Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dezg526 Dec01 An
Uploaded by
Vignesh VenkatasubramanianOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dezg526 Dec01 An
Uploaded by
Vignesh VenkatasubramanianCopyright:
Available Formats
Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani
Work-Integrated Learning Programmes Division
First Semester 2019-2020
Comprehensive Examination
(EC-3 Make-up)
Course No. : DE ZG526
Course Title : ADVANCED COMPOSITES
Nature of Exam : Open Book
Weightage : 40% No. of Pages =2
Duration : 3 Hours No. of Questions = 10
Date of Exam : Sunday, 01/12/2019 (AN)
Note:
1. Please follow all the Instructions to Candidates given on the cover page of the answer book.
2. All parts of a question should be answered consecutively. Each answer should start from a fresh page.
3. Assumptions made if any, should be stated clearly at the beginning of your answer.
Q.1. For a continuous and oriented fiber-reinforced composite, the moduli of elasticity in the
longitudinal and transverse directions are 19.7 and 3.66 GPa respectively. If the volume
fraction of fibers is 0.25, determine the moduli of elasticity of fiber and matrix phases. [2]
Q.2. Why is the surface perfection of glass fibers so important? State two measures that are taken
to protect the surface of glass fibers? [3]
Q.3. List at least four different sports implements that are made of, or contain composites. [2]
Q.4. A rod consists of a binder and two types of filamentous reinforcement with the following
constituent properties: [6]
Material Density Wt% E (GPa) σu(GPa)
(g/cm3)
Binder 1.3 35 3.5 0.06
Fiber A 2.5 45 70 1.4
Fiber B 1.6 20 6 0.45
Assume that the cross-sectional area of the rod =10 cm2
(a) What maximum load can this rod carry without rupturing any of the constituents?
(b) What is the maximum load the rod can carry?
Q.5. Why fiber reinforcements are of a thin diameter? Cite two reasons. [2]
Q.6. The variables Ex and νxy are the elastic modulus and Poisson ratio of a [ ± 45]S laminate
obtained in an off axis coupon tension test. Show that the shear modulus GLT of the
constituent laminae is given by: [3]
Ex
GLT =
2(I + v xy )
Q.7. Explain why a high-modulus unidirectional graphite-fiber-reinforced epoxy beam fractured
in impact breaks cleanly into two halves without delamination and with little fiber pullout,
whereas an equivalent glass-fiber composite exhibits considerable delamination on failure. [3]
DE ZG526 (EC-3 Make-up) First Semester 2019-2020 Page 1 of 2
DE ZG526 (EC-3 Make-up) First Semester 2019-2020 Page 2
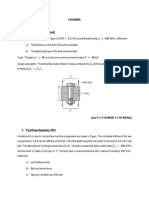
Q.8. Find the three stiffness matrices [A], [B], and [D] for a three-ply [0/30/–45] graphite/epoxy
laminate as shown in Figure below. [8]
Assume that each lamina has a thickness of 5mm. The elastic property for glass-epoxy is as
given: EL=181 GPa, ET=10.30 GPa, νLT=0.28, GLT=7.17GPa
Q.9. A glass-epoxy laminate is constructed with a stacking sequence (0/90)4S. Using the Whitney-
Nuismer-failure criteria (point stress and average stress criteria) for notched composites,
calculate the fracture-toughness-unnotched-strength ratio, KQ/σ0 for a half-crack length of
5mm. Assume that the characteristic distances are d0 = 1 mm and a0 = 4 mm for the point-
stress and average-stress criteria, respectively. [5]
Q.10. A balanced cross-ply laminate possessing midplane symmetry is made up of laminae having
the following Properties:
EL= 15 GPa, GLT = 3 GPa, ET= 6 GPa, νLT = 0.5
The laminate is subjected to a normal axial stress of 15 MPa and a shear stress of 1.0 MPa.
