Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Patfis CHF PDF
Patfis CHF PDF
Uploaded by
ayupurnamasariiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Patfis CHF PDF
Patfis CHF PDF
Uploaded by
ayupurnamasariiCopyright:
Available Formats
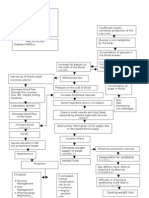
FIGURE 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DIAGRAM OF 49 YR.
OLD FEMALE CLIENT WITH CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE FUNCTIONAL
CAPACITY II SECONDARY TO VALVULAR HEART DISEASE SECONDARY TO RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE
RISK FACTORS: Infiltration of
· Lives in rural area Group A Beta- Tonsillitis
· Lack of access to Sore throat
Hemolytic (1980s)
medical services due
to low socioeconomic Streptococci
strata (unemployed)
· Poor nutrition
(inadequate food
intake)
· Environmental BLOOD CULTURE:
exposure to Activates antibodies that
No growth of MO
pathogens cause Acute Inflammation of
after 2 days of
the Heart X-RAY: Prominent incubation
prosthetic valves,
metal clicks on
RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE auscultation
CEFTRIAXONE PARACETAMOL
Vegetative lesions occur in heart
valves
PROSTHETIC
RISK FOR
VALVE Fever
INFECTION
HOLO- REPLACEMENT
ABDOMEN
UTZ: Fatty Risk Factors:
Infiltration or · Rheumatic
Heart Disease VALVULAR HEART
streaks in DISEASE
pancreas · Family history of
VHD (mother)
RISK FOR
· Family history of
PULMONARY COUMADIN
Hypertension
EMBOLISM
(father)
· Female, 49 y/o
· High sodium 2D ECHO: Mild
and cholesterol Tricuspid
in diet Triscupid, Mitral
regurgitation,
and Aortic
good opening
Insufficiency
and closing of
valves
Increased afterload, preload and
increased pressure
2D ECHO:
Concentric Left
Left Ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular
Hypertrophy
Myocardial Dysfunction
Myocardial Failure
Heart Pump failure
Continued on next page.
Page 1
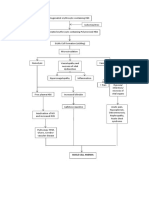
FIGURE 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DIAGRAM OF 49 YR. OLD FEMALE CLIENT WITH CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY II
SECONDARY TO VALVULAR HEART DISEASE SECONDARY TO RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE (CONT.)
2D ECHO: Ejection Fraction 53%
Teicholtz’s, 47% Simpson’s
Systolic ECG: 45 beats per min HR
2D ECHO: Mildly depressed
Dysfunction,
overall systolic function
Failure
DECREASED Easy Fatigability,
Decreased end- ACTIVITY
CARDIAC Walks only 3
systolic volume INTOLERANCE
OUTPUT flights of stairs
Decreased
Increased Venous
Perfusion of Increased Sodium and Water Increased Plasma
Pressure to the Pulmonary Edema
Tissues in the Aldosterone Retention Volume
Lungs
Body
Pulmonary
Congestion
Increased
Increased Renin, Peripheral Risk factor: HOLO-ABD
Vasoconstriction vascular · Genetic UTZ:Bilateral
Angiotensin
Resistance predisposition Renal cysts 2-Pillow
Orthopnea
Increased Increased Capillary
Renal
Sympathetic Peripheral endothelial INEFFECTIVE
Vasoconstriction
Activity Vasoconstriction damage URINALYSIS: BREATHING
Hematuria (Taces PATTERN
of Blood in Urine)
Decreased Blood
METOPROLOL Pressure, Heart
Rate
Decreased
Oxygen Supply to
Tissues
BRAIN: GASTROINTESTINAL
MYOCARDIUM: LIVER: Liver
Decreased TRACT: Decreased
Increased Cardiac dysfunction
Oxygen Supply to Oxygen Supply to GI
Workload
Cerebral Tissues Tract
URINALYSIS: Minimal
Decreased Blood Albumin in Urine
ACTIVITY Dizziness
Flow to
INTOLERANCE
Myocardium Increased Acid
RISK FOR Production
INEFFECTIVE
CEREBRAL OMEPRAZOLE
Ischemia TISSUE
PERFUSION Superficial mucosal
lesions of stomach and
duodenum develop
Anaerobic
Metabolism
Increased Lactic Decreased Appetite,
Acid Production Weight loss
Chest pain
IMBALANCED NUTRITION: LESS
THAN BODY REQUIREMENTS
RISK FOR INEFFECTIVE
MYOCARDIAL TISSUE PERFUSION
Page 2
You might also like
- Philippine Manual of Legal Citations (Feliciano)Document61 pagesPhilippine Manual of Legal Citations (Feliciano)Gilianne Kathryn Layco Gantuangco-Cabiling100% (14)
- Acute Ischemic Stroke Concept MapDocument6 pagesAcute Ischemic Stroke Concept MapMoonyeen Jann Casera Balic100% (2)
- Final Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesFinal Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology PDFDave JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CHFDocument1 pagePathophysiology of CHFImae Mayo60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failuresugarmontejo67% (3)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJames John Galac88% (8)
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAngina Pectoris Pathophysiologydana88% (8)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureTrixia Almendral100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Diseasekhrizaleeh100% (10)
- D2372547-001 SGRE On SG 6.0-170 Estimated Foundation Design T115-50ADocument3 pagesD2372547-001 SGRE On SG 6.0-170 Estimated Foundation Design T115-50AMarcelo GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeJoy Rachelle Fermin100% (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageCongestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument8 pagesCongestive Heart Failureiancel_038893% (27)
