Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homework Api 653 Module 4 Study Aid
Uploaded by
Pradeep Kumar Bowmaraju0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views29 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views29 pagesHomework Api 653 Module 4 Study Aid
Uploaded by
Pradeep Kumar BowmarajuCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 29
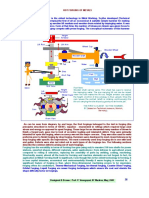
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
This following is a study aid that you can use to learn the details andl content of API 651 Cathodic Protection. There
will be about 4-8 questions from this publication on the APL exam. We do not spend much time in class discussing this
publication, so itis important that you become familiar wich this consent in your personal study sessions
‘The questions in this study aid are in she same order as APL asthe publication. It’s helpful to read a few pages of API
651 and then answer the questions associated with these pages. We suggest that you do this study aid at least ice
prior othe APL exam. The answers are provided at the end of this Study Ai.
Note! Only Sections 1-6,8 & I are included in the Body of Knowledge. There should be no questions from Sections 7-
9& 10,
Background Information: Onc of the greatest discoveries of all ime was made by a physicist named Volta
He discovered that corrosion actually creates electrical current flow! A battery is a corrosion cell! In a
corrosion cell a small voltage occurs between what is called the anode and cathode. ‘The anode is the negative
pole of the battery and the cathode is the positive pole, ‘The anode in a corrosion cell corrodes. ‘The cathode
does not corrode and is actually protected from corrosion, As corrosion occurs electrical current is generated.
The higher the current flow, the faster the corrosion, What causes current flow? Two factors, the fist is
VOLTAGE (in API.651 this is often called the “electrical potential”). The higher the voltage between the
‘anode and cathode, the greater the current flow, and the fastér the corrosion. ‘The second factor is
RESISTANCE, On a tank floor this is the resistance of the soil between the anode and cathode. Since
resistance reduces flow, the higher the resistance, the lower the current flow and the slower the corrosion.
Its important to understand the different causes of electrical potential (voltage) and factors that affect
resistance.
1, Cottosion of steel structures is a(n):
a. abrading process.
b. electrochemical process.
rare occurrence,
4. uniform process.
2. In order for a corrosion cell to occur, areas of with different:
a. crystalline structures must exist.
b. electric potentials must exist.
©. hardness must exist.
materials must exist
3. Which of the following is not a component of a corrosion cell?
a. Anode
b. Electrode
c. Metallic path
d. Cathode
Module 4 ~ API 651 1 MSTS
10.
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
In a corrosion cell, where does the corrosion occur’?
actually being protected
In a corrosion cell, where does the corrosion not occur? This,
from corrosion!
‘What chemical reaction happens at an anode?
a Fe > Fet2 +2c-
b. 0)-+2H:0 + 4e—> 40H
c. 2Fe +O;—> 2FeO
d. OH’ +H — H;,0
a. Fe —>Fet2 +2e-
b. 0) + 2H,O + 4e°—> 40H
ce. 2Fe +O)—> 2FeO
da OH +H—> HO
Moist soil under a tank floor is what part of a corrosion cell?
a. Anode,
b. Cathode.
ce. Electrolyte.
Metallic path.
What is a common electrolyte on the inside of the tank?
Tank floor
Floor lining
¢. Hydrocarbons
d. Water and sludge
ce
How does uniform corrosion occur?
a. Large anodes
b. Large cathodes
c. High electrical potential
d. Thousands of microscopic corrosion cells
Module 4 — API 651 2 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
12,
13.
14,
15.
16.
When corrosion cells are larger, the type of degradation that can occur is:
a, cracks.
b. large LTA’s,
c pits.
uniform
A tank floor is made of carbon steel components. Electrical potential (voltage) can be
created within the carbon steel by:
a. uneven distribution of elements within the metal’s structure.
b. using materials of different thickness.
€. having salt in sand pad.
4, having moisture in contact with the steel.
A tank floor is made of carbon steel components, Electrical potential (voltage) can be
created because of differences between the:
a. tank floor and the soil.
b. tank floor and stored product.
©. soil and stored product
d. weld metal and parent material.