Calculate the normal and shear stresses in the 0° and 90° plies. [6]
***********
DE ZG526 (EC-3 Make-up) First Semester 2019-2020 Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Composites Sheet Answers PDFDocument45 pagesComposites Sheet Answers PDFEng Mahmoud Khairy78% (9)
- Buckling Analysis of Laminated Composite PlatesDocument6 pagesBuckling Analysis of Laminated Composite PlatespdhurveyNo ratings yet
- Design of Column and Lacings for Axial and Bending LoadsDocument160 pagesDesign of Column and Lacings for Axial and Bending LoadsVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics ExercisesDocument33 pagesFracture Mechanics Exercises2luckystar100% (1)
- Complete RCC Design Very ImportantDocument41 pagesComplete RCC Design Very ImportantAmal PremachandranNo ratings yet
- Complete RCC Design Very ImportantDocument41 pagesComplete RCC Design Very ImportantAmal PremachandranNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Soil Liquefaction Engineering: A Unified and Consistent FrameworkDocument72 pagesRecent Advances in Soil Liquefaction Engineering: A Unified and Consistent FrameworkFederico Piccoli100% (1)
- Eccentric FootingDocument15 pagesEccentric FootingChandra Sekhar TalasilaNo ratings yet
- ENG - Workshop 01 - Transfer Chute - v41Document68 pagesENG - Workshop 01 - Transfer Chute - v41Vignesh Venkatasubramanian100% (1)
- Steel Beam DesignDocument27 pagesSteel Beam DesignSyazwi Akram Ab RazakNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument63 pagesIlovepdf MergedVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Sandwich Structures - An Overeview 7 Dec, RPT DeptDocument76 pagesSandwich Structures - An Overeview 7 Dec, RPT DeptRakesh BabuNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR ENGINEERING MATERIALS IDocument43 pagesSOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR ENGINEERING MATERIALS ISadiq Omar100% (1)
- Lecture5 AllDocument43 pagesLecture5 Alladeelyj100% (1)
- Is 14268 - 2022-1Document16 pagesIs 14268 - 2022-1Ramudu Kodur100% (18)
- IMPORT COMPOSITE SECTION FROM SECTION WIZARDDocument15 pagesIMPORT COMPOSITE SECTION FROM SECTION WIZARDS Abbas Ahmed0% (1)
- Synthesis, Characterization and Properties of The New Unsaturated Polyester Resins For Composite ApplicationsDocument39 pagesSynthesis, Characterization and Properties of The New Unsaturated Polyester Resins For Composite Applicationsdinahrakhim100% (4)
- Load Transfer From Matrix To FiberDocument10 pagesLoad Transfer From Matrix To FiberNisha RaniNo ratings yet
- 4.de ZG526 Ec-2r First Sem 2022-2023Document1 page4.de ZG526 Ec-2r First Sem 2022-2023aaquibkhanNo ratings yet
- 1.ae ZG614 Ec-3r First Sem 2022-2023 PDFDocument3 pages1.ae ZG614 Ec-3r First Sem 2022-2023 PDFaaquibkhanNo ratings yet
- X86910 (ST5006)Document2 pagesX86910 (ST5006)Kazi Tour DépenseNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials (Collection of Previous Final Exam) 110863Document8 pagesComposite Materials (Collection of Previous Final Exam) 110863habba3No ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics Exercises for Linear-Elastic and Elastic-Plastic BehaviorDocument10 pagesFracture Mechanics Exercises for Linear-Elastic and Elastic-Plastic BehaviorChuoiEmNo ratings yet
- DE5302 Strength of Materials. Semester 1, 2018 Exam and FormulaeDocument15 pagesDE5302 Strength of Materials. Semester 1, 2018 Exam and FormulaeGopal KrishanNo ratings yet
- DE ZG513 Finite Element MethodDocument3 pagesDE ZG513 Finite Element MethodinderNo ratings yet
- Enggzc232 Sep29 FNDocument2 pagesEnggzc232 Sep29 FNkasimNo ratings yet
- Department of Aeronautical Engineering: Answer All The Questions: Part - A (10 X 2 20 MARKS)Document2 pagesDepartment of Aeronautical Engineering: Answer All The Questions: Part - A (10 X 2 20 MARKS)RajakumariNo ratings yet
- 4.de ZG526 Ec-3r First Sem 2022-2023Document2 pages4.de ZG526 Ec-3r First Sem 2022-2023aaquibkhanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper CodeDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Codeeugin cebertNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials Properties Expressions ApplicationsDocument3 pagesComposite Materials Properties Expressions Applicationsandrw1987No ratings yet
