Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Waves of Technology-1 PDF
Uploaded by
Aira Jane Yaptangco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views3 pagesThe document discusses Smihula's concept of waves of technological innovation. It describes five waves: 1) the agricultural revolution, 2) the industrial revolution, 3) the information/knowledge age, 4) the electronics and microelectronics wave, and 5) the current wave beginning in the 1980s with computers and leading to globalization. Each wave creates conditions for the next through logical progression and brings dramatic changes to society. Waves are also getting shorter due to accelerated technological progress. The post-information technology revolution may see dynamic growth in pharmaceuticals, biomedical sciences, transhumanism, nanotechnology, and new energy sources.
Original Description:
Original Title
Waves_of_Technology-1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses Smihula's concept of waves of technological innovation. It describes five waves: 1) the agricultural revolution, 2) the industrial revolution, 3) the information/knowledge age, 4) the electronics and microelectronics wave, and 5) the current wave beginning in the 1980s with computers and leading to globalization. Each wave creates conditions for the next through logical progression and brings dramatic changes to society. Waves are also getting shorter due to accelerated technological progress. The post-information technology revolution may see dynamic growth in pharmaceuticals, biomedical sciences, transhumanism, nanotechnology, and new energy sources.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views3 pagesWaves of Technology-1 PDF
Uploaded by
Aira Jane YaptangcoThe document discusses Smihula's concept of waves of technological innovation. It describes five waves: 1) the agricultural revolution, 2) the industrial revolution, 3) the information/knowledge age, 4) the electronics and microelectronics wave, and 5) the current wave beginning in the 1980s with computers and leading to globalization. Each wave creates conditions for the next through logical progression and brings dramatic changes to society. Waves are also getting shorter due to accelerated technological progress. The post-information technology revolution may see dynamic growth in pharmaceuticals, biomedical sciences, transhumanism, nanotechnology, and new energy sources.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
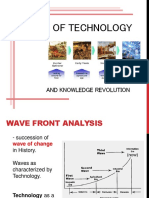
Waves of Technology
• Invention vs innovation
Invention - novel product, device, process, concept
Examples: Printing press, electricity, telephone
Innovation - Introduction of a newer and better solution that meet new requirements or
existing market needs
Examples: Examples: introduction of iPhone, tablet, flat screen TV, etc.
• Smihula’s concept of the wave of technological innovations
• The wave of technological innovations
• Frequency and radicality not distributed uniformly in the course of time
• Has innovation phase – real application
• Small and slow successes
• Has application phase – exploiting and extending existing innovations
• Quick progress and eventually slow as the limits are reached
• Need to improve, beat competitors, solve problem, or increase efficiency of work
• Waves of technological innovations
• Waves of innovation – tech revolutions follow each other in logical sequence (one creates the
conditions for the next)
• Length of waves are getting shorter as a result of acceleration of technological progress and
economic growth
• Economic crisis and stagnation characterizes the end of any wave and its application phase
• This condition demands new inventions and innovations “depression-trigger effect”
• First wave: Agricultural Revolution
Domestication
Farming and irrigation
Use of “living batteries” (people and animals)
Land as basis for economy, culture, power
Work = labor, animal (horsepower)
Decentralization of economy, stratification
First wave: agricultural revolution
Domestication Food security
Population Growth Formation of Settlements
Waste, disease, issues on resource distribution
• Second wave: Industrial Revolution
18th to 19th centuries
Discovery of new worlds
Population growth, movement into towns
Pressure on timber forest
Invention of engine
Second wave: industrial revolution
Factory = model efficiency
mass production
mass consumption
mass media
mass eduation
• Third wave: information/knowledge age
Transitions in the third wave
Integration of more functions into fewer parts
Massification, standardization (2nd wave) vs. customization (3rd wave)
Multiple intelligences and competencies (and higher educational attainment)
Third wave: information/knowledge age
Transitions on in the 3rd wave
“prosumers” (producers are consumers and vice versa)
“do-it-yourself” (service)
Technology as indicator of development
• Fourth wave/fifth wave: electronics and microelectronics
Informmersion (information invasion)
• Fifth wave of technological innovations
Vision of “information society” as excellent stimulus
5th wave started 1980s with cheap computers
Brought dramatic changes in the society
“globalization”
1980s to 1990s – rise of mass use of computers, internet, mobile phones, etc.
