Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Nyc Scopeandsequence 5-130606
Uploaded by
api-351301306Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Nyc Scopeandsequence 5-130606
Uploaded by
api-351301306Copyright:
Available Formats
NYC Go Math!
Grade 2
GO Math! Scope and Sequence
This document contains a high-level scope and sequence for the GO Math! program
intended to give teachers an overview of where instructional time will be spent across
the year through use of GO Math!. It provides a suggested sequence of instruction
and assessments, including where NYCDOE Periodic Assessments can be used to
gauge students’ understanding of concepts and skills taught at benchmark moments
throughout the year. Based on the Common Core Standards, Go Math! is divided into
critical areas that offer a focused and coherent study of the key concepts and skills for
each grade.
For each critical area, you will see the following:
• Essential Ideas: The key topics of the unit; chapters and lessons are built around
achieving understanding and mastery of these topics.
• Standards: The standards listed show the main standards covered throughout the
Critical Area. Instruction is focused on achieving a thorough knowledge of these
standards.
• Mathematical Practices: While all practices are integrated into each Critical
Area, the practices listed are ones that receive particular emphasis.
• Essential Questions: The essential question for each chapter is listed, showing
the goal of each chapter.
• Assessment Opportunities: This listing highlights the assessments that ensure
teachers can gauge student success on mastering the standards covered in the
Critical Area.
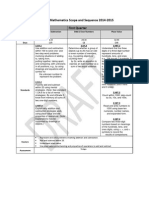
Grade K: Suggested Sequence Suggested Amount of Time
for the GO Math! program (in days)
Critical Area 1: Number Sense and Place Value 25 days
Critical Area 2: Addition and Subtraction 52 days
Critical Area 3: Measurement and Data 41 days
Critical Area 4: Geometry and Fractions 12 days
NYC3 Planning Guide
NYC Scope and Sequence
Critical Area 1: Number Sense and Place Value Critical Area 2: Addition and Subtraction
Chapters 1–2 Chapters 3–6
25 Days (Instructional Days: 21; Assessment Days: 4) 52 Days (Instructional Days: 44; Assessment Days: 8)
Focus or Main Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplica- Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction.
CC Standards tion. 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word
2.OA.3 Determine whether a group of objects (up to 20) has an odd or even problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together,
number of members, e.g., by pairing objects or counting them by 2s; write taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by
an equation to express an even number as a sum of two equal addends. using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to
Understand place value. represent the problem.
2.NBT.1 Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent Add and subtract within 20.
amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. By end of
and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases: Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers.
2.NBT.1a 100 can be thought of as a bundle of ten tens — called a Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplication.
“hundred.” 2.OA.4 Use addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangu-
2.NBT.1b The numbers 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 lar arrays with up to 5 rows and up to 5 columns; write an equation to
refer to one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine hundreds (and express the total as a sum of equal addends.
0 tens and 0 ones). Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add
2.NBT.2 Count within 1000; skip-count by 5s, 10s, and 100s. and subtract.
2.NBT.3 Read and write numbers to 1000 using base-ten numerals, number
names, and expanded form. 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place
2.NBT.4 Compare two three-digit numbers based on meanings of the hundreds, value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition
tens, and ones digits, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of and subtraction.
comparisons. 2.NBT.6 Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value
and properties of operations.
Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add 2.NBT.7 Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models or drawings and
and subtract. strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the rela-
2.NBT.8 Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given number 100–900, and mentally sub- tionship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written
tract 10 or 100 from a given number 100–900. method. Understand that in adding or subtracting three-digit numbers,
one adds or subtracts hundreds and hundreds, tens and tens, ones and
ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose or decompose tens or
hundreds.
2.NBT.9 Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work, using place value
and the properties of operations.
Highlighted MP.6 Attend to precision. MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.
Mathematical MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Practices MP.8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. MP.4 Model with mathematics.