- FLT-1 Paper-1 Question+SolutionDocument58 pagesFLT-1 Paper-1 Question+SolutionSHIVAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Dezg513 Mar09 FN PDFDocument1 pageDezg513 Mar09 FN PDFmishtinilNo ratings yet
- PMMD Mid Sem 2019-2020Document2 pagesPMMD Mid Sem 2019-20202019ht80591No ratings yet
- Academic Year 2018/19 ENG762s2 Advanced Materials: Online Second Attempt CourseworkDocument4 pagesAcademic Year 2018/19 ENG762s2 Advanced Materials: Online Second Attempt Courseworkexpert 60No ratings yet
- Midterm - S1 2018 2019 - MidtermDocument8 pagesMidterm - S1 2018 2019 - MidtermarifNo ratings yet
- Efa PaperDocument9 pagesEfa Paperyash guptaNo ratings yet
- GP208 HW2 Composition Elasticity and DuctilityDocument4 pagesGP208 HW2 Composition Elasticity and DuctilitySofiaNo ratings yet
- III Design of Steel Structures Unit 2Document72 pagesIII Design of Steel Structures Unit 2VikrantNo ratings yet
- 53106-mt - Mechanics of Composite MaterialsDocument2 pages53106-mt - Mechanics of Composite MaterialsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Problems in Compos Mater Questions PG PDFDocument15 pagesProblems in Compos Mater Questions PG PDFJimmyFigueroaANo ratings yet
- Tutorial Fastener Sesi Mac 2019Document4 pagesTutorial Fastener Sesi Mac 2019Faris DanialNo ratings yet
- 2011-12-07 APSC278 Final ExamDocument7 pages2011-12-07 APSC278 Final ExamNik AgarwalNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AE, MSNT)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- ABD Matrix of Single-Ply Triaxial Weave Fabric Composites: A.B.H. Kueh and S. PellegrinoDocument17 pagesABD Matrix of Single-Ply Triaxial Weave Fabric Composites: A.B.H. Kueh and S. PellegrinoVishnu Chemmanadu AravindNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation & Numerical Analysis of Composite Leaf SpringDocument6 pagesExperimental Investigation & Numerical Analysis of Composite Leaf SpringÑõmý ÅwăņNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Fastener Sesi Mac 2020Document4 pagesTutorial Fastener Sesi Mac 2020ilya danisyahNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 With SolutionsDocument3 pagesHomework 3 With SolutionsDaniel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials Question Paper 2017Document2 pagesComposite Materials Question Paper 2017SureshBabu MaramNo ratings yet
- II Biaxial LoadDocument7 pagesII Biaxial LoadNandit JadvaniNo ratings yet
- Numetrical Study On Carbon Fibre Pullout Using A Cohesive Zone ModelDocument6 pagesNumetrical Study On Carbon Fibre Pullout Using A Cohesive Zone ModelPandi IitmNo ratings yet
- Composites Part A: Wu Zhou, Tony Wente, Dahsin Liu, Xinyu Mao, Danielle Zeng, Homa Torab, Jeff Dahl, Xinran XiaoDocument11 pagesComposites Part A: Wu Zhou, Tony Wente, Dahsin Liu, Xinyu Mao, Danielle Zeng, Homa Torab, Jeff Dahl, Xinran XiaoKahar UnhaluNo ratings yet
- Yoon Et Al. - 2007 - Effects of Adhesive Joint On The Failure StrengthDocument6 pagesYoon Et Al. - 2007 - Effects of Adhesive Joint On The Failure StrengthHenrique QueirozNo ratings yet
- hossain2016Document4 pageshossain2016Beurus SamaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study On Carbon Fibre Pullout Ising A Cohesive Zone ModelDocument6 pagesNumerical Study On Carbon Fibre Pullout Ising A Cohesive Zone ModelRabee ShammasNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 6th Edition Groover Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 6th Edition Groover Solutions Manualduongnujl33q100% (31)
- Ansys 6Document10 pagesAnsys 6د. ثائر جبار نتيشNo ratings yet
- 17 1999Ply drops composites part BDocument12 pages17 1999Ply drops composites part BsergioNo ratings yet
- 2019 Winter DSS 5G - M - 17505 - CEDocument29 pages2019 Winter DSS 5G - M - 17505 - CESidd SuryaNo ratings yet
