Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gold7trp Test ch9 Shapes and Transformations
Uploaded by
api-445198464Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gold7trp Test ch9 Shapes and Transformations
Uploaded by
api-445198464Copyright:
Available Formats
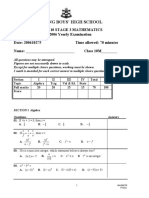
Chapter 9: Shapes and transformations
Test (40 marks)
Name: ___________________________________
Part A – Multiple-choice questions (10 marks)
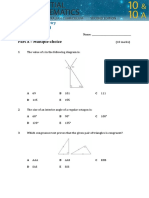
1 The angle sum of a triangle is always:
A 90 B 120 C 180
D 270 E 360
2 Which of the following types of triangles is not possible?
A A right triangle that is also isosceles
B A right triangle that is also equilateral
C An acute triangle that is also scalene
D An obtuse triangle that is also scalene
E An obtuse triangle that is also isosceles
3 A convex polygon has:
A all interior angles less than 90
B all interior angles greater than 90
C all interior angles less than 180
D all interior angles greater than 180
E at least one interior angle greater than 180
© Cambridge University Press 2012
1
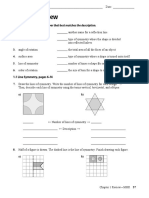
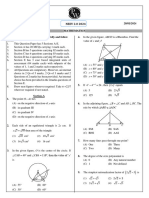
4 What type of special quadrilateral is shown below?
A square
B rectangle
C kite
D rhombus
E trapezium
5 The angle sum of a quadrilateral is always:
A 90 B 120 C 180
D 270 E 360
Questions 6 and 7 refer to the following letter of the alphabet:
Z
6 The number of lines of symmetry for the letter ‘Z’ is:
A 0 B 1 C 2
D 3 E 4
7 The order of rotational symmetry for the letter ‘Z’ is:
A 0 B 1 C 2
D 3 E 4
© Cambridge University Press 2012
2
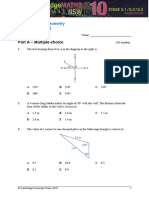
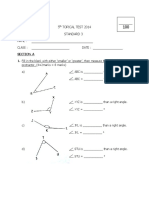
8 Which of the following transformations has this shape undergone?
A A reflection in the x-axis
B A reflection in the y-axis
C A rotation 180 about C
D A rotation 90 clockwise about C
E A rotation 90 anticlockwise about C
9 The translation that takes A(–3, 2) to A′(0, 1) could be described as:
A 1 unit down
B 1 unit left and 3 units up
C 3 units left and 1 unit up
D 1 unit right and 3 units down
E 3 units right and 1 unit down
10 The shape which has a top view of a circle and a side view of a rectangle is a:
A sphere B cylinder C cone
D hemi-sphere E rectangular prism
© Cambridge University Press 2012
3
Part B – Short-answer questions (15 marks)
1 Label the following triangles as either:
i scalene, isosceles or equilateral
ii acute, right or obtuse
a b c
i _________________ i _________________ i _________________
ii _________________ ii _________________ ii _________________
(3 2 = 6 marks)
2 Find the value of a in each of these triangles.
a b c
____________________ _____________________ ____________________
____________________ _____________________ ____________________
(1 + 1 + 2 = 4 marks)
3 This triangle has an exterior angle. Find the value of x by first finding a.
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
(2 marks)
4 Find the value of the pronumerals in each of these quadrilaterals.
© Cambridge University Press 2012
4
a b
____________________________ ____________________________
____________________________ ____________________________
(1 + 2 = 3 marks)
Part C – Extended-response questions (15 marks)
© Cambridge University Press 2012
5
1 Use a ruler and a protractor to draw a triangle ABC, with AB = 5 cm, ABC = 70,
and BAC = 30. Make sure you label all features of the triangle in your diagram.