Fully integrated part of everyday life by 2010
Larger profits and new ideas start to emerge in other sectors
• Post information technology revolution
• Prediction – areas of science & technology to experience dynamic growth:
• Pharmaceutical
• Biomedical sciences: genetic engineering, cloning, new pharmaceuticals
• Transhumanism – modifying to improve properties of living beings
• Nanotechnology and energy less harmful ecologically
• Increase consumption of energy due to use of hydrogen and oxygen as basic fuel
• Use of nuclear power as energy source
• robotics
You might also like
- Bitstream Case Solution and Analysis, HBR Case Study Solution & Analysis of Harvard Case StudiesDocument6 pagesBitstream Case Solution and Analysis, HBR Case Study Solution & Analysis of Harvard Case StudiesDeepesh Shenoy50% (2)
- 5 Waves of TechnologyDocument50 pages5 Waves of TechnologyNelzen Garay0% (1)
- VistexDocument6 pagesVistexRamesh Kumar B50% (2)
- 13 Cases Teaching NotesDocument77 pages13 Cases Teaching NotesJeanette LampitocNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technology: Currently Developing, or That Are Expected To Be Available Within The Next Five To Ten YearsDocument42 pagesEmerging Technology: Currently Developing, or That Are Expected To Be Available Within The Next Five To Ten YearsAddisalem Ganfure100% (2)
- FEU Quiz 2 Conso SYDocument6 pagesFEU Quiz 2 Conso SYclarissa paragas50% (2)
- Errors - Discussion ProblemsDocument2 pagesErrors - Discussion ProblemsHaidee Flavier SabidoNo ratings yet
- 5 - Waves of TechnologyDocument21 pages5 - Waves of TechnologyFlorence Lapinig100% (3)
- Waves of TechnologyDocument38 pagesWaves of TechnologyGABILAN, BENJAMIN KIRKNo ratings yet
- Emergence of Technology and Industrial RevolutionDocument8 pagesEmergence of Technology and Industrial RevolutionHarneet KaurNo ratings yet
- 5 Waves of TechnologyDocument50 pages5 Waves of TechnologyNelzen GarayNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document35 pagesChapter - 1Netsanet GetnetNo ratings yet
- Short Note For Emerging TehnologiesDocument90 pagesShort Note For Emerging TehnologiesworkinehamanuNo ratings yet
- Technology As A Way of RevealingDocument14 pagesTechnology As A Way of RevealingRaisa Louise Gamiao TattaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ETDocument48 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ETshukrihassan818No ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies - Lecture Notes - CH 1 & 2Document73 pagesEmerging Technologies - Lecture Notes - CH 1 & 2lemma4aNo ratings yet
- Emerging Chapt 1 (Oda) - 1Document36 pagesEmerging Chapt 1 (Oda) - 1shafi EsaNo ratings yet
- Globalization SummaryDocument21 pagesGlobalization SummaryTheaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Introduction To Emerging TechnologyDocument26 pagesChap 1 Introduction To Emerging TechnologyyonasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Emerging TechnologiesDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Emerging Technologiesghhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhfrtvcfg100% (1)
- #1 Introduction To Emerging TechDocument28 pages#1 Introduction To Emerging TechALIYI KEDIRNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction ToDocument26 pagesChapter One: Introduction ToMohammed AbdurhamanNo ratings yet
- ImT PPT For Reading-1Document223 pagesImT PPT For Reading-1johnjoa223No ratings yet
- Week 8Document9 pagesWeek 8Louis Knoll BrionesNo ratings yet
- Role of Information and Communications Technology (ICT)Document13 pagesRole of Information and Communications Technology (ICT)Lianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- STS Module-5-Technology and The Evolution of Human SocietyDocument44 pagesSTS Module-5-Technology and The Evolution of Human SocietyTERRIUS AceNo ratings yet
- Waves of Technology Group 1Document12 pagesWaves of Technology Group 1Aiko TaywanNo ratings yet
- Subject Name - Emerging Exponential Technologies Subject Code - 20mba301 Text BooksDocument32 pagesSubject Name - Emerging Exponential Technologies Subject Code - 20mba301 Text BooksKumar GkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-DS 102-STIDocument14 pagesLecture 1-DS 102-STIkomando kipensiNo ratings yet
- Emerging Techno Chap.1Document32 pagesEmerging Techno Chap.1KeneanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To Emerging TechDocument8 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To Emerging TechNoriel GalosoNo ratings yet
- Living in The IT ERADocument25 pagesLiving in The IT ERAAntonio Vicente Chua83% (6)
- Introduction To Emerging Technologies: What Is The Root Word of Technology and Evolution?Document9 pagesIntroduction To Emerging Technologies: What Is The Root Word of Technology and Evolution?Alemayehu NegashNo ratings yet
- Waves of TechnologyDocument26 pagesWaves of TechnologyJames Iwayan Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Short Note For Emerging TehnologiesDocument90 pagesShort Note For Emerging TehnologiesEYOB80% (5)
- Activity 1:: Introduction To Emerging Technologies 1.1 Evolution of TechnologiesDocument7 pagesActivity 1:: Introduction To Emerging Technologies 1.1 Evolution of TechnologiesAbdataa waaqaaNo ratings yet
- L&T - Unit - 1Document13 pagesL&T - Unit - 1Rishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document47 pagesChapter 1Binyam Bekele MogesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Emerging TechnologiesDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Emerging TechnologieskaleabNo ratings yet
- Unit ONE: Managerial Economics Basic LH (3) HrsDocument6 pagesUnit ONE: Managerial Economics Basic LH (3) HrsAnand Kumar BhagatNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Topic 1 #4Document2 pagesModule 1 Topic 1 #4Jorman LinejanNo ratings yet
- Waves of Technology: and Knowledge RevolutionDocument34 pagesWaves of Technology: and Knowledge RevolutionJewel Britney GayloaNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 Introductiontoemergingtechnologies 230303220604 F6d71aaeDocument29 pagesLesson1 Introductiontoemergingtechnologies 230303220604 F6d71aaeesiyasmengeshaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER IV - Technology and The Evolution of Human SocietyDocument4 pagesCHAPTER IV - Technology and The Evolution of Human SocietyKeannoNo ratings yet
- Law TechDocument44 pagesLaw TechPankhuri SharmaNo ratings yet
- Technology Globalization and EthicsDocument30 pagesTechnology Globalization and EthicsAinun NajibNo ratings yet
- Science Technology and SocietyDocument22 pagesScience Technology and SocietyDavid SamuelNo ratings yet
- 06 IndustrializationDocument30 pages06 IndustrializationKianna Chelsey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson#4 History-of-Market-Integration With TaskreminderDocument17 pagesLesson#4 History-of-Market-Integration With TaskreminderZeus P Diaz100% (1)
- Both CH1&2 EmergingDocument20 pagesBoth CH1&2 EmergingJiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Emerging TechnologiesDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Emerging TechnologiesAbdela Aman MtechNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Emerging TechnologiesDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Emerging TechnologiesBekuma GudinaNo ratings yet
- STS Continuation Module ActivityDocument9 pagesSTS Continuation Module ActivityChanzel RegineNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Unit 1 Information Technology RevolutionDocument6 pagesWuolah Free Unit 1 Information Technology RevolutionyaxiatrashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Emerging Exponential TechnologiesDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Emerging Exponential TechnologiesCherianXavierNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution PDFDocument10 pagesIndustrial Revolution PDFArooj ZamanNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Science and Technology On SocietyDocument23 pagesThe Effects of Science and Technology On SocietyJohn Lawrence MarianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1HabtamuNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, & Society in The 20th Century: Modern WorldDocument23 pagesScience, Technology, & Society in The 20th Century: Modern WorldJean MarkNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Emerged TechnologiesDocument11 pagesChapter One Emerged TechnologiesabdulfetaNo ratings yet
