Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Examples of Inertia
Uploaded by
preetha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesExamples of Inertia
Uploaded by
preethadf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
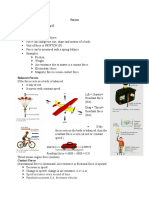
Examples of Inertia
_ An athlete runs some distance before jumping. Because, this
will help him jump longer and higher. (Inertia of motion)
_ When you make a sharp turn while driving a car, you tend to
lean sideways, (Inertia of direction).
_ When you vigorously shake the branches of a tree, some of the
leaves and fruits are detached and they fall down, (Inertia of
rest).
Figure 1.1 Inertia of motion
1.3 LINEAR MOMENTUM
The impact of a force is momentum in SI system is kg
more if the velocity and the m s–1 and in C.G.S system its
mass of the body is more. To unit is g cm s-1.
quantify the impact of a force
exactly, a new physical
quantity known as linear
momentum is defined. The
linear momentum measures
the impact of a force on a
body.
The product of mass and
velocity of a moving body
gives the magnitude of linear
momentum. It acts in the
direction of the velocity of the
object. Linear momentum is a
vector quantity.
Resultant Force
Linear Momentum = mass ×
velocity When several forces act
p = m v. . . . . . . . . . (1.1) simultaneously on the same
body, then the combined effect
It helps to measure the
of the multiple forces can be
magnitude of a force. Unit of
represented by a single force,
which is termed as ‘resultant
force’. It is equal to the vector
sum (adding the magnitude of
the forces with their direction)
of all the forces.
10th_Science_Unit-1.indd 3 21-
02-2019 18:32:41 4
If the resultant force of all the forces acting on a
body is equal to zero, then the body will be in
equilibrium. Such forces are called balanced
forces. If the resultant force is not equal to zero,
then it causes the motion of the body due to
unbalanced forces
Examples: Drawing water from a well, force
applied with a crow bar, forces on a weight
balance, etc.
A system can be brought to equilibrium by applying
another force, which is equal to the resultant force
in magnitude, but opposite in direction. Such force
is called as ‘Equilibrant’.
Rotating Effect of Force
Have you observed the position of the handle in a
door? It is always placed at the edge of door and
not at some other place. Why? Have you tried to
push a door by placing your hand closer to the
hinges or the fixed edge? What do you observe?
The door can be easily opened or closed when you
apply the force at a point far away from the fixed
edge. In this case, the effect of the force you apply
is to turn the door about the fixed edge. This
turning effect of the applied force is more when
the distance between the fixed edge and the point
of application of force is more.
You might also like
- Law of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Document13 pagesLaw of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5pujal dabasNo ratings yet
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- FORCEDocument2 pagesFORCEBuddhistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Forces & Turning Effect Of ForcesDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - Forces & Turning Effect Of ForcesSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- A Push or A Pull - The Definition of Force - Physics Book Grade 5 | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandA Push or A Pull - The Definition of Force - Physics Book Grade 5 | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document73 pagesLecture 3HamzahNo ratings yet
- CH-5 Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesCH-5 Laws of MotionSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument4 pagesForcesAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Icse Physics NotesDocument110 pagesIcse Physics Notess9605519No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of PhysicsDocument49 pagesFundamentals of PhysicsEkwama EwugaNo ratings yet
- Hit TerDocument29 pagesHit TerSai-Min Thit-KoNo ratings yet
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- A.2 Forces & Momentum: The Three Laws of MotionDocument16 pagesA.2 Forces & Momentum: The Three Laws of MotionVedant PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Physics Quantities and Forces ReviewDocument2 pagesPhysics Quantities and Forces ReviewLei StarosaNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS Module 1Document34 pagesENGINEERING MECHANICS Module 1rout79858No ratings yet
- Laws of Motion: - Dynamics Is The Branch of Physics in Which We StudyDocument18 pagesLaws of Motion: - Dynamics Is The Branch of Physics in Which We StudyVipeen BendaleNo ratings yet
- Force, TensionDocument41 pagesForce, TensionShanzay MateenNo ratings yet
- University Physics IDocument28 pagesUniversity Physics IKenn SenadosNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 CH 11 NOTESDocument9 pagesGRADE 8 CH 11 NOTESNikhat SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Physics Forces ExplainedDocument11 pagesPhysics Forces ExplainedKeerthan Manjunath50% (2)
- Dynamics: What Is A Force?Document13 pagesDynamics: What Is A Force?TorettoNo ratings yet
- PH110-CHAPTER 4 DynamicsDocument17 pagesPH110-CHAPTER 4 DynamicsNtape Knox SiwaleNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion ExplainedDocument24 pagesForces and Motion ExplainedKNEWTON EducationNo ratings yet
- What Is A ForceDocument12 pagesWhat Is A ForceSyed M HassanNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument26 pagesLaws of Motionaslamfiza06No ratings yet
- Forces and Pressure: A Guide to Key ConceptsDocument11 pagesForces and Pressure: A Guide to Key Conceptsmatho logyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Statics and ForcesDocument17 pagesIntroduction to Statics and ForcesIan Arnold FamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Laws of Motion NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Laws of Motion NotesSparkNo ratings yet
- 246_6384877186112223611Document11 pages246_6384877186112223611Abhiveerdahiya08No ratings yet
- Force, Motion and Energy ExplainedDocument5 pagesForce, Motion and Energy ExplainedMin Yoongi100% (1)
- Force: Acceleration (Change in Magnitude or Direction of Their Velocity)Document8 pagesForce: Acceleration (Change in Magnitude or Direction of Their Velocity)eka123No ratings yet
- 1.5newton's LawDocument39 pages1.5newton's LawEaintNo ratings yet
- Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument6 pagesContact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesBethlehem CuradaNo ratings yet
- Physics Newton'sLawsofMotionDocument44 pagesPhysics Newton'sLawsofMotionCamela LacsamaNo ratings yet
- Force: Force Is A Vector Quantity Expressing How Bodies Act On Each OtherDocument2 pagesForce: Force Is A Vector Quantity Expressing How Bodies Act On Each OtherWong Wei HanNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion ExplainedDocument7 pagesForces and Motion ExplainedMin YoongiNo ratings yet
- statics of rigid bodies (1)Document14 pagesstatics of rigid bodies (1)Mariya MariyaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Quarter 1 - Week 4 SSLMDocument6 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 1 - Week 4 SSLMCarmina Jane DomantayNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law Explained in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesNewton's Third Law Explained in 40 CharactersRayudu VVSNo ratings yet
- Resultant of Forces:: Maintaining Equilibrium or Changing MotionDocument68 pagesResultant of Forces:: Maintaining Equilibrium or Changing MotionRandy NatalNo ratings yet
- Physics (Forces)Document3 pagesPhysics (Forces)TVNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biomechanics - Mechanical Concepts and TermsDocument30 pagesClinical Biomechanics - Mechanical Concepts and Termsmihaela_moldova9128No ratings yet
- FORCESDocument6 pagesFORCESlemoniteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Forces: (I) What Is A Force?Document4 pagesChapter 3 Forces: (I) What Is A Force?Ahmed OmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter# 3: Mechanical StressDocument2 pagesChapter# 3: Mechanical StressFaisal BhattiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Statics: Quaid-e-Azam College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument19 pagesEngineering Statics: Quaid-e-Azam College of Engineering & TechnologyaliNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering B.E - Iii Year - V Semester Dynamics of Machines Unit I Force AnalysisDocument101 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering B.E - Iii Year - V Semester Dynamics of Machines Unit I Force Analysissuneel kumar rathoreNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton's Laws in MotionDocument23 pagesForces and Newton's Laws in Motionأيوب عبد الأمير هزبر /تقنية غازNo ratings yet
- Force And Pressure Class 8 Notes - Chapter 11 IntroductionDocument9 pagesForce And Pressure Class 8 Notes - Chapter 11 Introductionanushree ranadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 11 NotesChahat SanataniNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument6 pagesForce and Motionohnmarhtet09No ratings yet
- Types of forces: Contact and Non-Contact ForcesDocument9 pagesTypes of forces: Contact and Non-Contact Forcesaditya nimbalkarNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument9 pagesForceMohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Science 8Document86 pages1st Quarter Science 8John Ryan PiolNo ratings yet
- FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION NotesDocument3 pagesFORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION NotesyoutuberNo ratings yet
- Scalars and VectorsDocument11 pagesScalars and VectorsEFRAIM CAMBENo ratings yet
- SOM - English (2 & 3 Marks)Document25 pagesSOM - English (2 & 3 Marks)Kal Pathippagam75% (4)
- Class 8 Force and FriDocument8 pagesClass 8 Force and FriSourabh RanaNo ratings yet
- HygrosDocument4 pagesHygrospreethaNo ratings yet
- State of EquilibriumDocument7 pagesState of EquilibriumpreethaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Decomposition ReactionsDocument3 pagesThermal Decomposition ReactionspreethaNo ratings yet
- Neuron or Nerve CellDocument8 pagesNeuron or Nerve CellpreethaNo ratings yet
- AmalgamDocument5 pagesAmalgampreethaNo ratings yet
- 1 Laws of MotionDocument4 pages1 Laws of MotionpreethaNo ratings yet
- Radio ActivityDocument3 pagesRadio ActivitypreethaNo ratings yet
- Types of SolutionsDocument7 pagesTypes of SolutionspreethaNo ratings yet
- Properties of AlphaDocument6 pagesProperties of Alphapreetha0% (1)
- Stellar EnergyDocument6 pagesStellar EnergypreethaNo ratings yet
- Discovery of RadioactivityDocument6 pagesDiscovery of RadioactivitypreethaNo ratings yet
- Electron Displacement EffectsDocument6 pagesElectron Displacement EffectspreethaNo ratings yet