When a tank floor is in contact with a piece of clay, what causes soil-side tank floor
corrosion’
a. The clay pH is higher than rest of sand pad
b. Clay isa corrosion material
c. The soil resistivity range for clay is low
d. The oxygen concentration is lower under the clay ball than other parts of tank
On a tank floor, areas with lower oxygen concentrations become __ and
areas with higher oxygen concentrations become
‘What causes the electrical potential for galvanic corrosion?
a. Different metals
b. Different thicknesses.
©. Different temperatures
4. Different pad properties
Module 4— API 651 3 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
17.
20,
2.
22.
Which of the following is not a significant factor of galvanic corrosion?
Stray AC currents,
Relative areas of
Temperature
Position of materials in galvanic
athode & anode
ries
Galvanie corrosion can occur when an underground stainless stee! pipe is connected to a
carbon steel tank shell nozzle. Where is this corrosion most likely to occur?
8. The underground portion of the stainless steel pipe
b. The portion of the tank bottom nearest the pipe
¢. The carbon steel nozzle at the contact point with pipe (flange face)
d, The stainless steel pipe at contact point with nozzle (flange face)
Galvanic corrosion will be more severe when the:
a, anode is small and the cathode is large.
b. anode is large and the cathode is small.
c. anode and the cathode are both large.
anode and the cathode are both small.
Galvanic corrosion will be more severe when the:
a. soil resistance is high.
b. anode is large relatively to the size of the cathode,
cc. two metals are close in the galvanic series.
4. two metals are far apart in the galvanic series.
Hydrocarbons inside tanks are normally:
a. not corrosive.
b. mildly corrosive.
cc, moderately corrosive.
d. very corrosive.
Internal corrosion of a tank in hydrocarbon service is normally the result of:
type of hydrocarbon stored,
b. the type of pad the tank sits on.
a water and sediment.
d. operating temperature.
Module 4— API 651 4 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
24,
25.
26.
2:
28.
Module 4 — API 651 5
Which of the following is not a potential problem with secondary containment?
a. May trap corrosive liquids
b. Increases the difficulty of performing cathodic protection surveys.
©. Prevent flow of electrical current of cathodic protection system.
4. Cannot use a cathodic protection system with a deep ground-bed.
As soil resistivity inereases the:
cathodic protection is easier to achieve.
stray currents become an increasing concern.
the potential for corrosion decreases
the potential for corrosion increases.
eese
a. very corrosive.
b. — cortosive.
¢, moderately corrosive,
|. mildly corrosive.
€. progressively less corrosive.
very corrosive.
corrosive.
moderately corrosive.
mildly corrosive.
progressively less corrosive.
paose
Which of the following is not a recommendation for reducing bottom-side corrosion on a
tank floor?
a Pad material should be of high resistance materials
b, Pad particles should be small and uniform
¢, Tank floor should be elevated to allow for drainage
4, Install a liner on the top-side of tank floor
Which of the following will cause increased bottom-side corrosion?
a, Small vs. large pad particles
b. Thick vs. thin pad
c. Salt in the pad
Zine in the pad
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
29,
30.
31
32,
33.
34,
35.
In coastal areas, a very important factor in tank bottom corrosion is:
salt spray.
the potential for oil spills.
high humidity.
the potential for marshy soils.
esse
The sand pad should be free of
Clean sand should be used in the pad. Washing sand with municipal water may not be
acceptable because of:
chlorides in the water
sulfides in the water.
amount of water needed.
amount of time needed to dry the sand.
aes
ASME 36.10.
ASME 447,23
ASTM C778
ASTM D 2201
ASTM G57.
ASTM R46
NACE 89-37
NACE 98-233
‘The corrosion rate of the tank floor increases when the soil pH is:
a less than 5.0.
b. greater than 5.0.
cc. less than 8.0.
d. greater than 8.0.
‘The corrosion rate of the tank floor decreases when the soil pH is:
a. ess than 5.0,
b. greater than 5.0.
c. less than 8.0.
greater than 8.0.
Module 4 ~ API 651 6 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
36.
38,
39,
40.
4L
a ASTMGS1.
b. ASTM R46
c. NACE 89-37
d NACE 98-233
Pitting corrosion on steel begins to occur when the chloride levels reach:
a 10 ppm.
b. 50 ppm.
€. 100 ppm.