- Case Study Congestive Heart Failure Patho)Document8 pagesCase Study Congestive Heart Failure Patho)Mj Silva100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failurekristel_nicole18yaho100% (3)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesHypertension PathophysiologyJems60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaNo ratings yet
- Medicine Cheat SheetsDocument16 pagesMedicine Cheat SheetsRisa Muthmainah100% (1)
- Warhammer 40k Reference SheetDocument8 pagesWarhammer 40k Reference SheetDarren Luu50% (2)
- 1B ECSA Technologist AppformDocument21 pages1B ECSA Technologist AppformNithasha JeewanNo ratings yet
- Maritime Economics Ieb NSC Grade 12 Past Exam Papers 2016 Question PaperDocument12 pagesMaritime Economics Ieb NSC Grade 12 Past Exam Papers 2016 Question PaperRadhika Malhar100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- The Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesThe Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureMar Ble50% (2)
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart Failurea_samiane64% (11)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Heart FailureabbeeyyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 pagePathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVDDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesStroke PathophysiologyMaureen Balagtas89% (9)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HCVDDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of HCVDNicolne Lorraine100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Document7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramAbi Habiling100% (3)
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionDocument2 pagesHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionMiguel Carlos Tacderan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Document3 pagesPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument12 pagesRheumatic Heart DiseaseJonielyn LagunaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DefectsDocument7 pagesCongenital Heart DefectsJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Pericarditis Vs Mi: Internal Medicine: CvsDocument6 pagesPericarditis Vs Mi: Internal Medicine: CvsRojales FrancisNo ratings yet
- Surgery FADocument170 pagesSurgery FArafeekwalid551No ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot CASE STUDYDocument12 pagesTetralogy of Fallot CASE STUDYMaricel Agcaoili GallatoNo ratings yet
- Aortic Dissection (Schwartz's 11 Ed.) Pathology and Classification Causes and Clinical HX Clinical Manifestations Diagnostic Evaluation TreatmentDocument3 pagesAortic Dissection (Schwartz's 11 Ed.) Pathology and Classification Causes and Clinical HX Clinical Manifestations Diagnostic Evaluation TreatmentSean Dominique Cruz MaghinayNo ratings yet
- Case Chest Pain and DyspneaDocument1 pageCase Chest Pain and DyspneaVineeNo ratings yet
- Linician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaDocument6 pagesLinician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaSonia Rahma ANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyNikki RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsDocument39 pagesPulmonary Embolism: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsAsmaa ahmedNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology MaiaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Maiajia88No ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease CAD PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Disease CAD PathophysiologyKusum RoyNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Defects - CyanoticDocument3 pagesCongenital Heart Defects - Cyanoticr5ss7pq9tpNo ratings yet
- JJK s3Document7 pagesJJK s3achurocks561No ratings yet
- Disturbances in CirculationDocument12 pagesDisturbances in CirculationJoei OcampoNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Venous Thromboembolism Dr. ConstantinoDocument7 pagesLIGHT Venous Thromboembolism Dr. ConstantinoMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Cosare v. BroadcomDocument4 pagesCosare v. BroadcomAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Magna Financial v. ColarinaDocument3 pagesMagna Financial v. ColarinaAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Memo On Uniform Implementation of DO 174Document3 pagesMemo On Uniform Implementation of DO 174Anonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (2)
- Onapal v. CA FPIB v. CADocument5 pagesOnapal v. CA FPIB v. CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR0% (1)
- Salcedo v. ComelecDocument4 pagesSalcedo v. ComelecAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Salcedo v. ComelecDocument4 pagesSalcedo v. ComelecAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- CSC V BelaganDocument3 pagesCSC V BelaganAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- PNB v. PinedaDocument3 pagesPNB v. PinedaAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Candijay v. CADocument2 pagesCandijay v. CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Marohombsar v. AlontoDocument2 pagesMarohombsar v. AlontoAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Alhambra Cigar v. SECDocument3 pagesAlhambra Cigar v. SECAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- People v. CarantoDocument4 pagesPeople v. CarantoAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Iglesia