Essential • How do you use place value to find the values of numbers and describe num- • How can you use patterns and strategies to find sums and differences for basic
Questions bers in different ways? Chapter 1) facts? (Chapter 3)
• How can you use place value to model, write, and compare 3-digit numbers? • How do you use place value to add 2-digit numbers, and what are some differ-
(Chapter 2) ent ways to add 2-digit numbers? (Chapter 4)
• How do you use place value to subtract 2-digit numbers with and without
regrouping? (Chapter 5)
• What are some strategies for adding and subtracting 3-digit numbers? (Chapter
6)
Assessment Show What You Know Show What You Know
Opportunities Mid-Chapter Checkpoint Mid-Chapter Checkpoint
Chapter Review/Test Chapter Review/Test
Chapter Test Chapter Test
Chapter Performance Task Chapter Performance Task
Critical Area Performance Task Critical Area Performance Task
NYC Scope and Sequence NYC35
NYC Go Math! Grade 2
Critical Area 3: Measurement and Data Chapters 7–10 Critical Area 4: Geometry and Fractions Chapters 11
41 Days (Instructional Days: 33; Assessment Days: 8) 12 Days (Instructional Days: 10; Assessment Days: 2)
Focus or Main Measure and estimate lengths in standard units. Reason with shapes and their attributes.
CC Standards 2.MD.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools 2.G.1 Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given
such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes. number of angles or a given number of equal faces. Identify triangles,
2.MD.2 Measure the length of an object twice, using length units of different quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and cubes.
lengths for the two measurements; describe how the two measurements 2.G.2 Partition a rectangle into rows and columns of same-size squares and
relate to the size of the unit chosen. count to find the total number of them.
2.MD.3 Estimate lengths using units of inches, feet, centimeters, and meters. 2.G.3 Partition circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares,
2.MD.4 Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of, etc.,
expressing the length difference in terms of a standard length unit. and describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, four fourths. Recognize
Relate addition and subtraction to length. that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape.
2.MD.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving
lengths that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as
drawings of rulers) and equations with a symbol for the unknown number
to represent the problem.
2.MD.6 Represent whole numbers as lengths from 0 on a number line diagram
with equally spaced points corresponding to the numbers 0, 1, 2, ..., and
represent whole-number sums and differences within 100 on a number
line diagram.
Work with time and money.
2.MD.7 Tell and write time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest five
minutes, using a.m. and p.m.
2.MD.8 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and
pennies, using $ and ¢ symbols appropriately.
Represent and interpret data.
2.MD.9 Generate measurement data by measuring lengths of several objects to
the nearest whole unit, or by making repeated measurements of the same
object. Show the measurements by making a line plot, where the horizon-
tal scale is marked off in whole-number units.
2.MD.10 Draw a picture graph and a bar graph (with single-unit scale) to represent
a data set with up to four categories. Solve simple put together, take-
apart, and compare problems using information presented in a bar graph.
Highlighted MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.
Mathematical MP.6 Attend to precision. MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others.
Practices MP.8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. MP.6 Attend to precision.
Essential • How do you use the values of coins and bills to find the total value of a group • What are some two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional shapes, and
Questions of money, and how do you read times shown on analog and digital clocks? how can you show equal parts of shapes? (Chapter 11)
(Chapter 7)
• What are some of the methods and tools that can be used to estimate and
measure length? (Chapter 8)
• What are some of the methods and tools that can be used to estimate and
measure length in metric units? (Chapter 9)
• How do tally charts, picture graphs, and bar graphs help you solve problems?
(Chapter 10)
Assessment Show What You Know Show What You Know
Opportunities Mid-Chapter Checkpoint Mid-Chapter Checkpoint
Chapter Review/Test Chapter Review/Test
Chapter Test Chapter Test
Chapter Performance Task Chapter Performance Task
Critical Area Performance Task Critical Area Performance Task
NYC36 Planning Guide
You might also like
- Arizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsDocument8 pagesArizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsChino GarciaNo ratings yet
- Common Core Math Standards Grade 2Document4 pagesCommon Core Math Standards Grade 2mohammadNo ratings yet
- Arizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsDocument8 pagesArizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsJessie OrrettNo ratings yet
- Ma 2Document2 pagesMa 2api-335623629No ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade2Document16 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade2Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Whole Number OperationsDocument2 pagesWhole Number Operationsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- 1st Grade Math StandardsDocument7 pages1st Grade Math Standardsapi-470241740No ratings yet
- First Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence MathDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence Mathapi-234156613No ratings yet
- 2nd Math OasDocument2 pages2nd Math Oasapi-411338120No ratings yet
- Math g2 m5 Full Module PDFDocument312 pagesMath g2 m5 Full Module PDFSonu KumarNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 - Module 4: Mathematics CurriculumDocument432 pagesGrade 1 - Module 4: Mathematics CurriculumFatima GutlayNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Math Scopeand Sequence GuideDocument6 pagesGrade 5 Math Scopeand Sequence GuideDev MauniNo ratings yet
- CCSSI Math Standards 2Document4 pagesCCSSI Math Standards 2establoid1169No ratings yet
- 2nd Grade Pacing Plan 2013-14Document9 pages2nd Grade Pacing Plan 2013-14api-237255436No ratings yet
- Guiding Firsties Math Workshop CCSS Curriculum MapDocument18 pagesGuiding Firsties Math Workshop CCSS Curriculum MapCarlos GonzálezNo ratings yet
- g2 Mathematics Florida StandardsDocument5 pagesg2 Mathematics Florida Standardsapi-290541111No ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Maths Stage 7Document14 pagesScheme of Work Maths Stage 7Arumugam PalaniapanNo ratings yet
- Math g2 m5 Full ModuleDocument312 pagesMath g2 m5 Full ModuleRivka Share100% (1)
- 5th Common Core EngageNYDocument385 pages5th Common Core EngageNYLaurelNo ratings yet
- 2 ND Math ChecklistsDocument4 pages2 ND Math ChecklistsasdfasdfasNo ratings yet
- Math Common Core StandardsDocument5 pagesMath Common Core Standardsapi-167622228No ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade1Document16 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade1Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- 2021-22 - 3rd - Math - Scope and SequenceDocument15 pages2021-22 - 3rd - Math - Scope and SequenceGhada NabilNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson Plan 1Document5 pagesMath Lesson Plan 1api-372799212No ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade4Document17 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade4Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Math 7 DLL Quarter 1week 8Document8 pagesMath 7 DLL Quarter 1week 8Rosemarie IglesiaNo ratings yet
- g1 m4 Full - Module PDFDocument387 pagesg1 m4 Full - Module PDFJerick Enrique FegaridoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics StandardsDocument4 pagesMathematics Standardsapi-369625583No ratings yet
- MathContents - Unit 1Document3 pagesMathContents - Unit 1Meli ConcoguaNo ratings yet
- B9 Maths WK3Document4 pagesB9 Maths WK3Dennis ArkohNo ratings yet
- Vdoe FrameworkDocument9 pagesVdoe Frameworkapi-548452244No ratings yet
- K To 5 - Go Math Scope and SequenceDocument18 pagesK To 5 - Go Math Scope and SequenceMaram HabibNo ratings yet
- Analysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 2Document15 pagesAnalysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 2establoid1169No ratings yet
- g1 Mathematics Florida StandardsDocument5 pagesg1 Mathematics Florida Standardsapi-290541111No ratings yet
- 1 ST Math Checklists 2Document6 pages1 ST Math Checklists 2ddfsfsNo ratings yet
- CcmathDocument3 pagesCcmathapi-278469988No ratings yet
- Module in Industrial Mathematics Midterm OutlineDocument66 pagesModule in Industrial Mathematics Midterm Outlinekervin oñNo ratings yet
