Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Building Services - II (ARCH337), Sec-A CORE COURSE, L-2, T-1, (CU-3)
Uploaded by
Charu DuggalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Building Services - II (ARCH337), Sec-A CORE COURSE, L-2, T-1, (CU-3)
Uploaded by
Charu DuggalCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
Building Services –II [ARCH337], Sec-A
CORE COURSE, L-2,T-1, [CU-3]
Date 19 Dec 2018
Module 1: ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS Weightage 20% ( three weeks )
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Module 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Session Planning
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Protection devices in Electrical Instullation
1. Switches (https://www.electronicshub.org/switches/)
2. Fuses
3. Circuit Breakers
# Basics of earting and type of earting
# Variuos type of electrical installation in building
# Type of wire and their uses
Protectio Devices > Swithces
# A switch is a device which is designed to interrupt the current flow in a circuit, in
other words, it can make or break an electrical circuit.
# switches are the part of a control system.
Mechanical switches must be activated physically, by moving, pressing,
releasing, or touching its contacts.
Electronic switches do not require any physical contact in order to control a
circuit. These are activated by semiconductor action.
Mechanical Switches
1. Single Pole Single Throw Switch (SPST)
2. Single Pole Double Throw Switch (SPDT)
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
3. Double Pole Single Throw Switch (DPST)
4. Double Pole Double Throw Switch (DPDT)
5. Push Button Switch
6. Toggle Switch
7. Limit Switch
8. Float Switches
9. Flow Switches
10. Pressure Switches
11. Temperature Switches
12. Joystick Switch
13. Rotary Switches
Electronic Switches
1. Bipolar Transistors
2. Power Diode
3. MOSFET
4. IGBT
5. SCR
6. TRIAC
7. DIAC
8. Gate Turn-Off Thyristor
Protection Devices > Fuses
# A fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an
electrical circuit.
# Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows
through it, thereby interrupting the current.
# It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated it is an open circuit, and it must be
replaced or rewired, depending on type.
Protection Devices > Circuit Breakers
# A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an
electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit.
# Its basic function is to interrupt current flow after a fault is detected.
# Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be
reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation.
# often abbreviated as OCPD (Over Current Protection Device).
# Type Of Circuit Breakers
1. MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
2. MCCB-(Molded Case Circuit Breaker)
3. ELCB -(Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker)
4. AFCI (Arc-fault circuit interrupter)
5. Residual-current device (RCD) or Ground Fault Circuit interrupter
MCB
# An MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) function by interrupting the stability of electrical flow
through the circuit once an error is detected. It is a switch which routinely turns off when
the current flows through it and passes the maximum acceptable limit. Generally, these
are designed to guard against over current and overheating.
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
# Rated current is not more than 100 amperes, they are/have Thermal/thermal magnetic
operation.
MCCB
# This circuit Breaker is an electromechanical device which guards a circuit from short circuit
and over current.
# The range of rated current us up to 1000 amperes.
ELCB
# An Earth-leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations
with high Earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal
enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous voltage is
detected.
# There are two types of Earth-leakage circuit breaker:
a. voltage operated (referred as ELCB ) and,
b. current operated (referred to as RCCB ).
AFCI
# Arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI). An arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) also known as an
arc-fault detection device (AFDD), is a circuit breaker that breaks the circuit when it detects
an electric arc in the circuit it protects to prevent electrical fires.
# Conventional circuit breakers only respond to overloads and short circuits, so they do not
protect against arcing conditions that produce erratic, and often reduced current. An AFCI
is selective so that normal arcs do not cause it to trip.
RCD
# A residual-current device (RCD), or residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB), is a device that
instantly breaks an electric circuit to prevent serious harm from an ongoing electric shock.
# RCD is the name used in the United Kingdom. In the United States and Canada, the terms
ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI), ground fault interrupter (GFI) or appliance leakage
current interrupter (ALCI) are used.