(3 marks)
2 Consider the shape shown in the diagram below. On the same set of axes,
draw the image of the shape and give the coordinates of A′, B′, C′ and D′, after each of
the following transformations:
a a rotation 180 about the origin O
________________________________
________________________________
b a reflection in the vertical y-axis
________________________________
________________________________
c a translation 1 unit right and 5 units down
________________________________
________________________________
(3 4 = 12 marks)
© Cambridge University Press 2012
6
You might also like
- Chapter 4 Guided NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 4 Guided NotesdevikaNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions Differentiated SheetsDocument3 pagesSimplifying Expressions Differentiated Sheetsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test BDocument4 pagesEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test Bapi-445198464No ratings yet
- IB Mathematics AI SL Questionbank - TrigonometryDocument39 pagesIB Mathematics AI SL Questionbank - TrigonometryMaltiti Eman WUMBEI67% (3)
- Test (40 Marks) :: Polygons, Solids and TransformationsDocument8 pagesTest (40 Marks) :: Polygons, Solids and Transformationsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter Test - 02CDocument10 pagesChapter Test - 02Cweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test 02DDocument9 pagesChapter Test 02Dweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Lines and Angles WorksheetDocument4 pagesLines and Angles WorksheetLucky2503100% (1)
- Math Quiz Unit 5, 6, 7Document4 pagesMath Quiz Unit 5, 6, 7Chatarina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test - 02BDocument8 pagesChapter Test - 02Bweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Mock PaperDocument8 pagesMock Paperumerk.hyd.khiNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Packet 2018 - 2019Document41 pagesUnit 10 Packet 2018 - 2019Sameera ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 09ADocument11 pagesCambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 09Awillclyne19No ratings yet
- chapter 12 unit examDocument4 pageschapter 12 unit examapi-697430197No ratings yet
- Year 7 Transformations GuideDocument12 pagesYear 7 Transformations GuideAliya MarvellNo ratings yet
- Q3 Assessment Wk1&2Document4 pagesQ3 Assessment Wk1&2Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Angles and Polygons Resit TestDocument8 pagesAngles and Polygons Resit Testapi-461267688No ratings yet
- Q3 - Math 7 - Periodical ExamDocument4 pagesQ3 - Math 7 - Periodical ExamJudith CuevaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PDFDocument8 pagesMathematics PDFDhoni SuhendraNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 7 PERIODIC EXAMDocument5 pagesMATHEMATICS 7 PERIODIC EXAMMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Test 2 - Math 7 - Quarter III-week 3 and 4Document3 pagesTest 2 - Math 7 - Quarter III-week 3 and 4Vjacheslav D. FontillasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test - 02ADocument8 pagesChapter Test - 02Aweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Expressions and Equations Test A (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 3: Expressions and Equations Test A (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceJack William STAPLETONNo ratings yet
- 2015 ANA GR 7 Math Test Eng 2015Document20 pages2015 ANA GR 7 Math Test Eng 2015leaowa.mNo ratings yet
- 2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015Document20 pages2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015wadeNo ratings yet
- 2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015Document20 pages2015 ANA GR 7 Mathematics Test - 2015Mahisa Agni100% (1)
- Chapter Test - 01ADocument9 pagesChapter Test - 01Aweishun zhouNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 Third PT DivisionDocument4 pagesGRADE 7 Third PT DivisionKingGamer 4595100% (1)
- CambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 07BDocument8 pagesCambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 07BkwanNo ratings yet
- Gold7trp Test ch6 DecimalsDocument6 pagesGold7trp Test ch6 Decimalsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Math8q4 Summative TestDocument5 pagesMath8q4 Summative TestKristine Joy GutingNo ratings yet
- Gold7trp Test ch5 AlgebraDocument5 pagesGold7trp Test ch5 Algebraapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Waverley College Year 7 Mathematics Half Yearly Examination Term 2 - Past PaperDocument12 pagesWaverley College Year 7 Mathematics Half Yearly Examination Term 2 - Past PaperAstraX EducationNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Linear Relations Test A (45 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Linear Relations Test A (45 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDavid XuNo ratings yet
- Epping Boys 2006 Year 10 Maths YearlyDocument14 pagesEpping Boys 2006 Year 10 Maths YearlykevNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Final Examination P 2 2019Document8 pagesGrade 7 Math Final Examination P 2 2019CyrielNo ratings yet
- Ch5 CombinedDocument15 pagesCh5 Combined1F-17 Li Jasmine Tin YanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ReviewDocument3 pagesChapter 1 ReviewJosephNo ratings yet
- Answer Key G7 Summative Assessment - Criterion A#4Document9 pagesAnswer Key G7 Summative Assessment - Criterion A#4IzabelleNo ratings yet
- Assessment Jel PlanDocument5 pagesAssessment Jel Planprilyn albaricoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesThonette MagalsoNo ratings yet
- Q3 Math 7 Periodical ExamDocument6 pagesQ3 Math 7 Periodical ExamCarmina CunananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Trigonometry Test A (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 7: Trigonometry Test A (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-ChoicekwanNo ratings yet
- G7Q3Assessment - QADocument9 pagesG7Q3Assessment - QAEric VasquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - QuadrilateralsDocument28 pagesChapter 14 - QuadrilateralsRitu AryanNo ratings yet
- Geometry EXAM ReviewDocument6 pagesGeometry EXAM ReviewDrunk RussianNo ratings yet
- Geo 5 Practice TestDocument4 pagesGeo 5 Practice TestsrwaiyanNo ratings yet
- Math Review gr7 Exam 2 Third TermDocument6 pagesMath Review gr7 Exam 2 Third TermHoda RagabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice Questionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 QuadrilateralsDocument28 pagesChapter 14 QuadrilateralsPiyush YadavNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test NewDocument4 pagesAchievement Test NewKelly Cheng100% (1)
- Escuela de Sophia of Caloocan Inc.: 3 Quarterly Test Mathematics 6Document6 pagesEscuela de Sophia of Caloocan Inc.: 3 Quarterly Test Mathematics 6ROMNICK DIANZONNo ratings yet
- Q3-Math7-Periodical-Exam - CopyDocument5 pagesQ3-Math7-Periodical-Exam - CopyNono, Kathleen Joyce I.No ratings yet
- MD KeysDocument4 pagesMD Keysjhariprasad.sarmaNo ratings yet
- Topic Test 5 STD 3Document6 pagesTopic Test 5 STD 3Mahlini DeviNo ratings yet
- 3rd Math 7Document7 pages3rd Math 7Niña Ara Marie AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Geometry 2nd 9 Weeks 2018 QuizDocument18 pagesGeometry 2nd 9 Weeks 2018 QuizNicholas Rocchio-GiordanaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Mathematics 8 AnswersDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test in Mathematics 8 AnswersMelbourne Therese AraniadorNo ratings yet
- 2qz4 in GeometryDocument3 pages2qz4 in Geometrymark tronNo ratings yet
- BBPS - Class 3 - CU-2Document2 pagesBBPS - Class 3 - CU-2Priyanka ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 GeoTest PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 2 GeoTest PDFStephanie ValienteNo ratings yet
- Solid FiguresDocument10 pagesSolid FiguresHolly May MontejoNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions by Multiplying Terms LessonDocument9 pagesSimplifying Expressions by Multiplying Terms Lessonapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Year 8 Simplifying Expressions Home LearningDocument1 pageYear 8 Simplifying Expressions Home Learningapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Algebra Home Learning EasierDocument2 pagesSimplifying Algebra Home Learning Easierapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying by Multiplying ExpressionsDocument4 pagesSimplifying by Multiplying Expressionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying by Multiplying ExpressionsDocument6 pagesSimplifying by Multiplying Expressionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Algebra Home Learning HarderDocument2 pagesSimplifying Algebra Home Learning Harderapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Algebra Yr 7lDocument30 pagesAlgebra Yr 7lapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Ans ch7 Indices Test ADocument1 pageEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Ans ch7 Indices Test Aapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Substitution 8rsDocument10 pagesSubstitution 8rsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Ans ch7 Indices Test BDocument1 pageEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Ans ch7 Indices Test Bapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions Recap Yr 8Document10 pagesSimplifying Expressions Recap Yr 8api-445198464No ratings yet
- Algebra Yr 7rDocument27 pagesAlgebra Yr 7rapi-445198464No ratings yet
- 8Document12 pages8api-445198464No ratings yet
- Basic Substitution Matching CardsDocument2 pagesBasic Substitution Matching Cardsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- 9 7zero and Negative ExponentsDocument9 pages9 7zero and Negative Exponentsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Index LawsDocument41 pagesIndex Lawsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test ADocument8 pagesEmac Gold 2e Year 9 Ots Tests ch7 Indices Test Aapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Emac7trp Test Ans 09Document2 pagesEmac7trp Test Ans 09api-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Statistics and Probability Test Answers: C C E A B DDocument2 pagesChapter 8: Statistics and Probability Test Answers: C C E A B Dapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Gold7trp Test ch8 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument8 pagesGold7trp Test ch8 Statistics and Probabilityapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test Answers: © Cambridge University Press 2011 1Document2 pagesChapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test Answers: © Cambridge University Press 2011 1api-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Number Properties and Patterns Test (40 Marks) : Part A - Multiple-Choice Questionsapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions Algebra l2Document21 pagesSimplifying Expressions Algebra l2api-445198464No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Shapes and Transformations Test Answers: C B C D E A C D EDocument1 pageChapter 9: Shapes and Transformations Test Answers: C B C D E A C D Eapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions and TermsDocument13 pagesAlgebraic Expressions and TermsavgNo ratings yet
- AlgebraicexpressionsbingoDocument2 pagesAlgebraicexpressionsbingoapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Unit Test - Similar FiguresDocument2 pagesUnit Test - Similar Figuresapi-546077219No ratings yet
- Crystallography 1Document6 pagesCrystallography 1Rajasimha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Q4-Mathematics 6 - WEEK 1Document4 pagesQ4-Mathematics 6 - WEEK 1AILEEN D. PEREZNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Book 2022 2023 1st Term 2 155 232 37 78Document42 pagesEngineering Drawing Book 2022 2023 1st Term 2 155 232 37 78Epimaque NkurunzizaNo ratings yet
- Complete Subjective Test 06 (Maths) - Test Paper - (Neev 2.0 2024)Document5 pagesComplete Subjective Test 06 (Maths) - Test Paper - (Neev 2.0 2024)haisumitchauhan2009No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4 Illustrating The SAS, ASA and SSS Congruence PostulatesDocument31 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4 Illustrating The SAS, ASA and SSS Congruence PostulatesArnold A. Baladjay50% (2)
- Circles - Angles Formed by Radii Chords Tangents SecantsDocument3 pagesCircles - Angles Formed by Radii Chords Tangents Secantsapi-235135985No ratings yet
- World Wildlife Day by SlidesgoDocument17 pagesWorld Wildlife Day by SlidesgoCristy LapusNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics June 1995 P2 (Jamaica)Document10 pagesCSEC Mathematics June 1995 P2 (Jamaica)zarzsultan12No ratings yet
- Worksheet-1 VectorDocument8 pagesWorksheet-1 VectorGamaliel KunNo ratings yet
- Eoc Review 2019Document8 pagesEoc Review 2019api-28781631233% (3)
- Module 17 - Similar TrianglesDocument25 pagesModule 17 - Similar TrianglesLyca MasonNo ratings yet
- History of The Euclidean Parallel PostulateDocument35 pagesHistory of The Euclidean Parallel Postulatemajoha000No ratings yet
- Objective Question Bank On Engineering DRDocument56 pagesObjective Question Bank On Engineering DRpushpeshNo ratings yet
- U4 L4 (Sine, Cosine Law, Amb Case)Document6 pagesU4 L4 (Sine, Cosine Law, Amb Case)1jerushaNo ratings yet
- MPM1D Grade 9 Measurement Test 2Document4 pagesMPM1D Grade 9 Measurement Test 2TO ChauNo ratings yet
- Plastic ADocument33 pagesPlastic ARambito LKNo ratings yet
- Parallelograms: Properties, Tests, Area FormulasDocument19 pagesParallelograms: Properties, Tests, Area FormulasIsmail HashimNo ratings yet
- Geometry Calculator App with TkinterDocument4 pagesGeometry Calculator App with TkinterAnant SinghNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Overview of Multiple Image Geometry in 40 CharactersDocument645 pagesConceptual Overview of Multiple Image Geometry in 40 CharactersDonato FormicolaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1547387158156Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1547387158156menma chanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions - Practice Sheet For Nimcet and CHSLDocument8 pagesTrigonometric Functions - Practice Sheet For Nimcet and CHSLankitkumarusa02No ratings yet
- Math 7 Q3 Module 9Document18 pagesMath 7 Q3 Module 9Leah Gonzales83% (6)
- Practice Calc 3 - Section 11.4Document7 pagesPractice Calc 3 - Section 11.4Zachary SikuiNo ratings yet
- Math ReportDocument12 pagesMath Reportammarrosdan123No ratings yet
- NetsDocument4 pagesNetsDtdc SenthlNo ratings yet
- Geo CH 4 Test Review KEYDocument2 pagesGeo CH 4 Test Review KEYjosh bayneNo ratings yet
- KV Class 10 Pre Board Mock Question Paper MATHS (STD)Document7 pagesKV Class 10 Pre Board Mock Question Paper MATHS (STD)sreejaps45No ratings yet