Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ubc 97
Uploaded by
AdnanRasheed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views30 pages Here are the steps to solve this problem:
1. Given: 9 story steel moment frame office building in Muzaffarabad, AJK
2. Site class: Very dense soil and soft rock = D
3. Near fault factor = 1.5 (Table 16-S)
4. Seismic zone = 4 (Figure 16-2)
5. Occupancy category = II
6. Z = 1.5 (Table 16-I)
7. Ca = 0.6 (Table 16-Q)
8. Cv = 0.4 (Table 16-R)
9. Calculate base shear and distribute to stories.
Let me know if you need help with any of
Original Description:
UBC 97 with Examples
Original Title
UBC 97
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Here are the steps to solve this problem:
1. Given: 9 story steel moment frame office building in Muzaffarabad, AJK
2. Site class: Very dense soil and soft rock = D
3. Near fault factor = 1.5 (Table 16-S)
4. Seismic zone = 4 (Figure 16-2)
5. Occupancy category = II
6. Z = 1.5 (Table 16-I)
7. Ca = 0.6 (Table 16-Q)
8. Cv = 0.4 (Table 16-R)
9. Calculate base shear and distribute to stories.
Let me know if you need help with any of
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views30 pagesUbc 97
Uploaded by
AdnanRasheed Here are the steps to solve this problem:
1. Given: 9 story steel moment frame office building in Muzaffarabad, AJK
2. Site class: Very dense soil and soft rock = D
3. Near fault factor = 1.5 (Table 16-S)
4. Seismic zone = 4 (Figure 16-2)
5. Occupancy category = II
6. Z = 1.5 (Table 16-I)
7. Ca = 0.6 (Table 16-Q)
8. Cv = 0.4 (Table 16-R)
9. Calculate base shear and distribute to stories.
Let me know if you need help with any of
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
Equivalent Lateral
Loads using UBC-97
Structural Engineering by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 1
General Terms
• BASE is the level at which the earthquake motions are
considered to be imparted to the structure or the level at which
the structure as a dynamic vibrator is supported.
• BASE SHEAR, is the total design lateral force or shear at the
base of a structure.
• BRACED FRAME is an essentially vertical truss system of the
concentric or eccentric type that is provided to resist lateral
forces.
• BUILDING FRAME SYSTEM is an essentially complete space
frame that provides support for gravity loads.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 2
General Terms
• CANTILEVERED COLUMN ELEMENT is a column
element in a lateral-force-resisting system that cantilevers
from a fixed base and has minimal moment capacity at the
top, with lateral forces applied essentially at the top.
• COLLECTOR is a member or element provided to transfer
lateral forces from a portion of a structure to vertical
elements of the lateral-force-resisting system.
• COMPONENT is a part or element of an architectural,
electrical, mechanical or structural system.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 3
General Terms
• DESIGN BASIS GROUND MOTION is that ground motion
that has a 10 percent chance of being exceeded in 50
years as determined by a site-specific hazard analysis or
may be determined from a hazard map. A suite of ground
motion time histories with dynamic properties
representative of the site characteristics shall be used to
represent this ground motion. The dynamic effects of the
Design Basis Ground Motion may be represented by the
Design Response Spectrum.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 4
General Terms
• DIAPHRAGM is a horizontal or nearly horizontal system acting to
transmit lateral forces to the vertical-resisting elements. The term
“diaphragm” includes horizontal bracing systems.
• LATERAL-FORCE-RESISTING SYSTEM is that part of the structural
system designed to resist the Design Seismic Forces.
• MOMENT-RESISTING FRAME is a frame in which members and joints
are capable of resisting forces primarily by flexure.
• MOMENT-RESISTING WALL FRAME (MRWF) is a masonry wall
frame especially detailed to provide ductile behavior and designed in
conformance with Section 2108.2.5.
• ORDINARY BRACED FRAME (OBF) is a steel-braced frame designed
in accordance With the provisions of Section 2-9
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 5
General Terms
STORY is the space between levels. Story x is the story below Level x.
STORY DRIFT is the lateral displacement of one level relative to the level
above or below.
STORY DRIFT RATIO is the story drift divided by the story height.
STORY SHEAR, is the summation of design lateral forces above the story
under consideration.
STRENGTH is the capacity of an element or a member to resist factored
load as specified in Chapters 16, 18, 19, 21 and 22.
