Professional Documents
Culture Documents
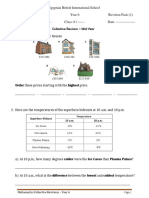
Test (40 Marks) :: Polygons, Solids and Transformations
Uploaded by
api-445198464Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test (40 Marks) :: Polygons, Solids and Transformations
Uploaded by
api-445198464Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9: Polygons, solids and transformations
Test (40 marks)
Name: ___________________________________
Part A – Multiple-choice questions (10 marks)
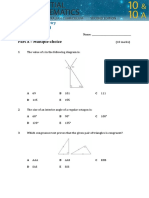
1 A convex polygon has:
A all interior angles less than 90
B all interior angles greater than 90
C all interior angles less than 180
D all interior angles greater than 180
E at least one interior angle greater than 180
2 Which of the following types of triangles is not possible?
A A right triangle that is also isosceles
B A right triangle that is also equilateral
C An acute triangle that is also scalene
D An obtuse triangle that is also scalene
E An obtuse triangle that is also isosceles
3 Which of the following is not sufficient information to construct a unique triangle?
A Three sides (SSS)
B Two sides and a non-included angle (SSA)
C Two angles and one side (AAS)
D Two sides and the included angle (SAS)
E A right angle, hypotenuse and one other side (RHS)
© Cambridge University Press 2011 1
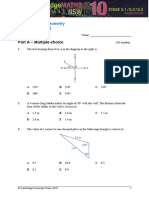
4 The angle sum of a triangle is always:
A 90 B 120 C 180
D 270 E 360
5 What type of special quadrilateral is shown below?
A square
B rectangle
C kite
D rhombus
E trapezium
6 The angle sum of a quadrilateral is always:
A 90 B 120 C 180
D 270 E 360
7 The order of line symmetry for a regular polygon with n sides is:
A n B n–1 C n+1
n
D 2n E
2
© Cambridge University Press 2011 2
8 Which of the following transformations has this shape undergone?
A A reflection in the x-axis
B A reflection in the y-axis
C A rotation 90 clockwise about C
D A rotation 90 anticlockwise about C
E A rotation 180 about C
9 The translation that takes A(–3, 2) to A’(0, 1) could be described as:
A 1 unit left and 3 units up
B 3 units left and 1 unit up
C 3 units right and 1 unit down
D 1 unit right and 3 units down
E 1 unit down
© Cambridge University Press 2011 3
10 Which of the nets match this solid?
© Cambridge University Press 2011 4
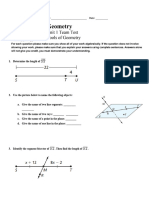
Part B – Short-answer questions (25 marks)
1 For the following polygons:
i state the type of polygon by considering its number of sides
ii classify the polygon as convex or non-convex
iii classify the polygon as regular or irregular
a b c
i ______________________ i ______________________ i ______________________
ii ______________________ ii ______________________ ii ______________________
iii ______________________ iii ______________________ iii ______________________
(3 1 = 3 marks)
2 Classify these triangles as:
i scalene, isosceles or equilateral
ii acute, right or obtuse
a b c
i ______________________ i ______________________ i ______________________
ii ______________________ ii ______________________ ii ______________________
(3 1 = 3 marks)
© Cambridge University Press 2011 5
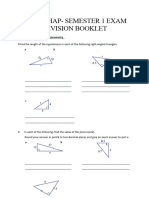
3 Find the value of a in each of these triangles.
a b c
___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________
(1 + 1 + 2 = 4 marks)
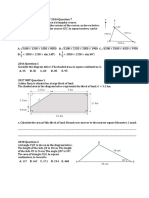
4 These triangles have exterior angles. Find the value of x by first calculating the
value of a.
a b
__________________________________________ __________________________________________
__________________________________________ __________________________________________
(2 + 2 = 4 marks)
5 Find the value of the pronumerals in each of these quadrilaterals.
a b c
___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________
___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________
(1 + 2 + 2 = 5 marks)
© Cambridge University Press 2011 6
6 For each of the following, give the order of:
i line symmetry
ii rotational symmetry
a b c
Z
i ______________________ i ______________________ i ______________________
ii ______________________ ii ______________________ ii ______________________
(3 1 = 3 marks)
7 On the axes provided, draw the image of this shape when it is reflected in the:
a x-axis
b y-axis
(2 1 = 2 marks)
8 On the grid provided, draw the image of this shape after a translation of 2 units up
and 3 units left.