- Math g2 m5 Full ModuleDocument275 pagesMath g2 m5 Full Modulemadhu63No ratings yet
- MN Elementary Math StandardsDocument9 pagesMN Elementary Math Standardsapi-322018148No ratings yet
- Math g2 m3 Full ModuleDocument343 pagesMath g2 m3 Full ModuleRivka ShareNo ratings yet
- JHS1 Maths T1Document49 pagesJHS1 Maths T1Medic Eathen SmartNo ratings yet
- Math g5 m2 Full ModuleDocument385 pagesMath g5 m2 Full ModuleghostreamNo ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade3Document17 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade3Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Goals Ccss 1Document5 pages4th Grade Goals Ccss 1api-287945109No ratings yet
- LongrangeplansteddiDocument12 pagesLongrangeplansteddiapi-242288854No ratings yet
- Everyday Math GoalsDocument4 pagesEveryday Math Goalsapi-441762465No ratings yet
- Math g2 m4 Full ModuleDocument405 pagesMath g2 m4 Full ModuleHirenkumar ShahNo ratings yet
- AZ Math Standards For Grade 1Document6 pagesAZ Math Standards For Grade 1shawnsblog100% (2)
- 5th Grade Math Rubric Q1 2012Document4 pages5th Grade Math Rubric Q1 2012nelly_marlina02100% (1)
- Commoncoremathcheatsheets 2 NDDocument1 pageCommoncoremathcheatsheets 2 NDapi-288064681No ratings yet
- Mathstandards2007 005247 Reposted 92815Document3 pagesMathstandards2007 005247 Reposted 92815api-369626876No ratings yet
- Mayugher For TerDocument19 pagesMayugher For Terhhfg hjggNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument20 pagesMATHEMATICSAei SarapNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Number and Number SenseDocument351 pagesLearning Module: Number and Number SenseMaria Martina Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- REading and Writing Whole Numbers Up To 10, 000Document2 pagesREading and Writing Whole Numbers Up To 10, 000danica ragutanaNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document32 pages2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Jwan DelawiNo ratings yet
- SMTH Grade 6 AAC Public OverviewDocument14 pagesSMTH Grade 6 AAC Public OverviewAshleyNo ratings yet
- PK2 Number-in-Context HandoutsDocument46 pagesPK2 Number-in-Context Handoutsnoaman.merchant7401No ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1Document9 pagesYearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1cikguakmal78100% (1)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6No ratings yet
- Longer Science Lesson ReflectionDocument2 pagesLonger Science Lesson Reflectionapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Math Letter To Parents For AssessmentDocument1 pageMath Letter To Parents For Assessmentapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Ascd Webinar CertificateDocument1 pageAscd Webinar Certificateapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Philosophy Statement On EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophy Statement On Educationapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Math NewsletterDocument2 pagesMath Newsletterapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Math Lesson ReflectionDocument1 pageMath Lesson Reflectionapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Poetry WorksheetDocument2 pagesPoetry Worksheetapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Math Chapter 7 NewsletterDocument1 pageMath Chapter 7 Newsletterapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Pa Landforms Webquest WorksheetDocument4 pagesPa Landforms Webquest Worksheetapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Authors Purpose SortDocument2 pagesAuthors Purpose Sortapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Daily Journal - Week 3Document3 pagesDaily Journal - Week 3api-351301306No ratings yet
- BB RubricDocument1 pageBB Rubricapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Math Letter To Parents For AssessmentDocument1 pageMath Letter To Parents For Assessmentapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Equivalent Fractions - BB ActivityDocument2 pagesEquivalent Fractions - BB Activityapi-351301306No ratings yet