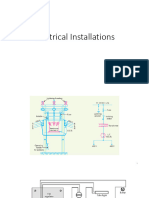
Basics of Earthing
Ref : - National Building code 2016, Part 8 , Section -2 , Clause 8.
# Earthing is an essential part of any electrical installation, essential for the safety from
electrical shock, and fire and for operation of most of the protective systems of the
electrical installation.
# The earthing system, sometimes simply called ‘earthing’, is the total set of measures used
to connect an electrically conductive part to earth. The earthing system is an essential part
of power networks at both high- and low-voltage levels.
# The earthing provides the necessary reference of zero potential
# The main earthing system of an electrical installation shall consist of,
a) an earth electrode, (electrode can be one vertical rod/pipe/buried plate or an
earth mat with several vertical installations or a ring earthing with vertical
installations.
b) A main earthing wire (earth Lead);
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
c) An earth bar (located on the main switchboard for small installation and
installed in the wall/room in case of large industrial electronic installations) for
the connection of the main earthing wire, protective earthing wires and/ or
bonding wires within the installation; and
d) A removable link, which effectively disconnects the neutral bar from the
earth bar.
Type of earthing
1. TT System
2. IT System (No point is connected
with earth (isolation), except
perhaps via a high impedance)
3. TN-S System
4. TN-C-S System
5. TN-C System (A combined PEN
conductor fulfils the functions of both a PE and an N conductor.)
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
Method of earthing
1. Plate Electrode (This may be made of copper, galvanized iron or steel. If made of copper
the minimum size is 60 cm x 60 cm x 3.15 mm. If of galvanized iron or steel, the minimum
size should be 60 cm x 60 cm x 6.3 mm )
2. Pipe Electrode (If should be made of ‘B’ class G.I pipe. the internal diameter should not be
smaller than 38 mm and it should be 100 mm for cast Iron pipe. The length of the pipe
electrode should not less than 2.5 mtrs. It should be embedded vertically. Where hard rock
is encountered it can be inclined to vertical. The inclination being limited 30% to vertical. ).
3. Strip Electrodes (Where strip electrode is used for earthing , it should not be less than 25
mm x 1.60 mm, if made of copper and 25 mm x 4 mm if made of G.I. or steel. The length of
the buried conductor should not be less than 15 mtrs. laid in a trench not less than 0.5
mtrs deep. The location of the earth plate and its depth should be such as to ensure that
the earth plate is surrounded by moist earth to possible extent.)
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
IS specification
The cross section of earth continuity conductor should not be less than 2.9 mm2 (14 SWG)
or half of the installation conductor size.
An earthing electrode shall not be situated with in a distance of 1.5 meter from the
building whose installation system is being earthed.
The earth wire and earth electrode will be of same material.
The earth wire shall be taken through G.I. pipe of 13 mm diameter for at least 30 cm length
above and below ground surface to the earth electrode to protect it against mechanical
damage
The earthing electrode shall always be placed in vertical position inside the earth or pit so
that it may not be in contact with all the different earth layers.
Wiring
The conductor for final sub-circuit for fan and light wiring shall have a nominal cross-
sectional area not less than 1.50 mm2 copper. The cross-sectional area of conductor for
power wiring shall be not less than 2.5 mm2 copper. The minimum cross-sectional area of
conductor of flexible cord shall be 1.50 mm2 copper
Type of wiring
1. Cleat wiring
2. batten wiring
It is a temporary wire.
Wire are exposed and is
connected with the help of cleat
Used in places were construction
is going on.
Wire are exposed to weather
Used for short duration.
3. Casing and capping wiring
4. Conduit wiring (Metal or PVC)
a. Surface conduit wiring
b. Canceled conduit wiring
As per the
recommendations of ISI
the maximum number of
points of lights, fans and
socket outlets cannot be
exceed beyond 10 and the
maximum load that can be
connected in such a circuit
is 800 watt.
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
Type of wire.
