Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHY13L Experiment405
Uploaded by
anon_422073337Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PHY13L Experiment405
Uploaded by
anon_422073337Copyright:
Available Formats
Diffraction
2017100386
PHY13L/B1
CE/2
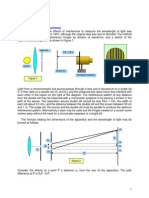
1. DATA
For single slit diffraction, we obtained a 4.7% error to the true value of 670 nanometer from the
wavelength of light wavelength from the diode laser. When slit distance and its length from the screen is
held constant while the magnitude of integer representing the position of a dark fringe represented by m is
increased, its distance from the center line increases. For the two slit interference, we have obtained less
than 1% error for the computed wavelength to the true value of light wavelength. In addition, when
distance between two slits and its horizontal length to the screen is held constant, the computed distance
of a point of a constructive interference from the center line increases as we increase the magnitude of m.
2. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Diffraction occurs when light waves pass through obstacles or slits and manifests its bending capabilities.
From Huygen’s principle, every point between a wave source lies secondary wavelets that travels the
same speed of propagation as the wave source and when passing through slits, tendency is formation of
diffraction patterns. Bright fringes represent the point of constructive interference and dark fringes for
destructive interference. In finding the location of dark fringes in single slit diffraction and bright fringes
mxλ
in double slit interference is given by Y m= wherein m is the integer representing position of dark
a
fringe for single slit and bright fringe for double slit, x for length from slit to screen, lambda as
wavelength of the light wave and a as the distance between slits. This was derived from the relationship
that path difference is equal to the phase difference, as since the slits are divided into elements that serves
as starting points for diffracted waves, others travel at a longer distance at specific points than the others,
λ
and therefore has a phase difference equal to for single slit and λ for double slits. Utilizing the
2
formula aided us in getting accurate experimental values. We attribute our errors to our measurement and
recording as it was very difficult to measure diffraction patterns due to its minuscule spaces between
fringes.
3. CONCLUSION
Diffraction is the bending of light waves when passing through obstacles or slits and follows the
Huygen’s principle. Single slit diffraction pattern is due to the interference of light waves from one half of
slit length and the other half. Double slit interference is due to the interference of light waves from two
separate slits.
You might also like
- E09 InterferenceDocument5 pagesE09 InterferenceDeidei LopezNo ratings yet
- Slit Diffraction Technical PaperDocument8 pagesSlit Diffraction Technical PapervinzkeenangoNo ratings yet
- ECE Syllabus (Total)Document32 pagesECE Syllabus (Total)শেখ আরিফুল ইসলাম100% (3)
- A Comparative Study of Single Slit Diffraction and Double Slit DiffractionDocument13 pagesA Comparative Study of Single Slit Diffraction and Double Slit Diffractiondhakshesh02No ratings yet
- Phenomenon of Diffraction of LightDocument26 pagesPhenomenon of Diffraction of LightAditya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 DiffractionDocument10 pagesExpt 1 DiffractionSuyash SardaNo ratings yet
- 7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFDocument9 pages7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFWakkuNo ratings yet
- Lab Diffraction and InterferenceDocument12 pagesLab Diffraction and InterferencerodneyperuNo ratings yet
- Single Photon Double Slit ExperimentDocument4 pagesSingle Photon Double Slit ExperimentAnastasia MarchenkovaNo ratings yet
- TR2 FIJ Aycardo, Bandonil, HaroDocument5 pagesTR2 FIJ Aycardo, Bandonil, HaroChino BandonilNo ratings yet
- 1.laser Diffraction PDFDocument10 pages1.laser Diffraction PDFyashika bairwaNo ratings yet
- Michelsen InterferometerDocument22 pagesMichelsen InterferometerSelvaraju ChellappanNo ratings yet
- Dewi Kurnia 60400118035 - Difraksi LaserDocument9 pagesDewi Kurnia 60400118035 - Difraksi LaserDewi KurniaNo ratings yet
- Dewi Kurnia 60400118035 - Jurnal JFT Difraksi LaserDocument9 pagesDewi Kurnia 60400118035 - Jurnal JFT Difraksi LaserDewi KurniaNo ratings yet
- Diffraction ExperimentsDocument5 pagesDiffraction ExperimentsArooj Mukarram100% (2)
- Experiment 405: Diffraction: 1. AbstractDocument3 pagesExperiment 405: Diffraction: 1. AbstractArvn Christian Santicruz FloresNo ratings yet
- Phenomenon of Diffraction of Light WaveDocument23 pagesPhenomenon of Diffraction of Light WaveM A V E R I C K musicNo ratings yet
- Remarks/Analysis of DataDocument2 pagesRemarks/Analysis of DataChrispin BarnigoNo ratings yet
- Diffraction and InterferenceDocument40 pagesDiffraction and InterferenceUnexpected TheoryNo ratings yet
- DiffractionDocument4 pagesDiffractionmira.120230131No ratings yet
- Hhwphysics 12 THDocument11 pagesHhwphysics 12 THArnav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Modified Aug2011Document93 pagesDiffraction Modified Aug2011Shrinivas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Michelson InterferometerDocument5 pagesMichelson InterferometerSajadSidiqNo ratings yet
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument72 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsSIDDHARTHANo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Notes Optics 2022 23Document20 pagesUNIT 2 Notes Optics 2022 23MannPlayZNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 2Document142 pagesPhysics Unit 27csnty5wvgNo ratings yet
- Single Slit Diffraction ExpDocument5 pagesSingle Slit Diffraction ExpNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Physical Optics and Optical Fibers L02Document44 pagesPhysical Optics and Optical Fibers L02Moamen MohamedNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Grating: Condition For Maximum Intensity Double Slit Multiple Slits High Resolution Peak IntensitiesDocument8 pagesDiffraction Grating: Condition For Maximum Intensity Double Slit Multiple Slits High Resolution Peak IntensitiesGhannam MomoNo ratings yet
- E405 ph4Document2 pagesE405 ph4Marc OlivaNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of LightDocument12 pagesDiffraction of LightSalama RagabNo ratings yet
- Interferometry PresentationDocument26 pagesInterferometry PresentationbathinsreenivasNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Note at A LevelDocument11 pagesDiffraction Note at A LevelBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- Jiya Sukhija - Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesJiya Sukhija - Physics ProjectTejaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 DiffractdionDocument124 pages2 DiffractdionShrinivas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio PropagationDocument42 pagesMobile Radio PropagationShakeel HashmiNo ratings yet
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument72 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDhyey DESAIIINo ratings yet
- DiffractionDocument11 pagesDiffractionAnuj TomarNo ratings yet
- Phy 4215 Lecture NoteDocument15 pagesPhy 4215 Lecture NoteMohammed Abdulhamid BabiNo ratings yet
- Young's Double SlitDocument2 pagesYoung's Double SlitSrikanth VaranasiNo ratings yet
- Lab4 PDFDocument7 pagesLab4 PDFKing EverestNo ratings yet
- 07 InterferenceDocument10 pages07 InterferenceHelenNo ratings yet
- Fabry-Pérot Interferometer: TheoryDocument5 pagesFabry-Pérot Interferometer: TheorychandreshwarNo ratings yet
- Exer 11 Physics 82Document12 pagesExer 11 Physics 82Jezreel SumagangNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Multiframe Ultrasonic TOFD Weld Inspection Imaging Based On Wavelet Transform and Image RegistrationDocument9 pagesResearch Article: Multiframe Ultrasonic TOFD Weld Inspection Imaging Based On Wavelet Transform and Image Registrationphan hoang diepNo ratings yet
- Lab 4: Diffraction of LightDocument7 pagesLab 4: Diffraction of LightShouryaNo ratings yet
- Single Double NSlit DiffractionDocument24 pagesSingle Double NSlit DiffractionsayantikdalalNo ratings yet
- 文件Document19 pages文件4C14 Lee Sze YiuNo ratings yet
- Double SlitDocument8 pagesDouble SlitFaizNo ratings yet