STRUCTURE is an assemblage of framing members designed to support
gravity loads and resist lateral forces. Structures may be categorized as
building structures or non-building structures.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 6
CRITERIA SELECTION
1629.1 Basis for Design
The procedures and the limitations for the design of structures
shall be determined considering
1) seismic zoning
2) site characteristics
3) occupancy configuration,
4) structural system and
5) height in accordance with this section
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 7
CRITERIA SELECTION
1629.1 Basis for Design (contd)
Structures shall be designed with adequate strength to
withstand the lateral displacements induced by the Design
Basis Ground Motion, considering the inelastic response of
the structure and the inherent redundancy, over-strength and
ductility of the lateral-force- resisting system.
The minimum design strength shall be based on the Design
Seismic Forces determined in accordance with the static
lateral force procedure of Section 1630, except as modified by
Section 1631.5.4.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 8
1. Occupancy Category
1629.2 Occupancy Categories.
For purposes of earthquake resistant design, each structure
shall be placed in one of the occupancy categories listed in
Table 16-K.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 9
1. Occupancy Category
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 10
2. Site Geology and Soil Chracteristics
1629.3 Site Geology and Soil Characteristics.
Each site shall be assigned a soil profile type based on
properly substantiated geotechnical data using the site
categorization procedure set forth in Division V, Section 1636
and Table 16-J.
EXCEPTION: When the soil properties are not known in sufficient detail to
determine the soil profile type, Type SD shall be used. Soil Profile Type SE
or SF need not be assumed unless the building official determines that
Type SE or SF may be present at the site.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 11
2. Site Geology and Soil Chracteristics
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 12
3. Site Seismic Hazard Characteristics and Zones
1629.4 Site Seismic Hazard Characteristics.
Seismic hazard characteristics for the site shall be established
based on the seismic zone and proximity of the site to active
seismic sources, site soil profile characteristics and the
structure’s importance factor.
1629.4.1 Seismic zone.
Each site shall be assigned a seismic zone in accordance with
Figure 16-2. Each structure shall be assigned a seismic zone
factor Z in accordance with Table 16-I.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 13
1. Occupancy Category
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 14
4. Seismic Zone factor
1629.4.2 Seismic Zone 4 near-source factor.
In Seismic Zone 4, each site shall be assigned a near-source
factor in accordance with Table 16-S and the Seismic Source
Type set forth in Table 16-U.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 15
4. Near Source Factors
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 16
5. Seismic Response Coefficients
1629.4.3 Seismic response coefficients.
Each structure shall be assigned a seismic coefficient, Ca, in
accordance with Table 16-Q and a seismic coefficient, Cv, in
accordance with Table 16-R.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 17
5. Seismic Response Coefficients
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 18
Height Limitations
1629.7 Height Limits.
Height limits for the various structural systems in Seismic
Zones 3 and 4 are given in Table 16-N.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 19
Height Limitations
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 20
Static Lateral Force Procedure
1629.8.3 Static.
The static lateral force procedure of Section 1630 may be
used for the following structures:
1. All structures, regular or irregular, in Seismic Zone 1 and in
Occupancy Categories 4 and 5 in Seismic Zone 2.
2, Regular structures under 240 feet (73 152 mm) in height
with lateral force resistance provided by systems listed in
Table 16-N, except where Section 1629.8.4, Item 4, applies.
3. Irregular structures not more than five stories or 65 feet (19
812 mm) in height.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 21
Static Lateral Force Procedure
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 22
Static Lateral Force Procedure
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 23
Static Lateral Force Procedure
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 24
Static Lateral Force Procedure
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 25
Static Lateral Force Procedure
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 26
Problem-1
Determine the UBC-97 design seismic forces for a three-story
concrete shear Wall office building. It is located in Dir District
KPK province on rock with a shear Wave velocity of 3000 ft/
sec. The story heights are 13 feet for the first floor and 11 feet
for the second and third floors. The story dead loads are 2200,
2000 and 1700 kips from the bottom up. The plan dimensions
are 180 feet by 120 feet. The Walls in the direction under
consideration are 120 feet long and are Without openings.
The shear walls do not carry vertical loads.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 27
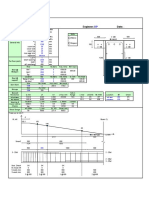
Problem-1
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 28
Problem-2
Determine the UBC-97 design seismic forces for a nine story
ductile moment resisting steel frame office building located in
Muzaffarabad on very dense soil and soft rock. The building is
located 5km from a fault capable of large magnitude
earthquakes and that has a moderate slip rate (M>7,
SR>2mm/yr). The story heights are all thirteen feet. The plan
area is 100 feet by 170 feet. The total dead load is 100
pounds per square foot at all levels. The moment frames
consist of two four bay frames in the transverse direction and
two seven bay frames in the longitudinal direction.