500 ppm.
A tank has been operating at 100°F. ‘The tank temperature is raised to 118 °F. The
corrosion rate on the bottom-side of the tank will probably:
stay the same,
decrease by 10%
decrease by about half.
increase by 10%.
double.
peer
Release prevention barriers:
are always a non-metallic membrane,
b. may cause accelerated bottom-side corrosion.
¢. always enhance the cathodic protection system.
. are designed to NACE standards.
A Galvanic CP system:
a, must have an anode which is electrically connected to the tank.
must have a rectifier specifically designed for the system.
has an anode containing metals materials that are less active than the tank
materials,
is most often used on large-diameter tanks.
Which of the following is an advantage of a galvanic CP system?
Itis a practical system for tanks of all sizes
Current output is high
Maintenance costs are minimal
Works well in soils with high resistivity
pegs
Module 4 — API 651 7 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
42. Sacrificial anodes are normally made of:
lead and zinc
magnesium and zine
copper and stainless steel.
copper and lead.
ae oP
43, Galvanic CP systems are normally limited to tanks less than:
a. 20 feet in diameter:
b. 30 feet in diameter.
60 feet in diameter.
100 feet in diameter.
<4, Shin tei i Ef GomBde When eonned Yo clean carbon sea?
a Cast iron
b. Copper
ce Pure aluminum:
d. Zine
eee
a Carbon
b. Cast iron
c. Clean carbon steel
d. Rusty steel
46. Which of the following is an advantage of an impressed current CP system?
Practical system for tanks of all sizes
Safety aspects are minimized
Maintenance costs are minimal
Requires infrequent monitoring
47. A rectifier on an impressed current CP system:
8. provides a place to test the driving potential of tank to tank pad.
b. eliminates stray currents.
¢. changes eleetrical altemating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
4d. isclectrical connected to the tank grounding system
Module 4 ~ API 651 8 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
48.
49.
51
52.
An old tank bottom has failed. A new bottom is placed 4” above the old bottom. A new
impressed-current CP system is added to the tank. This tank may experience:
a accelerated corrosion on the old bottom.
b. accelerated corrosion on the new bottom.
€. accelerated product side corrosion.
4. accelerated corrosion on the bottom shell course.
For an impressed current CP system, the generally accepted current density is:
0.85 t0 0.100 volts per square foot
110 or 220 volts per tank,
1 {0 2 milliamps per square foot.
100 to 200 milliamps per diameter foot
nese
For an impressed current CP system on a tank operating at elevated temperatures, the
generally accepted current density is:
0,85 60.100 volts per square foot
b. 0.5 or 2.2 volts per square foot.
c, 1 to 2 milliamps per square foot.
d. 2 to 8 milliamps per square foot.
A successful operating CP system should have a negative (cathodic) potential of at least
a. 850 mVolts.
b. 1225 mVolts.
ce. 2000 mVolts.
4. 3500 mVolts.
An impressed current cathodic protection system was sized for a specific tank in a tank
farm. At first inspection it was determined that the corrosion rate was extremely high,
What is a likely cause?
a. Leads on the rectifier are reversed
b, Adjacent tank has become cathode
c. Stray alternating currents
d. Soil resistance is higher than expected
Module 4 — API 651 9 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
53. An impressed current CP system on a tank has failed. What is a possible cause?
a, The tank reference cell has become disbonded,
b. The wire connecting the rectifier to the tank had a hole in the insulation.
¢. The wire connecting the rectifier to the anode had a hole in the insulation.
d. The sacrificial anode is expended.
54, Impressed current sources should be checked to ensure they are operating at least every:
a. week.
b.-2months,
c. 6 months.
d. year
55. Impressed current sources should be inspected every:
a, months.
Db. 6 months.
ec. year.
d. every 2 years.
