Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACFrOgC3jygAvXXrHAJ33uk tuLN53TtI31ayYMsio0nl-C8Y92TIuIQE2yTfrSCx9-zf w87Rc6B9 Wo9-fdcTsfQ93BHFVSP STbD-0QnS8layyeWKyTyt5fmLmxo PDF
ACFrOgC3jygAvXXrHAJ33uk tuLN53TtI31ayYMsio0nl-C8Y92TIuIQE2yTfrSCx9-zf w87Rc6B9 Wo9-fdcTsfQ93BHFVSP STbD-0QnS8layyeWKyTyt5fmLmxo PDF
Uploaded by
Malik Mohammad AsifOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ACFrOgC3jygAvXXrHAJ33uk tuLN53TtI31ayYMsio0nl-C8Y92TIuIQE2yTfrSCx9-zf w87Rc6B9 Wo9-fdcTsfQ93BHFVSP STbD-0QnS8layyeWKyTyt5fmLmxo PDF
ACFrOgC3jygAvXXrHAJ33uk tuLN53TtI31ayYMsio0nl-C8Y92TIuIQE2yTfrSCx9-zf w87Rc6B9 Wo9-fdcTsfQ93BHFVSP STbD-0QnS8layyeWKyTyt5fmLmxo PDF
Uploaded by
Malik Mohammad AsifCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
CE-119 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS – I (Spring 2019)
HOME WORK # 2
NOTE: Submission deadline is 17-05-2019.
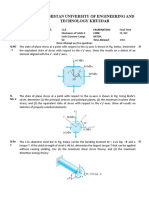
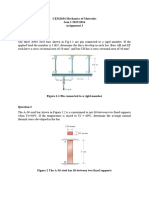
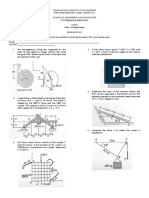
Q1) A rigid slab is hanging from three vertical rods. The slab is carrying a point load as shown in
the figure…. The slab is initially horizontal but it does not necessarily remain horizontal after
loading. Compute the load in each rod . [CLO3,C3,PLO2]
Figure 1
Q2) A hollow steel cylinder surrounds a solid copper cylinder and the assembly is subjected to an
axial load of 50,000 lb as shown in figure 1. The cross-sectional area of the steel is 3in2, while that
of the copper is 10in2. Both cylinders are the same length before the load is applied. Determine the
temperature rise of the entire system required to place all of the load on the copper cylinder. The
cover plate at the top of the assembly is rigid. For copper E = 16 x 106 lb/in2, a = 9.3 x 10-6/F, while
for steel E = 30 x 106 lb/in2, a = 6.5 x 10-6/F [CLO3,C3,PLO2]
Figure 2
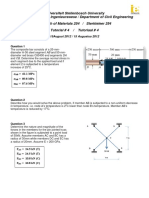
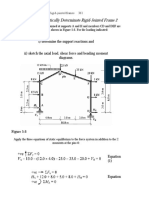
Q3) The rigid bar AD is pinned at A and attached to the bars BC and ED, as shown in figure 2. The
entire system is initially stress free and the weights of all bars are negligible. The temperature of bar
BC is lowered 25C and that of the bar ED is raised 25C. Neglecting any possibility of lateral
Course instructor's email: awais.ahmed@uetpeshawar.edu.pk UET, Peshawar
buckling, Determine the normal stresses in bars BC and ED. For BC, which is brass, assume E =
90 GPa, a = 20 x 10-6/C and for ED, which is steel, take E = 200 GPa and a = 12 x 10-6/C. The
cross-sectional area of BC is 500 mm2 and of ED is 250 mm2. [CLO4,C4,PLO2]
Figure 3
Course instructor's email: awais.ahmed@uetpeshawar.edu.pk UET, Peshawar
You might also like
- answer The Followings: (20 Points) What Is Local Buckling CouldDocument4 pagesanswer The Followings: (20 Points) What Is Local Buckling CouldAhmed Pshtiwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Ahmad ElosmanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structural AnalysisDocument19 pagesAdvanced Structural AnalysisMohammed AbidNo ratings yet
- 1213sem2 Ce5611Document11 pages1213sem2 Ce5611Yu Tian LiNo ratings yet
- CVEN3302 Final Exam S2 2012Document5 pagesCVEN3302 Final Exam S2 2012Avinash SinghNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics BCS Previous Year Questions PDFDocument3 pagesSolid Mechanics BCS Previous Year Questions PDFjjoe joliNo ratings yet
- Test PDFDocument5 pagesTest PDFMahyah SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Plate No. 2Document13 pagesPlate No. 2Karl SeparaNo ratings yet
- 3B3 Mechancis of Solids Exam 23Document7 pages3B3 Mechancis of Solids Exam 23Emer DuffNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesDocument24 pagesStatically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesBuddy SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 18 Portiques BA-Exemple Calcul-Corr09Document87 pagesChapitre 18 Portiques BA-Exemple Calcul-Corr09Mohamed Bouzidi FSNo ratings yet
- Internal 1 Set I - DME1Document12 pagesInternal 1 Set I - DME1A VasanthkumarNo ratings yet
- EMT 3102 SUPP Solids & Structural Mechanics 1 SUPPDocument4 pagesEMT 3102 SUPP Solids & Structural Mechanics 1 SUPPGausss TjNo ratings yet
- 4 ME Som Model Examination 2013Document3 pages4 ME Som Model Examination 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Ce221 Midsem 16Document16 pagesCe221 Midsem 16Radha BhojNo ratings yet
- Paper Summer Camp Final Term MOS-IIDocument2 pagesPaper Summer Camp Final Term MOS-IIZohaibShoukatBalochNo ratings yet
- Taller No 2 Resistencia I 2013BDocument4 pagesTaller No 2 Resistencia I 2013BAsep Bin UjangNo ratings yet
- Istability of A Column - LAB MENUDocument3 pagesIstability of A Column - LAB MENUAlan LeungNo ratings yet
- CE2001 MS Ass1Document1 pageCE2001 MS Ass1Varghese NjaliathNo ratings yet
- 2122 MTCC5020 S2 A3 Fa QPDocument8 pages2122 MTCC5020 S2 A3 Fa QPZoay7 I 6No ratings yet
- CE 4103-Prestressed ConcreteDocument2 pagesCE 4103-Prestressed ConcretePranto KhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1anandNo ratings yet
- Watertank GSDocument38 pagesWatertank GSSushobhit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Tut4 PDFDocument3 pagesTut4 PDFGregorNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress and StrainDocument3 pagesSimple Stress and StrainManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Mid Term ExamDocument1 pageMid Term ExamEman SalahNo ratings yet
