Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Doc. AP Bio Cellular Respiration - Photosynthesis Chart
Doc. AP Bio Cellular Respiration - Photosynthesis Chart
Uploaded by
Michael JuniorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Doc. AP Bio Cellular Respiration - Photosynthesis Chart
Doc. AP Bio Cellular Respiration - Photosynthesis Chart
Uploaded by
Michael JuniorCopyright:
Available Formats
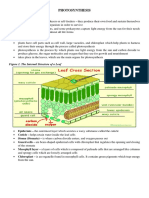
Similarities and Differences between Cell Respiration and Photosynthesis
Similarities: Differences:
1. ATP is a key molecule in each 1. Goals: ATP synthesis is main reason for cell respiration, whereas ATP
is only a required product for photosynthesis to be able to create
glucose.
2. G-3-P is formed in both processes- In Glycolysis (cell respiration) 2. Reactants: glucose and oxygen, Cell respiration, carbon dioxide and
and in Calvin cycle (photosynthesis) water, photosynthesis
3. Both have 2 processes feeding into one main one: Cell Respiration 3. Products: carbon dioxide and water, Cell respiration and glucose and
utilizes Glycolysis and Citric Acid Cycle to funnel energized oxygen, photosynthesis
electrons to Oxidative Phosphorylation process, PSII and PSI
provide ATP and reducing power to Calvin Cycle
4. Both utilize cycles where starting material is regenerated after 4. Oxygen is exhaust of photosynthesis whereas carbon dioxide is
molecules leave the cycles (Citric acid cycle- Cell Respiration, exhaust of cell respiration
Calvin cycle- Photosynthesis)
5. Both rely on movement of electrons for operation 5. Source of elections: in photosynthesis, electrons come from water and
end-up in glucose. In cell respiration, electrons extracted from glucose
and end up in water
6. Both use electron transport chains in production of ATP 6. Electron Carriers: NADH and FADH2 carry electrons in cell
respiration, NADPH carries electrons in photosynthesis
7. Both use chemiosmosis to generate ATP 7. Location: chloroplasts for photosynthesis and mitochondria for cell
respiration
8. Mitochondria of cell respiration and chloroplasts of photosynthesis 8. Proton movement:
have distinct similarities, for example Protons are pumped into the inner membrane space of the
as above, proton pumps pump H+ across a membrane from low to mitochondria (cell respiration), protons are pumped into the thylakoid
high concentration. An endergonic process requiring energy space of the chloroplasts (photosynthesis)
protons diffuse back across membrane through ATP synthase, Protons diffuse back into the matrix of the mitochondria (cell
driving synthesis of ATP respiration), protons diffuse into the stroma of the chloroplast
(photosynthesis)
9. Can observe emergent properties via multiple steps in both
processes
You might also like
- CIV4286 Practice Exercise 2 - Semester1-19Document1 pageCIV4286 Practice Exercise 2 - Semester1-19Xin Yi YauNo ratings yet
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Edexcel A Level 2 Biology Answers Combined FINAL PDFDocument71 pagesEdexcel A Level 2 Biology Answers Combined FINAL PDFbgtes123No ratings yet
- Chloroplasts UpdatedDocument4 pagesChloroplasts Updateddrug123addict25No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFatima DariaNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument4 pagesEnergy TransformationAsh Nico BanquilloNo ratings yet
- SSGBIO1 - CM Week 7Document61 pagesSSGBIO1 - CM Week 7christine ManuelNo ratings yet
- Condensed VersionDocument3 pagesCondensed Versiondrug123addict25No ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest EnergyDocument26 pagesHow Cells Harvest EnergyMarita YaghiNo ratings yet
- NHM - Ar Etapa 2 - LNDVDocument10 pagesNHM - Ar Etapa 2 - LNDVNatalia Hernandez MontelongoNo ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGY - Module 1,2,3Document24 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGY - Module 1,2,3CLIER GEROMALANo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Photosynthesiswkwhui100% (6)
- Bio 123Document2 pagesBio 123SHEMAR STEWARTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 FuelingDocument5 pagesChapter 6 FuelingRossi100% (1)
- Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Review: K A L E BDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Review: K A L E BDestiny DunkleyNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedDocument37 pagesGen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedMichaela CasabaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and CRDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis and CRKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Carbohydrate-GlycolysisDocument20 pagesLecture 4 Carbohydrate-GlycolysisBiology BảoNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Cellular RespirationDraver ZemaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesNotes On Cellular Respirationaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument35 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantssaikanishkhaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 13 To 15: Energy TransformationDocument8 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 13 To 15: Energy Transformationkent ignacioNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Energy Part 1Document14 pagesHow Cells Release Energy Part 1Jiro SarmientoNo ratings yet
- ItineraryDocument5 pagesItineraryJaisa Jean Eucogco EsposadoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument21 pagesCellular RespirationAbirami SankarNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationMercy NdungeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology RevisionDocument27 pagesMicrobiology RevisionShevani KumarNo ratings yet
- Hotosynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesHotosynthesis: Big Picturehomamunfat100% (1)
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mod 9-11Document7 pagesGen Bio Mod 9-11Arabella BrionesNo ratings yet
- Elemental Composition of BacteriaDocument11 pagesElemental Composition of Bacteriaishmist04No ratings yet
- Unit Five Last One Grade 11 Biology Energy TransformationDocument55 pagesUnit Five Last One Grade 11 Biology Energy TransformationaxumfunNo ratings yet
- Cellular1 2Document16 pagesCellular1 2Kaeshamaureen DresNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Document5 pagesReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ExplanationDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration Explanationvestermail50% (2)
- Ellular Espiration: Big PictureDocument3 pagesEllular Espiration: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesAp Biology PhotosynthesisMinh Triet LyNo ratings yet
- Biology Test ReviewDocument3 pagesBiology Test ReviewjunializriveraNo ratings yet
- Biology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Document3 pagesBiology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Sel 7No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsAjay JamwalNo ratings yet
- Respiration Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesRespiration Crossword PuzzleerikabeltranNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY Q2 WEEK 6 Glycolysis and Kreb CycleDocument14 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY Q2 WEEK 6 Glycolysis and Kreb CycleAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument28 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationGlena MendozaNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument4 pagesElectron Transport Chainavilashabas39No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 PDFDocument10 pagesLesson 3 PDFEdsa BaruaNo ratings yet
- 7th Lect. 2017 MetabolismDocument46 pages7th Lect. 2017 MetabolismNedhal Mahmoud KaleefahNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration-0Document49 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration-0Zulhanif IdrisNo ratings yet
- Measure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerDocument17 pagesMeasure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerTootsie100% (12)
- (Cellular Respiration) : Organisms Capture and Store Free Energy For Use in Biological ProcessesDocument41 pages(Cellular Respiration) : Organisms Capture and Store Free Energy For Use in Biological Processesapi-373344212No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Energy TransformationsDocument49 pagesUnit 5 Energy TransformationsFiguracion, Zhass Naye D.No ratings yet
- Ch. 7 Pre Reading QuestionsDocument8 pagesCh. 7 Pre Reading QuestionsDJ ISAACS25% (4)
- Form Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyDocument5 pagesForm Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer.Document3 pagesScience Reviewer.harlanecarlsNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Key PointsDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Key PointsKathleen RamiloNo ratings yet
- Lecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Document14 pagesLecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Andre NesbethNo ratings yet
- 2 Peg Test For SurveyingDocument1 page2 Peg Test For SurveyingXin Yi YauNo ratings yet
- BS 8110-1-1997 - (2019-09-16 - 05-31-52 Am)Document168 pagesBS 8110-1-1997 - (2019-09-16 - 05-31-52 Am)Xin Yi YauNo ratings yet
- Scribd Is So Troublesome It Keeps Forcing Me To Upload Something in Order To Get Something FreeDocument1 pageScribd Is So Troublesome It Keeps Forcing Me To Upload Something in Order To Get Something FreeXin Yi YauNo ratings yet
- HelllllllllllllllllllllllllooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooDocument1 pageHelllllllllllllllllllllllllooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooXin Yi YauNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 4-Mr King Eng SingDocument11 pagesChemistry Chapter 4-Mr King Eng SingXin Yi Yau0% (1)
- Interact HandbookDocument39 pagesInteract HandbookXin Yi YauNo ratings yet