56. The effectiveness of a CP should be checked with cathodic protection surveys that are
performed every:
a. 2months.
b. 6 months.
c year,
dS years
Module 4 ~ API 651 10 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 651
Homework - Answer Key
is 4.11 a: a
2 ob 4.11 38. ¢
ay tb 4.11 39. b
4. Anode 4.1.La 40. a
5. Cathode 4.1.1.6 41 ce 6.2.2
(tS 4.1..a 42 b 6.2.1
2 ob 4.1.1. Bc 6.2.1
2 © 4.1.1. 44d Table 2
9 a 4.1.1. 45. Table 2
10. 4.1.2 46. a 6.3.2
i 4.1.2 47, 6.3.4
ott 413 48. b 7.24.3 Outside BOK
Bd 4.13 49. 7.3.5.2.2.1 Outside BOK
Mod 4.14 50. d 73.5.2.2.1 Outside BOK
15. Anodic 414 5a 8.2.2.1
Cathodic 52a 93.4.3 Outside BOK
16. a 42.2 53, 9.3.5.1 Outside BOK
Te Hal 42.2 54. 11.3.2.2
18. b 42.2 55. 113.23
1. a 42.2 56. ¢ 113.12
20. d 42.2
2a 5.13
2. 5.13
23. b 5.14
24. Table |
25. b Table |
26. Table |
2. od 53.11
2. 5.3.1.4
29. a
30. debris
3h
32.
33. a
34.
35. d
36. a
Module 4 — API 651 u
O
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
This following is a study aid that you can use to learn the details and content of API 652 Tank Linings, There will be
about 4-6 questions from this publication on the API exam. We do not spend much time in class discussing this
publication, so it is important that you become familiar with this content in your personal study sessions:
The questions in this study aid are in the same order as APL as the publication. It’s helpful to read afew pages of API
652 and then ansiver the questions associated with these pages. We suggest that you do this study aid at least twice
prior to the APL exam. The answers are provided at the end ofthis Study Aid.
1. A discontinuity in a coating that exposes the metal to the surface is called a:
a. blister.
b. holiday.
¢. rounded indication.
dvoid.
2. A thin-film Lining is defined in API 652 as one that is less than:
a -20mils
b.30mils
© SOmils.
80 mils,
3. Which of the following is the primary cause of product-side corrosion on a tank floor?
a. Deposits that settle to the tank bottom.
b. Flexing of the tank bottom breaks the natural protective coating
c. Stray CP currents
d. Water that settles to the bottom of the tank
4, Which of the following is not a common way for water to enter a tank?
a “Breathing” of the tank
b. Bypass the seals
©. Capillary action through holes in bottom
4. Enters with produet
5, Added to water, which of the following makes a strong electrolyte?
a, Bromides and sulfides
b. Chlorides and sat.
ce Chlorides and sulfides.
d. Sulfides and salt.
e. Salt & pepper
Module 4 ~ API 652 1 MSTS
6.
10.
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
What is a primary cause of concentration cell corrosion?
a. Anarea that creates a lower concentration of oxygen
b. — Amarea that creates a higher concentration of oxygen
c. Amarea that creates a lower concentration of nitrogen
d. — Amarea that creates a higher concentration of nitrogen
Concentration cell corrosion occurs it
primary area of concer?
specific areas, Which of the following is not a
a In crevices
b. Under deposits
At bulges
d. Under mill seale
Concentration cell corrosion can cause pitting on bare steel at a rate as high as:
20 mils per year.
b. 35 mils per year.
c. 50 mils per year.
80 mils per year.
Describe the corrosion that can occur to a tank bottom because a bottom plate has both
mill scale and bare base metal
a. Galvanic corrosion with the mill scale being anodic
b. Galvanic corrosion with the bare metal being anodic
c. Galvanic corrosion with the bare metal and mill scale both being cathodic
d. Micro bacteria corrosion
‘The large difference in the microstructure between the base and weld metals can create:
concentration cell,
a galvanic couple.
an area that has very high toughness.
a likely spot for micro bacteria corrosion
Sulfate-reducing bacteria can cause corrosion in steel by:
a. actually “eating” the steel.
b. creating a bacterial deposit that creates a concentration cel
©. creating an iron sulfide deposit that is cathodic to bare steel,
d. creating a bacterial deposit that creates a concentration cell and creating an iron
sulfide deposit that is cathodic to bare steel.
