Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biomolecules: Revision Map
Uploaded by
Harsh KeshriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biomolecules: Revision Map
Uploaded by
Harsh KeshriCopyright:
Available Formats
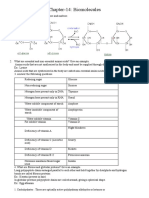
REVISION MAP
Biomolecules
These are the macromolecules essential for survival of life, e.g. carbohydrates, proteins, etc.
Carbohydrates Proteins Vitamins, Nucleic Acids
These are polyhydroxy aldehydes or These are polymers of a
-amino acids. and Hormones
ketones or their derivatives, e.g. glucose.
Amino Acids Vitamins
These contain amino as well as carboxyl These are essential but in very small
functional group. amounts. Vitamins A, D, E and K are fat
Sugars
They may be essential or non-essential. soluble while rest are water soluble.
These are the carbohydrates having sweet
taste.
They may be reducing (e.g. glucose)or
=
Zwitter Ion Deficiency Diseases
non-reducing (e.g. starch).
Ion containing positive as well as negative Vitamin Deficiency Disease
charge is called Zwitter ion. A Xerophthalmia
O B1 Beri-beri
Glucose B12 Pernicious anaemia
e.g. R—CH—C—O–
It is obtained by hydrolysing starch or
? C Scurvy
—
cane sugar. +NH
3 D Rickets
? Its reactions are as: E Muscular weakness
HI
Glucose D
n-hexane Denaturation
NH2OH
Oxime ?
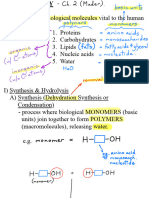
It is the process of destroying 2° or 3°
3 mol structure of protein by heating and by Nucleic Acids
Br2 water changing pH. These are the polymer of nucleotides (sugar
Gluconic acid + base + phosphoric acid).
Acetylation ?
Due to this, protein losts its biological
Pentaacetate
CH3COCl activity.
HNO3
Saccharic acid ?
e.g. Coagulation of egg white on boiling. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
It contains pentose sugar (deoxyribose),
purine base (adenine, A and guanine, G)
Sucrose pyrimidine base (Thymine, T and
It contains D-(+)-glucose and
? Structure of Proteins cytosine, C) and phosphoric acid.
D(–)-fructose joined together by
b-1,2-glycosidic linkage.
? It is also called invert sugar. Primary Structure
It shows the sequence of amino acids Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
in a protein. It contains sugar (ribose), purine base
Starch (adenine, A and guanine, G) and
pyrimidine base (uracil, U and cytosine, C)
It contains two components: amylose
?
Secondary Structure and phosphoric acid.
(water soluble, 20%) and amylopectin
(80%, water insoluble). It is formed due to hydrogen bonding
and may be a -helix or b
-pleated sheet
? It is the reserve food of plants.
structure.
Hormones
Cellulose These are the secretions of endocrine glands.
Most abundant in plants and contains
? Enzymes
glucose units, joined together by These are the proteins which catalyse
b-1,4-glycosidic linkage. reactions occurring in human body, so also
called biocatalysts, e.g. maltase, zymase,
etc. Steroid Hormones
e.g. Sex hormones, bile acids, etc.
Non-steroid Hormones
These do not have steroid ring, e.g.
insulin.
