0% found this document useful (0 votes)
355 views1 pageLocal Buckling Analysis of Compression Plates
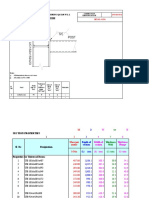
This document analyzes the local and global buckling capacity of a double angle steel compression member with given dimensions and material properties. It is determined that:
1) The member meets the criteria for local buckling based on its plate slenderness ratios.
2) The member will buckle inelasticially along its longer axis based on a calculation of its kL/r limits.
3) The member's critical buckling strength is calculated to be 26,962 lbs and its design strength considering member dimensions and a strength reduction factor is 281,484 lbs.
Uploaded by
Joseph BundalianCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
355 views1 pageLocal Buckling Analysis of Compression Plates
This document analyzes the local and global buckling capacity of a double angle steel compression member with given dimensions and material properties. It is determined that:
1) The member meets the criteria for local buckling based on its plate slenderness ratios.
2) The member will buckle inelasticially along its longer axis based on a calculation of its kL/r limits.
3) The member's critical buckling strength is calculated to be 26,962 lbs and its design strength considering member dimensions and a strength reduction factor is 281,484 lbs.
Uploaded by
Joseph BundalianCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd