Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Generally Dielectrics Are Also Called Insulators Because They Are Poor Conductors of Electricity
Uploaded by
Sher EjazOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Generally Dielectrics Are Also Called Insulators Because They Are Poor Conductors of Electricity
Uploaded by
Sher EjazCopyright:
Available Formats
Dielectrics are known as insulators because they are bad conductors of electricity.
Somehow,
they still permit the motion of a few electrons at high temperature creating a negligible drift of
current. For Example: glass, mica, ebonite, rubber etc. The main difference between dielectrics
and insulators is their applications.
APPLICATIONS IN A CAPACITOR:
In capacitors, we have two oppositely charged plates that are separated by an insulating
medium with a high permittivity. The purpose of high permittivity is to store greater charge at a
given voltage. This medium is known as dielectric, and can be mentioned as the dielectric of
capacitor. The key purpose of doing this is to prevent the conducting plates having charges
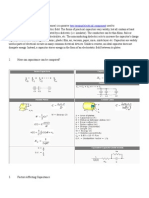
from coming into direct contact with each other. Now consider the situation of a linear
dielectric with permittivity ε and thickness d between the two conducting plates with uniform
charge density σε.. . Then the charge density is as follows
σε = ε V/d
and the capacitance per unit area is as follows
C= σε /V= ε /d
The foremost duty of dielectric inside the capacitor is to stock electric energy. Depending on the
types of dielectric between the plates of the capacitor, the capacitors can be divided into three types.
1. Gaseous dielectric
2. Liquid dielectric
3. Solid dielectric
Radio frequency and other low frequency circuits use vacuum, air, or other gases as dielectric. For
higher voltage applications, mineral oil can be used as dielectric. Whenever we require a high
capacitance, a mixture of solid and liquid dielectric is used in capacitors. (for example: such
capacitors are used for power factor correction in electric power distribution systems. Whereas in
laboratory we use capacitors with solid dielectrics (sodium, glass and titanium oxide) as standard
capacitors.
The dielectric in between the plates of the capacitor serves three main purposes.
1. They prevent the plates from coming together, thereby maintaining higher capacitances.
2. Decreases the strength of electric field to increase the effective capacitance, which
demonstrates we get the identical charge at a lesser voltage.
3. Lessens the likelihood of shorting out during process at high voltage.
Dielectric strength can be defined as the strength of electric field beyond which the insulating
material starts to break down and conduct. A dielectric can upsurge the capacitance. This brings into
account the phenomenon of polarization. Increasing the ease with which the material is polarized
also increases the value of dielectric constant k. This constant k is defined as k=Eo/E.
You might also like
- ففففففففففففDocument8 pagesففففففففففففhaker linkisNo ratings yet
- Tiger Emt 1Document30 pagesTiger Emt 1CharavanaNo ratings yet
- Describe Dielectric MaterialDocument1 pageDescribe Dielectric MaterialKathy ChuaNo ratings yet
- CAPACITORSDocument39 pagesCAPACITORSKobby BrineNo ratings yet
- ExtraDocument23 pagesExtradharshanbskNo ratings yet
- NV6111Document23 pagesNV6111దేవల్ రాజు మహేష్ రాజుNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument86 pagesCapacitorsarunNo ratings yet
- Loss and Applications in DielectricsDocument3 pagesLoss and Applications in DielectricsChidolue OnyinyechukwuNo ratings yet
- PDO Course 3Document27 pagesPDO Course 31MM1R HL'No ratings yet
- BasementDocument19 pagesBasementProxima YusNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes High Voltage WEEK # 02Document6 pagesLecture Notes High Voltage WEEK # 02AttaUrRahmanNo ratings yet