You might also like
- Non-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseFrom EverandNon-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesFrom EverandThe Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Revision MapDocument1 pageBiomolecules: Revision MapS SanjayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - General and Characteristics. Water Soluble VitaminsDocument29 pagesLecture 6 - General and Characteristics. Water Soluble VitaminsEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- Unit I Nitrogen of Metabolism.Document100 pagesUnit I Nitrogen of Metabolism.Carlos LandaNo ratings yet
- 3rdsem Biochem AROMATIC AND ALIPHATIC AMINO ACIDS ContinuedDocument17 pages3rdsem Biochem AROMATIC AND ALIPHATIC AMINO ACIDS ContinuedRiyazNo ratings yet
- Binomial, 4710144a2189Document2 pagesBinomial, 4710144a2189vikashrajrn10No ratings yet
- Printable Lecture On Enzymes and Vitamins Main 1Document37 pagesPrintable Lecture On Enzymes and Vitamins Main 1Izzy ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule-Short Cut TipsDocument2 pagesBiomolecule-Short Cut TipsEbe JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Vit CDocument31 pagesVit CsatyadbaNo ratings yet
- Vit CDocument31 pagesVit CsatyadbaNo ratings yet
- Unit-14 Biomolecules Mini 2023Document5 pagesUnit-14 Biomolecules Mini 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and CoenzymesDocument46 pagesVitamins and CoenzymesPertunia MulatedziNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Coenzymes PharmacyDocument55 pagesVitamins and Coenzymes PharmacywithneyNo ratings yet
- XII Biomolecules OrganizedDocument9 pagesXII Biomolecules OrganizedKazi afroz SultanNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument14 pagesBiomoleculesnadeemmessi30No ratings yet
- I. 1° Structure Determination of A Polypeptide General StepsDocument6 pagesI. 1° Structure Determination of A Polypeptide General StepsAllyson CarlosNo ratings yet
- Vitamin CDocument38 pagesVitamin CDR JIJIN J UNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism: Inborn ErrorsDocument18 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism: Inborn ErrorsAdedoyin BankoleNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Proteins, Viamins, Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pagesBiomolecules - Proteins, Viamins, Nucleic Acidsharshmahto223No ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism 2Document29 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism 2Francis GacheruNo ratings yet
- Carbs 2Document6 pagesCarbs 2Biang AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Harper's Biochemistry - C3 Amino Acids & PeptidesDocument2 pagesHarper's Biochemistry - C3 Amino Acids & PeptidesKim LlamasNo ratings yet
- Vitamins N MSC 2019Document105 pagesVitamins N MSC 2019Shasha Reverse AgingNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Key Points ExplanationsDocument2 pagesBiomolecules: Key Points ExplanationsAgasthyaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MicroelementsDocument94 pagesVitamins and MicroelementsDrRanjeet Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Proteins BiochemDocument10 pagesProteins BiochemRein TopacioNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document14 pagesCH 14Tr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Bio Mole CuleDocument13 pagesBio Mole CuleaayanNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Metabolism Intro - BC I 2565-SheetDocument43 pagesVitamin and Metabolism Intro - BC I 2565-SheetWirawit SIWONGTRAKULNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Food SupplementsDocument36 pagesVitamins and Food SupplementsSuphitchaKatroopNo ratings yet
- Gen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid CrossDocument2 pagesGen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid CrossDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- FKUH - Vit Mineral PDFDocument37 pagesFKUH - Vit Mineral PDFZafa AiharaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin CDocument50 pagesVitamin CMaya DasmaselaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Name Molecular FunctionDocument1 pageVitamin Name Molecular Functionajayterdal8471No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument454 pagesUntitledMegan Grace EbreoNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry - Activity 2Document3 pagesFood Chemistry - Activity 2Leda PeñaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Lec NotesDocument6 pagesCarbohydrates Lec NotesriveraallexaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Chemistry Every Day LifeDocument5 pagesBiomolecules and Chemistry Every Day LifeNeel SiddhpuraNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument15 pagesBio Moleculescoleen paraynoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Metabolism, Functions, and NutritionDocument17 pagesAmino Acids Metabolism, Functions, and NutritionJulio de Sousa100% (1)
- Biomolecules RevisionDocument12 pagesBiomolecules Revisionpk2637932No ratings yet
- Vitamin E & K-BdsDocument50 pagesVitamin E & K-BdsIsaiah JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Chemical Composition in A TissueDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Chemical Composition in A TissueThe RevolutionNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument7 pagesBIOMOLECULESMasum AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture Vitamins 2020Document99 pagesLecture Vitamins 2020Lawal Bello DanchadiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes HoDocument9 pagesEnzymes Hochristian redotaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Comprehensive2514897212738Document15 pagesBiomolecules Comprehensive2514897212738DeepanshuNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument21 pagesBiochemistryeagleawesome4No ratings yet
- Mls 218 Protein-MetDocument45 pagesMls 218 Protein-MetZainabNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument12 pagesBio MoleculesDiya ChawanNo ratings yet
- Gen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid CrossDocument2 pagesGen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid CrossDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument19 pagesBIOMOLECULESarviindkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Table For Exam 3Document3 pagesTable For Exam 3raybuaNo ratings yet
- 07 Amino Acid MetabolismDocument108 pages07 Amino Acid MetabolismMuhammad Awais NoorNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - 2 - ProteinsDocument5 pagesBiochemistry - 2 - ProteinsSugar DCNo ratings yet
- LEC 03 - Amino Acids & PeptidesDocument90 pagesLEC 03 - Amino Acids & Peptideseliza makNo ratings yet
- PDH and TCeDocument9 pagesPDH and TCeManila MedNo ratings yet
- Study Rate: Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument21 pagesStudy Rate: Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 BiomoleculesYASH SONARNo ratings yet
- Co- and Post-Translational Modifications of Therapeutic Antibodies and ProteinsFrom EverandCo- and Post-Translational Modifications of Therapeutic Antibodies and ProteinsNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base CalculationsDocument9 pagesAcid and Base CalculationsDaniel McDermott0% (1)
- CP-29 Carbopol Aqua SF-1 Product SummaryDocument2 pagesCP-29 Carbopol Aqua SF-1 Product SummaryadrianaNo ratings yet
- List of h2 Chemistry DefinitionsDocument7 pagesList of h2 Chemistry Definitionsapi-342193969100% (1)
- Bhopal Gas TragedyDocument14 pagesBhopal Gas Tragedypiyu_43No ratings yet
- For Teachers Only P .S.-CH: Physical Setting/ChemistryDocument10 pagesFor Teachers Only P .S.-CH: Physical Setting/ChemistryAAVANINo ratings yet
- Colorimeter Chlorine Eutech C201Document60 pagesColorimeter Chlorine Eutech C201gintaniNo ratings yet
- Additive Solutions For Low Sulphur Fuelsadditive Solutions For Low Sulphur Fuels July 10Document35 pagesAdditive Solutions For Low Sulphur Fuelsadditive Solutions For Low Sulphur Fuels July 10Mazhar HussainNo ratings yet
- Aimst University School of General & Foundation Studies: Problem Based AssessmentDocument6 pagesAimst University School of General & Foundation Studies: Problem Based AssessmentChan Jun YeeNo ratings yet
- Astm B 316 Acero InoxidableDocument9 pagesAstm B 316 Acero InoxidableMajo BárcenasNo ratings yet
- Operational Pollution of ShippingDocument24 pagesOperational Pollution of ShippingKamal RahimNo ratings yet
- Laundry Detergents An Overview Bajpai 2007Document14 pagesLaundry Detergents An Overview Bajpai 2007IsaacVandermeulen100% (1)
- Confidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)Document9 pagesConfidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)ThilagaNo ratings yet
- HetshortDocument4 pagesHetshortSallyCroyNo ratings yet
- Biological WastwaterDocument486 pagesBiological WastwaterLeanne MartinNo ratings yet
- 2021 Master CatalogDocument330 pages2021 Master Cataloggeetha raniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 MoldingDocument46 pagesChapter 4 MoldingTamirat NemomsaNo ratings yet
- Alkane and AlkeneDocument40 pagesAlkane and AlkenePawankumar Gupta91% (11)
- SFBK WhitegoldChris CortiDocument18 pagesSFBK WhitegoldChris Corti7013131870131318No ratings yet
- The Role of Oxygen and Hydrogen in Refining - tcm17-416854Document8 pagesThe Role of Oxygen and Hydrogen in Refining - tcm17-416854alhag alhebirNo ratings yet
- Answer 1:: (Chapter 1) (Chemical Reactions and Equations)Document2 pagesAnswer 1:: (Chapter 1) (Chemical Reactions and Equations)apfc epfoNo ratings yet
- PMI ProcedureDocument9 pagesPMI ProcedureKarrar TalibNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Modular GasProcessing Plants BrochureDocument8 pagesHoneywell Modular GasProcessing Plants BrochureCHE.ENG1734No ratings yet
- The Gabriel Synthesis of Benzylamine: An Undergraduate Organic ExperimentDocument2 pagesThe Gabriel Synthesis of Benzylamine: An Undergraduate Organic ExperimentJuan MartínezNo ratings yet
- What Is Heat TreatmentDocument2 pagesWhat Is Heat TreatmentPradyot DeoliaNo ratings yet
- Nicored 182 PDFDocument1 pageNicored 182 PDFDương Quang KhánhNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1025 Reactions of AromaticsDocument5 pagesChemsheets A2 1025 Reactions of AromaticsdodoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Stabilized Pavement MaterialsDocument46 pagesChapter Four Stabilized Pavement Materialsyeshi janexoNo ratings yet
- SILVERFREE - SE0089G - Holistic Hair Repigmenting Serum v1Document2 pagesSILVERFREE - SE0089G - Holistic Hair Repigmenting Serum v1PaoloMMNo ratings yet
- Preparation of P-Nitroacetanilide, Hydrolysis of P-Nitroacetanilide, Preparation of P-Nitroaniline (Student's Handout) PDFDocument8 pagesPreparation of P-Nitroacetanilide, Hydrolysis of P-Nitroacetanilide, Preparation of P-Nitroaniline (Student's Handout) PDFNarayan Deshmukh25% (4)
- EE Lab Manual Final DraftDocument186 pagesEE Lab Manual Final DraftVamshi ChaitanyaNo ratings yet