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 29
Problem-2
Structural Engineering (CE 401) by Dr. Muhammad Burhan Sharif 30
You might also like
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pages From Earthquake Resistant Design of StructuresDocument31 pagesPages From Earthquake Resistant Design of StructuresEJOUMALENo ratings yet
- BIS Earthquake Design Standards IndiaDocument8 pagesBIS Earthquake Design Standards IndiaVivin N VNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresFrom EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- DSS Lecture Note 4 - Lateral Loads - Seismic LoadDocument25 pagesDSS Lecture Note 4 - Lateral Loads - Seismic LoadMrSamspartNo ratings yet
- Earthquake-Resistant Structures: Design, Build, and RetrofitFrom EverandEarthquake-Resistant Structures: Design, Build, and RetrofitRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Po 11Document6 pagesPo 11Axmed ShirwacNo ratings yet
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- DINEN1998-1 - 2003 - DesignOfBuildingsDocument7 pagesDINEN1998-1 - 2003 - DesignOfBuildingsIZPNo ratings yet
- Earthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyFrom EverandEarthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics in Bulding CodesDocument63 pagesStructural Dynamics in Bulding CodesThomas ClarkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - NSCP 2015) Base Shear - Introduction-1Document14 pagesChapter 10 - NSCP 2015) Base Shear - Introduction-1ysaapparelphNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument18 pagesMethodologyfayez sadedNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Seismic Design of Nonstructural Components, Elements of Structures and Non-Building StructuresDocument5 pages3.3 Seismic Design of Nonstructural Components, Elements of Structures and Non-Building StructuresboyzesNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Intro To Earthquake Resistant StructureDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Intro To Earthquake Resistant StructureClarize MikaNo ratings yet
- How To Retrofit RCC StructureDocument25 pagesHow To Retrofit RCC StructureAmit GargNo ratings yet
- IS 1893 Part 1 2016 Criteria for Earthquake DesignDocument27 pagesIS 1893 Part 1 2016 Criteria for Earthquake DesignkapilshwetaNo ratings yet
- Building IrregularitiesDocument16 pagesBuilding Irregularitieskalpanaadhi100% (1)
- Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument21 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design of Structures: Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpurrashmi100% (1)
- Seismic Evaluation of Equipment Supporting Structures: Corresponding Author E-Mail: Burhansharif@uet - Edu.pkDocument4 pagesSeismic Evaluation of Equipment Supporting Structures: Corresponding Author E-Mail: Burhansharif@uet - Edu.pkajayg1234No ratings yet
- Comparative Study On Dynamic Analysis of Irregular Building With Shear WallsDocument9 pagesComparative Study On Dynamic Analysis of Irregular Building With Shear WallsKyle NewmanNo ratings yet
- Earth Quake Resistant Design Codal - ProvisionsIS 1893Document30 pagesEarth Quake Resistant Design Codal - ProvisionsIS 1893SudharsananPRSNo ratings yet
- ABBREVIATIONS FOR STRUCTURAL DESIGNDocument35 pagesABBREVIATIONS FOR STRUCTURAL DESIGNPrasanth Nair50% (2)
- Is 13920 1993 R 1998Document21 pagesIs 13920 1993 R 1998chawla20208819No ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document14 pagesLecture 6ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis and Design Literature ReviewDocument24 pagesStructural Analysis and Design Literature ReviewWai Yann ZawNo ratings yet
- Ojce 2016033013512711 PDFDocument7 pagesOjce 2016033013512711 PDFmehdi taheriNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of Coupled Shear WallDocument50 pagesConceptual Design of Coupled Shear WallPiyush12feb100% (1)
- Building Codes: Structural Dynamics and Seismic AnalysisDocument63 pagesBuilding Codes: Structural Dynamics and Seismic Analysiseli700No ratings yet
- NPTEL Earthquake Design Ground MotionsDocument8 pagesNPTEL Earthquake Design Ground MotionsYHTRTRNo ratings yet
- BART TunnelRequirementsDocument11 pagesBART TunnelRequirementssufiyan azharNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Frame Design PerformanceDocument14 pagesEarthquake Frame Design Performancepradeepjoshi007No ratings yet
- Design Methodology and Seismic Analysis Techniques for Earthquake EngineeringDocument22 pagesDesign Methodology and Seismic Analysis Techniques for Earthquake EngineeringSuthakar DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- Design Criteria FG x3cDocument6 pagesDesign Criteria FG x3cvigil vigilNo ratings yet