- Law and Technology: Industrial RevolutionDocument5 pagesLaw and Technology: Industrial RevolutionYogendra JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument35 pagesChapter Onehamza tureNo ratings yet
- Little SistaaDocument64 pagesLittle SistaaEyob BirhaneNo ratings yet
- Game Theory and ExternalitiesDocument21 pagesGame Theory and ExternalitiesAira Jane YaptangcoNo ratings yet
- College of Business and Accountancy Junior Philippine Institute of AccountantsDocument1 pageCollege of Business and Accountancy Junior Philippine Institute of AccountantsAira Jane YaptangcoNo ratings yet
- Philippine National DevelopmentDocument31 pagesPhilippine National DevelopmentAira Jane YaptangcoNo ratings yet
- Community Immersion: A Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesCommunity Immersion: A Reaction PaperAira Jane Yaptangco100% (1)
- National Income AnalysisDocument58 pagesNational Income AnalysisharshNo ratings yet
- Date Transaction Description Amount (In RS.) : Card No: 0036 1135 XXXX 3831 AAN: 0001015340002833839Document2 pagesDate Transaction Description Amount (In RS.) : Card No: 0036 1135 XXXX 3831 AAN: 0001015340002833839Satish RengarajanNo ratings yet
- Project BS ItemsDocument25 pagesProject BS ItemsSumeet BhatereNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance 1 - 2 LectureDocument122 pagesCorporate Finance 1 - 2 LectureMónika NémethNo ratings yet
- Induatrial Dispute Act 1947Document88 pagesInduatrial Dispute Act 1947prakhar chaudharyNo ratings yet
- MT 103 Gpi 23.8M CodesDocument2 pagesMT 103 Gpi 23.8M CodesEllerNo ratings yet
- PayStub - Penny Ruth BrownDocument1 pagePayStub - Penny Ruth BrownHee Classique100% (1)
- Class 1Document19 pagesClass 1Rahul BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Tax Rates - Expanded Withholding TaxDocument6 pagesTax Rates - Expanded Withholding TaxMiko Angelo BuezaNo ratings yet
- UAE New ListDocument18 pagesUAE New ListForline Fernando100% (1)
- DTC FormatoDocument17 pagesDTC FormatoJAVIER LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Land Acquisition in India-Past and Present: Prof. Kahkashan Y. DanyalDocument3 pagesLand Acquisition in India-Past and Present: Prof. Kahkashan Y. DanyalANANo ratings yet
- The Wealth of NationsDocument786 pagesThe Wealth of Nationsleosilveira100% (1)
- LEAN - TPM - Autonomous Maintenance Steps - Step 0: EducationDocument3 pagesLEAN - TPM - Autonomous Maintenance Steps - Step 0: EducationkeshunaNo ratings yet
- Annexure - III Process Flow ChartDocument1 pageAnnexure - III Process Flow ChartIbrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Banco de Oro or BDO Unibank, Inc. Is The Largest Bank Based in Makati CityDocument7 pagesBanco de Oro or BDO Unibank, Inc. Is The Largest Bank Based in Makati CityErfan TanhaeiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Agricultural EconomicsDocument179 pagesFundamentals of Agricultural EconomicsBright MelbaNo ratings yet
- Qs 2 BSTDocument8 pagesQs 2 BSTSachin Gupta100% (1)
- Master Thesis Examples FinanceDocument4 pagesMaster Thesis Examples Financenikkismithmilwaukee100% (2)
- Is Frontrow A ScamDocument3 pagesIs Frontrow A ScamRuthlyn MigrinoNo ratings yet
- CH 24Document61 pagesCH 24Aldi HerialdiNo ratings yet
- UBIQUITY India CorporationDocument7 pagesUBIQUITY India CorporationUBIQUITY India CorporationNo ratings yet
- Break Even Analysis Is The Critical Tool For Determining The Capacity A Facility Must Have ToDocument4 pagesBreak Even Analysis Is The Critical Tool For Determining The Capacity A Facility Must Have ToJoven QuibalNo ratings yet
- Gains and Losses On Futures ContractsDocument3 pagesGains and Losses On Futures Contractshkm_gmat4849No ratings yet
- Labor Standards CasesDocument6 pagesLabor Standards CasesJuan Luis LusongNo ratings yet