Copper (High Conductivity, High Tensile Strength)
Aluminum (Low conductivity, Low tensile strength)
a. V.I.R. wires-(Vulcanized India Rubber) In this type of wire a tinned copper conductors or
aluminum conductors are used. The conductors are covered by Vulcanized India
Rubber. It is then covered with cotton tape and cotton braiding. Finally, it is dipped in
bitumen compound. The copper conductor is tinned to provide protection against
corrosion due to presence of traces of sulphur, zinc oxide and other mineral ingredients
in the V.I.R. It is available in single cotton covered, double cotton. It is available in 1/18,
3/20, 3/22, 7/20, 7/22, 7/16, 19/22, 19/16 sizes. It is suitable for indoor conduct wiring,
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
Lecture Notes Building Services-II
casing capping wiring and cleat wiring. This type of wire is available in single core only.
It is suitable for low and medium voltage supply only.
b. C.T.S. wire-(Cabe Tyre Sheath wire) In this type of wires, a tinned copper conductors
are used. These conductors are covered by red and black color rubber. It is then coated
with a layer of hard rubber. It is available in sizes 1/18, 3/20, 7/22 etc. It does not absorb
moisture. It is used in batten wiring service lines and short distance overhead lines. It is
available in 250/440 voltage grade only.
c. T.R.S. wires-(Tough Rubber Sheath) V.I.R., C.T.S., T.R.S. wires are old types wires
which are not used in market.
d. PVC wires In this type of wire, copper or aluminum conductors are used. Conductors are
covered by polyvinyl chloride insulation. It is available in sizes 1mm2, 1.5mm2, 2.5mm2,
4mm2 etc. It is available in single core, twin core and three core. Now a days PVC wires
are widely used. Its life is long. It can be used in PVC conducts PVC casing capping,
overhead wiring etc. These are not sensitive to mild dose of water, heat, oil, acid, alkalis,
sunrays, ultraviolet rays etc. It is available in 600, 660, 1100 Voltage grade. F.R. wires
and F.R.L.S. wires are widely used, because current carrying capacity and voltage
rating is more than old PVC wires.
Uses of wires
1. Multistranded wires are used in domestic wiring.
2. Stranded wires are used in domestic and small industries wiring.
3. Solid wires are generally used in domestic wiring. Standard Wire Gauge The standard
wire gauge (SWG) is an instrument used for determining the size of a conductor of the wire
and cable. It is a thin circular plate of steel with a number of slots on its circumference. Each
slot is marked with specific number denoting gauge. Holes are provided at the end of each
slot for removing the wire easily.
Ar. Bhuvan Mitra Amity School of Architecture and Planning
You might also like
- Installing Electrical Protective Devices For Distribution, Power, Lightning Protection and Grounding SystemsDocument23 pagesInstalling Electrical Protective Devices For Distribution, Power, Lightning Protection and Grounding SystemsYamut Si ako67% (6)
- Electrical WiringDocument11 pagesElectrical WiringRasydan AliNo ratings yet
- Electrical NotesDocument11 pagesElectrical NotesEr Prince KhalidNo ratings yet
- SS 316 04Document12 pagesSS 316 04Muhammad Asif IqbalNo ratings yet
- ZXK 1200 Ascensor Hidrocableado Chino - User Manual (Hydraulic Drive System)Document24 pagesZXK 1200 Ascensor Hidrocableado Chino - User Manual (Hydraulic Drive System)BrianEstebanNo ratings yet
- Training Report On 132/33 KV Sub-StationDocument25 pagesTraining Report On 132/33 KV Sub-StationAbrar Ahmad77% (47)
- Welding Procedure Specification: Wps For Ss To Cs Material (Gtaw+Smaw)Document1 pageWelding Procedure Specification: Wps For Ss To Cs Material (Gtaw+Smaw)Lipika GayenNo ratings yet
- Eim-9 Quarter IVDocument25 pagesEim-9 Quarter IVmanolito mercado jr.No ratings yet
- Protection Circuits: by Murtuza Bohari Sanket Patil Ankit KhandekarDocument21 pagesProtection Circuits: by Murtuza Bohari Sanket Patil Ankit KhandekarSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit According To The IEC 61660 - Open ElectricalDocument6 pagesShort Circuit According To The IEC 61660 - Open ElectricalDoly Damanik100% (1)
- BEE Unit-5 Notes Basic Electrical InstallationDocument22 pagesBEE Unit-5 Notes Basic Electrical InstallationTapendra Tailor100% (10)
- Electrical Installation: The Most Common Types of Faults in Domestic Systems AreDocument23 pagesElectrical Installation: The Most Common Types of Faults in Domestic Systems Arekrishnareddy_chintala100% (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bye Laws - Jaipur PDFDocument14 pagesBye Laws - Jaipur PDFCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Ircuit Reakers: (Theory, Classification, & Applications)Document28 pagesIrcuit Reakers: (Theory, Classification, & Applications)Syed Muhammad Munavvar Hussain100% (5)
- Graduar Avr GeneracDocument4 pagesGraduar Avr GeneracJose Godoy0% (1)
- SUN ReportDocument10 pagesSUN Reportpratham sutharNo ratings yet
- Protective Device A SwtichgearDocument24 pagesProtective Device A SwtichgearVarun Ghagare 03No ratings yet
- Mod 1 Part 2Document16 pagesMod 1 Part 2Bikash SarrafNo ratings yet
- Electrical System Design NotesDocument15 pagesElectrical System Design Notesdilja aravindan100% (1)
- Switchgear NTCCDocument21 pagesSwitchgear NTCCHoney Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Protective DeviceDocument6 pagesElectrical Protective DeviceEstelito C. YlaganNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document13 pagesAssignment 3Ifeoluwa VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Switchgear Lab ManualDocument40 pagesSwitchgear Lab ManualTahirNo ratings yet
- IJERT A Review On Switchgear Analysis AnDocument4 pagesIJERT A Review On Switchgear Analysis Angtecnica129No ratings yet
- Training Report On 220 To 132KV SubstationDocument22 pagesTraining Report On 220 To 132KV SubstationRaendraNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument57 pagesTheorymaaahiiNo ratings yet
- Philippine Elctrical CodeDocument15 pagesPhilippine Elctrical CodeRaeniel SoritaNo ratings yet
- Project Report Name-Shahil Kumar Singh REG NO - 19110126051 Roll No - 19eee43 Branch - Eee College - Bce BakhtiyarpurDocument20 pagesProject Report Name-Shahil Kumar Singh REG NO - 19110126051 Roll No - 19eee43 Branch - Eee College - Bce BakhtiyarpurShahilsingh SinghNo ratings yet
- Inplanttrainingreport123 180416062216Document45 pagesInplanttrainingreport123 180416062216asura22novNo ratings yet
- Chapther ThreeDocument3 pagesChapther ThreeMufutau Kayode LawalNo ratings yet
- Shakir Seminar Report On Ultra ConductorsDocument18 pagesShakir Seminar Report On Ultra ConductorsMeer ShakirNo ratings yet
- IPD & Illu Practical 1Document8 pagesIPD & Illu Practical 1Viktor IartavNo ratings yet
- Disection A InstrumentDocument14 pagesDisection A InstrumentWaseem KhanNo ratings yet
- Digital Testing of Voltage CircuitDocument23 pagesDigital Testing of Voltage CircuitpraneethNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document11 pagesCH 6Vikas UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- EXP 1-9 FinalDocument28 pagesEXP 1-9 FinalMonika KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Inevitable in Almost All Electrical Switchboards - Residual Current Device (RCDDocument19 pagesInevitable in Almost All Electrical Switchboards - Residual Current Device (RCDJoaquim PedroNo ratings yet
- TVE 1st Quarter ReviewerDocument12 pagesTVE 1st Quarter ReviewerGaming DeathNo ratings yet
- Protective DevicesDocument7 pagesProtective Devicesbolt sparkNo ratings yet
