Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Post Diploma IN Plastics Mould Design With Cad/Cam (PD-PMD With Cad/Cam)
Post Diploma IN Plastics Mould Design With Cad/Cam (PD-PMD With Cad/Cam)
Uploaded by
NithOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Post Diploma IN Plastics Mould Design With Cad/Cam (PD-PMD With Cad/Cam)
Post Diploma IN Plastics Mould Design With Cad/Cam (PD-PMD With Cad/Cam)
Uploaded by
NithCopyright:
Available Formats
CIPET
POST DIPLOMA
IN
PLASTICS MOULD DESIGN WITH CAD/CAM
(PD-PMD WITH CAD/CAM)
SYLLABUS & CURRICULUM
2014
REVISED: AUGUST 2016
Implemented from Academic Year:2016-17
Academic Cell
Central Institute of Plastics Engineering &
Technology
Department of Chemicals & Petrochemicals, Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers,
Govt. of India
Head Office, Guindy, Chennai – 600 032.
Tel. No.: 91-44-22254780 Fax: 91-44-22254787
Email: hocipetolc@gmail.com Web: www.cipet.gov.in
1 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
POST DIPLOMA IN PLASTICS MOULD DESIGN WITH CAD/CAM
(PD-PMD WITH CAD/CAM)
SYLLABUS
SEMESTER - I
THEORY
MARKS
SUBJECT CH TH EH
CODE INT EXT TOTAL
PD 101 Plastics Materials 36½ 4 3 40 60 100
PD 102 Plastics Product Design 51 3 3 40 60 100
PD 103 Plastics Mould Design – I 51 3 3 40 60 100
Plastics Processing
36½ 4
PD 104 Technology 3 40 60 100
174 15
Total (18 weeks – 10½ hours per week) 12 160 240 400
189
PRACTICAL
PDL 105 Plastics Testing & QC Lab 27 4 50 50 100
PDL 106 Plastics Processing Lab 27 4 50 50 100
PDL 107 Design Lab – I 270 8 200 200 400
Library 27 - - - -
Total (18 weeks – 19½ hours per week) 351 16 300 300 600
SEMESTER - II
THEORY
MARKS
CODE SUBJECT
TOTAL
CH TH EH INT EXT
PD 201 Plastics Mould Design – II 51 3 3 40 60 100
Mould Manufacturing
24 3 3 40 60 100
PD 202 Technology
Reverse Engineering And Rapid
Prototyping 24 3 3 40 60 100
PD 203
Process Planning & Cost
24 3 3 40 60 100
PD 204 Estimation
123 12
Total (18 weeks – 7½ hours per week) 12 160 240 400
135
PRACTICAL
PDL 205 Manufacturing Practice 108 8 100 100 200
PDL 206 Design Lab - II 270 8 200 200 400
Library 27 - - - -
Total (18 weeks – 22½ hours per week) 405 16 300 300 600
CH- Contact Hours TH-Tutorial Hours EH- Examination Hours
2 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
POST DIPLOMA IN PLASTICS MOULD DESIGN WITH CAD/CAM
(PD-PMD WITH CAD/CAM)
SYLLABUS
SEMESTER - III
MARKS
CODE SUBJECT HOURS INT EXT TOTAL
PDL 301 Project Work 378 200 200 400
PDL 302 In plant training in industry ** 54 - - 100 100
PDL 303 Seminar – 20 weeks 4 hrs a week 54 100 100
Library – 20 weeks 4 hrs a week 54 - - - -
Total 540 600
0CH- Contact Hours TH-Tutorial Hours EH- Examination Hours
Note:
** - Industrial Training should be of two weeks duration during the semester.
- Training Report from the Industry needs to be submitted.
3 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – I (2014 Syllabus)
PD 101 - PLASTICS MATERIALS ( 40½ Hours)
UNIT I Polymers ( 6 Hours)
Introduction to polymers, Natural polymers – Polymerization – types of polymerization
techniques. Types of plastics – thermoplastic & Thermoset – Amorphous & crystalline
polymer. Introduction to thermal, mechanical, electrical, chemical & optical properties.
UNIT II Commodity Plastics ( 7½ Hours)
General properties and application of Polyethylene - Polypropylene and their co-polymers -
Vinyl Polymers and Co-polymers - Polystyrene and Copolymers - Acrylic and copolymers -
Cellulose Polymers. Manufacturers & availability of various grades.
UNIT III Engineering Plastics ( 7½ Hours)
General Properties and application of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene - Polyamides(PA-6,
PA-6,6 & PA-11) - Polycarbonates - Polyacetal & Copolymers - Thermoplastic Polyesters
(PET & PBT)-Polyphenylene oxide – Polysulfones - Fluoro polymers (PVF, PVDF, PTFE,
PCTFE) - Thermoplastic Polyurethane. Manufacturers & availability of various grades.
UNIT IV Specialty Plastics ( 12 Hours)
General properties and applications of Polyphenyline Sulphide - Polyphenylene ether-
Polyether ether ketone-Polyimide and related polymers- Liquid Crystal Polymers- Conductive
Polymers- Plastic alloys and blends. Manufacturers & availability of various grades.
Polymer composites, Blends & Alloys: Definition, Properties, Advantages & Applications.