- Prof. Hossam Shalaby Paper 5Document4 pagesProf. Hossam Shalaby Paper 5drhammoudaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Interferometer....Document14 pagesLab Report Interferometer....musabNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Concept of Resolving Power in The FabryPerot Interferometer Using A Digital Simulation Ejp6 5 010Document9 pagesUnderstanding The Concept of Resolving Power in The FabryPerot Interferometer Using A Digital Simulation Ejp6 5 010Rousse AldavaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mobile Communication Unit 2Document34 pagesWireless Mobile Communication Unit 2Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument3 pagesWave Opticsmili groupNo ratings yet
- Propagation of WavesDocument19 pagesPropagation of WavesBIRENDRA BHARDWAJNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of Light WavesDocument24 pagesDiffraction of Light Wavesbenjamin swokaNo ratings yet
- 1997 UTD Multiple Edge Transition Zone DiffractionDocument5 pages1997 UTD Multiple Edge Transition Zone DiffractionMudita ChandraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 2Document27 pagesUnit 1 Part 2Bhuvanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsK. KurokawaNo ratings yet
- Math22 1ReviewerIntegrationDocument10 pagesMath22 1ReviewerIntegrationanon_422073337No ratings yet
- PHY13 Lesson 4 Diffraction and InterferenceDocument44 pagesPHY13 Lesson 4 Diffraction and InterferenceLeBron JamesNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Force and TorqueDocument56 pagesMagnetic Force and TorqueAlvin Dave GalasinaoNo ratings yet
- PHY13 Lesson 2 Sources of Magnetic FieldsDocument45 pagesPHY13 Lesson 2 Sources of Magnetic Fieldspauline aerielNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Antidifferentiation Generalized Power Formula Simple SubstitutionDocument12 pagesLesson 1 Antidifferentiation Generalized Power Formula Simple Substitutionanon_422073337No ratings yet
- Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionDocument5 pagesDerivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functionanon_422073337No ratings yet
- Special Series: Geometric and P-Series: Del Socorro, Trevorr R. Math23-1/C1 1 Term AY 2018-2019Document29 pagesSpecial Series: Geometric and P-Series: Del Socorro, Trevorr R. Math23-1/C1 1 Term AY 2018-2019anon_422073337No ratings yet
- Math22 1ReviewerDerivativeTrigonometricFunctionDocument6 pagesMath22 1ReviewerDerivativeTrigonometricFunctionanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 3 Light and Geometric OpticsDocument69 pages3 Light and Geometric Opticsanon_422073337No ratings yet
- General Differentiation Formula 1. Derivative of A Constant ( ) 0Document10 pagesGeneral Differentiation Formula 1. Derivative of A Constant ( ) 0anon_422073337No ratings yet
- Math22 1ReviewerIntegrationDocument10 pagesMath22 1ReviewerIntegrationanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 17.4.2 - Homogeneous Equations With Constant Coefficients Higher OrderDocument14 pages17.4.2 - Homogeneous Equations With Constant Coefficients Higher Orderanon_422073337100% (1)
- ReviewerDocument33 pagesRevieweranon_422073337No ratings yet
- Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionDocument5 pagesDerivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functionanon_422073337No ratings yet
- Day 24 MATH24-1 (Differential Equations) : CH 3.7 Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations (Page 192-207)Document36 pagesDay 24 MATH24-1 (Differential Equations) : CH 3.7 Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations (Page 192-207)anon_422073337No ratings yet
- Math22 1ReviewerDerivativeTrigonometricFunctionDocument6 pagesMath22 1ReviewerDerivativeTrigonometricFunctionanon_422073337No ratings yet
- Day 14 MATH24-1 (Differential Equations) : CH 2.8 The Existence and Uniqueness Theorems (Page 112-122)Document21 pagesDay 14 MATH24-1 (Differential Equations) : CH 2.8 The Existence and Uniqueness Theorems (Page 112-122)anon_422073337No ratings yet
- 03.1.2 - Solutions of Some Differential EquationsDocument11 pages03.1.2 - Solutions of Some Differential Equationswe_spidus_2006No ratings yet
- 09&10.2.3 - Modeling With First Order EquationsDocument49 pages09&10.2.3 - Modeling With First Order Equationsanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 11.2.5 - Autonomous Equations and Population DynamicsDocument25 pages11.2.5 - Autonomous Equations and Population Dynamicsanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 16.3.1 - Homogeneous Equations With Constant Coefficients Second OrderDocument16 pages16.3.1 - Homogeneous Equations With Constant Coefficients Second Orderanon_422073337100% (1)