- Heerapura Training ReportDocument28 pagesHeerapura Training ReportDurgeshManeshwarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Report On "Switch Gear and Protection" Government College of Engineering AmravatiDocument13 pagesIndustrial Report On "Switch Gear and Protection" Government College of Engineering AmravatiSominath HarneNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Power DistributionDocument43 pagesChapter-1 Power Distributionrajendra88No ratings yet
- Presentation On: New Technology Circuit BreakersDocument28 pagesPresentation On: New Technology Circuit BreakersR. K. ViralNo ratings yet
- Turbo Generator at NalcoDocument13 pagesTurbo Generator at NalcoSanjay Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- Lastactivity NapiliDocument10 pagesLastactivity NapiliMArk BarenoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Building Services Training Day 3 - Session 2Document12 pagesElectrical Building Services Training Day 3 - Session 2Anwar SalimNo ratings yet
- Five Switching Devices You Are Likely To Spot in Most of The Low Voltage SwitchgearDocument15 pagesFive Switching Devices You Are Likely To Spot in Most of The Low Voltage SwitchgearHaris MakrigiannakisNo ratings yet
- Mcbs or Miniature Circuit Breakers Are Electromechanical Devices Which ProtectDocument9 pagesMcbs or Miniature Circuit Breakers Are Electromechanical Devices Which ProtectDivyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- InstallationDocument45 pagesInstallationshaadi220622No ratings yet
- Starter PanelDocument7 pagesStarter PanelsaravananNo ratings yet
- Automatic Circuit Breaker ACB For Low Voltage SubsDocument23 pagesAutomatic Circuit Breaker ACB For Low Voltage Subsallan kiplimoNo ratings yet
- Training Report of Grid Substation: Presented byDocument11 pagesTraining Report of Grid Substation: Presented byତୁଷାର ମିଶ୍ର100% (1)
- 1 Three Phase Power Measurement, Electrical Safety - Fuses and Earthing, Residential WiringDocument49 pages1 Three Phase Power Measurement, Electrical Safety - Fuses and Earthing, Residential WiringUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breakers D1Document18 pagesCircuit Breakers D1Fatih KayalarNo ratings yet
- Smart Distribution System Members: A Seminar Presentation ONDocument18 pagesSmart Distribution System Members: A Seminar Presentation ONPratima ChavanNo ratings yet
- Switches and BreakersDocument32 pagesSwitches and BreakersJely Taburnal BermundoNo ratings yet
- Prateek ReportDocument27 pagesPrateek ReportGirijesh YadavNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document9 pagesCH 16siya shahNo ratings yet
- Lab Session 5 Contactor Controlled Motor Starting Circuits: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Session 5 Contactor Controlled Motor Starting Circuits: ObjectiveHermain Fayyaz KarimNo ratings yet
- Lab Session 5 Contactor Controlled Motor Starting Circuits: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Session 5 Contactor Controlled Motor Starting Circuits: ObjectiveHermain Fayyaz KarimNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument8 pagesDocumentutharun3No ratings yet
- PSP Notes PDFDocument8 pagesPSP Notes PDFpriyank srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Image © 2020 Maxar TechnologiesDocument1 pageImage © 2020 Maxar TechnologiesCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Commercial Destination: Impeccable Business EnvironmentDocument16 pagesUltimate Commercial Destination: Impeccable Business EnvironmentCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Image © 2020 Maxar TechnologiesDocument1 pageImage © 2020 Maxar TechnologiesCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Brochure InfoDocument3 pagesBrochure InfoCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi International Airport Development Project: Submitted ToDocument22 pagesIndira Gandhi International Airport Development Project: Submitted ToCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Alternate Way of