UNIT V Thermosetting Plastics ( 7½ Hours)
agents - General properties and applications of
Additives - Curing and cross linking Phenol
Formaldehyde - Urea Formaldehyde - Melamine Formaldehyde - Unsaturated Polyesters -
Epoxy resins - Polyurethane and Silicones. Manufacturers & availability of various grades.
Text / Reference Books
1. Hand Book of Plastic Materials & Technology, Rubin Irwin J
2. Plastics Materials, Brydson, J.A
3. Plastics Materials & Processes , Schwartz & Goodman
4. Text book of Polymer Science, Fred W Billmeyer
5. Polymer Science V.R. Gowariker
6. Principles Polymer Science P.Bahaabur& N.V. Sastry,Narosa Publishing House
Note: Minimum of one assignment is mandatory from each unit.
4 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – I (2014 Syllabus)
PD 102 - PLASTICS PRODUCT DESIGN ( 54 Hours)
UNIT I Product Design Requirement ( 12 Hours)
Concept to commercial products – Product specification – Material selection – Process
selection – Design for Manufacture & Assembly (DFMA). Tooling Aspects on Product
Design – Product Design Appraisal. Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerances on Product.
Product design criteria – Structural, Environmental, Assembly, Aesthetics & Decoration.
Product design check list, Good design practices, Safety in product design.
UNIT II Product Design Features ( 21 Hours)
Shrinkage, Wall thickness – variations in wall thickness – suggested wall thickness for
various plastics materials – Tapers or draft angles. – Design of radii, fillets, ribs and bosses.
Undercuts – External & Internal –. Moulded Holes - through holes – blind holes – threaded
holes – side holes – holes parallel to draw – nearness of holes to each other and side wall –
moulding holes not parallel to draw – drilled and tapped holes.
Design of integral hinges, hinges and snap fits for boxes and assembly of moulded parts.
Moulded threads – thread types. Interference between the threads. Inserts – materials –
selection of metal for inserts – minimum wall thickness of material around inserts –
anchorage - relieving moulding stresses around inserts – location of inserts in the part –
moulded inserts – pressed in inserts.
UNIT III Design of Structural Elements ( 10½ Hours)
Tension bars – columns – beams – pipes – plates and shells. Design of joints – bolted joints
– bonded joints, etc.
Designing with plastics for load bearing applications like gears,
bearing, spring. Assembly – Mechanical fasteners
UNIT IV Composite Product Design ( 10½ Hours)
Concepts of composite product design – Design requirements – functional – safety –
reliability – cost effectiveness.
Design constraints – factor of safety for uncertainties in design – design failure criteria –
optimization in design.
Design data – physical, mechanical and functional properties of composites – code of
practice of loading on structures – structure and property relation of composites.
Text / Reference Books
1. Plastics Product Design, Beck
2. Plastic part design hand book, Rosato
3. The complete part design hand book (Injection Mould of Thermo Plastics), E.
Alfredocampo
Note: Minimum of one assignment is mandatory from each unit.
5 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – I (2014 Syllabus)
PD 103 - PLASTICS MOULD DESIGN – I ( 54 Hours)
UNIT I Mould Design Fundamentals ( 16½ Hours)
Introduction: Basic construction of mould – Types of moulds – Mould parts – mould plates, sprue
bush, locating ring, core and cavity, Guide pillar & guide bush, Bolsters, Types of Bolsters, Mould
clamping methods, Mould lifting arrangements
Feed System: Sprue, Runner & Gate – cross section and size of runner –runner layout – balancing
of runners – types of gates for various materials – cross section of gate – gate balancing. Empirical
formulae
Parting Surface: Parting line/Parting surface: Flat parting surface – Non flat parting surface –
stepped parting surface, irregular parting surface, angled surface, local stepped and profile parting
surface, complex edge forms –Mould Venting.
UNIT II ( 12 Hours)
Ejection System:
Types of ejector grid – Ejector plate assembly – Guiding & Supporting ejector plate assembly -
Types of ejection – position & critical area of ejection – pin ejection – stepped pin-part of pin-“D” –
Pin-blade ejection – sleeve ejection – stripper ring ejection – stripper plate ejection – air ejection –
double ejection – Delayed action ejection – Types of sprue pullers – calculation of support pillar
requirements. Calculation of Ejection force, ejection stroke etc.
Mould Temperature Control System:
Mould cooling – Integer type cavity and core plates cooling, angled hole systems, baffled hole
systems, stepped circuit – Types of bolster cooling – Insert cooling, Deep chamber design, Bubbler
cooling, Baffle cooling, spiral cooling –cooling circuits – Principle of heat pipe, heat rod, capillary
tube and its applications – Cooling for sprue bush – O-rings – cooling nipples – Calculation of
cooling efficiency, cooling time. Mould heating methods, Mould temperature controller.
UNIT III Types of Injection Moulds ( 13½ Hours)
Two Plate / Part Mould and Three Plate / Part Mould Design, Split moulds: External undercuts -
Splits – Guiding and retention of splits – finger cam and dog leg cam actions – cam track – spring –
hydraulic actuation – side cores and side cavities – Calculation of split movement – Split safety
arrangements –Angled lift split – form pin and Angled pin action – split cores– Collapsible core.
UNIT IV Selection of Machines ( 6 Hours)
Types of injection moulding machines – specifications – shot capacity – shot weight – plasticising
capacity – projected area – locking forces – platen details – maximum and minimum daylight –
nozzle details – locating mould on machines– ejection systems – Machine platen locking methods –
dry cycle time and its application in Mould Design.Calculating No. of impressions –projected area,
injection pressure, clamping tonnage. Lay-out of impressions.
UNIT V Standard Mould Parts ( 6 Hours)
Standard Mould Base- Advantages and limitations, manufacturers etc., Standard ejector pins, guide
pins, bushes, mould date indicators, mould springs, cooling baffles, nipples, parting locks etc
Text / Reference Books
1. Injection Mould Design – Pye R.G.W
2. Injection Moulds 130 Proven Design Gastrow
Note: Minimum of one assignment is mandatory from each unit.
6 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – I (2014 Syllabus)
PD 104 - PLASTICS PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY ( 40½ hours)
UNIT I Injection Molding ( 10½ hours)
Introduction - process variables - moulding cycle - cylinder temperatures - shear and
orientation - runner systems - balancing of impressions - injection nozzles - insulated nozzles -
hot runner moulds - insulated runner moulds - semi automatic and automatic moulds -
operation and maintenance.
Types of injection moulding machines - machine specifications - projected area - plasticizing
capacity - shot weight - type of locking systems - mould clamping - hydraulics - basic principles
- hydraulics - hydraulic control - oil requirements - routine maintenance - safety rules.
Mould setting – effect variables on mouldings - shrinkage - quality control aspects - faults -
causes and remedies.
UNIT II ( 10½ hours)
Blow Moulding:
Introduction to blow moulding - types of blow moulding operations - extrusion blow moulding -
injection blow moulding - stretch blow moulding - basic principles - parison control - wall
thickness in relation to parison - types of extruders for blow moulding - blow mould
construction - setting and operation - mould cooling - clamping force - cycle time - moulding
faults - causes and remedies - quality control - operator safety.
Extrusion:
Introduction - extruder parts - extrusion screw - design features - design variables - extruder
output - extrusion process parameters - their effects on product - extruder faults - causes and
remedies. Extrusion of film, pipe, sheet, profile and coating - dies for different extrusion
process - sizing units - hauloff units - process control systems - process variables - quality
control and safety.
UNIT III ( 6 hours)
Compression &Transfer Moulding:
Compression moulding - fundamental principles - bulk factor - flow properties - processing
temperatures - mould temperature control - moulding pressure - press tonnage - limitations -
curing time - influence of processing paramters on the quality of the moulding - moulding
conditions - raw material quantity (charge size) - by volume/weight - pelleting - preheating the
pellets - simple test for rate of cure - defects - causes and remedies of the common moulding
faults - operator safety and routine quality control.
UNIT IV ( 9 hours)
Thermoforming:
Introduction - thermoforming methods - thermoforming dies - thermoforming equipment
description - temperature control - cycle time - defects, causes and remedies - quality control
and safety
Roto-Moulding:
Introduction to rotomoulding – principle of bi-axial rotation –
equipment description – temperature control systems – cycle time – defects, causes and
remedies.
7 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
Post Moulding Operations:
Printing and decoration of moulded items - films - pipes - sheets, etc. - hot stamping - pad
printing - screen printing – rotogravure printing - heating ceiling - ultrasonic welding - adhesive
bonding - fastening with metal inserts - limitations of post moulding operations - their
advantages
UNIT V ( 4½ hours)
Advanced Processing Techniques:
Reaction injection moulding - principles - machine description - process control - cycle time -
defects, causes and remedies - quality control and safety. Twin screw injection moulding
machine, Twin barrel Injection moulding machine.
Structural foam moulding - principles - process description - process control - defects and
remedies - quality control.
Resin transfer moulding - principles - process description - process control - defects and
remedies - quality control.
Text / Reference Books
1. Hand Book of Plastic Materials & Technology, Rubin Irwin J
2. Plastics Materials, Brydson, J.A
3. Plastics Materials & Processes, Schwartz & Goodman
4. Plastics Processing, Beadle
Note: Minimum of one assignment is mandatory from each unit.
8 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – I
PDL 105- PLASTICS TESTING & QC LAB ( 27 hours)
Practical Exercises
1. Chemical Lab 2 Hours
2. Specimen Preparation Lab 2 Hours
3. Thermal Lab 6 Hours
4. Mechanical Lab 6 Hours
5. Electrical & Optical Lab 2 Hours
6. Product Testing Lab 3 Hours
7. Rheological Lab 3 Hours
8. Characterization Lab 3 Hours
9 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – I
PDL 106 - PLASTICS PROCESSING LAB ( 27 hours)
Practical Exercises
1. Injection moulding machines : 10 Hours
a) Hand operated
b) Semi-automatic & automatic
c) Microprocessor controlled automatic injection
moulding process
2. Blow moulding machines: 2 Hours
Hand operated, semi & automatic machines
3. Compression & transfer moulding machines: 2 Hours
Hand operated, semi & automatic
4. Extrusion : 9 Hours
a) Pipe & profile extrusion
b) Blown film extrusion
c) Multilayer blown film extrusion
5. Rotomoulding machines 1 Hours
6. Thermoforming machines 1 Hours
7. Fibre reinforced plastics processing 2 Hours
10 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – I
PDL 107 - DESIGN LAB - I ( 270 Hours)
(To be conducted in CAD/CAM Lab)
1. Introduction and Practice on 2D drafting on CAD software 27 Hours
2. Introduction and practice on 3D Modeling using Creo/UG/CATIA software 50 Hours
3. Design of standard Mould Base 14 Hours
4. Design ofHand Injection mold for single impression 8 Hours
5. Design of Single impression two plate Injection Mould 21 Hours
6. Design of Multi impression two plate Injection Mould 27 Hours
7. Study & detail for the Exercise No. 5/ 6 21 Hours
8. Design of Three Plate Injection Mould (multi impression) 27 Hours
9. Design of Split Injection Mould - without delayed action 27 Hours
10. Design of Split Injection Mould - with delayed action 27 Hours
11. Design of Injection Mould for internal undercut components 21 Hours
Note : Design Practicals Sl.No.:3 to 10 shall be carried out by utilizing CAD software.
11 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014
SYLLABUS
PD 201 PLASTICS MOULD DESIGN – II ( 54 Hours)
UNIT I Advance Injection Mould Design ( 22 Hours)
Moulds for threaded components – automatic unscrewing – various unscrewing methods – inline
layout – pitch circle layout – mould movements – hydraulic and pneumatic core systems for mould
movement – runner less moulds – insulated and hot runner moulds – Types of manifold block,
primary nozzle & secondary nozzle design – flow way system – types of shut off valve system – Hot
runner mould – Water Assisted & Gas Assisted Injection Mould – multi-colour moulding – insert
moulding – outsert moulding – stack mould – two and three level.
UNIT II Compression & Transfer Mould Design ( 14 Hours)
Compression Mould Design:
Types of compression moulds, open flash, semi-positive, positive, displacement moulds, types of
loading chambers, bulk factor, flash thickness, projected area, compression pressure, clamping
force, no. of impression by technological method, heating system, types of heaters, heat loss, heat
requirement & heater capacity.
Transfer Mould Design:
Types of transfer moulds, integral pot transfer mould, auxiliary ram , transfer pot design,
projected area, transfer pressure, clamping force, pressure pad design, design of sprue runner
and gate, advantages and disadvantages of transfer mould - design related calculations.
UNIT III Blow Mould Design ( 6 Hours)
Types of blow moulds - extrusion - injection stretch blow moulds - blow ratio - parison design -
pinch off design - parting line - clamping force - mould venting, mould cooling - mould alignment.
Design for industrial applications.
UNIT IV Extrusion Die Design (6 Hours)
Principles of extrusion - die geometry - die swell - die land design - sizing die design - construction
of extrusion dies - blown film - pipe - profile - flat film - sheet - wire coating and co-extrusion dies.
UNIT V Rotational Mould Design ( 6 Hours)
Introduction – Mould material – Mould design: Mould frame, Moulded in inserts, Moulded
handles, Movable cores. – Mould venting – Mould cooling.
Text / Reference Books
1. Plastics Product Design Beck, R
2. Injection Mould Design – Pye R.G.W
3. Injection Moulds 130 Proven Design Gastrow
Note: Minimum of one assignment is mandatory from each unit.
12 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014
SYLLABUS
PD 202 - MOULD MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY ( 27 hours)
Unit I Material for Mould Making ( 7½ Hours)
Ferrous - non ferrous materials - copper - bronze - beryllium copper, Al - Mg alloys and its
significance as a materials for mould making - miscellaneous materials - mould steel - alloying
elements - material selection for different parts of the mould and their heat treatment, IS
standards, British standards for mould materials.
Unit II Machinery for Mould Manufacture ( 7½ Hours)
Tool room machinery - their recognition, appreciations and limitations - machining operations
and accuracy.
Conventional tooling machines - shaper - planner - lathe – drilling - milling - horizontal, vertical
& universal type – jig boring - grinding - pantograph engraving.
Unit III CNC Machines ( 6 Hours)
Different types of CNC machine tools - Lathe, Milling, VMC, EDM, Wire EDM - CAD integrated
with CAM.
Introduction to tool room inspection-measuring instruments-co-ordinate measuring machine -
taper and angle measurement techniques.
Unit IV ( 3 Hours)
Hours)
Polishing Technology in Mould Making: Definition of surface roughness, basis of polishing
technology - Effect of mould materials on polishability, Types of polishing tools, Methods of
polishing - Basic information on ultra sonic polishing – Principles of Electro deposition in
damaged moulding surfaces/Protective Coating.
Surface Texturing of Moulds – Process description, types of moulds, types of patterns and
mould shapes, metals that can be etched, mould preparation, limitations of chemical texturing.
Unit V ( 3 Hours)
Mould assembly-check list for mould assembly-fitting and assembly of various mould
elements- core insert, cavity insert, sprue bush-ejection system assembly-blue matching and
die spoting-venting - final inspection-fitting of locating ring and carrier bar- mould trial.
Text / Reference Books
1. Mould Making Hand Book, Stoeckert
2. Plastics Moulds and Dies, Sors
3. Injection Moulds, V.D.I
4. Mould Finishing and Polishing Manual, S.P.E
5. Computer Numerical Control Machines (CNC), Radhakrishnan, P
6. Fundamentals of Numerical Control Lock Wood F.B
7. CNC Setting & Operation Work Book Renshaw, Tom
Note: Minimum of one assignment is mandatory from each unit.
13 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014
SYLLABUS
PD 203 REVERSE ENGINEERING AND RAPID PROTOTYPING ( 27 hours)
Unit I Reverse Engineering ( 6 Hours)
Geometric Modeling: Types of Geometric models and Solid Models
Reverse Engineering: Meaning, Definition & application, Computer aided reverse engineering,
Measuring devices -contact type, non contact type-CAD model construction from point cloud-
preprocessing, point clouds to surface model creation, Geometric data acquistion,3D
reconstruction, Applications and Case Studies
Unit II Rapid Prototyping ( 3 Hours)
Introduction : Need - Development of RP systems – RP process chain - Impact of Rapid
Prototyping and Tooling on Product Development – Benefits- Applications.
Unit III Liquid and Solid Based Rapid Prototyping systems ( 6 Hours)
Stereo lithography Apparatus, Fused deposition Modelling, Laminated object manufacturing,
three dimensional printing: Working Principles, details of processes, products, materials,
advantages, limitations and applications
Unit IV Powder Based Rapid Prototyping Systems ( 6 Hours)
Selective Laser Sintering, Direct Metal Laser Sintering, Three Dimensional Printing, Laser
Engineered Net Shaping, Selective Laser Melting, Electron Beam Melting: Processes,
materials, products, advantages, applications and limitations
Unit V Rapid Tooling ( 6 Hours)
Classification: Soft tooling, Production tooling, Bridge tooling; direct and indirect – Fabrication
processes, Vacuum casting - Applications.
Text / Reference Books
1. Tool Design – Cyril Donaldson,
2. Production Technology by P.C.Sharma, S.Chand & Company,
3. Production Technology by Dr.R.K.Jain,
4. Jig and Fixture Design by Edward G.Hoffman, Thomson Delmer Learning,
5. Fundamentals of Press Tool Design by William Francis Walker.
6. Rapid prototyping: Principles and applications, second edition, Chua C.K.,
LeongK.F., and Lim C.S., World Scientific Publishers, 2003.2.
7. Rapid Tooling: Technologies and Industrial Applications, Peter
D.Hilton,Hilton/Jacobs, Paul F.Jacobs, CRC press, 2000.
8. Rapid prototyping, Andreas Gebhardt, Hanser Gardener Publications, 2003.
9. Rapid Prototyping and Engineering applications : A tool box for
prototypedevelopment, Liou W.Liou, Frank W.Liou, CRC Press, 2007.
10. Rapid Prototyping: Theory and practice, Ali K. Kamrani, Emad Abouel Nasr
Note: Minimum of one assignment is mandatory from each unit.
14 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014 SYLLABUS
PD 204 – PROCESS PLANNING & COST ESTIMATION ( 27 HOURS)
Unit I Introduction ( 1½ Hours)
Process planning and control – Introduction – objectives & importance – process planning –
scheduling & control of production – Selection & Analysis – Steps involved in manual planning and
computer aided process planning – merits and demerits.
Unit II Process planning activities for Mould manufacture ( 4½ Hours)
Introduction to Mould Manufacturing system, Details of mould manufacturing process - operation
sequence, machine selection.
Documents in process planning (process layout, process sheets and route sheets with example) –
process plans for machining typical components.
Unit III Estimating and Costing for mould manufacturing ( 7½ Hours)
Costing– Meaning, Types of costing and cost accounting methods.
Functions of estimation - Importance and aims of Cost estimates Difference between costing and
estimation - Importance of realistic estimates - Estimation procedures.
Unit IV Elements of Costing ( 6 Hours)
Introduction - Material Cost - Determination of Material Cost - Labour Cost - Determination of Direct
Labour Cost - Expenses - Cost of Product (Ladder of cost) - Illustrative examples. Analysis of
overhead expenses - Factory expenses - Depreciation - Causes of depreciation - Methods of
depreciation - Administrative expenses - Selling and Distributing expenses - Allocation of overhead
expenses.
Unit V Cost Estimation ( 7½ Hours)
Proforma for cost estimation – product cost – estimation of machining time & costs - mould cost -
Processing cost - project costing.
Text / Reference Books
1. Industrial Engineering Management – Khanna O. P.
2. T.R.Banga and S.C.Sharma, “Mechanical Estimating and Costing”
3. Sinha.B.P., Mechanical Estimating and Costing”, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
4. Russell R.S. and Taylor, B.W.”Operations Management”, PHI,
5. Chitale.A.V. and R.C.Gupta, “Product Design and Manufacturing”, PHI,
6. Production Technology by P.C.Sharma, S.Chand & Company.
7. Adithan, M. S., and Pabla, Estimating and Costing, Konark Publishers Pvt., Ltd, 1989
8. Chitale, A. K., and Gupta, R. C., Product Design and manufacturing, Prentice Hall of India, New
Delhi, 1997
Note: Minimum of one assignment is mandatory from each unit.
