Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roark's - Max. Bending Stress at The Saddle Horn of Horizontal Vessel
Uploaded by
Rey FiedacanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Roark's - Max. Bending Stress at The Saddle Horn of Horizontal Vessel
Uploaded by
Rey FiedacanCopyright:
Available Formats
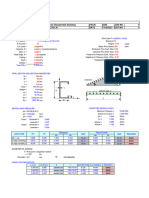
ROARKS IN FINDING THE MAXIMUM CIRCUMFERENTIAL BENDING MOMENT ON TOP OF SADDLE HORN
Given Data:
Thickness of shell t = 0.75 in.
Inside Diameter Di = 60.0 in.
Angle of contact ɸ = 130 (Saddle angle)
Fabricated Wt. of vessel Wv = 7,700 Lb
Total Operating Wt. Wo = 26,400 Lb (Seismic Loading)
Fluid Density = 62.4 Lb/ft3
Width of saddle b = 11.5 in. (Including wear plate)
Saddle Reaction (qty=2) Q = 13,200 Lb (per Saddle)
Bending stress,psi
Outside Diameter, Do = 61.500 in.
5,336.03
Mean Diameter Dm = 60.750 in.
Mean Radius R = 30.375 in.
Moment Area I = 66,042.9 in4 I = π (Do 4 - Di 4)/64
Cross Sectional A = 2,827.43 in2 A = π R2
α = 0.025316358 α = I/AR2
k2 = 1 0.975
(Note: if α = β = 0, then all k = 1)
2*w*R*sin Ꝋ = 3,954.66 lb
Let X = 112 (Maximum bending stress at horn at 3 deg above the wear plate)
Case 15: By its circumferential ring weight Load Case 15 Case 16 Case 12 Summation
Geometry Given: MA 9306.066 253.005 -4597.172 4961.899
Wt. acted on saddle plane = 3,850 Lb NA 306.373 24.988 -327.600 3.761
Circumferential Length = 190.85 in VA 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
w = 20.17 Lb/in Mc 27918.199 759.016 -25207.428 3469.787
Table 9.2 page 326 for KT = 1 (for thin ring) and α = β = 0 Moment, Hoop, Radial values at 130 deg. Max stress at , x =112
MA = 9306.066 Lb-in wR2/2 Mx -3012.091 -316.321 9081.320 5752.907
NA = 306.373 Lb wR/2 Nx -1225.327 6.245 122.721 -1096.361
VA = 0 Lb Vx 732.758 50.813 -303.745 479.826
MC = 27918.199 lb-in ΔDH 21.678 0.000 21.678
then X = 112 degrees u= -0.3746 rad. cosx POINT LOAD ANALYSIS
then = 1.954768762 radians z= 0.9272 rad. sinx 1 Maximum bending moment above the horn at 112 degrees
LTM = - 8,148.83 lb/in M= 5,752.91 Lb-in
LTN = - 1,110.56 lb/in 2 Maximum shear forces above the horn at 112 degrees
LTV = 448.69 lb/in VA= 479.83 Lb
3 Maximum compressive stress at 112 degrees
Find Moment, Hoop, Shear at 112 degrees NA = - 1,096.36 Lb
Mx = -3012.091 lb-in 4 Maximum bending moment at plane of saddle per unit width
Nx = -1225.327 lb of pad above the horn
Vx = 732.758 lb M= 500.25 Lb-in/in.
ΔDH = 21.678 in. 5 Bending Stress
σ = 6 * M / ts2
= 5,336.03 psi
6 Allowable Bending Stress = S (material)*E (Joint Efficiency)
Case 16: By its filled weight Note: When Bending stress is high
Geometry 1 Requires reinforcement ring on top saddle horn (at plane of the saddle)
2 Increase thickness of shell (Option)
Given:
ρ = 0.0361 lb/in3
MA = 253.005 Lb-in
NA = 24.988 Lb
VA = 0 Lb
MC = 759.016 lb-in
X= 112 degrees u= -0.3746 = cosx
= 1.954768762 radians z= 0.9272 = sinx
LTM = 474.02 lbf-in/in
LTN = 15.61 lbf/in.
LTV = 27.64 lbf/in.
Find Moment, Hoop, Shear at 112 degrees
Mx = -316.321 lb-in.
Nx = 6.245 lb
Vx = 50.813 lb
ΔDH = in.
Case 12: By the reaction of saddle
Geometry Given:
Ꝋ = 112 degrees s = 0.9272 = SinꝊ
= 1.954768762 radians c= -0.3746 = cosꝊ
w = 70.210 lb/in Contact unit reaction (Total)
MA = -4597.172 Lb-in.
MC = -25207.428 Lb-in.
NA = -327.600 lb
VA = 0 lb
for Ꝋ = X
X= 112 degrees u= -0.3746 = cosx
= 1.954768762 radians z= 0.9272 = sinx
LTM = - lbf/in.
LTN = - lbf/in.
LTV = - lbf/in.
Find Moment, Hoop, Shear at 112 degrees
Mx = 9081.320 lb-in.
Nx = 122.721 lb
Vx = -303.745 lb
ΔDH = in.
You might also like
- Lifting Lug Calculation For Small Horizontal VesselDocument2 pagesLifting Lug Calculation For Small Horizontal VesselshaishavNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet: H2So4 Neutralization TankDocument43 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet: H2So4 Neutralization TankEkki Petrus BubunNo ratings yet
- Flange Pad CalcsDocument4 pagesFlange Pad CalcstomNo ratings yet
- Godrej & Boyce calculations for weld strength and size of RIL equipmentDocument10 pagesGodrej & Boyce calculations for weld strength and size of RIL equipmentSajal KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- NozzleDocument11 pagesNozzleharyfadlyNo ratings yet
- AISC2005 Anchor Bolt5 Pin Connection NewDocument6 pagesAISC2005 Anchor Bolt5 Pin Connection NewThuyTranNo ratings yet
- Trunnion AnalysisDocument45 pagesTrunnion AnalysisChiragJansariNo ratings yet
- Davit Cal 2251B Davit Arm CalculationDocument4 pagesDavit Cal 2251B Davit Arm Calculationnitin400No ratings yet
- Lug - On - FlangeDocument17 pagesLug - On - Flangeshaishav100% (1)
- Design of Flat Head For HydrotestDocument12 pagesDesign of Flat Head For HydrotestSAGAR100% (1)
- Anchor Bolt Loading Calculation For 101-B-10 29.02.16Document6 pagesAnchor Bolt Loading Calculation For 101-B-10 29.02.16kkaranagNo ratings yet
- Tailing LugDocument2 pagesTailing Lugjagannadha varmaNo ratings yet
- Tailing Lug - 173004-05Document1 pageTailing Lug - 173004-05shazan100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Strength Calculation: Shell Side Design Data Tube Side Design DataDocument2 pagesHeat Exchanger Strength Calculation: Shell Side Design Data Tube Side Design DataSteve MoonNo ratings yet
- Support Lug CalculationsDocument26 pagesSupport Lug CalculationsDinesh ChouguleNo ratings yet
- Design of Circular Flat Endplate With Stiffeners - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-TipsDocument2 pagesDesign of Circular Flat Endplate With Stiffeners - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-Tipsisrar khanNo ratings yet
- Davit Cal 2251B Davit Arm CalculationDocument4 pagesDavit Cal 2251B Davit Arm CalculationKarina RoquelNo ratings yet
- Roark's - Discontinuity Stress at Junction of Shell & HeadDocument13 pagesRoark's - Discontinuity Stress at Junction of Shell & HeadRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- LIFTING LUG AND LIFTING COVER DESIGN REFERENCEDocument4 pagesLIFTING LUG AND LIFTING COVER DESIGN REFERENCERohith V VNo ratings yet
- Lifting LugDocument39 pagesLifting LugSasikumar JothiNo ratings yet
- AISC360 05 LRFD Shear Plate Bolted Connection Check 17-09-2013Document8 pagesAISC360 05 LRFD Shear Plate Bolted Connection Check 17-09-2013RUBEN BARTOLOME GARCIANo ratings yet