Evangelica v. Bishop LazaroDocument3 pagesIglesia Evangelica v. Bishop LazaroAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Tax Syllabus (Spit) 2015Document15 pagesTax Syllabus (Spit) 2015Anonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Nieva v. Alvarez-EdadDocument2 pagesNieva v. Alvarez-EdadAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- PLM v. IAC Case DigestDocument3 pagesPLM v. IAC Case DigestAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Hassan v. ComelecDocument2 pagesHassan v. ComelecAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Case Concerning Oil Platforms (Iran V US)Document9 pagesCase Concerning Oil Platforms (Iran V US)Anonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Merrill v. CADocument2 pagesMerrill v. CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR50% (2)
- Compiled Digests Letters of CreditDocument9 pagesCompiled Digests Letters of CreditAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Loong v. ComelecDocument4 pagesLoong v. ComelecAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Civil Liberties Union v. Exec. Sec.Document6 pagesCivil Liberties Union v. Exec. Sec.Anonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Akbayan-Youth v. ComelecDocument4 pagesAkbayan-Youth v. ComelecAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Insolvency Proceedings Under FRIADocument13 pagesInsolvency Proceedings Under FRIAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- GSIS v. KapisananDocument2 pagesGSIS v. KapisananAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Sanchez Agency ReviewerDocument85 pagesSanchez Agency ReviewerAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- People v. LeeDocument4 pagesPeople v. LeeAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- Walton v. AramcoDocument1 pageWalton v. AramcoAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- PLUM Federation V NorielDocument2 pagesPLUM Federation V NorielAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNo ratings yet
- 2nd SemesterDocument2 pages2nd SemesteralokNo ratings yet
- Parenteral TechnologyDocument162 pagesParenteral TechnologyDharly RamirezNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety Sil Basics For Process Control GuideDocument4 pagesFunctional Safety Sil Basics For Process Control GuidemohdthasthakirNo ratings yet
- Welcome To High Commission of India, Colombo, Sri LankaDocument3 pagesWelcome To High Commission of India, Colombo, Sri LankaPRASENJIT CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- SteelHead - Deployment Installation Gui08Document90 pagesSteelHead - Deployment Installation Gui08Partha DashNo ratings yet
- Mecanica de Fluidos SolucionarioDocument27 pagesMecanica de Fluidos SolucionarioFrankcTecsiSenciaNo ratings yet
- Command Line Basics - Everything CurlDocument2 pagesCommand Line Basics - Everything Curlnot hereNo ratings yet
- English 7 1st PT ReviewerDocument47 pagesEnglish 7 1st PT ReviewerJeinill CalmateoNo ratings yet
- Domestic Consolidated Lounge List 1st June 2023Document11 pagesDomestic Consolidated Lounge List 1st June 2023Prateek PanjwaniNo ratings yet
- 1 CellsDocument4 pages1 CellsSheniqua GreavesNo ratings yet
- Gaslands FAQDocument8 pagesGaslands FAQCTO100% (1)
- CET Modular Inverter User Manual Nova TSI 48Vdc - 230vac EN v7.3Document53 pagesCET Modular Inverter User Manual Nova TSI 48Vdc - 230vac EN v7.3AndY NothNo ratings yet
- Free Exercise Guide For Physiotherapy StudentsDocument14 pagesFree Exercise Guide For Physiotherapy StudentssenthilkumarNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current RatingsDocument1 pageVoltage and Current RatingsArmanNo ratings yet
- Financial Control of Public FundsDocument136 pagesFinancial Control of Public FundsDavid Abbam AdjeiNo ratings yet
- Calendar For Examinations - 2010Document9 pagesCalendar For Examinations - 2010nitin_verma30No ratings yet
- Teaching Methods in EconomicsDocument20 pagesTeaching Methods in EconomicsKintu GeraldNo ratings yet
- Effect of Storage Time On Fish Feed Stored at Room Temperature and Low Temperature M. N. Hossen, M. Das, K. R. Sumi and M. T. HasanDocument8 pagesEffect of Storage Time On Fish Feed Stored at Room Temperature and Low Temperature M. N. Hossen, M. Das, K. R. Sumi and M. T. HasanmamunNo ratings yet
- Economic Survey 2071-72 English (Final) - 20150716082638Document339 pagesEconomic Survey 2071-72 English (Final) - 20150716082638Pramod Pyara ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Connected TAC Security OverviewDocument8 pagesConnected TAC Security OverviewNisobaNo ratings yet
- Module 9 10Document40 pagesModule 9 10kevoarcher093No ratings yet
- Alfa VapDocument2 pagesAlfa Vapkresimir.mikoc9765No ratings yet
- Presentation - India Entry Services SIRC 17062021 1 PDFDocument75 pagesPresentation - India Entry Services SIRC 17062021 1 PDFashok babuNo ratings yet
- Camille Realty Journal To FSDocument9 pagesCamille Realty Journal To FSVenus AriateNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Topics For The Scarlet LetterDocument8 pagesTerm Paper Topics For The Scarlet Letterc5q1thnj100% (1)
- African Child - Poem by Eku Mcgred2Document10 pagesAfrican Child - Poem by Eku Mcgred2Jovert ManadongNo ratings yet