15 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014 SYLLABUS
PDL 205 - MANUFACTURING PRACTICE ( 108 Hours)
Practical Exercises on Mould Parts
1. Milling & Boring 12 Hours
2. Turning, thread cutting 10 Hours
3. Drilling, reaming & tapping 10 Hours
4. Grinding- wheel dressing, setting, balancing & grinding 10 Hours
5. EDM 10 Hours
6. Wire-EDM - programming & machining 10 Hours
7. CNC milling - programming & machining 12 Hours
8. CNC lathe - programming & machining 12 Hours
9. CNC EDM - programming & machining 12 Hours
10. Inspection & CMM 10 Hours
16 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014 SYLLABUS
PDL 206 - DESIGN LAB - II ( 270 Hours)
(To be conducted in CAD/CAM lab)
1. Introduction and practice on 3D modeling using UG NX /CREO/CATIA ( 50 Hours)
2. Demonstration and practice on Mould Flow software ( 50 Hours)
3. Compression mould design -open flash ( 21 Hours)
4. Compression mould design - positive, semi-positive, ( 21 Hours)
5. Transfer mould design ( 21 Hours)
6. Extrusion Die Design ( 21 Hours)
7. Design of Blow mould ( 21 Hours)
8. Mould design for internal threaded components (automatic unscrewing) ( 22 Hours)
9. Hot Runner Mould ( 22 Hours)
10. Rotomould and thermoform mould design ( 21 Hours)
Note : Design Practicals Sl.No. : 3 to 11 shall be carried out by utilizing CAD software.
17 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014 SYLLABUSI
PDL 301 - PROJECT WORK ( 378 Hours)
Project work shall be carried out by the Students in a group comprising of 4 to 5
members. The type of project shall be selected by the course in-charge in consultation
with the local industries.
The scope of the project work is given below:
1. Development of Product Design and Mould Design Drawings using any CAD
Software
2. Checking the Mould Design using Mould Flow Analysis
3. Preparing Project report highlighting features of Product Design and steps
followed in development of Mould Design and report on Mould Flow analysis
4. Students shall be encouraged to involve themselves in the mould development
process
5. The final assessment will be through a Viva-voce by a committee of officials
working in industries and department officials.
18 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014 SYLLABUSI
PDL 302 – INPLANT / INDUSTRIAL TRAINING: ( 54 Hours)
A report should be submitted by the student after successful completion of the same along with a
certificate from the Industry. It will help the student to understand the Industry requirement for
selection of product and executing the Project.
19 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
CIPET
PD-PMD With CAD/CAM
SEMESTER – II 2014 SYLLABUSI
PDL 303 SEMINAR - CASE STUDIES ON PRODUCT & MOULD DESIGN ( 54 Hours)
Each student shall present a case study with part drawing and mould design as part of seminar in
the class room in front of the students and shall be evaluated by the faculty. Suggested topics are
given below for selection by faculty and allocation to the student. Student maybe encouraged to
select automobile, electrical and other engineering products.