© Cambridge University Press 2011 7
(1 mark)
Part C – Extended-response questions (5 marks)
1 a In the space provided, use the following steps to construct triangle ABC.
Step 1: Draw a segment, AB, 6 cm in length.
Step 2: Use a protractor to measure a 40 angle at B, and then draw the ray BC.
Step 3: Construct an arc centred at A, using a radius of 4 cm, which intersects
ray BC.
Step 4: Mark the point C and join with points A and B.
b Is triangle ABC a unique triangle? Give a reason.
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
(3 + 2 = 5 marks)
© Cambridge University Press 2011 8
You might also like
- Gold7trp Test ch9 Shapes and TransformationsDocument6 pagesGold7trp Test ch9 Shapes and Transformationsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter Test - 02CDocument10 pagesChapter Test - 02Cweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test 02DDocument9 pagesChapter Test 02Dweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test - 02ADocument8 pagesChapter Test - 02Aweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test - 02BDocument8 pagesChapter Test - 02Bweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Transformations GuideDocument12 pagesYear 7 Transformations GuideAliya MarvellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Linear Relations Test A (45 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Linear Relations Test A (45 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDavid XuNo ratings yet
- CambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 09ADocument11 pagesCambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 09Awillclyne19No ratings yet
- Chapter Test - 01ADocument9 pagesChapter Test - 01Aweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Math Quiz Unit 5, 6, 7Document4 pagesMath Quiz Unit 5, 6, 7Chatarina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Final Examination P 2 2019Document8 pagesGrade 7 Math Final Examination P 2 2019CyrielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Linear Relations Test B (45 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Linear Relations Test B (45 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDavid XuNo ratings yet
- YEAR 9 HAP 2023 Sem 1 Exam RevisionDocument33 pagesYEAR 9 HAP 2023 Sem 1 Exam Revisionlenajorden202No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ReviewDocument3 pagesChapter 1 ReviewJosephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Expressions and Equations Test A (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 3: Expressions and Equations Test A (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceJack William STAPLETONNo ratings yet
- Gold7trp Test ch5 AlgebraDocument5 pagesGold7trp Test ch5 Algebraapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Epping Boys 2006 Year 10 Maths YearlyDocument14 pagesEpping Boys 2006 Year 10 Maths YearlykevNo ratings yet
- Angles and Polygons Resit TestDocument8 pagesAngles and Polygons Resit Testapi-461267688No ratings yet
- 11: Measurement Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument7 pages11: Measurement Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice Questionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice Questionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- St. Paul's College Secondary 1 Mathematics QuizDocument8 pagesSt. Paul's College Secondary 1 Mathematics Quizbuck albinoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key G7 Summative Assessment - Criterion A#4Document9 pagesAnswer Key G7 Summative Assessment - Criterion A#4IzabelleNo ratings yet
- Waverley College Year 7 Mathematics Half Yearly Examination Term 2 - Past PaperDocument12 pagesWaverley College Year 7 Mathematics Half Yearly Examination Term 2 - Past PaperAstraX EducationNo ratings yet
- CambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 07BDocument8 pagesCambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 07BkwanNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Lessons 4-12: GeometryDocument2 pagesUnit Test Lessons 4-12: Geometryumm_aasiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Trigonometry Test A (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 7: Trigonometry Test A (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoicekwanNo ratings yet
- Lines and Angles WorksheetDocument4 pagesLines and Angles WorksheetLucky2503100% (1)
- Homework 12.2Document2 pagesHomework 12.2Stephanie ValienteNo ratings yet
- Secondary 2 Normal (A) Mathematics Test 2 Algebraic Fractions, Equations and Inequalities 1 HourDocument7 pagesSecondary 2 Normal (A) Mathematics Test 2 Algebraic Fractions, Equations and Inequalities 1 HourHira HassanNo ratings yet