- LIFTING LUG Weld Check KGDocument4 pagesLIFTING LUG Weld Check KGjoerijiNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Bending Stress: M1 Allowable Limit RemarkDocument16 pagesLongitudinal Bending Stress: M1 Allowable Limit RemarkSandal JepitNo ratings yet
- Design of Flanges - Loose Hub Type 2010Document58 pagesDesign of Flanges - Loose Hub Type 2010bakellyNo ratings yet
- Calculation LugDocument20 pagesCalculation LugKartika ZuhraNo ratings yet
- Trunnion Check - Node 710Document13 pagesTrunnion Check - Node 710Prashant ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Anchor Chair Design CheckDocument5 pagesAnchor Chair Design CheckHomer SilvaNo ratings yet
- 吊耳计算Document4 pages吊耳计算huangjlNo ratings yet
- Saddle CalcDocument26 pagesSaddle CalcVamsi S100% (2)
- 28 Roark Flat PlatesDocument4 pages28 Roark Flat PlatesJorge Silva100% (1)
- Design of End Plate ConnectionDocument2 pagesDesign of End Plate ConnectionAndro RebuyasNo ratings yet
- BAFFLE PLATE AND STIFFENER DESIGN CALCULATION FOR HYDRO CARBON/WASTE WATER DRAIN DRUMDocument6 pagesBAFFLE PLATE AND STIFFENER DESIGN CALCULATION FOR HYDRO CARBON/WASTE WATER DRAIN DRUMshaishavNo ratings yet
- Design Lifting Hook Plate LiftingDocument3 pagesDesign Lifting Hook Plate LiftingSaravan KumarNo ratings yet
- Saddle AnalysisDocument17 pagesSaddle AnalysisAntonio Perez ZornozaNo ratings yet
- Tailing LugDocument12 pagesTailing LuguvarajmecheriNo ratings yet
- Design of Flanges - Full-Face Gasket 2010Document29 pagesDesign of Flanges - Full-Face Gasket 2010bakelly100% (2)
- DG Consulting EngineersDocument8 pagesDG Consulting EngineersThakshayani SellavelNo ratings yet
- Roark's Circular PlateDocument2 pagesRoark's Circular PlatePaulo MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Calculation of left and right saddle supports for offshore tankerDocument12 pagesCalculation of left and right saddle supports for offshore tankerrustamriyadiNo ratings yet
- Finding Stresses at Junction of Cylinder and Reinforcing RingDocument4 pagesFinding Stresses at Junction of Cylinder and Reinforcing RingRey Fiedacan100% (1)
- plant pressure vessel training manual 6 of 6 권-2007 div.2-pd번역-1 (강도계산포함) -4-2-간력sampleDocument36 pagesplant pressure vessel training manual 6 of 6 권-2007 div.2-pd번역-1 (강도계산포함) -4-2-간력samplekangrimNo ratings yet
- Bolt Connection Design Based On AISC 360-10/16: Input Data & Design SummaryDocument1 pageBolt Connection Design Based On AISC 360-10/16: Input Data & Design SummaryKaren Esther Acuña VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Padeye .5MT CHKDocument12 pagesPadeye .5MT CHKDhanraj VasanthNo ratings yet
- Trunion Calc Node 2000&2010Document4 pagesTrunion Calc Node 2000&2010Naveen RaoNo ratings yet
- Stress at Junction of Shell & HeadDocument13 pagesStress at Junction of Shell & HeadRey Fiedacan100% (1)
- TRUNNION CALCULATION SHEETDocument1 pageTRUNNION CALCULATION SHEETAtty Atty100% (1)
- CAL-ST-070!17!01 Rev01 Shipping Saddles CalculationDocument11 pagesCAL-ST-070!17!01 Rev01 Shipping Saddles CalculationgiubelloNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Cylindrical Pressure Vessvessel Zick 03Document12 pagesHorizontal Cylindrical Pressure Vessvessel Zick 03bakelly0% (1)
- BlindDocument3 pagesBlindSajal KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- WHP-East Piatu-Roark Calc & Stiffener-Rev0Document18 pagesWHP-East Piatu-Roark Calc & Stiffener-Rev0namasral100% (4)
- Design of Box CulvertDocument24 pagesDesign of Box CulvertAl Patrick Dela CalzadaNo ratings yet
- Design of Box CulvertDocument34 pagesDesign of Box CulvertAl Patrick Dela CalzadaNo ratings yet
- Design of Anchor Bolts and Saddle Components for Vessel SupportDocument5 pagesDesign of Anchor Bolts and Saddle Components for Vessel SupportAKSHAY BHATKARNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolts DesignDocument6 pagesAnchor Bolts DesignAKSHAY BHATKARNo ratings yet
- Design of Pilecaps BS 8110Document3 pagesDesign of Pilecaps BS 8110thanigai veluNo ratings yet
- Lifting Calculation AnalysisDocument10 pagesLifting Calculation AnalysisrustamriyadiNo ratings yet
- Design of Mullion For C W Wall System: Project NameDocument3 pagesDesign of Mullion For C W Wall System: Project NameSales AlufacadesNo ratings yet
- Design of Purlins - NSCP 2015Document1 pageDesign of Purlins - NSCP 2015Ferdinand AlbarNo ratings yet
- Kalkulasi Rotary Screen 3 X 9 MTRDocument4 pagesKalkulasi Rotary Screen 3 X 9 MTRclays piezkaal setyabudiNo ratings yet
- Storage TankDocument1 pageStorage TankRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- WRC Bulletin 537 - Rectangular Attachment (Excel)Document21 pagesWRC Bulletin 537 - Rectangular Attachment (Excel)Rey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Calculator - U Tubes - HSA & QtyDocument4 pagesCalculator - U Tubes - HSA & QtyRey Fiedacan100% (1)
- Table - Factor of EvaporationDocument4 pagesTable - Factor of EvaporationRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Calculator - Length of Eco - TubesDocument2 pagesCalculator - Length of Eco - TubesRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Saddle Angle - Formula K - 12.28.20Document2 pagesSaddle Angle - Formula K - 12.28.20Rey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- ASME UG 16.1 - Nozzle Conn. in Vessel No PadDocument24 pagesASME UG 16.1 - Nozzle Conn. in Vessel No PadRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Dearator Mass BalanceDocument3 pagesDearator Mass BalanceRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- CalBOM - Formed ConicalDocument5 pagesCalBOM - Formed ConicalRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Torque of StirrerDocument1 pageProcedure For Torque of StirrerRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Roark's - Discontinuity Stress at Junction of Shell & HeadDocument13 pagesRoark's - Discontinuity Stress at Junction of Shell & HeadRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Anchor Chair Design - Version 1Document3 pagesAnchor Chair Design - Version 1Rey Fiedacan100% (2)
- Flange From Plate - Asme 16.5Document1 pageFlange From Plate - Asme 16.5Rey Fiedacan100% (1)
- Stress at Junction of Shell & HeadDocument13 pagesStress at Junction of Shell & HeadRey Fiedacan100% (1)
- Finding Stresses at Junction of Cylinder and Reinforcing RingDocument4 pagesFinding Stresses at Junction of Cylinder and Reinforcing RingRey Fiedacan100% (1)
- Header & Piping SizingDocument9 pagesHeader & Piping Sizingmedicbest0% (1)
- Sample Torque of Stirrer Frictional PowerDocument2 pagesSample Torque of Stirrer Frictional PowerRey FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Technical Inquiries To API 1104Document20 pagesTechnical Inquiries To API 1104Rey Fiedacan92% (12)
- 9 Beam DeflectionDocument34 pages9 Beam DeflectionBharat JajoriaNo ratings yet
- ECEM - Analysis of Pin Jointed Plane Trusses - Method of JointsDocument15 pagesECEM - Analysis of Pin Jointed Plane Trusses - Method of JointsAnupEkbote100% (1)