1. Two Plate Injection Mould
2. Three Plate Injection Mould
3. Multi Cavity Injection Mould
4. Stripper Plate Mould
5. Standard Mould Bases
6. Split Cavity Mould
7. Core Puller Mould
8. Collapsible Mould
9. Cooling System
10. Submarine Gate multi Cavity Mould
11. Automatic Unscrewing Mould
12. Gas assisted Injection Mould
13. Hot Runner Mould
14. Stack Mould
15. Multi Stage Injection Mould
16. Metal to Plastic replacement
17. Insert Moulding
18. Two layer two colour Injection moulding concept
19. Injection Blow moulding Process and Design
20. Stretch Blow moulding process and design
21. Thermoforming moulding process and design
22. Rotational moulding process and design
23. Mould elements – material selection process
24. Various heat treatment process for Mould elements
25. Mould Polishing & Mould maintenance
26. Product design features and requirement
27. Fastening / Assembly / Welding / joining of Plastics
28. Composite Material based Product design & Applications.
29. Rapid prototyping techniques
30. Reverse Engineering
31. Dealing with undercuts – Lifter / Collapsible core / Angle pin / Dog leg cam
32. Shrinkage Analysis for various plastic materials
*****************************
20 PD-PMD with CAD/CAM SYLLABUS
You might also like
- Exercises Programming CNC MillingDocument1 pageExercises Programming CNC Millingmarlina bieNo ratings yet
- Case Study of BMW WELT MUSEUMDocument3 pagesCase Study of BMW WELT MUSEUMAnafNo ratings yet
- Design and Manufacturing of 8 Cylinder Hydraulic Fixture For Boring Yoke On VMC 1050Document8 pagesDesign and Manufacturing of 8 Cylinder Hydraulic Fixture For Boring Yoke On VMC 1050The ash Designe GalaryNo ratings yet
- Section A-A: Assignment - 3Document5 pagesSection A-A: Assignment - 3Ankit BhadesiaNo ratings yet
- Shortcut KeysDocument28 pagesShortcut KeysSuresh Dhanasekar0% (1)
- Jyoti CNCDocument46 pagesJyoti CNCAmit Vora100% (1)
- Akshay GTTCDocument32 pagesAkshay GTTCGaurav JM100% (1)
- Catalogo Holders TungaloyDocument156 pagesCatalogo Holders Tungaloyabsalon_jarvNo ratings yet
- EdgeCAM 2015Document12 pagesEdgeCAM 2015Daniela UlianNo ratings yet
- Cadcam Module 2Document433 pagesCadcam Module 2Ahsan IftikharNo ratings yet
- SolidCAM 2017 2.5D Milling Training Course PDFDocument320 pagesSolidCAM 2017 2.5D Milling Training Course PDFAdnan MustafićNo ratings yet
- MAPAL Competence ISO enDocument206 pagesMAPAL Competence ISO enMarcio ParrachoNo ratings yet
- Vericut CAM InterfacesDocument2 pagesVericut CAM InterfacessivakumarsambandamNo ratings yet
- Incremental Sheet Metal Forming On CNC Milling Machine-ToolDocument4 pagesIncremental Sheet Metal Forming On CNC Milling Machine-ToolDionysius WahyoeNo ratings yet
- Turning Tools - General InformationDocument22 pagesTurning Tools - General Informationenamicul50No ratings yet
- NX Total Machining PDFDocument5 pagesNX Total Machining PDFHussein ZeinNo ratings yet
- Machining LatheDocument219 pagesMachining LathehareshNo ratings yet
- CNC Machining Designing For SpeedDocument9 pagesCNC Machining Designing For SpeedjaimeNo ratings yet
- Design of A Milling Cutter by Using Catia: D Ravi TejaDocument48 pagesDesign of A Milling Cutter by Using Catia: D Ravi Tejanaveen mylapilliNo ratings yet
- C16 NX11 PDFDocument82 pagesC16 NX11 PDFVignesh WaranNo ratings yet
- New in CncKad v95Document29 pagesNew in CncKad v95caredasNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in ManufacturingDocument13 pagesRecent Trends in ManufacturingAmbarish100% (2)
- Top Solid Integration 2003 UsDocument12 pagesTop Solid Integration 2003 Usapi-3725036No ratings yet
- Micromatic ChuckDocument24 pagesMicromatic ChuckmadhavikNo ratings yet
- H - Additional MachiningDocument51 pagesH - Additional MachiningedsaregNo ratings yet
- Delcam - PowerMILL 2017 Toolpath PointParameters en - 2016Document11 pagesDelcam - PowerMILL 2017 Toolpath PointParameters en - 2016Sergey ZubovNo ratings yet
- Contour Milling Programming On A CNC MachineDocument3 pagesContour Milling Programming On A CNC Machinebhaskarjalan0% (1)
- Solid Cam 2007 Turning Training CourseDocument31 pagesSolid Cam 2007 Turning Training Coursedpdpd1234No ratings yet
- VericutDocument20 pagesVericutStanko Radovanovic0% (1)
- Manual de CNC TornoDocument147 pagesManual de CNC TornoAbraham Pool100% (1)
- NX Custom Reuse Library PartsDocument4 pagesNX Custom Reuse Library PartsHiren SonarNo ratings yet
- Eccentric TurningDocument57 pagesEccentric TurningNitin100% (1)
- MpgugDocument96 pagesMpgugiagomouNo ratings yet
- Turner 4 TH Sem TTDocument223 pagesTurner 4 TH Sem TTSubhranil Dutta100% (1)
- Final Thesis On CNCDocument55 pagesFinal Thesis On CNCFranco100% (1)
- NX Sheet Metal Design PDFDocument2 pagesNX Sheet Metal Design PDFHussein Zein0% (1)
- MasterCAM BrochureDocument28 pagesMasterCAM BrochurePhúc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Powerinspect Manual CmmsDocument2 pagesPowerinspect Manual CmmsFelipe Cordeiro100% (1)
- Lecture Cad CamDocument84 pagesLecture Cad Camismail_69No ratings yet
- EMX Basic Best Practices For PTC CreoDocument55 pagesEMX Basic Best Practices For PTC CreoanilpagarNo ratings yet
- PBT mt11060 GDocument250 pagesPBT mt11060 Gandreeaoana45No ratings yet
- MasterCAM Price ListDocument5 pagesMasterCAM Price ListEmilian PopaNo ratings yet