Module 4 — API 652 2 MsTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
12. Which area of the tank is most likely to experience fretting-related corrosion?
Critical zone
Nozzle
Roof plate
Striker plates
aese
13, What basically happens during fretting-related corrosi
Lower oxygen concentrations causes a corrosion cell
Moving particles remove steel
Repeat contacts between {wo parts removes protective layer of rust
Contact of two different materials causes a corrosion cell
eege
14. Which of the following is of a primary factor in shortening the life of a tank lining?
Failure by operations to drain water from tank
Flexing of tank bottom
Making significant changes in the tank product
Increasing the operation temperature
Inadequate surface preparation prior to coating installation
saece
15, Flexing of a tank floor is primarily caused by:
filling and empting the tank.
changing the product's specific gravity.
edge settlement.
any type of settlement,
eose
16. Thick-film linings are defined as linings that:
a. are greater than or equal to LO mils thick.
b, are greater than or equal to 20 mils thick.
©, are greater than or equall to 50 mils thick:
d. use reinforcement (e.g. fibers, glass cloth).
17. A lining is installed on a new tank bottom, Which of the following linings is probably
installed?
Thin-film lining without reinforcement
‘Thin-film lining with reinforcement
Thick-film lining without reinforcement
‘Thick-film lining with reinforcement
Module 4 — API 652 3 MSTS
18,
20.
21.
22.
23.
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
A lining is installed on a tank bottom with deep pits. Which of the following linings is,
probably installed?
Thin film lining without reinforcement
Thin film lining with reinforcement
‘Thick film lining without reinforcement
Thick film lining with reinforcement
nese
|
Coal tar epoxy
Epoxy phenolic/amine
c. _Isophthalic polyester
4. Vinyl ester
Coal tar epoxy
Epoxy phenolic/amine
Isophthalic polyester
Vinyl ester
aege
According to API 652, a properly applied lining may provide:
LO or more years of life.
b. 15 or more years of life.
20 or more years of life.
d. 30 or more years of life.
©. 100 or more years of life, and 1 also believe in the Easter Bunny!
Which of following is not a primary cause of lining failure?
An increase in temperature
b. Inadequate surface preparation
c. The product’s specific gravity increases
The product in the tank is changed
A major cause of tank lining failures is inadequate:
a. liner thickness.
b. surface preparation prior to liner installation
c. time period between Liner layers.
4. inspection of sand pad for foreign debris.
Module 4 ~ API 652 4 MSTS
24,
25.
26.
21,
28.
29.
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
‘The minimum surface preparation prior to installing a tank lining is:
a. NACENo.I (white metal finish).
NACE No.2 (near-white metal finish).
NACE No.3 (commercial blast cleaning).
NACE No.4 (brush-off blast cleaning).
aes
When installing a tank-bottom lining, abrasive blasting should not be performed if the
steel surface is less than
a. 5°F above the dew point.
b. 20°F above the dew point.
c 32°F,
a 80°F,
When installing a tank-bottom lining, abrasive blasting should jot be performed if the
relative humidity is greater than:
a 5%,
b. 50%,
15%,
d 80%.
Abrasive blasting cleans the metal surface and creates an anchor pattern for liner
adhesion. What anchor pattern is typically required?
a, 1.0 - 2.0 mils
b, 1.5-4.0 mils
ce. .2.0-5.0 mils
d 25-60 mils
Most of the guidelines for lining installation come from:
a APIGSL
bv. API652,
ce. Liner’s Manufacturer.
d. NACE.
Liners should nof be installed if the steel surface is less than:
S°F above the dew point.
a
b. 20°F above the dew point.
©. 32°F.
a, 80°F,
Module 4 — API 652 5 MsTS
30.
3.
32,
33,
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
Liners should not be installed if the relative humidity is greater than:
a 3%,
b. 50%,
c 75%,
d 80%,
What is an effective way to make sure there is uniform coverage of each coating layer?
a Alternate colors between coats
b. Take wet film thickness readings every 6”
¢. Calculate film thickness based on size of tank and amount of liner material used
d. Make a wish on a falling star
A major cause of tank lining failures is inadequate:
a curing time.
b. inspection of sand pad for foreign debris.
c. liner manufacturer's specifications.
d. control of water in the tank.
Afiera lining is applied, which of the following is extremely important?
a Humidity inside the tank does not exceed 50%
b. Tank is not closed until curing is complete
c. The liner is inspected by someone with a NACE certification
The liner is holiday tested with a high-voltage detector
‘The inspector inspecting the installation of tank linings must be:
an APL653 inspector.
b. a NACE inspector.