- 6e Lesson Plan - ScienceDocument5 pages6e Lesson Plan - Scienceapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Tongue TwistersDocument1 pageTongue Twistersapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Roseman ReferenceDocument1 pageRoseman Referenceapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Clewell ReferenceDocument1 pageClewell Referenceapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Math Vocab - BB ActivityDocument2 pagesMath Vocab - BB Activityapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Cambria Heights - LessonDocument5 pagesCambria Heights - Lessonapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Classroom Management PlanDocument9 pagesClassroom Management Planapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Longer - Math LessonDocument5 pagesLonger - Math Lessonapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - Culminating ExperienceDocument5 pagesLesson 11 - Culminating Experienceapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Assessment PlanDocument11 pagesAssessment Planapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Kelli ReferenceDocument2 pagesKelli Referenceapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Math NewsletterDocument2 pagesMath Newsletterapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Assessment PlanDocument11 pagesAssessment Planapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - Culminating ExperienceDocument3 pagesLesson 11 - Culminating Experienceapi-351301306No ratings yet
- Module 2 - TrigonometryDocument15 pagesModule 2 - TrigonometryJake Canlas100% (1)
- 2nd Periodical TESTDocument3 pages2nd Periodical TESTEvangelyn Bartolay67% (6)
- Math 20.3 - Mathworks 11 Workbook PDFDocument125 pagesMath 20.3 - Mathworks 11 Workbook PDFKarol Kamieniecki100% (1)
- Solving word problems involving ratios, speeds, and geometryDocument12 pagesSolving word problems involving ratios, speeds, and geometryprasadkvssNo ratings yet
- ASpT PPoPP19Document15 pagesASpT PPoPP19Xiaowen ChuNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics and Its ApplicationsDocument47 pagesDiscrete Mathematics and Its ApplicationsAbdul MaalikNo ratings yet
- Lab #6 - Second Order Systems Rev 1Document5 pagesLab #6 - Second Order Systems Rev 1ahmed shahNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive ControlDocument42 pagesModel Predictive Controlzohaib319No ratings yet
- Gear CalculationDocument2 pagesGear CalculationkonikomiNo ratings yet
- Elective 5 Mathematical Systems PDFDocument54 pagesElective 5 Mathematical Systems PDFAlan Peter100% (3)
- Engineering Mathematics Statistics Finance ProposalDocument8 pagesEngineering Mathematics Statistics Finance ProposalXiaokang WangNo ratings yet
- Calculus Self Taught Well Summarized Lecture Notes With Relevant Examples For BetterDocument31 pagesCalculus Self Taught Well Summarized Lecture Notes With Relevant Examples For BetterApril IngramNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 DerivativeDocument27 pagesLesson 3 DerivativeRich Ian MontalvaNo ratings yet
- MR3 SolutionsDocument27 pagesMR3 SolutionsViet Quoc HoangNo ratings yet
- CN3421 Lecture Note 1 - IntroductionDocument20 pagesCN3421 Lecture Note 1 - IntroductionKiang Teng LimNo ratings yet
- China China Girls Math Olympiad 2003Document3 pagesChina China Girls Math Olympiad 2003PremMehtaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Real Numbers - Activities 1 (4º ESO)Document3 pagesUnit 1 Real Numbers - Activities 1 (4º ESO)lumaromartinNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: ProblemsDocument67 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: ProblemsangelicaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Slides DFT Sampling TheoremDocument32 pagesLecture 4 Slides DFT Sampling TheoremhaldoisNo ratings yet
- 3E Price List Order Form Authorwise September 2021Document47 pages3E Price List Order Form Authorwise September 2021Kawshika BoyagodaNo ratings yet
- FP2C7 Maclaurin and Taylor SeriesDocument2 pagesFP2C7 Maclaurin and Taylor SeriesLoh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- INF 120 Project 1 PDFDocument4 pagesINF 120 Project 1 PDFAnonymous wvWYp3N944No ratings yet
- Thesis PDFDocument76 pagesThesis PDFAnthonny Gabryell LimaNo ratings yet
- CN2116-HW7-Solution (XJP - 2011)Document12 pagesCN2116-HW7-Solution (XJP - 2011)Brian WatsonNo ratings yet
- Bernard P. Zeigler, Alexandre Muzy, Ernesto Kofman - Theory of Modeling and Simulation-Academic Press (2019) PDFDocument674 pagesBernard P. Zeigler, Alexandre Muzy, Ernesto Kofman - Theory of Modeling and Simulation-Academic Press (2019) PDFSebastián Cáceres G100% (4)
- Lesson 21Document7 pagesLesson 21Jeany Pearl EltagondeNo ratings yet
- MSC Handbook15-16Document49 pagesMSC Handbook15-16Brian PreciousNo ratings yet
- Least Leared Skills 2ND 2018Document10 pagesLeast Leared Skills 2ND 2018marichu_labra_1No ratings yet
- Functional Geometry and The Traite de LutherieDocument9 pagesFunctional Geometry and The Traite de Lutheriejsennek100% (1)
- Module 1 2nd Quarter d11Document5 pagesModule 1 2nd Quarter d11Abbie RañosaNo ratings yet