LivingDocument2 pagesAlternate Way of LivingCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Blackwell Encyclopedia of Urban and Regional Studies, Chichester: Wiley-BlackwellDocument5 pagesBlackwell Encyclopedia of Urban and Regional Studies, Chichester: Wiley-BlackwellCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Housing Project Management PDFDocument11 pagesHousing Project Management PDFCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Native Plants Type of Plant S.No. Name Image: 1 MangoDocument10 pagesNative Plants Type of Plant S.No. Name Image: 1 MangoCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- Stone Mosaic PDFDocument37 pagesStone Mosaic PDFCharu DuggalNo ratings yet
- HumeraRafique 2553 15200 2S17-EMS7-DC MachinesDocument28 pagesHumeraRafique 2553 15200 2S17-EMS7-DC MachinesZeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Mps 2 120 - eDocument1 pageMps 2 120 - emillon thomasNo ratings yet
- 4a Digital System - Number System & ConversionDocument59 pages4a Digital System - Number System & ConversionAhmad IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesElectricity: Multiple Choice QuestionsRamagya SinghNo ratings yet
- Emcs STDocument124 pagesEmcs STTESLA- Alessandro LucasNo ratings yet
- Manual K8004Document12 pagesManual K8004b3nyNo ratings yet
- ITAPower-SMART PLUS 6-10K User Manual ENDocument33 pagesITAPower-SMART PLUS 6-10K User Manual ENAbdelwhab ElsaftyNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Instrumentation Objective Questions With AnswersDocument3 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation Objective Questions With AnswersMohan Raj100% (1)
- Impact of Distributed Generation On Protection and Voltage Regulation of Distribution Systems: A ReviewDocument28 pagesImpact of Distributed Generation On Protection and Voltage Regulation of Distribution Systems: A Reviewjijo123408No ratings yet
- 1.0A Low Dropout Linear Regulator Az1117EDocument13 pages1.0A Low Dropout Linear Regulator Az1117EShames ElhoryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Example of Maintenance 1Document7 pagesChapter 22 Example of Maintenance 1Ij OooNo ratings yet
- BE21 - Genset Control PDFDocument2 pagesBE21 - Genset Control PDFFreddy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Underwater Biorobots A Wireless System For Power TransferDocument7 pagesAutonomous Underwater Biorobots A Wireless System For Power TransfermarwanNo ratings yet
- Procedure ADocument29 pagesProcedure ADEBASISDAS19790% (1)
- 218 Units: M/S Subhan Allah BuildersDocument2 pages218 Units: M/S Subhan Allah BuildersHasan ShahNo ratings yet
- EEE 202S Exp3Document8 pagesEEE 202S Exp3Sudipto PramanikNo ratings yet
- 966h Wheel Loader Ryf00001-Up (Machine) Powered by c11 Engine (Sebp5426 - 38) - DocumentaciónDocument4 pages966h Wheel Loader Ryf00001-Up (Machine) Powered by c11 Engine (Sebp5426 - 38) - Documentaciónjulio100% (1)
- LG 42pc55 (ET)Document53 pagesLG 42pc55 (ET)Andy CoyneNo ratings yet
- Flyback Diode - WikipediaDocument3 pagesFlyback Diode - WikipediaMatias RamosNo ratings yet
- Complete PhysicsDocument54 pagesComplete PhysicsAbhinandan KhajuriaNo ratings yet
- DE2 115 Pin AssignmentDocument4 pagesDE2 115 Pin AssignmentKamal HaydarNo ratings yet
- GBLCDocument8 pagesGBLCtai08cdt2No ratings yet
- Sistemet Elektronike - Ciftimi NegativDocument5 pagesSistemet Elektronike - Ciftimi NegativINGNo ratings yet
- 750wrms For 2ohm 75vdc Af Pa Fpa Ab 750 l2 Ab 2e STD Rev 2Document2 pages750wrms For 2ohm 75vdc Af Pa Fpa Ab 750 l2 Ab 2e STD Rev 2Nanang Rachman0% (1)
- Application of IEC 61724 Standards To Analyze PV System Performance in Different ClimatesDocument14 pagesApplication of IEC 61724 Standards To Analyze PV System Performance in Different ClimateslllNo ratings yet
- Advanced DWDM TrainingDocument144 pagesAdvanced DWDM TrainingCarlosNo ratings yet