€. either an API 653 inspector or a NACE inspector.
4, either a NACE inspector or someone knowledgeable of lining practices,
‘A new tank bottom liner has just been installed. What should the inspector check?
a. Surface preparation prior to liner installation,
b. Wet film thickness of each coat.
©. Dry filim thickness of each coat
d. That curing time is adequate (between coats and prior to putting the tank in
operation).
e. — Allthe above
f. None of the above, inspectors are paid to think not act!
Module 4 — API 652 6 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
36. Wet film thickness readings should be done in accordance with:
a. API6SO.
APL653.
. ASME B&PV-Seetion Il
ASTM D-4414
c. NACE RP-02-88
37. New thin-film liners should be checked with a:
low-voltage detector.
medium-voltage detector.
high-voltage detector.
divining rod,
pes
38. New thick-film liners should be checked with a:
low-voltage detector.
medium-voltage detector
high-voltage detector.
MPL machine.
39. Holiday testing of liners is recommended for:
only new liners
b. only existing liners.
¢. both new and existing liners.
4. in-service swimming pool liners. (could be a shocking experience)
Module 4 ~ API 652 7 MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
40. Complete the following table by placing a check in the appropriate column, Thin Film or
Thick Film. If the variable is equally true for both liners, then place a check in both
columns,
Tank Liner Variables
- Thin
Film
Thick
Film
1 Lowest cost liner.
Easiest liner to apply
Less susceptible to mechanical damage
. Most prone to crack with bottom flexing
During installation adequate climate conditions are important
‘Sometimes reinforcement is added to liner
2.
A
4
5. During installation adequate surface prep is important
6.
7.
8.
Most often used with new construction
9, Most often used on existing tanks that experienced corrosion
Module 4 ~ Al
652 8
MSTS
API 653 Certification
Module 4 Study Aid - API 652
Answer Key
L b 3.22 20. b Table |
oa 333 2c 654
3. d 41 2. c Various
pene 4 2. b 1
5. b 41 24. b Td
6 a 43 ee
mite 43 aoe a
8 od 43 Bee a
9 44 2% ¢ 82
10. b 44 2. 8 83
od 45 eoeHe Le
2 od 47 Shee ee
isice 47 32a 85
14. a Various atte eS
1. a sa ete 92
16. b 61 oote 93
i a 6i 36. d 93.2
18. d 63.1 soe eae
wd Table 2 oote ae
3. a 102
Question # 40 -Tank Liner Variables qe | ae
1. Lowest cost liner. iv
2. Basiest liner to apply v
3. Less suseepiile to mechanical damage v
“4, Most prone to crack with bottom flexing v
5. During installation alequate sorace prep i important v v
| 6. During installation adequate climate conditions are important v v
7. Sometimes reinforcement is added 1 liner v
8, Mos often used with new constuction v
9. Most often used on existing tanks that experienced corrosion v
Module 4—API 651 9
MSTS
API 653 Homework
API 651 & 652 - CP & Linings
Name:
Closed Book
Is
Which of the following is nof a component of a corrosion cell?
a Anode
b. Electrode
Metallic path
Cathode
‘What chemical reaction happens at an anode?
Fe > Fet2 + 2e-
0 + 210 + 4e > 4011
2Fe + Op ---> 2FeO
OH’ +H > 1,0
nese
What chemical reaction happens at a cathode?
Fe --> Fet2 + 2e-
0) + 2H,0 + de" > 40H
Fe + 2H ---> FeHp
OH’ +H > 0
When a tank floor is in contact with a piece of clay, what causes soil-side tank floor
corrosion?
The clay pH is higher than rest of sand pad
Clay is a corrosion material
‘The soil resistivity range for clay is low
‘The oxygen concentration is lower under the clay ball than other parts of tank
Which of the following is not a significant factor of galvanic corrosion?
a. Stray AC currents
b. Relative areas of cathode & anode
© Soil resistance
4d. Position of materials in galvanie series
Module 4 L MSTS
ul
API 653 Homework
API 651 & 652 - CP & gs
Galvanic corrosion can occur when an underground stainless steel pipe is connected to a
carbon steel tank shell nozzle. Where is this corrosion most likely to occur?
a, The underground portion of the stainless steel pipe
b. The portion of the tank bottom nearest the pipe
c. The carbon steel nozzle at the contact point with pipe (flange face)
d, The stainless steel pipe at contact point with nozzle (flange face)
As soil resistivity increases the:
a, cathodic protection is easier to achieve.
b, stray currents become an increasing concern.