- Seismic Evaluation of Buildings & RetrofittingDocument17 pagesSeismic Evaluation of Buildings & RetrofittingHage Tajang100% (1)
- Disaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationDocument9 pagesDisaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationSujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Design of Shallow FootingDocument28 pagesDesign of Shallow FootingDeepak Singh93% (14)
- Ijret - Comparison of Percentage Steel and Concrete Quantities of A R.C Building in Different Seismic ZonesDocument11 pagesIjret - Comparison of Percentage Steel and Concrete Quantities of A R.C Building in Different Seismic ZonesInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- IRS BR CS With CommentsDocument19 pagesIRS BR CS With CommentsSiddhartha SinghNo ratings yet
- Peru's 2003 Earthquake Design StandardDocument27 pagesPeru's 2003 Earthquake Design StandardSubhadra SinghNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical design requirementsDocument9 pagesGeotechnical design requirementsMuhamad MukhrizNo ratings yet
- Load Path Connections in Wood Frame ConstructionDocument10 pagesLoad Path Connections in Wood Frame ConstructionaliomairNo ratings yet
- Is 1893 Pt3 - F CommentedDocument54 pagesIs 1893 Pt3 - F CommentedSangrah MauryaNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Project Analysis and ControlDocument30 pagesReinforcement Project Analysis and ControlFerhat YılmazNo ratings yet
- Residential Apartment Structural Design BriefDocument5 pagesResidential Apartment Structural Design Brieftaz_taz3No ratings yet
- Design Life vs. Seismic Return PeriodDocument19 pagesDesign Life vs. Seismic Return PeriodShivamMishraNo ratings yet
- Performance of Reinforced Concrete Frames Using Force and Displacement Based Seismic Assessment MethodsDocument12 pagesPerformance of Reinforced Concrete Frames Using Force and Displacement Based Seismic Assessment Methodsyasser_goldstoneNo ratings yet
- Pushover Analysis of A 19 Story Concrete Shear Wall BuildingDocument6 pagesPushover Analysis of A 19 Story Concrete Shear Wall BuildingGirish DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 2 11 1582886010 1ijcseierdapr20201Document10 pages2 11 1582886010 1ijcseierdapr20201TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design and Disaster Management FactorsDocument21 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design and Disaster Management FactorsathiraprNo ratings yet
- Design Criteria FGDocument6 pagesDesign Criteria FGvigil vigilNo ratings yet
- Design of Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument21 pagesDesign of Earthquake Resistant StructuresChandra Prakash KhatriNo ratings yet
- 1997 UNIFORM BUILDING CODE CHAPTER 16 DESIGN REQUIREMENTSDocument38 pages1997 UNIFORM BUILDING CODE CHAPTER 16 DESIGN REQUIREMENTSOscar Esquivel MarroquinNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Analysis and Design of Regular and Irregular Configuration of Multi Story Building in Various Seismic Zones and Various Type of SoilsDocument7 pagesComparison of Analysis and Design of Regular and Irregular Configuration of Multi Story Building in Various Seismic Zones and Various Type of SoilsDivya B MNo ratings yet
- Machine Fouindation 1 PDFDocument20 pagesMachine Fouindation 1 PDFjohn streetNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storied Building With Shear Walls Using ETABS-2013Document11 pagesSeismic Analysis of Multi-Storied Building With Shear Walls Using ETABS-20138790922772No ratings yet
- Dbybhy 2007 en PDFDocument161 pagesDbybhy 2007 en PDFYashu HandaNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of RC Buildings in the PhilippinesDocument12 pagesStructural Design of RC Buildings in the PhilippinesJohnson SambranoNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Code For TurkeyDocument161 pagesEarthquake Code For Turkeywpchen2No ratings yet
- Vendor Form PDFDocument2 pagesVendor Form PDFAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Vendor Form PDFDocument2 pagesVendor Form PDFAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Addendum No 1Document183 pagesAddendum No 1AdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Comp PalnDocument1 pageComp PalnAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering MSc Curricula at University of PécsDocument26 pagesStructural Engineering MSc Curricula at University of PécsAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Net SpeedDocument1 pageNet SpeedAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- 171524Document15 pages171524AdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering MSc Curricula at University of PécsDocument26 pagesStructural Engineering MSc Curricula at University of PécsAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Calculating outstanding arrears for civil servantsDocument5 pagesCalculating outstanding arrears for civil servantsAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Naveed - House PlanDocument1 pageNaveed - House PlanAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Calculating outstanding arrears for civil servantsDocument5 pagesCalculating outstanding arrears for civil servantsAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Asghar SB 2Document3 pagesAsghar SB 2AdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- CC FaqsDocument3 pagesCC FaqsAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- 2 - Sarwar SB 29x35 F.F PDFDocument1 page2 - Sarwar SB 29x35 F.F PDFAdnanRasheedNo ratings yet
- Vendor Presentation-3 (Hardware Product Portfolio) - 0801Document61 pagesVendor Presentation-3 (Hardware Product Portfolio) - 0801btsupersuper100% (1)
- Ms Orient CFBC ManualDocument148 pagesMs Orient CFBC ManualkarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Risk Management GuidelinesDocument16 pagesRisk Management GuidelinesG_RanjithNo ratings yet
- Low Pressure Steam Curing of Precast UnitsDocument4 pagesLow Pressure Steam Curing of Precast Unitsdash1991No ratings yet
- BV Rules For The Classification and The Certification of Yachts Feb 08 Edition v1Document65 pagesBV Rules For The Classification and The Certification of Yachts Feb 08 Edition v1فضيلة عبدالرحمنNo ratings yet
- Sanet - St.basics Office DesignDocument73 pagesSanet - St.basics Office Designenterlog100% (2)
- 17th CenturyDocument32 pages17th CenturyhariniNo ratings yet
- Canal Trough DesignDocument27 pagesCanal Trough DesignVenkatarathnam PulipatiNo ratings yet
- Concrete Beam DesignDocument4 pagesConcrete Beam DesignpetersiglosNo ratings yet
- Cladding Report-Version 3 (Print Out)Document31 pagesCladding Report-Version 3 (Print Out)Henry NgNo ratings yet
- PD 1096 AdditionalDocument11 pagesPD 1096 Additionalraegab100% (7)
- Design of Shear Wall: Reference DataDocument8 pagesDesign of Shear Wall: Reference DataKiranNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis 9th Edition Hibbeler Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesStructural Analysis 9th Edition Hibbeler Solutions Manualtauridoraiblins17jw100% (14)
- 009-3240-018 (39XX 51XX SAOS 6.12 SoftwareMgmtLicensing) RevADocument68 pages009-3240-018 (39XX 51XX SAOS 6.12 SoftwareMgmtLicensing) RevAReno TkNo ratings yet
- How To Convert A Project From IAR To CCS - Texas Instruments WikiDocument11 pagesHow To Convert A Project From IAR To CCS - Texas Instruments Wikiteomondo100% (1)
- Daikin UnitsDocument3 pagesDaikin UnitsEdNo ratings yet
- THERMAFLEX (Isolasi Pipa & Isolasi Ducting)Document142 pagesTHERMAFLEX (Isolasi Pipa & Isolasi Ducting)Irvika RomanaNo ratings yet
- CV Janko NikolićDocument4 pagesCV Janko NikolićJanko NikolićNo ratings yet
- Win 8 For DummiesDocument144 pagesWin 8 For DummiesVal ArtNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Computers Through GenerationsDocument21 pagesEvolution of Computers Through Generationssiva prasadNo ratings yet
- Top 160 ATM Locations in BangladeshDocument20 pagesTop 160 ATM Locations in BangladeshTanmoy HasanNo ratings yet
- Industrial air cooler VCI with capacities up to 149 kWDocument16 pagesIndustrial air cooler VCI with capacities up to 149 kWAleksandarAndric100% (1)
- Spiral Towers: Finalist Mode GakuenDocument4 pagesSpiral Towers: Finalist Mode GakuenEko Aji Prasojo SubagioNo ratings yet
- VS2005 JSharp En-Us PDFDocument6,421 pagesVS2005 JSharp En-Us PDFAlicia Mary PicconeNo ratings yet
- HSEP 13 8 A1 Fall Prevention System Requirement Rev 5Document5 pagesHSEP 13 8 A1 Fall Prevention System Requirement Rev 5mojgfdNo ratings yet
- Acer Travelmate 240/250 Series: Service GuideDocument155 pagesAcer Travelmate 240/250 Series: Service GuideVlad TnskNo ratings yet
- Drafting Module 10 Ab 2nd QDocument20 pagesDrafting Module 10 Ab 2nd QKC JaymalinNo ratings yet
- Excel Engineering College, Komarapalayam: Department of Ece Class Room Furniture Arrangement DetailsDocument4 pagesExcel Engineering College, Komarapalayam: Department of Ece Class Room Furniture Arrangement DetailsPreethi RathinamNo ratings yet
- 3D Artistry WallcoveringsDocument27 pages3D Artistry WallcoveringsAcro PaintsNo ratings yet
- HVAC System OverviewDocument150 pagesHVAC System OverviewSeth Patrick ArceoNo ratings yet