- A. What Types of Materials Do We Test? Three Types of Material - ConductorDocument12 pagesA. What Types of Materials Do We Test? Three Types of Material - ConductorDaniel GravadorNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument17 pagesCapacitorsWani SageerNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument10 pagesCapacitorAshwini ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Capacitors 2Document65 pagesCapacitors 2miniNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis 1 Learner Guide Capacitor PDFDocument27 pagesNetwork Analysis 1 Learner Guide Capacitor PDFtheresa crawford100% (1)
- Introduction To Capacitors: ResistorDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: ResistorDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Passive Energy Electrostatically Electric Field Electrical Conductors Dielectric InsulatorDocument3 pagesPassive Energy Electrostatically Electric Field Electrical Conductors Dielectric InsulatorRenielDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Eee3352 L4Document38 pagesEee3352 L4Desmond CheweNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction To CapacitorsDocument5 pagesNtroduction To CapacitorsJohn Renzo Vibar ToribioNo ratings yet
- Pajaczarina e Ia 104 HandoutsDocument8 pagesPajaczarina e Ia 104 Handoutsjeanilauliga30No ratings yet
- Lectures 1Document8 pagesLectures 1Ravichandran SekarNo ratings yet
- 04 CapacitanceDocument27 pages04 Capacitanceade saputraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsDocument16 pagesLesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- What Is Capacitor and Capacitance - Types of Capacitors - Electrical4uDocument8 pagesWhat Is Capacitor and Capacitance - Types of Capacitors - Electrical4uteju2812No ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: Electronics Tutorial About CapacitorsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: Electronics Tutorial About CapacitorsVenkatesh VenkiNo ratings yet
- Rain AlarmDocument25 pagesRain AlarmEkta Jolly100% (4)
- Long Answer Questions: X y Z X y ZDocument5 pagesLong Answer Questions: X y Z X y ZJulie OsborneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: ResistorDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: ResistorsxpNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Constant KitDocument12 pagesDielectric Constant KitNeha AgarwallaNo ratings yet
- Ese Ed QP Answer KeyDocument40 pagesEse Ed QP Answer Keyசெல்வம் முத்துராமன்No ratings yet
- EOTDocument57 pagesEOTabcNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument28 pagesBasic Electronic ComponentsJafar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Electric DoubleDocument47 pagesElectric DoubleJoanne ReillyNo ratings yet
- Idea of Capacitance & CapicitorDocument7 pagesIdea of Capacitance & CapicitoradimeghaNo ratings yet
- Capacitor and CapacitanceDocument48 pagesCapacitor and CapacitanceDave Serapion50% (2)
- Original PRJDocument10 pagesOriginal PRJlordbravoriousNo ratings yet
- Electrical Material ScienceDocument10 pagesElectrical Material SciencesushinkNo ratings yet
- Capacitor PDFDocument21 pagesCapacitor PDFMøñəßh ßîñğh ŁøđhîNo ratings yet
- Electric Power CablesDocument6 pagesElectric Power CablesVENKATESAN RNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document3 pagesTopic 1Alwi HanafiNo ratings yet
- Capacitor - WikipediaDocument210 pagesCapacitor - WikipediaHarshit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Capacitors: II. CompositionDocument5 pagesCapacitors: II. CompositionJustine jerome FloranteNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentraviNo ratings yet
- IE CapacitorsDocument3 pagesIE CapacitorsParas Singh Negi 536No ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument5 pagesCapacitorAina shivhareNo ratings yet
- 4th WeekDocument7 pages4th WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- Transient Response in RC Circuits: ECE 3300 Electrical Circuits: LaboratoryDocument13 pagesTransient Response in RC Circuits: ECE 3300 Electrical Circuits: LaboratoryGlenn VirreyNo ratings yet
- Dielectric BreakdownDocument3 pagesDielectric BreakdownMas LilikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 23 06 19Document7 pagesChapter 1 - 23 06 19Sazzad HossainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: Tutorial 1 of 9Document37 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: Tutorial 1 of 9Noli LlaneraNo ratings yet
- Polymer Dielectrics For Capacitor ApplicationDocument29 pagesPolymer Dielectrics For Capacitor ApplicationFerryTimothyNo ratings yet
- TLE-EPAS 10 WK5 - Name: - DateDocument6 pagesTLE-EPAS 10 WK5 - Name: - DateNoli LlaneraNo ratings yet
- Homew ORK #1: Types of Capacito RSDocument11 pagesHomew ORK #1: Types of Capacito RSElisha LopezNo ratings yet
- Capacitance: Figure 8-177Document8 pagesCapacitance: Figure 8-177Sandeep Guha NiyogiNo ratings yet
- InsulationDocument2 pagesInsulationKumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Discrete Electronic ComponentsDocument4 pagesDiscrete Electronic ComponentsIsla VermilionNo ratings yet
- Substance Chemistry Lesson 1Document28 pagesSubstance Chemistry Lesson 1samsonNo ratings yet
- Vibrator Head H25HA: Material Number 5000610058Document2 pagesVibrator Head H25HA: Material Number 5000610058Luis ZavalaNo ratings yet
- LP2 Lubrication Pinion For Lubrication of Open Girth Gears, Tooth Wheels and Gear RodsDocument44 pagesLP2 Lubrication Pinion For Lubrication of Open Girth Gears, Tooth Wheels and Gear RodsThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- 19-104 ResearchPaperDocument6 pages19-104 ResearchPaperGimhani KavishikaNo ratings yet
- Is Structure AnswerDocument2 pagesIs Structure AnswerJay JayNo ratings yet
- EION VIP App148Document5 pagesEION VIP App148Javier QuirosNo ratings yet
- T1 SeriesDocument1 pageT1 SeriesFabricio GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- FCUBS Database Practices Db11gr2 Fc12.0.1Document38 pagesFCUBS Database Practices Db11gr2 Fc12.0.1cuonglunNo ratings yet
- Lipid Analysis: Melisa Intan BarlianaDocument38 pagesLipid Analysis: Melisa Intan BarlianaChantique Maharani0% (1)
- WL 80250 4 EA 0510 MainCat Equipment and ServicesDocument116 pagesWL 80250 4 EA 0510 MainCat Equipment and ServicesApetrei Ioan CristianNo ratings yet
- 17-7 PHDocument48 pages17-7 PHsunsirNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument5 pagesAnswer Key Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesREGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Bionic ReportDocument11 pagesBionic ReportIgor HorvatNo ratings yet
- 16-9 Accuracy of Erected SteelworkDocument8 pages16-9 Accuracy of Erected SteelworkZuberYousufNo ratings yet
- Prmo 2018 QPDocument2 pagesPrmo 2018 QPJatin RatheeNo ratings yet
- Door SheetDocument9 pagesDoor SheetAnilkumarNo ratings yet
- LIS2sl - 0911 - en SIEMENS SLDocument456 pagesLIS2sl - 0911 - en SIEMENS SLAntonio VazquezNo ratings yet
- Mani Kaul AnswerDocument10 pagesMani Kaul AnswerKeshab RNo ratings yet
- Integration Iit KanpurDocument5 pagesIntegration Iit KanpurAnsh KapoorNo ratings yet
- Fleishman AP 1975 - Towards A Taxonomy of Human PerformanceDocument23 pagesFleishman AP 1975 - Towards A Taxonomy of Human PerformanceCatalina Elena100% (2)
- Ashirwad Carbonics (India) Private Limited: Co2 Recovery Plant Technical LiteratureDocument5 pagesAshirwad Carbonics (India) Private Limited: Co2 Recovery Plant Technical LiteratureRaul BautistaNo ratings yet
- Appian Training CurriculumDocument3 pagesAppian Training CurriculumKumarReddy100% (1)
- XT1C 160 TMD 25-450 4p F F: General InformationDocument3 pagesXT1C 160 TMD 25-450 4p F F: General InformationHenrics MayoresNo ratings yet
- Assigment1 Jan30-2023Document4 pagesAssigment1 Jan30-2023Vaquas aloNo ratings yet
- Segger Eval SoftwareDocument24 pagesSegger Eval Softwarefercho573No ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Cse 245)Document58 pagesUnit-1 (Cse 245)Harsh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Keyop Functions 9F3715Document114 pagesKeyop Functions 9F3715Art MessickNo ratings yet
- Fast Web View PDF TomcatDocument2 pagesFast Web View PDF TomcatEddieNo ratings yet
- A 1008 - A 1008M - 04 Qtewmdgvqtewmdhnlvjfra - PDFDocument9 pagesA 1008 - A 1008M - 04 Qtewmdgvqtewmdhnlvjfra - PDFMarcos Verissimo Juca de PaulaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Index Values and PerformanceDocument5 pagesCalculating Index Values and Performancemuneebmateen01No ratings yet