- EGR 2208 Assignment 3 - Composite Materials CalculationsDocument2 pagesEGR 2208 Assignment 3 - Composite Materials CalculationsIhsan Samoh เพี่อนดีดีNo ratings yet
- AE8603 Composite Materials and StructuresDocument3 pagesAE8603 Composite Materials and StructuresmuthugpalavesaNo ratings yet
- QP EVL561 Dec2020Document2 pagesQP EVL561 Dec2020akash rawatNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials ExamDocument7 pagesEngineering Materials ExamMoses Daniels-OsasNo ratings yet
- Theotoglou Main PDFDocument8 pagesTheotoglou Main PDFHako KhechaiNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Spring Session 2010: Universityy Western SydneyDocument48 pagesFinal Examination Spring Session 2010: Universityy Western SydneykakaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter6Document29 pages11 Chapter6SuneethaNo ratings yet
- 3D Woven Composites' Enhanced Interlaminar PropertiesDocument8 pages3D Woven Composites' Enhanced Interlaminar PropertiesGowthaman SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Failure ModeDocument9 pagesFailure ModealfborbrNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Modeling For Delamination Analysis of Double Cantilever Beam SpecimenDocument7 pagesFinite Element Modeling For Delamination Analysis of Double Cantilever Beam SpecimendeepakmitrNo ratings yet
- Eg2010 2021 SP2Document8 pagesEg2010 2021 SP2Edwin JomonNo ratings yet
- 61 Ijmperdaug201961Document6 pages61 Ijmperdaug201961TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- A DSM Wall For Excavation SupportDocument14 pagesA DSM Wall For Excavation SupportmarmeiraisNo ratings yet
- Ishihara1985 01 Ishihara-0007Document57 pagesIshihara1985 01 Ishihara-0007Mario Antonio Navarro TejadaNo ratings yet
- Conveyor Gallries - MMDocument40 pagesConveyor Gallries - MMVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- 905 025 2 AnchorDocument24 pages905 025 2 AnchorAndrés Esteban Garzón RamírezNo ratings yet
- 905 019 02 DruckDocument52 pages905 019 02 DruckVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Excavation Support For TBM Retrieval Shaft Using Deep Soil Mixing Technique, Kuala LumpurDocument7 pagesExcavation Support For TBM Retrieval Shaft Using Deep Soil Mixing Technique, Kuala LumpurVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Design of Isolated RCC FootingDocument26 pagesDesign of Isolated RCC Footingshah younisNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument101 pagesIlovepdf MergedVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Sensors 21 04868 v2Document20 pagesSensors 21 04868 v2Vignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- LSD Doubly Reinforced Simple Supported Beam-BestDocument12 pagesLSD Doubly Reinforced Simple Supported Beam-BestVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission: Group-V.A ServicesDocument26 pagesTamil Nadu Public Service Commission: Group-V.A ServicesVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Gratings CatalogDocument33 pagesGratings CatalogLupul50No ratings yet
- CPS Idler DCI - 01.08.17Document5 pagesCPS Idler DCI - 01.08.17Vignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- HFSHS Secpropsdimsprops BS5950 UK 12 - 22 - 2017Document20 pagesHFSHS Secpropsdimsprops BS5950 UK 12 - 22 - 2017Vignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Staad Analysis & Load Data Calculation of Pulley FramesDocument19 pagesStaad Analysis & Load Data Calculation of Pulley FramesVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- CPS Idler DCI - 01.08.17Document5 pagesCPS Idler DCI - 01.08.17Vignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- ChangedDocument23 pagesChangedVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Problem: Process For Changing STAAD Database For Tata Structura - Steel Hollow SectionsDocument10 pagesProblem: Process For Changing STAAD Database For Tata Structura - Steel Hollow SectionsVignesh VenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Stochastic Damage Evolution and Failure in Fiber-Reinforced CompositesDocument91 pagesStochastic Damage Evolution and Failure in Fiber-Reinforced CompositesDavid AcostaNo ratings yet
