity SAnonymous STRYVGKNo ratings yet
- Fleet ManagementDocument20 pagesFleet ManagementMarco Antônio Claret TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Capgemini TestsDocument50 pagesCapgemini TestsObli Narasimha RajanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 History of The Company: Part Two 2. Company BackgroundDocument7 pages2.1 History of The Company: Part Two 2. Company Backgroundhabtamu100% (2)
- en Volvo D49Document84 pagesen Volvo D49Lucas MarquesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Short Notes 7 PageDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure Short Notes 7 PageSubhajit GoraiNo ratings yet
- Script For UptDocument9 pagesScript For UptJohn CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Operation Husky Sicily 1943: Maj R L SimmonsDocument27 pagesOperation Husky Sicily 1943: Maj R L SimmonsStent21No ratings yet
- Dual Operational Amplifier: NJM4560D, NJM4560M, NJM4560E NJM4560LDocument4 pagesDual Operational Amplifier: NJM4560D, NJM4560M, NJM4560E NJM4560LPablo Diego Cecere CasadoNo ratings yet
- Genicular Nerves BlockDocument14 pagesGenicular Nerves BlocknsatriotomoNo ratings yet