- Q3 Assessment Wk1&2Document4 pagesQ3 Assessment Wk1&2Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- 2015 ANA GR 7 Math Test Eng 2015Document20 pages2015 ANA GR 7 Math Test Eng 2015leaowa.mNo ratings yet
- 2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015Document20 pages2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015wadeNo ratings yet
- 2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015Document20 pages2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015Mahisa Agni100% (1)
- Mini Core A Level Grade ADocument18 pagesMini Core A Level Grade AyukiNo ratings yet
- Gold7trp Test ch6 DecimalsDocument6 pagesGold7trp Test ch6 Decimalsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Unit 10 Packet 2018 - 2019Document41 pagesUnit 10 Packet 2018 - 2019Sameera ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Constructing Perpendicular BisectorsDocument6 pagesConstructing Perpendicular BisectorsAbeer Amin ElmogyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Guided NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 4 Guided NotesdevikaNo ratings yet
- BBPS - Class 3 - CU-2Document2 pagesBBPS - Class 3 - CU-2Priyanka ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class VI CH 7 ObjectiveDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class VI CH 7 Objectivetariqarslan30No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 GeoTest PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 2 GeoTest PDFStephanie ValienteNo ratings yet
- Mock PaperDocument8 pagesMock Paperumerk.hyd.khiNo ratings yet
- Math Review gr7 Exam 2 Third TermDocument6 pagesMath Review gr7 Exam 2 Third TermHoda RagabNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Quiz on ParabolasDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry Quiz on Parabolasjonathan_2906No ratings yet
- chapter 12 unit examDocument4 pageschapter 12 unit examapi-697430197No ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa International Gcse Mathematics Extension Geometry and MeasuresDocument26 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa International Gcse Mathematics Extension Geometry and Measureslas lasNo ratings yet
- Revision Pack 1Document11 pagesRevision Pack 1osara11084No ratings yet
- 3 MarksDocument40 pages3 MarksRicky JacobNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Sample Exam PaperDocument14 pagesYear 10 Sample Exam Papererikyo3No ratings yet
- Geo Unit 1 Team TestDocument3 pagesGeo Unit 1 Team Testapi-601573297No ratings yet
- Exam 1 Solution - Fall 2010Document11 pagesExam 1 Solution - Fall 2010akjhasd kjhasdkjhNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review 2023Document12 pagesFinal Exam Review 2023Rayan AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test BDocument4 pagesEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test Bapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter Test 02BDocument8 pagesChapter Test 02BxuauNo ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test ADocument8 pagesEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test Aapi-445198464No ratings yet
- 1 IPS EoT2 Revision+Pack G8Document31 pages1 IPS EoT2 Revision+Pack G8ipsj.20214570No ratings yet
- Y8 U3-5 Assessment (E2) (Tracing Paper NOT Needed - No Rotations)Document15 pagesY8 U3-5 Assessment (E2) (Tracing Paper NOT Needed - No Rotations)Hana JuiceNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Set Notation, Conditional, Converse, Inverse, and Contrapositive Statements - Review AssignmentDocument10 pagesUnit 1 - Set Notation, Conditional, Converse, Inverse, and Contrapositive Statements - Review AssignmentRahman IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Area Extension QuestionsDocument10 pagesArea Extension QuestionsBob CrossNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions by Multiplying Terms LessonDocument9 pagesSimplifying Expressions by Multiplying Terms Lessonapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Year 8 Simplifying Expressions Home LearningDocument1 pageYear 8 Simplifying Expressions Home Learningapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Algebra Home Learning EasierDocument2 pagesSimplifying Algebra Home Learning Easierapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying by Multiplying ExpressionsDocument4 pagesSimplifying by Multiplying Expressionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying by Multiplying ExpressionsDocument6 pagesSimplifying by Multiplying Expressionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions Differentiated SheetsDocument3 pagesSimplifying Expressions Differentiated Sheetsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Algebra Home Learning HarderDocument2 pagesSimplifying Algebra Home Learning Harderapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Algebra Yr 7lDocument30 pagesAlgebra Yr 7lapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Ans ch7 Indices Test ADocument1 pageEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Ans ch7 Indices Test Aapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Substitution 8rsDocument10 pagesSubstitution 8rsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test BDocument4 pagesEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test Bapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Ans ch7 Indices Test BDocument1 pageEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Ans ch7 Indices Test Bapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions Recap Yr 8Document10 pagesSimplifying Expressions Recap Yr 8api-445198464No ratings yet
- Algebra Yr 7rDocument27 pagesAlgebra Yr 7rapi-445198464No ratings yet
- 8Document12 pages8api-445198464No ratings yet
- Basic Substitution Matching CardsDocument2 pagesBasic Substitution Matching Cardsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- 9 7zero and Negative ExponentsDocument9 pages9 7zero and Negative Exponentsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Index LawsDocument41 pagesIndex Lawsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Shapes and Transformations Test Answers: C B C D E A C D EDocument1 pageChapter 9: Shapes and Transformations Test Answers: C B C D E A C D Eapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test ADocument8 pagesEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test Aapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac7trp Test Ans 09Document2 pagesEmac7trp Test Ans 09api-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Statistics and Probability Test Answers: C C E A B DDocument2 pagesChapter 8: Statistics and Probability Test Answers: C C E A B Dapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Gold7trp Test ch8 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument8 pagesGold7trp Test ch8 Statistics and Probabilityapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test Answers: © Cambridge University Press 2011 1Document2 pagesChapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test Answers: © Cambridge University Press 2011 1api-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice Questionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions Algebra l2Document21 pagesSimplifying Expressions Algebra l2api-445198464No ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions and TermsDocument13 pagesAlgebraic Expressions and TermsavgNo ratings yet
- AlgebraicexpressionsbingoDocument2 pagesAlgebraicexpressionsbingoapi-445198464No ratings yet
- IXL PerimeterDocument5 pagesIXL PerimeterMuhammad Waqqas HasanNo ratings yet
- FG 201429Document4 pagesFG 201429Dũng Nguyễn TiếnNo ratings yet
- Balkan Mathematical Olympiad 2014Document6 pagesBalkan Mathematical Olympiad 2014Science Olympiad Blog83% (6)
- (CKRaju) MathEducation1EuclidDocument7 pages(CKRaju) MathEducation1EuclidnameNo ratings yet
- BallDocument3 pagesBalloggyvukovichNo ratings yet
- Construction of QuadDocument1 pageConstruction of QuadRitesh SethiaNo ratings yet
- CIE08 Straight LinesDocument17 pagesCIE08 Straight Linesbiologyexpert158No ratings yet
- GRADE 7 Third PT DivisionDocument4 pagesGRADE 7 Third PT DivisionKingGamer 4595100% (1)
- Comprehensive Trigonometry For IIT JEE Main and Advanced Rejaul Makshud McGraw Hill (PDFDrive) - 151-200Document50 pagesComprehensive Trigonometry For IIT JEE Main and Advanced Rejaul Makshud McGraw Hill (PDFDrive) - 151-200sanjayb1976gmailcom0% (1)
- Assignment (MID) Mat 101Document9 pagesAssignment (MID) Mat 101shantoNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci's Perfect Spiral: Middle SchoolDocument8 pagesFibonacci's Perfect Spiral: Middle SchoolrenatovivNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Maths Understanding Elementary Shapes WorksheetsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 6 Maths Understanding Elementary Shapes WorksheetsParth Aggarwal (Parth)No ratings yet
- 10 Math Sample Paper-5Document7 pages10 Math Sample Paper-5mryuvi.127No ratings yet
- Q3 Math 9 Module 5Document33 pagesQ3 Math 9 Module 5Dexter CorajeNo ratings yet
- Module 5 MMW BSIT-1Document10 pagesModule 5 MMW BSIT-1Francisco PonceNo ratings yet
- Sheet Books SJSNDocument21 pagesSheet Books SJSNArya GuptaNo ratings yet
- NVSU Civil Engineering Solid Geometry ReviewDocument4 pagesNVSU Civil Engineering Solid Geometry ReviewPENDON, JORELLENo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument12 pagesMensurationapi-520249211No ratings yet
- TrianglesDocument15 pagesTriangleschand7790100% (2)
- Chapter 7 Sec 2 GeoDocument14 pagesChapter 7 Sec 2 GeoMary Grace G. Catubigan0% (2)
- Tle Tech Drafting 10-q1-m5Document14 pagesTle Tech Drafting 10-q1-m5JUNARY DUMALAURONNo ratings yet
- Geom82015 ExamDocument28 pagesGeom82015 ExamBenjaminAgalliuNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument13 pagesPythagoras TheoremGauravGrover100% (1)
- Demystifying Barycentric CoordinatesDocument2 pagesDemystifying Barycentric CoordinatesCody JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Math 05 Right TrianglesDocument3 pagesMath 05 Right TrianglesJose Luis Rodriguez InterianoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsDocument15 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsHammad AmjadNo ratings yet
- History and uses of tessellationsDocument5 pagesHistory and uses of tessellationsمحمد ربانيNo ratings yet
- Ashley Lawson Final Project StudentDocument2 pagesAshley Lawson Final Project Studentapi-315324639No ratings yet
- Tran Quang Hung and Pham Huy HoangDocument4 pagesTran Quang Hung and Pham Huy HoangRizky Rajendra AnantadewaNo ratings yet
- Course 3 5-5 Class Notes - Geometry and Similar TrianglesDocument34 pagesCourse 3 5-5 Class Notes - Geometry and Similar TrianglesBarbie Custodio - MangulabnanNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Book of Shadows: Discover the Power of the Ancient Wiccan Religion. Learn Forbidden Black Magic Spells and Rituals.From EverandThe Book of Shadows: Discover the Power of the Ancient Wiccan Religion. Learn Forbidden Black Magic Spells and Rituals.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- My Spiritual Journey: Personal Reflections, Teachings, and TalksFrom EverandMy Spiritual Journey: Personal Reflections, Teachings, and TalksRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (26)
- Becoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonFrom EverandBecoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1478)
- Between Death & Life: Conversations with a SpiritFrom EverandBetween Death & Life: Conversations with a SpiritRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (179)
- The Wim Hof Method: Activate Your Full Human PotentialFrom EverandThe Wim Hof Method: Activate Your Full Human PotentialRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Three Waves of Volunteers & The New EarthFrom EverandThe Three Waves of Volunteers & The New EarthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (179)
- Conversations with God: An Uncommon Dialogue, Book 1From EverandConversations with God: An Uncommon Dialogue, Book 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (66)
- Adventures Beyond the Body: How to Experience Out-of-Body TravelFrom EverandAdventures Beyond the Body: How to Experience Out-of-Body TravelRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- A New Science of the Afterlife: Space, Time, and the Consciousness CodeFrom EverandA New Science of the Afterlife: Space, Time, and the Consciousness CodeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Notes from the Universe: New Perspectives from an Old FriendFrom EverandNotes from the Universe: New Perspectives from an Old FriendRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (53)
- The Essence of the Bhagavad Gita: Explained by Paramhansa Yogananda as remembered by his disciple, Swami KriyanandaFrom EverandThe Essence of the Bhagavad Gita: Explained by Paramhansa Yogananda as remembered by his disciple, Swami KriyanandaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Four-Fold Way: Walking the Paths of the Warrior, Teacher, Healer and VisionaryFrom EverandThe Four-Fold Way: Walking the Paths of the Warrior, Teacher, Healer and VisionaryNo ratings yet
- The Happy Medium: Life Lessons from the Other SideFrom EverandThe Happy Medium: Life Lessons from the Other SideRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- It's Easier Than You Think: The Buddhist Way to HappinessFrom EverandIt's Easier Than You Think: The Buddhist Way to HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (60)
- The Art of Happiness: A Handbook for LivingFrom EverandThe Art of Happiness: A Handbook for LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1205)
- Seven Sermons to the Dead: Septem Sermones ad MortuosFrom EverandSeven Sermons to the Dead: Septem Sermones ad MortuosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (31)
- Good Mourning: Moving Through Everyday Losses with Wisdom from the Other SideFrom EverandGood Mourning: Moving Through Everyday Losses with Wisdom from the Other SideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Wisdom Distilled from the Daily: Living the Rule of St. Benedict TodayFrom EverandWisdom Distilled from the Daily: Living the Rule of St. Benedict TodayRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)