- 19.3.3 - Complex Roots of The Characteristic EquationDocument9 pages19.3.3 - Complex Roots of The Characteristic Equationanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 20.3.4 - Repeated Roots Reduction of OrderDocument16 pages20.3.4 - Repeated Roots Reduction of Orderanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 24.3.6 - Variation of Parameters Second OrderDocument11 pages24.3.6 - Variation of Parameters Second Orderanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 13.2.6 - Exact Equations and Integrating FactorsDocument17 pages13.2.6 - Exact Equations and Integrating Factorsanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 23.4.3 - The Method of Undetermined Coefficients Higher OrderDocument7 pages23.4.3 - The Method of Undetermined Coefficients Higher Orderanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 22.3.5 - Non-Homogeneous Equations Method of Undetermined Coefficients Second OrderDocument17 pages22.3.5 - Non-Homogeneous Equations Method of Undetermined Coefficients Second Orderanon_422073337No ratings yet
- 14.2.7 - Numerical Approximation Euler's MethodDocument23 pages14.2.7 - Numerical Approximation Euler's Methodanon_422073337No ratings yet
- K JR CH©VQ: Syllabus For Written ExaminationDocument152 pagesK JR CH©VQ: Syllabus For Written ExaminationExam DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Elementary Quantum Physics 20160926Document81 pagesElementary Quantum Physics 20160926Aruna KumarasiriNo ratings yet
- LEP WebDocument244 pagesLEP WebCristhoper MeraNo ratings yet
- Cc107-N-Engineering PhysicsDocument5 pagesCc107-N-Engineering PhysicsAnkur RanpariyaNo ratings yet
- 3.091 - Introduction To Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 5 X-Rays and X-Ray DiffractionDocument22 pages3.091 - Introduction To Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 5 X-Rays and X-Ray DiffractionVipin83% (6)
- 10 Wave OpticsDocument5 pages10 Wave OpticsSimon PradeepNo ratings yet
- AP 101 SyllabusDocument3 pagesAP 101 SyllabusTamandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Optical Sensing Techniques and Signal Processing-3Document68 pagesOptical Sensing Techniques and Signal Processing-3SB AmaleshNo ratings yet
- Jentoft Diffusereflectance 101204Document56 pagesJentoft Diffusereflectance 101204Joe Vito MorabitoNo ratings yet
- BSNL Tta Exam PaperDocument8 pagesBSNL Tta Exam PaperRajnish Chandra Prasad100% (1)
- Homota - Limit ApproachDocument13 pagesHomota - Limit ApproachLeiva CasemiroNo ratings yet
- Activity Notes BookDocument12 pagesActivity Notes Bookkaran singh class 11 aNo ratings yet
- Characterstics of Laser LightDocument23 pagesCharacterstics of Laser Light131dhi.2503No ratings yet
- L01 Default VesselDocument16 pagesL01 Default VesselAliNo ratings yet
- Aqwa Vs SeaFEM Vs WamitDocument4 pagesAqwa Vs SeaFEM Vs Wamitrajumj66No ratings yet
- Physics Olympiad Syl Lab UsDocument3 pagesPhysics Olympiad Syl Lab UsMohammad ArikNo ratings yet
- MQ 53448Document145 pagesMQ 53448José Manuel Cortés CortésNo ratings yet
- HAFTA XRD-1-dönüştürüldüDocument26 pagesHAFTA XRD-1-dönüştürüldüKatrina Ranee RamosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To High Resolution X-Ray Diffraction of Epitaxial Thin FilmsDocument53 pagesIntroduction To High Resolution X-Ray Diffraction of Epitaxial Thin FilmsPorto GeeNo ratings yet
- BS DD ENV 583-6 Ed.2000Document18 pagesBS DD ENV 583-6 Ed.2000chinezu06No ratings yet
- XRDDocument4 pagesXRDnonickNo ratings yet
- G12 Summative 2 HL: MarkschemeDocument20 pagesG12 Summative 2 HL: MarkschemeJNo ratings yet
- The Apparent Dual Nature of Cathode RaysDocument4 pagesThe Apparent Dual Nature of Cathode RaysFrederick David TombeNo ratings yet
- WCC Module-1 NotesDocument33 pagesWCC Module-1 Notessadiqul azamNo ratings yet
- Nature of LightDocument3 pagesNature of Lightapi-231880547No ratings yet
- Chapter 38Document31 pagesChapter 38Matius BiuSarraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics (UniversityAcademy MCQS)Document35 pagesEngineering Physics (UniversityAcademy MCQS)SAMAIRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 - 8 Practice PapersDocument59 pagesPhysics Class 12 - 8 Practice PaperssidharthNo ratings yet
- Laser PDFDocument13 pagesLaser PDFNIKITH ACHANTANo ratings yet