- D 5448 - D 5448M - 93 R00 Rdu0ndgvrdu0ndhnDocument12 pagesD 5448 - D 5448M - 93 R00 Rdu0ndgvrdu0ndhnlucasNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Types of Composite MaterialsDocument42 pagesFabrication and Types of Composite MaterialsAmmar SafwtNo ratings yet
- A Fundamental Review On Composite Materials and Some of Their Applications in Biomedical EngineeringDocument13 pagesA Fundamental Review On Composite Materials and Some of Their Applications in Biomedical EngineeringAndreza SousaNo ratings yet
- COMPOSITE MATERIALS Unit - 1 and 2 MCQ QuestionDocument16 pagesCOMPOSITE MATERIALS Unit - 1 and 2 MCQ QuestionDURLAB DASNo ratings yet
- Natural Fibers Plastics and Composites 2004 PDFDocument368 pagesNatural Fibers Plastics and Composites 2004 PDFMaria Inês Vasconcellos FurtadoNo ratings yet
- Design EngineeringDocument11 pagesDesign EngineeringzainabNo ratings yet
- Lectures 1 CompositeDocument4 pagesLectures 1 CompositeMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledLuigi BortolottiNo ratings yet
- Banthia - Fibre-Reinforced ConcreteDocument29 pagesBanthia - Fibre-Reinforced ConcretesthakshyNo ratings yet
- Development and Characterization of Sisal Fiber and Wood Dust Reinforced Polymeric CompositesDocument11 pagesDevelopment and Characterization of Sisal Fiber and Wood Dust Reinforced Polymeric CompositesGosa GutaNo ratings yet
- Surface Treatments of Plant Fibers and Their Effects On Mechanical Properties of Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A ReviewDocument16 pagesSurface Treatments of Plant Fibers and Their Effects On Mechanical Properties of Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Reviewmkumar_234155No ratings yet
- BEM IntroductionDocument46 pagesBEM Introductionkaiser tsarNo ratings yet
- Common failure mechanisms in non-metallic materials explainedDocument4 pagesCommon failure mechanisms in non-metallic materials explainedYousuf MemonNo ratings yet
- Jsce Recommendations For Upgrading of Concrete Structures With Use of Continuous Fiber SheetsDocument91 pagesJsce Recommendations For Upgrading of Concrete Structures With Use of Continuous Fiber SheetsgedikoNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering Sample QuestionsSyed Ali Jawad AbidiNo ratings yet
- Composites NotesDocument42 pagesComposites NotesNehemiah LemombianNo ratings yet
- Sheet3 - Composites - Fiber ReinforcedDocument3 pagesSheet3 - Composites - Fiber ReinforcedAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- HW1 SolutionDocument8 pagesHW1 Solutionblakk archimedesNo ratings yet
- Jute Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive ReviewDocument21 pagesJute Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive ReviewbiniyamNo ratings yet
- 2003 Reliability of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Laminate PlatesDocument19 pages2003 Reliability of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Laminate Platesdhiraj.biswasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16: Composites: Issues To Address..Document27 pagesChapter 16: Composites: Issues To Address..Navish KotwalNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Fiber Reinforced CompositesDocument34 pagesAnalyzing Fiber Reinforced CompositesGovind sharmaNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Standard Built-In User Subroutines For LaRC05 Composite Failure CriteriaDocument5 pagesAbaqus Standard Built-In User Subroutines For LaRC05 Composite Failure Criteriajunjie yi100% (1)
- Title Defense InvitationDocument10 pagesTitle Defense InvitationnhieldazaNo ratings yet
- Progressive Failure Analysis of Fiber-Reinforced Laminated CompositesDocument17 pagesProgressive Failure Analysis of Fiber-Reinforced Laminated Compositesjunjie yiNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Green Compression and Shear Strength in Green Sand Mould Using Ant Hill ClayDocument43 pagesOptimization of Green Compression and Shear Strength in Green Sand Mould Using Ant Hill ClaySeçmeli DerslerNo ratings yet