- (5157) - 3002 Second Year B. Arch (End-Semester) : (2015 Pattern)Document3 pages(5157) - 3002 Second Year B. Arch (End-Semester) : (2015 Pattern)Dagadu bhika PiwaleNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and PlasticityDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity and PlasticityNaren GujjarNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam 2009 2010Document2 pagesMid Term Exam 2009 2010محمد معوضNo ratings yet
- 15AES213 Aerospace Structures 1: Assignments 2Document3 pages15AES213 Aerospace Structures 1: Assignments 2songs everythingNo ratings yet
- Assignment Concept of StressDocument3 pagesAssignment Concept of StressYasser ZubaidiNo ratings yet
- AE May 2013 98 Civ A2Document3 pagesAE May 2013 98 Civ A2NikhilBennyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1jermainpeart4No ratings yet
- Final ExamSOMFinal 2016 FinalDocument11 pagesFinal ExamSOMFinal 2016 Finalkhalil alhatabNo ratings yet
- CEN 479 Mid Term Exam Fall 2020Document2 pagesCEN 479 Mid Term Exam Fall 2020Hasibur RashidNo ratings yet
- CEMB1034 Assignment 3 - Sem 1 2324Document2 pagesCEMB1034 Assignment 3 - Sem 1 2324alolqigoNo ratings yet
- SEAA3313 Final 2223-1 AnsDocument19 pagesSEAA3313 Final 2223-1 AnsharithNo ratings yet
- Ae2203 Ut 2 QP (Set A)Document2 pagesAe2203 Ut 2 QP (Set A)Aravindan SivanandanNo ratings yet
- END Examination: F'CL, F'CTDocument1 pageEND Examination: F'CL, F'CTGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids (CIE 1001) RCS-1Document2 pagesMechanics of Solids (CIE 1001) RCS-1Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Material ExerciseDocument4 pagesMechanics of Material ExerciseFaiz Fauzi0% (1)
- Assignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126Document7 pagesAssignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126MOHAMMAD AELEEF BIN PATRICK A20ET0356No ratings yet
- Som Iat - 1 Question Paper Answer Key NewDocument6 pagesSom Iat - 1 Question Paper Answer Key NewSelvaraj GNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document4 pagesHW 2Aziz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Som Assignment 1 For Iat 1Document2 pagesSom Assignment 1 For Iat 1Selvaraj GNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Generation, Transmission & Distribution R19-Model PaperDocument3 pagesElectrical Power Generation, Transmission & Distribution R19-Model PaperSagar MudunuriNo ratings yet
- Pal Em025Document5 pagesPal Em025Syafriza SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- University of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Note: All Questions Are Compulsory For Section A and BDocument8 pagesUniversity of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Note: All Questions Are Compulsory For Section A and BVed PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- CE 4103 Prestressed Concrete MakeupDocument2 pagesCE 4103 Prestressed Concrete MakeupPranto KhanNo ratings yet
- Question B.Tech (CE) PDFDocument148 pagesQuestion B.Tech (CE) PDFLawrence NgariNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns Centric Load Ec2Document9 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Columns Centric Load Ec2wuletzkyNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Degree Examination Civil, EEE, ME & AE: (April-18) (EME-102)Document5 pagesB.Tech. Degree Examination Civil, EEE, ME & AE: (April-18) (EME-102)Maheshpoetry teluguNo ratings yet
- Send It To: Sanaka Educational Trust'S Group of InstitutionDocument2 pagesSend It To: Sanaka Educational Trust'S Group of InstitutionAyan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids (CIE 1051) (Makeup)Document5 pagesMechanics of Solids (CIE 1051) (Makeup)Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering and SurveyingDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering and SurveyingWataNo ratings yet
- Note Chapt IIDocument27 pagesNote Chapt IIRitesh KishoreNo ratings yet
- Example PDFDocument6 pagesExample PDFMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Matlab Code Bisection MethodDocument2 pagesMatlab Code Bisection MethodMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Astm c40 TestDocument1 pageAstm c40 TestMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Properties of Nonmetals.: Temperature 10 Substance C W/M C KG/M KJ/KG C M /s Structural and Heat-Resistant MaterialsDocument3 pagesProperties of Nonmetals.: Temperature 10 Substance C W/M C KG/M KJ/KG C M /s Structural and Heat-Resistant MaterialsMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
- 1st Semester PDFDocument5 pages1st Semester PDFMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines College of Engineering and Architecture CE 001 Problem Set # 1Document2 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines College of Engineering and Architecture CE 001 Problem Set # 1Malik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
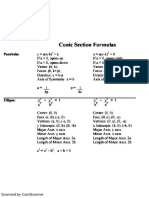
- CONICSDocument4 pagesCONICSMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Second YearDocument31 pagesChemistry Second YearMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet