Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus: Engineering Thermodynamics
Uploaded by
Vpr Naturals0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pageseVs
Original Title
Cop o Environmental
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumenteVs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesSyllabus: Engineering Thermodynamics
Uploaded by
Vpr NaturalseVs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
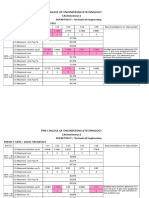
SYLLABUS
PSN College of Engineering and Technology Regulation 2018
Department: Mechanical Branch Code/
Engineering Degree/Branch B.E - MECH
(mention all branches for
Semester: V which the subject is
offered)
Subject Code: 210007 L T P C
Subject Title: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS 3 0 0 3
OBJECTIVE:
To achieve an understanding of principles of thermodynamics and to be able to use it in accounting
for the bulk behavior of the simple physical systems, to provide in-depth study of thermodynamic
principles, thermodynamics of state, basic thermodynamic relations, principles of psychrometry and
properties of pure substances, to enlighten the basic concepts of vapour power cycles.
Unit 1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW OF Total Hrs 9+3
THERMODYNAMICS
Basic concepts - concept of continuum, macroscopic approach. Thermodynamic systems - closed, open and
isolated. Property, state, path and process, quasi-static process, work, modes of work, Zeroth law of
thermodynamics – concept of temperature and heat. Concept of ideal and real gases. First law of
thermodynamics – application to closed and open systems, internal energy, specific heat capacities,
enthalpy, steady flow process with reference to various thermal equipments.
Unit 2 SECOND LAWOF THERMODYNAMICS Total Hrs 9+3
Second law of thermodynamics – Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements of second law, Reversibility and
irreversibility. Carnot theorem, Carnot cycle, reversed Carnot cycle, efficiency, Coefficient of Performance
(COP). Thermodynamic temperature scale, Clausius inequality, concept of entropy, entropy of ideal gas,
principle of increase of entropy – vailability (Elementary treatment only).
Unit 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCE Total Hrs 9+3
Properties of pure substances, thermodynamic properties of pure substances in solid, liquid and vapour
phases, phase rule, P-V, P-T, T-V, T-S, H-S diagrams, PVT surfaces, thermodynamic properties of steam,
Calculations of work done and heat transfer in non-flow and flow processes.
Unit 4 IDEAL AND REAL GASES AND THERMODYNAMIC Total Hrs 9+3
RELATIONS
Properties of ideal and real gases, equation of state, Avogadro’s Law, Van der Waals equation of state,
compressibility factor, Exact differentials. Thermodynamic relations, Maxwell relations, Clausius -
Clapeyron equations, relations for changes in Entropy, Enthalpy & Internal Energy, Joule-Thomson
coefficient & inversion curve.
Unit 5 PROPERTIES OF MIXTURES Total Hrs 9+3
Ideal gas mixtures – Evaluation of properties, Dalton’s law of partial pressure, properties of air-water
vapour mixtures: DBT, WBT, RH, dew point temperature, degree of saturation, thermodynamic wet bulb
temperature, enthalpy of moist air, sensible heating and cooling, bypass factor, calculations using
psychrometric table and chart.
Total Hours to be taught 60
Outcome:
CO 1 :Explain the basic concepts of thermodynamics such as system, state, state postulate, equilibrium,
properties, process and cycle.
CO 2 :Demonstrate the procedures for determining thermodynamic properties of pure substances from
tables of property data and calculate the same when two independent properties are known.
CO 3 :Calculate work in case of a system executing various thermodynamic, processes that involve either
ideal gas or pure substance as working fluid.
CO 4 :State and Apply the first law of thermodynamics for a closed and open systems.
CO 5 :State & Apply the concept of entropy
Text Book:
1. Nag.P.K, “Engineering Thermodynamics”, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 5th Edition. 2013.
2. Yunus Cengel, Michael Boles, ‘Thermodynamics – An Engineering Approach’ 8th Edition 2014 –
Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
Reference (s):
1. Holman.J.P, “Thermodynamics”, 3rd Ed. McGraw-Hill, 1995.
2. Vanwylen and Sontag, “Classical Thermodynamics”, Wiley Eastern, 4th Edition 1994.
3. Arora C.P, “Thermodynamics”, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2008.
4. Merle C, Potter, Craig W, Somerton, “Thermodynamics for Engineers”, Schaum Outline Series,
Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 3rd Edition 2013.
CO/PO Mapping
(S/M/W indicates strength of
1-Weak, 2-Medium, 3-Strong
correlation)
PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12 PSO 1 PSO 2
CO1 3 3 1
CO2 3 3 2 2 1 1 1 1
CO3 3 3 1 1 2 1
CO4 3 3 1 1 1 1
CO5 3 3 2 1 1 1
You might also like
- Padeepz App - AE3351 SyllabusDocument2 pagesPadeepz App - AE3351 SyllabusNAVIN NNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Course PlanDocument5 pagesThermodynamics and Heat Transfer Course PlanHemang ChopraNo ratings yet
- ME 8391 Engineering Thermodynamics Workbook - UNIT 1Document154 pagesME 8391 Engineering Thermodynamics Workbook - UNIT 1BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Etd Syllabus - 2019Document2 pagesEtd Syllabus - 2019KARTHIKEYANNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 2nd Year Aeronautical Engineering AERO-ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICSDocument2 pagesSyllabus 2nd Year Aeronautical Engineering AERO-ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICSChandrakant PrajapatNo ratings yet
- THERMAL ENGINEERING SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesTHERMAL ENGINEERING SYLLABUSVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Etd SyllabusDocument2 pagesEtd SyllabusDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- ETD SyllabusDocument2 pagesETD SyllabusBuckshu PhdNo ratings yet
- Digital Notes on ThermodynamicsDocument123 pagesDigital Notes on Thermodynamicssubhash chandraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Question BankDocument13 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Question BankInduPalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Jj207 Thermodynamics 1 Grandcont 16 SeptDocument9 pagesJj207 Thermodynamics 1 Grandcont 16 SeptRaz MieNo ratings yet
- ME 205 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesME 205 ThermodynamicsSherwinNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics L T P CDocument2 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics L T P CHariharan HariNo ratings yet
- R.V.R. & J.C. College of Engineering (Autonomous), Guntur-522019, A.P. R-18Document2 pagesR.V.R. & J.C. College of Engineering (Autonomous), Guntur-522019, A.P. R-18Venkata GiriNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Syllabus FinalDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Syllabus FinalVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- ME 6301 Engineering Thermodynamics QBDocument194 pagesME 6301 Engineering Thermodynamics QBYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Course OverviewDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Course Overviewnandan144No ratings yet
- Single Page Me6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageSingle Page Me6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsManoj PepiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics SyllabusDocument1 pageThermodynamics SyllabusRam KumarNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS - II COURSE OUTLINEDocument3 pagesENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS - II COURSE OUTLINEOkay 123No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester - III Subject Name: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics-IDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Semester - III Subject Name: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics-IPatel AmaanNo ratings yet
- TD Course FileDocument18 pagesTD Course FileBadari Narayan P100% (1)
- THERMODocument1 pageTHERMOamireddysugunaNo ratings yet
- 03 Me8391Document56 pages03 Me8391BALAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester - III Subject Name: Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Semester - III Subject Name: Engineering ThermodynamicsYagnesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics III Sem Syllabus 01092021Document3 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics III Sem Syllabus 01092021Milind KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering & Technology First Year Bachelor of Engineering Course Code: 102000214 Course Title: Process Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering & Technology First Year Bachelor of Engineering Course Code: 102000214 Course Title: Process Engineering Thermodynamicsharshangrana55No ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Course OverviewDocument2 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Course Overviewسيد محمود بن مسرورNo ratings yet
- Moodle Basic ThermodynamicsDocument14 pagesMoodle Basic ThermodynamicsArpan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics-IDocument3 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics-IElsyNo ratings yet
- Me 2202 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesMe 2202 Engineering ThermodynamicsDinesh MechNo ratings yet
- Course Plan (Version No.:1 & Date: 04-07-2016) : Accredited by NAAC With A' Grade (Accredited by NBA)Document3 pagesCourse Plan (Version No.:1 & Date: 04-07-2016) : Accredited by NAAC With A' Grade (Accredited by NBA)Tamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- BTD SyllabusDocument3 pagesBTD SyllabusSubuddhi DamodarNo ratings yet
- BMEE203L Engineering Thermodynamics SyllabusDocument3 pagesBMEE203L Engineering Thermodynamics SyllabusKrijayNo ratings yet
- Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesEngineering ThermodynamicsSajal DhimanNo ratings yet
- Co-Requisite: Prerequisite: Data Book / Codes/Standards Course Category Course Designed by ApprovalDocument3 pagesCo-Requisite: Prerequisite: Data Book / Codes/Standards Course Category Course Designed by Approvalrajkumar rNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Key ConceptsDocument57 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Key ConceptsBasu SbNo ratings yet
- ETD-PREPARATION GUIDE - StrategyDocument2 pagesETD-PREPARATION GUIDE - Strategytamilselvan nNo ratings yet
- BNMIT Thermodynamics Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesBNMIT Thermodynamics Lesson PlanHemanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Syllabus, 2&16 Mark QuestionsDocument43 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Syllabus, 2&16 Mark Questionsdellibabu509No ratings yet
- Me8391 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageMe8391 Engineering ThermodynamicsAiam PandianNo ratings yet
- Thermo MEX SyllabusDocument3 pagesThermo MEX SyllabusPra GoNo ratings yet
- BTD Course FileDocument23 pagesBTD Course FilePrashant S HadagaliNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument32 pagesEnergyRaja RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Finite Physical Dimensions Optimal Thermodynamics 1: FundamentalsFrom EverandFinite Physical Dimensions Optimal Thermodynamics 1: FundamentalsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan EtdDocument3 pagesLesson Plan EtdJoe Kamal RajNo ratings yet
- BE Syllabus of Mumbai Uni2Document9 pagesBE Syllabus of Mumbai Uni2Rajendra B PawarNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument334 pagesThermodynamicshayat100% (1)
- Obe Reports Hec - Report Section OutlineDocument2 pagesObe Reports Hec - Report Section OutlineMUHAMMAD HAMZANo ratings yet
- BTD Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesBTD Lesson Planpratik039No ratings yet
- C20 - Revamping - M 303 TSESDocument12 pagesC20 - Revamping - M 303 TSESdilchintala25phdNo ratings yet
- CryogenicDocument23 pagesCryogenicmgskumar100% (1)
- Nptel: Advanced Thermodynamics - Web CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Advanced Thermodynamics - Web CourseAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument6 pagesThermal Engineeringtarek ali ahmedNo ratings yet
- Automoius sem III & IV SYLLABUSDocument21 pagesAutomoius sem III & IV SYLLABUS10rajNo ratings yet
- Jadavpur University: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument65 pagesJadavpur University: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyArchisman HazraNo ratings yet
- VTU SyllabusDocument164 pagesVTU SyllabusChethan KSNo ratings yet
- High-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationFrom EverandHigh-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering SyllabusDocument144 pagesThermal Engineering SyllabusVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering SyllabusDocument144 pagesThermal Engineering SyllabusVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Final Thermal 2014Document34 pagesFinal Thermal 2014Vpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Controlvalvesmcq 181016115431Document12 pagesControlvalvesmcq 181016115431Vpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- PROCESS PLANNING COST ESTIMATIONDocument3 pagesPROCESS PLANNING COST ESTIMATIONVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering Course DescriptionDocument21 pagesAutomobile Engineering Course DescriptionVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesSyllabus: Engineering ThermodynamicsVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Composite MaterialsDocument1 pageComposite MaterialsVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Upto 5 SemDocument23 pagesUpto 5 SemVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- THERMAL ENGINEERING SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesTHERMAL ENGINEERING SYLLABUSVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- PROCESS PLANNING COST ESTIMATIONDocument3 pagesPROCESS PLANNING COST ESTIMATIONVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Pre-Requisite: Thermal Engineering: Automobile Engineering LTPC 3 0 0 3 ObjectiveDocument10 pagesPre-Requisite: Thermal Engineering: Automobile Engineering LTPC 3 0 0 3 ObjectiveVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- PSN College COE FEA Subject CO Attainment ReportDocument34 pagesPSN College COE FEA Subject CO Attainment ReportVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Thermadynamics QB FinalDocument24 pagesThermadynamics QB FinalVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- AFMM Registration FormDocument1 pageAFMM Registration FormVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- 2-4 Feb'2017 2-4 Feb'2017 2-4 Feb'2017: Electron Microscopy WEM'14Document3 pages2-4 Feb'2017 2-4 Feb'2017 2-4 Feb'2017: Electron Microscopy WEM'14Vpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Syllabus FinalDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Syllabus FinalVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Question SomDocument2 pagesQuestion SomVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- PSN CAD/CAM LAB MANUALDocument90 pagesPSN CAD/CAM LAB MANUALVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Anna University Chennai SyllabusDocument95 pagesAnna University Chennai SyllabusRAAM MECHNo ratings yet
- Register NoDocument39 pagesRegister NoVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- Hot Water Circulating Pump Cal2Document3 pagesHot Water Circulating Pump Cal2mansidaughtNo ratings yet
- Advaita and Science-: Term Paper Concept of EnergyDocument8 pagesAdvaita and Science-: Term Paper Concept of EnergyggeatNo ratings yet
- Monitoring of Temperature EffectsDocument27 pagesMonitoring of Temperature EffectsisuzveduNo ratings yet
- Perry TabsDocument3 pagesPerry TabsJayvee FranciscoNo ratings yet
- HRAC 112 Lecture Week 2 PressureDocument25 pagesHRAC 112 Lecture Week 2 PressureYuk man LawNo ratings yet
- Format of Lab Report Example 8609Document14 pagesFormat of Lab Report Example 8609herrk167% (3)
- Chapter A 06 RefrigerationDocument18 pagesChapter A 06 RefrigerationСергей КороткийNo ratings yet
- A Ultra REX DUO PLUSDocument34 pagesA Ultra REX DUO PLUSמשה אביסדריסNo ratings yet
- Electric Aircraft SystemDocument9 pagesElectric Aircraft SystemSélim BoutlaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Shell energy balances and temperature distributions in solid and laminar flowDocument43 pagesChapter 10 Shell energy balances and temperature distributions in solid and laminar flowCecilia CelineNo ratings yet
- Silver Oak University: Subject: Basic of Mechanical EngineeringDocument58 pagesSilver Oak University: Subject: Basic of Mechanical EngineeringRhydham PNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics PDFDocument30 pagesIntroductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics PDFDanery RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CE Topic 2 & 3Document2 pagesCE Topic 2 & 3CARL IJADE PINONo ratings yet
- Heat Lab ManualDocument96 pagesHeat Lab ManualNourAldin AbuSaleh100% (2)
- 03 Air Conditioning and Ventilation - MEL522 SHF ADP BFDocument19 pages03 Air Conditioning and Ventilation - MEL522 SHF ADP BFShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- ASTM C 186 - Heat of Hydration of Hydraullic Cement ASTM C 186 PDFDocument7 pagesASTM C 186 - Heat of Hydration of Hydraullic Cement ASTM C 186 PDFMaritza Adasme100% (1)
- Plane Crash Survival Activity in Tropical ForestDocument3 pagesPlane Crash Survival Activity in Tropical ForestDenialAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Cal U Mechanical Engineering Lab Experiment on Refrigeration CyclesDocument12 pagesCal U Mechanical Engineering Lab Experiment on Refrigeration CyclesMohamad FaizNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations in Food Processing (FSPT 2083)Document113 pagesUnit Operations in Food Processing (FSPT 2083)zekariyas kuneNo ratings yet
- 500 MCQDocument55 pages500 MCQkirki pNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Problems: The Solution Below Illustrates How To Solve, Even Though The Numbers in This Problem Are DifferentDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Problems: The Solution Below Illustrates How To Solve, Even Though The Numbers in This Problem Are Differentsmirnov2591No ratings yet
- HT - PR MCQ)Document5 pagesHT - PR MCQ)gniemvivekNo ratings yet
- Energy Audit and Energy ConservationDocument46 pagesEnergy Audit and Energy ConservationPARVATHI PK100% (1)
- Is The Capacity To Do Work.: EnergyDocument7 pagesIs The Capacity To Do Work.: EnergyElla Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Direct-Contact Heat Transfer BookDocument400 pagesDirect-Contact Heat Transfer BookHarsha Nagesh75% (4)
- SolarDocument19 pagesSolarMaria Isabel Martinez NorenaNo ratings yet
- Modul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaDocument5 pagesModul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Reynolds Transport Theorem (RTT) ExplainedDocument19 pagesReynolds Transport Theorem (RTT) ExplainedNarayana Swamy G100% (1)
- 2019 - ACA-1A - Physical Chemistry - Class XIthDocument13 pages2019 - ACA-1A - Physical Chemistry - Class XIthYash DhokeNo ratings yet
- Shop 7Document2 pagesShop 7mktNo ratings yet