- Post Processor ReferenceDocument437 pagesPost Processor Referencennn765100% (1)
- 3d Modeling Fea CATIA v5Document25 pages3d Modeling Fea CATIA v5Jasime IhocuNo ratings yet
- EML2322L-Drilling and Milling Speeds and FeedsDocument9 pagesEML2322L-Drilling and Milling Speeds and Feedsjromero_rpgNo ratings yet
- Mastercam 2017 Mill Advanced Training Tutorial SAMPLE PDFDocument36 pagesMastercam 2017 Mill Advanced Training Tutorial SAMPLE PDFsekhon875115No ratings yet
- 26 Broaching - Principles, Systems and ApplicationsDocument16 pages26 Broaching - Principles, Systems and ApplicationsPRASAD326100% (2)
- SolidWorks Tutorial 5 For Prepatory and Advanced Vocational TrainingDocument33 pagesSolidWorks Tutorial 5 For Prepatory and Advanced Vocational TrainingagingagentNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Face Milling On CNC MachineDocument5 pagesLab 6 - Face Milling On CNC MachineHaris NaveedNo ratings yet
- 5XCAMDocument10 pages5XCAMTrường GiangNo ratings yet
- Mechanism and Machine Theory: Enea Olivoni, Rocco Vertechy, Vincenzo Parenti-CastelliDocument15 pagesMechanism and Machine Theory: Enea Olivoni, Rocco Vertechy, Vincenzo Parenti-Castelli马懿No ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Vertical Machining CenterDocument27 pagesOperation Manual: Vertical Machining CenterAmauriGarciaNo ratings yet
- NC-5-axis ProductionDocument674 pagesNC-5-axis ProductionVladimir MagocNo ratings yet
- Cam Lab ManualDocument14 pagesCam Lab Manualelangandhi0% (1)
- List of Revised Required Standards - 04 05 09Document11 pagesList of Revised Required Standards - 04 05 09Navnath TamhaneNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IiDocument5 pagesAssignment - IichritNo ratings yet
- Fine-Fin: High Performance Tubes For Heat ExchangersDocument12 pagesFine-Fin: High Performance Tubes For Heat ExchangersPankaj RaneNo ratings yet
- Name of The College:: Government Polytechnic, SaharsaDocument17 pagesName of The College:: Government Polytechnic, SaharsaMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- YM Cargo WorthyDocument109 pagesYM Cargo WorthyHoan Vu100% (1)
- Ex9m Su20s Eu en 20210623 PDFDocument29 pagesEx9m Su20s Eu en 20210623 PDFOgnjen DevicNo ratings yet
- AT3 Post Tensioning Miroslav Vejvoda FINALDocument30 pagesAT3 Post Tensioning Miroslav Vejvoda FINALptqc2012No ratings yet
- Truss DesignDocument3 pagesTruss DesignJake CortezNo ratings yet
- Displacement-Based Method of Analysis For Regular Reinforced-Concrete Wall Buildings: Application To A Full-Scale 7-Story Building Slice Tested at UC-San DiegoDocument14 pagesDisplacement-Based Method of Analysis For Regular Reinforced-Concrete Wall Buildings: Application To A Full-Scale 7-Story Building Slice Tested at UC-San Diegojoelmt30No ratings yet
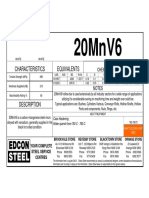
- Characteristics Equivalents: Chemical Analysis (%)Document1 pageCharacteristics Equivalents: Chemical Analysis (%)Ali TalebiNo ratings yet
- Block Work Mathod Statements 2024Document7 pagesBlock Work Mathod Statements 2024ShahzebNo ratings yet
- Trisha Banerjee at 2010Document7 pagesTrisha Banerjee at 2010Physics InstrumentsNo ratings yet
- Company Details - 駐龍 - 仁武廠-1 - eAuditNetDocument2 pagesCompany Details - 駐龍 - 仁武廠-1 - eAuditNetYORK NEWNo ratings yet
- Engg Utilities 1Document39 pagesEngg Utilities 1ricaosio91No ratings yet
- W17 Approval of Consumables For Welding Normal and Higher Strength Hull Structural Steels W17Document35 pagesW17 Approval of Consumables For Welding Normal and Higher Strength Hull Structural Steels W17Beshoy RedaNo ratings yet
- SUNPAL Architectural System-BrochureDocument20 pagesSUNPAL Architectural System-BrochureGirish Dhawan0% (1)
- Design of Beams 1: Act BCXDocument27 pagesDesign of Beams 1: Act BCXleimrabottNo ratings yet
- Stem B RocksDocument3 pagesStem B RocksarlesjohngabrielmirasolNo ratings yet
- Elastoplastic BehaviourDocument8 pagesElastoplastic BehaviourHalef Michel Bou KarimNo ratings yet
- Rana Plaza BuildingDocument15 pagesRana Plaza BuildingBianca LegoNo ratings yet
- 03 - Lost Circulation MaterialsDocument42 pages03 - Lost Circulation MaterialsandreaNo ratings yet
- Unidad Interior Mitsubishi PDFDocument40 pagesUnidad Interior Mitsubishi PDFthemob eddinNo ratings yet
- Effects of Non-Standard Curing On Strength of ConcreteDocument3 pagesEffects of Non-Standard Curing On Strength of ConcreteFarhanNo ratings yet
- EditedDocument14 pagesEditedDaniel DanaoNo ratings yet
- Determining The Effective Elastic Parameter For X-Ray Diffraction Measurements of Residual StressDocument4 pagesDetermining The Effective Elastic Parameter For X-Ray Diffraction Measurements of Residual StresssanthakumarNo ratings yet
- General Notes: Mnisi New Propossed Dwelling ERF 43 Estate D' AfriqueDocument1 pageGeneral Notes: Mnisi New Propossed Dwelling ERF 43 Estate D' AfriqueanzaniNo ratings yet
- Uniflair LE Tdav-Tuav: Direct Expansion Air-Cooled Units With Backward-Curved Fans Equipped With EC MotorDocument5 pagesUniflair LE Tdav-Tuav: Direct Expansion Air-Cooled Units With Backward-Curved Fans Equipped With EC MotorDuy ChuNo ratings yet
- Cable Stayed Bridge ThesisDocument4 pagesCable Stayed Bridge ThesisPayToWritePapersCorona100% (2)
- Outdoor Sealing End ManualDocument15 pagesOutdoor Sealing End ManualSRG100% (1)