- Kong and Evans Reinforced and Prestressed Concrete-صور-102-172Document71 pagesKong and Evans Reinforced and Prestressed Concrete-صور-102-172Malak ShatiNo ratings yet
- 25m 3 Girder SuperstructureDocument43 pages25m 3 Girder SuperstructureVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Chirukhistsqali Weir RHS Manhole Chamber Calculation ReportDocument36 pagesChirukhistsqali Weir RHS Manhole Chamber Calculation Reporthasan_kygszNo ratings yet
- Is 15912 - 2012Document2 pagesIs 15912 - 2012kalpanaadhi100% (1)
- Civil Engineering Reference BookDocument463 pagesCivil Engineering Reference Bookenggakter58% (12)
- Civil EngineeringDocument22 pagesCivil EngineeringSudeepSMenasinakaiNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Durma PDFDocument17 pagesCatalogo Durma PDFAlfredo Orellana100% (1)
- Calculating effective area and length of base plate T-stubsDocument1 pageCalculating effective area and length of base plate T-stubsNimeshkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Aguero - Equivalent Geometric Imperfection Definition - CompressionDocument18 pagesAguero - Equivalent Geometric Imperfection Definition - CompressionDawid GabrysiakNo ratings yet
- Kwan Golden GateDocument10 pagesKwan Golden GateLuis G WeigertNo ratings yet
- CE2401 - Design of Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument4 pagesCE2401 - Design of Reinforced Concrete DesignSabarinath MuruganNo ratings yet
- (PSE) - PSA TrainingDocument67 pages(PSE) - PSA TrainingDenstar Ricardo SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Study of Beam Bending BehaviorDocument3 pagesAnalytical Study of Beam Bending Behavioranass anasNo ratings yet
- PART-B QUESTIONS STEADY STRESSES AND VARIABLE STRESSESDocument12 pagesPART-B QUESTIONS STEADY STRESSES AND VARIABLE STRESSESMadhu MithaNo ratings yet
- Design of Shoe PlateDocument4 pagesDesign of Shoe PlatePraveshNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Masonry StructuresDocument73 pagesSeismic Design of Masonry StructuresB JNo ratings yet
- SSC JE Mains Test Series ProblemsDocument6 pagesSSC JE Mains Test Series ProblemsAble KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Solving Overhanging Beam for SFD and BMD: Prob 5.5Document6 pagesSolving Overhanging Beam for SFD and BMD: Prob 5.5Samuel Antobam100% (1)
- GEO5 Pile Horizontal Capacity P-Y MethodDocument7 pagesGEO5 Pile Horizontal Capacity P-Y MethodDidik JunaidiNo ratings yet
- 01 - Fundamentals of MetalworkingDocument50 pages01 - Fundamentals of MetalworkingriyamondalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Module 2Document32 pagesEngineering Mechanics Module 2Abigail SiatrezNo ratings yet
- Ce2257 Lab ManualDocument53 pagesCe2257 Lab ManualNiranjanNo ratings yet
- Solutions Ch20Document12 pagesSolutions Ch20Joyce Casiano100% (2)
- Use of Mathcad As A Teaching and Learning Tool ForDocument9 pagesUse of Mathcad As A Teaching and Learning Tool ForTarek Ed ENo ratings yet
- 7.3.6.4 Bending Moments - Load Cases: Prestress EffectsDocument16 pages7.3.6.4 Bending Moments - Load Cases: Prestress Effectstailieuxaydung2019No ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics Practical FileDocument21 pagesFracture Mechanics Practical Filesubashish100% (1)
- E-50 - Aeroengine Gearbox Design - BAPT 09 - P 595Document6 pagesE-50 - Aeroengine Gearbox Design - BAPT 09 - P 595Nikos VaxevanidisNo ratings yet
- Flat Slab: Advanced RCC RoofsDocument21 pagesFlat Slab: Advanced RCC RoofsIMRAN KHANNo ratings yet