- Relative Motion Between A Source and A ListenerDocument3 pagesRelative Motion Between A Source and A ListenerpreethaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument5 pagesAtoms and MoleculespreethaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FusionDocument5 pagesNuclear FusionpreethaNo ratings yet
- Our EnvironmentDocument3 pagesOur EnvironmentpreethaNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument4 pagesReproductionpreethaNo ratings yet
- Resonance or Mesomeric EffectDocument4 pagesResonance or Mesomeric EffectpreethaNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessDocument8 pagesLife ProcesspreethaNo ratings yet
- AlveoliDocument7 pagesAlveolipreethaNo ratings yet
- Control and CoDocument9 pagesControl and CopreethaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument7 pagesThe Periodic TablepreethaNo ratings yet
- Elimination ReactionDocument5 pagesElimination ReactionpreethaNo ratings yet
- HomozygousDocument4 pagesHomozygouspreethaNo ratings yet
- The Branch of ScienceDocument7 pagesThe Branch of SciencepreethaNo ratings yet
- Chemical CoDocument10 pagesChemical CopreethaNo ratings yet
- Structure of The EyeDocument5 pagesStructure of The EyepreethaNo ratings yet
- Select The Correct PronounDocument1 pageSelect The Correct PronounpreethaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Breathing and RespirationDocument8 pagesDifference Between Breathing and RespirationpreethaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 19 20 XIII Phy Study Package 1 Level 1 Chapter 1Document4 pagesCLS Aipmt 19 20 XIII Phy Study Package 1 Level 1 Chapter 1Optics Career Institute -OCI100% (1)
- MOTION2Document81 pagesMOTION2Zaenul Akbar SantosoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1270963809001060 Main PDFDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S1270963809001060 Main PDFali_raza117No ratings yet
- The Symmetric Spinning Top: Deriving The Equations of MotionDocument13 pagesThe Symmetric Spinning Top: Deriving The Equations of MotionPermadiNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Visual Arts Geometry Syllabus FALL2021Document8 pagesVisual Arts Geometry Syllabus FALL2021YordinVanegasMeloNo ratings yet
- Senior High School A.Y 2020 - 2021 Modern Physics: RELATIVITY I. Modern PhysicsDocument8 pagesSenior High School A.Y 2020 - 2021 Modern Physics: RELATIVITY I. Modern PhysicsKyle Cedric MitalNo ratings yet
- 2 D MotionDocument28 pages2 D Motionmusic_is_mypassionNo ratings yet
- 03-Motion in A St. Line (32-63)Document32 pages03-Motion in A St. Line (32-63)nvsl SumadhuraNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Speed 2019 7P1.1Document42 pagesForces and Motion Speed 2019 7P1.1Andrew nateNo ratings yet
- English Medium Lec. Physics-2 2020-Ok PDFDocument23 pagesEnglish Medium Lec. Physics-2 2020-Ok PDFSakib KhanNo ratings yet
- Cartesian Coordinate SystemDocument17 pagesCartesian Coordinate SystemertyuNo ratings yet
- Time Allowed: 20 Minutes Marks: 12: Section - ADocument3 pagesTime Allowed: 20 Minutes Marks: 12: Section - AAliNo ratings yet
- Speed Velocity and AccelerationDocument31 pagesSpeed Velocity and AccelerationTeacher EducationNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Calc 3Document392 pagesConcepts of Calc 3John SchrageNo ratings yet
- Does Science Make Belief in God Obsolete?: Keith WardDocument2 pagesDoes Science Make Belief in God Obsolete?: Keith WardLaxman ThapaNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 1 CapeDocument32 pagesPhysics Unit 1 Caperonese augustusNo ratings yet
- Puri Tensor 2Document38 pagesPuri Tensor 2uday singhNo ratings yet
- Presentation On "Separation Axioms": School of Studies in MathematicsDocument22 pagesPresentation On "Separation Axioms": School of Studies in MathematicsChetan Patel CpNo ratings yet
- LEC-7 Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDocument62 pagesLEC-7 Kinematics of Rigid BodiesMenatalla MohamedNo ratings yet
- By Robert L. Piccioni, PH.D.: "Einstein For Everyone"Document2 pagesBy Robert L. Piccioni, PH.D.: "Einstein For Everyone"Shivam kumarNo ratings yet
- AP FR Quiz #5 2D MotionDocument7 pagesAP FR Quiz #5 2D MotionRobbyNo ratings yet
- Unit I Engineering Mechanics - StaticsDocument17 pagesUnit I Engineering Mechanics - Staticsbpal1970No ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF RIGID BODY MECHANICSDocument14 pagesFUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF RIGID BODY MECHANICSTarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Quantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime: Peng ZhaoDocument30 pagesQuantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime: Peng Zhaohimanshudhol25No ratings yet
- Costant Acceleation - Horizontal Motion Exam Questions 2Document11 pagesCostant Acceleation - Horizontal Motion Exam Questions 2Dominic SavioNo ratings yet
- Lecture DynamicsDocument13 pagesLecture DynamicsmarkosNo ratings yet
- Theory of RelativityDocument51 pagesTheory of RelativityRDNo ratings yet
- The Hyperbolic Theory of Special RelativityDocument109 pagesThe Hyperbolic Theory of Special RelativityscribblemanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Chernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandChernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (264)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsFrom EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityFrom EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (380)