Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid Cross
Uploaded by
Dharsinero Sabandal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Biology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesGen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid Cross
Uploaded by
Dharsinero SabandalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
GEN.
BIO REBYUWER by huwebes TYPE A
–Universal recipient
Carries antigen A and B
DIHYBRID CROSS
TYPE O
–mating of 2 different traits –Universal donor
–two different parents wt 2 different traits e.g
e.g
a. Color of the seeds (YELLOW vs. GREEN)
IA IB
b. Shape of the seeds (ROUND vs. WRINKLED)
SOLUTION: i IAi IBi
YYRR x YYRr i IAi IBi
YR YR YR YR YR Yr YR Yr
DNA- DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID
YR YR YR YR –nucleic acid-macromolecule/ biomolecule
YR YYRR YYRR YYRR YYRR –blueprint of life.
Yr YYRr YYRr YYRr YYRr –code –coding of amino acids
YR YYRR YYRR YYRR YYRR
Yr YYRr YYRr YYRr YYRr 3 COMPONENTS OF AMINO ACIDS
Genotype:8 YYRR & 8YYRr GR: 8:8 a. 4 NITROGENOUS BASES:
Phenotype: 16 yellow round PR:16:0
PURINES
NON-MENDELIAN Adenine and Guanine
PYRAMIDINES
–any pattern of inheritance in which traits do not Uracil/Thymineand Cytosine
segregate in accordance with mendelian laws.
When complementary:
INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE A-T
– Pattern of inheritance resuling to the blending G-C
of traits
When we want to duplicate DNA:
–neither of the traits is dominace
1st trait = R1 R1 2nd trait= R2R2 3rd trait= R1R2
T-A
e.g: C-G
Black & White
B1B1 x B2B2 e.g
=B1B2, B1B2, B1B2, B1B DNA STRAND: GCTAATCGACGTACG
CODOMINANCE COMPLIMENTARY: CGATTAGCTGCATGC
–The expression of both traits
e.g THYMINE TO URACIL WHEN CODING
Red & White RNA:
RR x WW RNA STRAND: GCU/AAU/CGA/CGU/ACG
RW RW RW RW *need 3 bases to create codons- amino acid
*ANTICODON- 4th process
MULTIPLE ALLEILISM
– Third non-mendelian patterns that contains 3 or
more alleles. b. PHOSPATE GROUP
–ABO Blood Groups – Compose of phosphorous
Type A= IAIA or IAi c. DEOXYRIBOSE SUGAR
Type B= IBIB or IBi –compose of Carbon atoms
Type O= ii
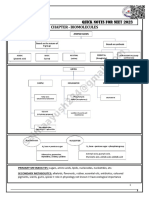
3 PROCESS CENTRAL DOGMA OF which disrupt the stabilizing structures.S tructure
becomes random and disorganized.
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
–can also be denatured by heavy-metal ions such as
Hg2+, Ag+, and Pb2+ that interact with —SH and
A. REPLICATION carboxylate groups.
cmost important .
-Complemtary DNA strand SUBSTANCES THAT DENATURED PROTEIN:
1. Heat and ultraviolet light -Disrupt hydrogen
bonds and ionic attractions by making
B. TRANSCRIPTION molecules vibrate too violently; produce
-codons coagulation, as in cooking an egg
C. TRANSLATION 2. Organic solvents (ethanol and others
-message is translated miscible with water) - Disrupt hydrogen
Amino acid+amino acid bonds in proteins and probably form new
=Nucleotides ones with the proteins
3. Strong acids or bases- Disrupt hydrogen
MAIN CLASS SOME TYPE OF bonds and ionic attractions; prolonged
SUBCLASSES REACTION exposure results in hydrolysis of protein
CATALYZED 4. Detergents- Disrupt hydrogen bonds,
hydrophobic interactions, and ionic
Hydrolases Lipases Hydrolysis of an attractions.
Nucleases ester group
5. Heavy-metal ions (Hg2+, Ag+, and Pb2+)-
Proteases Hydrolysis of a
Phosphate Form bonds to thiol groups and precipitate
group proteins as insoluble heavy-metal salts
Hydrolysis of an
amide group
Isomerases Epimerases Isomerization of
stereocenter
Ligases Carboxylases Addition of
Synthesases Carbon Dioxide
Formation of
New bond
Lyases Decarboxylases Loss of Carbon
Dehydrases Dioxide
Loss of Water
Oxidoreductases Dehydrogenases Introduction of
Oxidases double bond by
Reductases removal of H2
Oxidation
Reduction
Ligases Kinases Transfer of a
Transaminases phosphate
group
Transfer of an
amino group
PROTEIN DENATURATION
–caused when the folded native structures break
down because of extreme temps. or pH values,
You might also like
- Asme B18.24-2020Document190 pagesAsme B18.24-2020윤규섭0% (1)
- MCAT - BiologyDocument15 pagesMCAT - BiologyEmily Teo100% (1)
- SECURED TRANSACTION BAR CHECKLISTDocument4 pagesSECURED TRANSACTION BAR CHECKLISTatw4377100% (1)
- Chemical Basis of Life: Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemical Basis of Life: Basic ChemistryMauanay, Marjelyn P.No ratings yet
- MCAT Biochem Amino Acids Review: Protein Structure & EnzymesDocument4 pagesMCAT Biochem Amino Acids Review: Protein Structure & EnzymesNicole Ann LimNo ratings yet
- UP - Organic ChemistryDocument14 pagesUP - Organic ChemistryKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Pricing For International Markets 1. Discuss The Causes of and Solutions For Parallel (Grey Markets) Imports and Their Effects On PriceDocument23 pagesPricing For International Markets 1. Discuss The Causes of and Solutions For Parallel (Grey Markets) Imports and Their Effects On PricePeter Mboma100% (1)
- E-Way BillDocument1 pageE-Way BillShriyans DaftariNo ratings yet
- Chem 40.1 PostlabDocument6 pagesChem 40.1 PostlabaraneyaNo ratings yet
- Bartending and Catering: Agenda: Basics of Bartending Bar Tools and EquipmentDocument146 pagesBartending and Catering: Agenda: Basics of Bartending Bar Tools and EquipmentMars Mar100% (1)
- Passenger Handling Presentation 2020Document305 pagesPassenger Handling Presentation 2020Elshaikh100% (1)
- Airport Design GuidelinesDocument408 pagesAirport Design Guidelinesnickolololo67% (9)
- Issues in First Language AcquisitionDocument4 pagesIssues in First Language AcquisitionKatrina BuhianNo ratings yet
- Improve Product Packaging at Annual Board MeetingDocument9 pagesImprove Product Packaging at Annual Board Meetingizzat89% (9)
- Batu Belah Batu BertangkupDocument2 pagesBatu Belah Batu BertangkupZnyjean Sophia69% (109)
- Gen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid CrossDocument2 pagesGen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid CrossDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Crash Course NotesDocument22 pagesBiomolecules Crash Course NotesAayush sainiNo ratings yet
- Note (Khan)Document5 pagesNote (Khan)Daniel LiNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Db014 Molecule of Life 2020Document26 pages1.0 Db014 Molecule of Life 2020Aisya YezidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - EnzymesDocument19 pagesLecture 3 - EnzymesEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document8 pagesAssignment 2Nesha VincentNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Unit 1 Chemistry of Life - BWDocument2 pagesAP Bio Unit 1 Chemistry of Life - BWstudynote155No ratings yet
- J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 1951−1958Document8 pagesJ. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 1951−1958NoimurNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 5Document25 pagesPDF Document 5miriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Unit-14 Biomolecules Mini 2023Document5 pagesUnit-14 Biomolecules Mini 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Properties, Structures, and Functions in ProteinsDocument9 pagesAmino Acids: Properties, Structures, and Functions in ProteinsZari NovelaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration Requires O2Document46 pagesAerobic Respiration Requires O2Alexander LotukhovNo ratings yet
- Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDDocument46 pagesGly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDketakeeNo ratings yet
- Biochem MidtermsDocument6 pagesBiochem MidtermskizzaymenteraNo ratings yet
- RevisDocument28 pagesRevisPrabhakar BandaruNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class X Chemistry 086 TheoryDocument12 pagesCbse Class X Chemistry 086 TheoryBara' HammadehNo ratings yet
- Xii CH14 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesXii CH14 BiomoleculesKrish KambojNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesHydrocarbonsMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Particle Size: 1-1000 NM, Dispersed Large Molecules or Aggregates Particle Size: Over 1000 NM, Suspended Large Particles or AggregatesDocument2 pagesParticle Size: 1-1000 NM, Dispersed Large Molecules or Aggregates Particle Size: Over 1000 NM, Suspended Large Particles or Aggregatessaiid astaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids - R GroupsDocument24 pagesAmino Acids - R GroupsAakash HaiderNo ratings yet
- BMM LEC 5 SN Structure & Function of Amino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsDocument2 pagesBMM LEC 5 SN Structure & Function of Amino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- Lec. 4Document6 pagesLec. 4Dr. Mohamed ShamsNo ratings yet
- P-Block Elements - Carbon Family - Chemistry Notes For IITJEE - NEETDocument14 pagesP-Block Elements - Carbon Family - Chemistry Notes For IITJEE - NEETAdarsh AnandNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesMolecular BiologySapreen KaurNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument16 pagesBiological MoleculesThandeka NcubeNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature Organic Chemistry SummaryDocument5 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature Organic Chemistry SummaryJoanna MalizaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Reactions, Properties and PreparationDocument25 pagesAldehydes and Ketones: Reactions, Properties and PreparationBhavesh KNo ratings yet
- Harper's Biochemistry - C3 Amino Acids & PeptidesDocument2 pagesHarper's Biochemistry - C3 Amino Acids & PeptidesKim LlamasNo ratings yet
- Biochem TemplateDocument8 pagesBiochem TemplateHyacinth Lei CuynoNo ratings yet
- Mic180 - Chapter 7 - Nucleic Acid - EditedDocument59 pagesMic180 - Chapter 7 - Nucleic Acid - EditedNur ShahirahNo ratings yet
- Lipids and Nucleic Acids: Structures, Functions and ExamplesDocument5 pagesLipids and Nucleic Acids: Structures, Functions and ExamplesJ Twenty-sevenNo ratings yet
- Rhettbro Amino Acid Protein StructureDocument1 pageRhettbro Amino Acid Protein StructureFatiya ShariffNo ratings yet
- PHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerDocument8 pagesPHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerMarie Eloise BugayongNo ratings yet
- Intro To Chemistry 1 of 2Document53 pagesIntro To Chemistry 1 of 2Jolly Ducoy PuertosNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis:: Variations On The ThemeDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis:: Variations On The ThemeHaq ChandioNo ratings yet
- Bio Mole CuleDocument13 pagesBio Mole CuleaayanNo ratings yet
- 32 Vitamins Bioenergetics PDFDocument12 pages32 Vitamins Bioenergetics PDFAkram ZayedNo ratings yet
- Desulfosarcina: Widdel 1981, 382 (Effective Publication: Widdel 1980, 382)Document7 pagesDesulfosarcina: Widdel 1981, 382 (Effective Publication: Widdel 1980, 382)Jose SuarezNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 Biology Chapter 1Document187 pagesSem 1 Biology Chapter 1Safwan AliNo ratings yet
- Reactions and Mechanisms of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesReactions and Mechanisms of Carbonyl CompoundsSamNo ratings yet
- Antecedentes - FermentationsDocument21 pagesAntecedentes - FermentationsSchenckii MtNo ratings yet
- Chemical Research. Institute Non-Aqueous Solutions Tohoku University Katahira Sendai Japan Received AprilDocument3 pagesChemical Research. Institute Non-Aqueous Solutions Tohoku University Katahira Sendai Japan Received AprilliangkyawswarNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure ATEDocument31 pagesProtein Structure ATErollyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: An Introduction Trudy Mckee 6th SolutionDocument46 pagesBiochemistry: An Introduction Trudy Mckee 6th Solution전상영No ratings yet
- Chen Zhang 2012Document7 pagesChen Zhang 2012yussefmontplaisirNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Water Chemistry and Operation of DM PlantDocument126 pagesWelcome: Water Chemistry and Operation of DM PlantahmadrNo ratings yet
- Test 2 - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTest 2 - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsChrisNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi - Key Highlights from Chemistry NotesDocument20 pagesNamma Kalvi - Key Highlights from Chemistry NotesLoyal FriniteNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Energy TransformationDocument1 pageCellular Respiration and Energy TransformationRhaven GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Structure of GlucoseDocument25 pagesStructure of GlucoseHassan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Revision MapDocument1 pageBiomolecules: Revision MapS SanjayNo ratings yet
- Biology HL SL Specimen Papers 1a 2b 2 enDocument164 pagesBiology HL SL Specimen Papers 1a 2b 2 enRichard ShinNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Revision MapDocument1 pageBiomolecules: Revision MapHarsh KeshriNo ratings yet
- Strained Organic Molecules: Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 38From EverandStrained Organic Molecules: Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 38No ratings yet
- Point Column1 Rank PercentDocument7 pagesPoint Column1 Rank PercentDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- How Language Theorists Can Help You Learn a Second LanguageDocument5 pagesHow Language Theorists Can Help You Learn a Second LanguageDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Impromptu SpeechDocument2 pagesImpromptu SpeechDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesBiomoleculesDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- English CG!Document247 pagesEnglish CG!Ronah Vera B. TobiasNo ratings yet
- Lewis Carroll's Nonsensical Poem "JabberwockyDocument1 pageLewis Carroll's Nonsensical Poem "JabberwockyDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Egypt's Culture and TraditionsDocument29 pagesEgypt's Culture and TraditionsDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- What Is An Entrepreneurial Behaviour?Document2 pagesWhat Is An Entrepreneurial Behaviour?Dharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Audience and Purpose of TranslationDocument9 pagesAudience and Purpose of TranslationDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- History of Translation: January 2013Document10 pagesHistory of Translation: January 2013Dharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Purpose of Translation Part I - Understanding Between Nations and CulturesDocument3 pagesPurpose of Translation Part I - Understanding Between Nations and CulturesDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egypt: Beginning in 3200 Ancient Egypt Was A Time of Pharaohs, Conquest, and Great Architectural GrowthDocument29 pagesAncient Egypt: Beginning in 3200 Ancient Egypt Was A Time of Pharaohs, Conquest, and Great Architectural GrowthDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Movie ReviewDocument7 pagesHow To Write A Movie ReviewDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Egypt's Ancient Culture and TraditionsDocument1 pageEgypt's Ancient Culture and TraditionsDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Gen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid CrossDocument2 pagesGen - Bio Rebyuwer: Dihybrid CrossDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- CWDocument2 pagesCWDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 2Document66 pages08 - Chapter 2Dharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Ex 46Document1 pageEx 46Dharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- A Linguistic Theory of Translation An EsDocument65 pagesA Linguistic Theory of Translation An EsDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- What Is TranslationDocument64 pagesWhat Is TranslationsellcoksNo ratings yet
- SylDocument7 pagesSylDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Identifying Errors ActivityDocument1 pageIdentifying Errors ActivityDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- DLL 21st Century Lit Wk18Document9 pagesDLL 21st Century Lit Wk18Dharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Makato and The Cowrie ShellDocument1 pageMakato and The Cowrie ShellHanie Balmedina-RazoNo ratings yet
- The Authors: Bente Pers ReviewerDocument1 pageThe Authors: Bente Pers ReviewerDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- PEOPLE IN MY TOWN - Song Worksheet PAULA 2019Document2 pagesPEOPLE IN MY TOWN - Song Worksheet PAULA 2019PauNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current Testing Exam Questions Assignment2Document1 pageEddy Current Testing Exam Questions Assignment2Narotam Kumar GupteshwarNo ratings yet
- SRV210 - 250TC Spare PartsDocument2 pagesSRV210 - 250TC Spare PartsEnzo SovittiNo ratings yet
- K - LP - Week 24 - Journeys Unit 3 Lesson 14Document8 pagesK - LP - Week 24 - Journeys Unit 3 Lesson 14englishwithmslilyNo ratings yet
- Report-Teaching English Ministery of EduDocument21 pagesReport-Teaching English Ministery of EduSohrab KhanNo ratings yet
- Sax AltoDocument2 pagesSax AltoJohnny GervasioNo ratings yet
- Forum Ex 2 2Document5 pagesForum Ex 2 2Didan EnricoNo ratings yet
- Document Revision TableDocument11 pagesDocument Revision Tableseva1969No ratings yet
- Tugas 3vDocument4 pagesTugas 3vRomie SyafitraNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Becoming EntrepreneurDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Becoming EntrepreneurbxndNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument4 pagesNumber SystemGlenn ThomasNo ratings yet
- Exclusion and Lack of Accessibility in TheatreDocument12 pagesExclusion and Lack of Accessibility in TheatrebethanyslaterNo ratings yet
- Beef Steaks: MethodDocument2 pagesBeef Steaks: MethodGoshigoshi AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Educ 580 - Edpuzzle PD HandoutDocument3 pagesEduc 580 - Edpuzzle PD Handoutapi-548868233No ratings yet
- Piano: Grade 2: PiecesDocument4 pagesPiano: Grade 2: PiecesnolozeNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing and Managing Acute and Chronic SinusitisDocument14 pagesDiagnosing and Managing Acute and Chronic SinusitisAnonymous y3TIOwX8100% (1)
- Clinical Presentation of Ectopic Pregnancy Turned Out to Be Ectopic PregnancyDocument33 pagesClinical Presentation of Ectopic Pregnancy Turned Out to Be Ectopic PregnancyRosiNo ratings yet
- Certified Islamic Professional Accountant (Cipa) ProgramDocument13 pagesCertified Islamic Professional Accountant (Cipa) ProgramTijjani Ridwanulah AdewaleNo ratings yet
- Beowulf The Monsters and The Critics SevDocument20 pagesBeowulf The Monsters and The Critics SevNirmala GaneshNo ratings yet
- Repport Btech FinalDocument49 pagesRepport Btech FinalSuzelle NGOUNOU MAGANo ratings yet
- ID Strategi Integrated Marketing Communication Imc Untuk Meningkatkan Loyalitas AngDocument17 pagesID Strategi Integrated Marketing Communication Imc Untuk Meningkatkan Loyalitas AngAiman AzhariNo ratings yet
- AS400 Config Audit Checklist Security BrigadeDocument4 pagesAS400 Config Audit Checklist Security BrigadeAlok DriveqNo ratings yet