¢. the potential for corrosion decreases.
4d. the potential for corrosion increases.
Which of the following is nof a potential problem with secondary containment?
a, May trap corrosive liquids
b. Increases the difficulty of performing cathodie protection surveys.
c. Prevent flow of electrical current of cathodic protection system.
d. Cannot use a cathodic protection system with a deep ground-bed.
In coastal areas, a very important fact
a. salt spray.
b. the potential for oil spills.
c. high humidity
d. the potential for marshy soils.
A galvanic CP system:
a. must have an anode which is electrically connected to the tank.
‘must have a rectifier specifically designed for the system:
has an anode containing metals materials that are less active than the tank
materials.
a is most often used on large-diameter tanks.
Which of the following is an advantage of a galvanic CP systen
a Iisa practical system for tanks of all sizes
b. Current output is high
c Maintenance costs are minimal
d, Works well in soils with high resistivity
Module 4 2 MSTS
14.
16.
API 653 Homework
API 651 & 652 - CP & Linings
Which of the following is an advantage of an impressed current CP system’?
Practical system for tanks of all sizes
Safety aspects are minimized
Maintenance costs are minimal
Requires infrequent monitoring
nese
A rectifier on an impressed current CP system:
a. provides a place to test the driving potential of tank to tank pad,
b. eliminates stray currents,
¢. changes electrical alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC),
d, _ iselectrical connected to the tank grounding system,
An old tank bottom has failed. A new bottom is placed 4” above the old bottom. A new
impressed-current CP system is added to the tank. ‘This tank may experience:
accelerated corrosion on the old bottom.
accelerated corrosion on the new bottom,
accelerated product side corrosion.
accelerated corrosion on the bottom shell course.
aes
Which of the following is not a common material used for sacrificial anodes?
a Zine
b. Magnesium alloys ribbons
Aluminum
4. Cast magnesium alloys
For an impressed current CP system the generally accepted current density is:
0,85 t0 0.100 volts per square foot.
b. — 110.0r 220 volts per tank
€. 10 2 milliamps per square foot.
100 to 200 milliamps per diameter foot.
A cathodic protection system was sized for a specific tank ina tank farm, At first
inspection it was determined that the cathodic system was not totally effective since some
of the needed current has been going to adjacent tanks, What is a likely cause?
Tanks share a common reference station
‘Tanks share a common product
c. Tanks share a common electrolyte
d. Tanks share a common grounding system
Module 4 3 MSTS
42.
43.
44,
45.
46.
41.
API 653 Homework
API 651 & 652 - CP & Linings
Liners should no# be installed if the relative humidity is:
a 5%,
b. > 50%.
c > 75%,
d > 80%.
What is an effective way to facilitate uniform coverage of each coating layer?
a. Altemate colors between coats
b. Take wet film thickness readings every 6”
c. Calculate film thickness based on size of tank and amount of liner material used.
The inspector inspecting the installation of a tank linings must be:
an API 653 inspector
a NACE inspector
either an API 653 inspector or a NACE inspector.
cither a NACE inspector or someone knowledgeable of lining practices.
eee
A new tank bottom liner is installed. What should the designated inspector check?
a. Surface preparation prior to liner installation.
Wet film thickness of each coat.
Dry film thickness of each coat.
‘That curing time is adequate (between coats and prior to putting the tank in
operation).
All the above.
f None of the above, inspectors are paid to think not act.
aos
New thin-film liners should be checked with a:
a. low-voltage detector
b. _ medium-voltage detector.
c. high-voltage detector.
New thick-film liners should be checked with a:
a. low-voltage detector.
b. medium-voltage detector.
c. high-voltage detector.
Module 4 8 MSTS
API 653 Homework
API 651 & 652 - CP & Linings
48. Complete the following table by placing a check in the appropriate column, Thin Film or
Thick Film. If the variable is equally true for both liners, then place a check in both
columns,
Tank Liner Variables
Thin
Film
Thick
Film
1, Lowest cost liner.
. Easiest liner to apply
Less susceptible to mechanical damage
‘Most prone to crack with bottom flexing
During installation adequate surface prep is important
During installation adequate climate conditions are important
. Sometimes reinforcement is added to liner
Most often used with new construction
Most often used on existing tanks that experienced corrosion
Module 4 9
MSTS
API 653 Homework
API 651 & 652 - CP & Lining:
Open Book
Suggestion! Write the API paragraph references next to each question
Soil with a resistivity of 5000 Ohm-cm is considered:
very corrosive.
corrosive.
moderately corrosive.
mildly corrosive.
progressively less corrosive.
f the soil has a ph of 5.5, the soil is considered:
very corrosive.
corrosive.
moderately corrosive.
mildly corrosive,
eoge
If the soil has a chloride content of 1500 ppm, the soil is considered:
a. very corrosive.
b. corrosive.
c moderately corrosive.
4. mildly corrosive.
If the soil has a sulfate content of 1500 ppm, the soil is considered:
avery corrosive.
b. corrosive.
c, moderately corrosive.
d. mildly corrosive.
Which material is more likely to corrode when connected to clean carbon steel?
Cast iron
Copper
aore
Module 4 10 MSTS
API 653 Homework
API 651 & 652 - CP & Linings
6, fin the presence of an electrolyte, which material is more likely to corrode when
connected to carbon steel with mill scale?
a Carbon
b. Cast iron
Clean carbon steel
4. Rusty steel
7. Which liner would be most suited for an existing tank with a corroded tank bottom? The
tank service is alcohol service?
a. Coal tar epoxy
b. Epoxy phenolic/amine
¢. _Isophthalic polyester
a. Vinyl ester
8 Which liner would be most suited for a new tank? ‘The tank service is gasoline service?
a. Coal tar epoxy
b. Epoxy phenolic/amine
c. __Isophthalic polyester
d.— Vinylester
9. Wet fill thickness readings should be done in accordance with:
a API650
b.API653
c. ASME B&PV Section II
d. ASTM D-4414
c. NACERP-02-88
Module 4
u MSTS
API 653 Homework
API 651 & 652 - CP & gs
Homework - Answer Key
2.
Closed Book Open Book
b 2% 1 d
a 2. b 2b
b 28. ob 3. a
d 202 d 4 b
a 30. ob 5. d
b 3h a 6. ©
© 32 b 7 4
b 33.0 a 8. b
a 34d 9 4
a 4% 8
c 36. b
a 37. b
© 38. a
b 39. d
c 40. b
« 4a
d 42. 6d
a 4B. a
© 4d
b 45. e
© 46. a
e 47, 0c
b 48. See chart below
d
ih 1 Thin Thick
Tank Liner Variables Film Film
1. Lowest cost liner x z
2. Basiest Finer v0 apply x
3. Less susceptible to mechanical damage x
4 Most prone to crack with bottom flexing x
5. Daring installation adequate surface prep i important x x
6. During installation adequate climate conditions ae important x x
7. Sometimes reinforcement is added to finer x
8. Most often used with new constuction x
9, Most often used on existing tanks that experienced corrosion x
Module 4 2
MSTS
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- RT-L3 Q&aDocument8 pagesRT-L3 Q&aPradeep Kumar Bowmaraju100% (1)
- Note API 651 652 CP LiningDocument15 pagesNote API 651 652 CP LiningPradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- Homework Api 653 Module 3 - 2 PDFDocument14 pagesHomework Api 653 Module 3 - 2 PDFPradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- RT11 PDFDocument20 pagesRT11 PDFPradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- RT III Question PDFDocument25 pagesRT III Question PDFAmit GabaniNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Process and DefectsDocument7 pagesMetal Forming Process and DefectsPradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- Basic8 RTDocument4 pagesBasic8 RTPradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- Hot ForgingDocument7 pagesHot ForgingPradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- PT17Document30 pagesPT17Pradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- PT11Document18 pagesPT11Pradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet