Professional Documents
Culture Documents
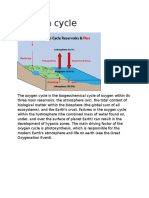
Oxygen
Oxygen
Uploaded by
Piero ZanussiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oxygen
Oxygen
Uploaded by
Piero ZanussiCopyright:
Available Formats
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8.
It is a member of
the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that
readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. By mass, oxygen is the third-
most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and
pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with
the formula O
2. Diatomic oxygen gas constitutes 20.8% of the Earth's atmosphere. As compounds including oxides,
the element makes up almost half of the Earth's crust.
Dioxygen is used in cellular respiration and many major classes of organic molecules in living
organisms contain oxygen, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as do the major
constituent inorganic compounds of animal shells, teeth, and bone. Most of the mass of living
organisms is oxygen as a component of water, the major constituent of lifeforms. Oxygen is
continuously replenished in Earth's atmosphere by photosynthesis, which uses the energy of sunlight to
produce oxygen from water and carbon dioxide. Oxygen is too chemically reactive to remain a free
element in air without being continuously replenished by the photosynthetic action of living organisms.
Another form (allotrope) of oxygen, ozone (O
3), strongly absorbs ultraviolet UVB radiation and the high-altitude ozone layer helps protect
the biosphere from ultraviolet radiation. However, ozone present at the surface is a byproduct
of smog and thus a pollutant.
Oxygen was isolated by Michael Sendivogius before 1604, but it is commonly believed that the element
was discovered independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, in Uppsala, in 1773 or earlier, and Joseph
Priestley in Wiltshire, in 1774. Priority is often given for Priestley because his work was published first.
Priestley, however, called oxygen "dephlogisticated air", and did not recognize it as a chemical element.
The name oxygen was coined in 1777 by Antoine Lavoisier, who first recognized oxygen as a chemical
element and correctly characterized the role it plays in combustion.
Common uses of oxygen include production of steel, plastics and textiles, brazing, welding and
cutting of steels and other metals, rocket propellant, oxygen therapy, and life support
systems in aircraft, submarines, spaceflight and diving.
You might also like
- Corona VetaphoneDocument64 pagesCorona VetaphoneMellissa E Fernando100% (3)
- Bio Chem Labbb EditDocument37 pagesBio Chem Labbb EditAlbert Azura100% (1)
- Oxygen: Characteristics and PropertiesDocument2 pagesOxygen: Characteristics and PropertiesCrisle TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Is The Chemical Element With The Symbol O and Atomic Number 8. It Is A Member ofDocument1 pageOxygen Is The Chemical Element With The Symbol O and Atomic Number 8. It Is A Member ofaryan jainNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen and Carbon Cycle: (Citation Car42 /L 13321) (Citation Mci10 /L 13321)Document6 pagesThe Oxygen and Carbon Cycle: (Citation Car42 /L 13321) (Citation Mci10 /L 13321)Jersey Mae PerlasNo ratings yet
- OxygenDocument19 pagesOxygenCharm_27No ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument5 pagesOxygen Cycleakms_Saif2521No ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument7 pagesOxygen CycleVivek DholeNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen CycleDocument9 pagesThe Oxygen CycleAngeloLorenzoSalvadorTamayoNo ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument4 pagesOxygen CyclePradnya GoreNo ratings yet
- ARUN KOTNALA Chemistry PresentationDocument10 pagesARUN KOTNALA Chemistry PresentationArun KotnalaNo ratings yet
- Co2 O2 CycleDocument8 pagesCo2 O2 CycleJenny AnnuaNo ratings yet
- English 1Document3 pagesEnglish 1Awalia Santi RNo ratings yet
- RQ57CP. Ass6Document6 pagesRQ57CP. Ass6Zlata TumanovaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Cycle: PlantsDocument3 pagesOxygen Cycle: PlantsApam BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Is A: Reactive NonmetalDocument3 pagesOxygen Is A: Reactive NonmetalDominic CabaloNo ratings yet
- OxygenDocument1 pageOxygenslyothersNo ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument3 pagesOxygen Cycleزيد صباح الحلوNo ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument3 pagesOxygen CycleAstrid Harfera PassadanaNo ratings yet
- Element Atomic Number: Uses of OxygenDocument1 pageElement Atomic Number: Uses of OxygenAiman-xxNo ratings yet
- Carbon, Nitrogen and Oxygen CyclesDocument14 pagesCarbon, Nitrogen and Oxygen CyclesHirizza Junko YamamotoNo ratings yet
- Carbon, Nitrogen and Oxygen CycleDocument4 pagesCarbon, Nitrogen and Oxygen CycleHirizza Junko YamamotoNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Cycle: Biology ProjectDocument7 pagesOxygen Cycle: Biology Projectsayooj tvNo ratings yet
- Inbound 1831348127465516057Document5 pagesInbound 1831348127465516057gruezo.roiNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen Cycle - Explained (With Diagram) : in This Process The Oxygen Is Liberated As Shown by The Following EquationDocument3 pagesThe Oxygen Cycle - Explained (With Diagram) : in This Process The Oxygen Is Liberated As Shown by The Following EquationMochammad Syehfu Aref GhozaliNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Is ADocument11 pagesOxygen Is AChidinma Glory EjikeNo ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument2 pagesOxygen CycleMarie Mae Beloy CatapteNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument16 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesMadeline Castro PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Cc4 10 Biogeochemical CycleDocument5 pagesCc4 10 Biogeochemical CyclemadamekanishkaNo ratings yet
- What Is Oxygen CycleDocument3 pagesWhat Is Oxygen CycleMary Grace LerinNo ratings yet
- Uses of Oxygen: Nitrogen CycleDocument7 pagesUses of Oxygen: Nitrogen CycleSyed Sulman SheraziNo ratings yet
- Made By-: Bhavika Deepit Krutika Lakshay Malika MekhlaDocument15 pagesMade By-: Bhavika Deepit Krutika Lakshay Malika MekhladeepitNo ratings yet
- Oxygen N Carbon CycleDocument12 pagesOxygen N Carbon CycleScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument11 pagesOxygen CycleMarc Jonas DiazNo ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument6 pagesOxygen CyclejosevitorromualdoNo ratings yet
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- OxygenDocument32 pagesOxygenjosevitorromualdoNo ratings yet
- Environmental SciencesDocument17 pagesEnvironmental SciencesSayan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Nutrient CyclesDocument2 pagesNutrient CyclesKumail AliNo ratings yet
- Almost All Living Things Need Oxygen. They Use This Oxygen During The Process of Creating Energy in Living CellsDocument12 pagesAlmost All Living Things Need Oxygen. They Use This Oxygen During The Process of Creating Energy in Living CellsAngel LacabaNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument12 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesFazilaNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Today I, Kaustubh Goge Is Going To Show You My PresentationDocument8 pagesWelcome: Today I, Kaustubh Goge Is Going To Show You My PresentationPDG InfratechNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Research PaperDocument17 pagesOxygen Research PapersamirpriyanvadaNo ratings yet
- RTD#6 - Oxygen Cycle-GROUP 2Document2 pagesRTD#6 - Oxygen Cycle-GROUP 2Maria Therese DominguianoNo ratings yet
- Stages of The Oxygen CycleDocument1 pageStages of The Oxygen CycleMary PaladanNo ratings yet
- Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide CycleDocument9 pagesOxygen-Carbon Dioxide Cyclesheryll manlapasNo ratings yet
- CJR English For ChemistryDocument7 pagesCJR English For ChemistrySholeh KNo ratings yet
- CHEM 124 Group 5 Chemistry of The Atmosphere Written ReportDocument12 pagesCHEM 124 Group 5 Chemistry of The Atmosphere Written ReportsiegfredmauroNo ratings yet
- What Is The Oxygen Cycle?: Human BodyDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Oxygen Cycle?: Human BodyJEANY ROSE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and The AnthrosphereDocument22 pagesChemistry and The AnthrosphereMichelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of The Concept of LifeDocument3 pagesHistorical Development of The Concept of LifeShiene MarieNo ratings yet
- The Habitable Planet Unit 1 - Many Planets, One Earth - Online TextbookDocument4 pagesThe Habitable Planet Unit 1 - Many Planets, One Earth - Online TextbookSomtirtha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReportDocument40 pagesEarth Science ReportHyacinth CurativoNo ratings yet
- Chem BrochureDocument2 pagesChem BrochureHanis AliaNo ratings yet
- Biogeography Power Point CH 3Document23 pagesBiogeography Power Point CH 3naolseyoum01No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Global WarmingDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Global WarmingVamsi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Envisci BioDocument7 pagesEnvisci Biojay classroomNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CycleDocument58 pagesBiogeochemical CycleElanie SaranilloNo ratings yet
- Carbon Oxygen CycleDocument28 pagesCarbon Oxygen CycleGeorgette MatinNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Fisiologi Hewan AirDocument27 pagesLaporan Praktikum Fisiologi Hewan AirRobiansyahNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Ball Valve DS-25 - D1K.doc - ValvesDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Word - Ball Valve DS-25 - D1K.doc - Valvesmtpiping2572No ratings yet
- TIG Welding PDFDocument16 pagesTIG Welding PDFmesayan100% (4)
- Curriculum Vitae: I. Personal DataDocument21 pagesCurriculum Vitae: I. Personal DataAndri YunusNo ratings yet
- 2019 Use Price 161 PaperDocument33 pages2019 Use Price 161 PaperShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Erythritol Tetranitrate. Part I: Physical PropertiesDocument5 pagesCharacterization of Erythritol Tetranitrate. Part I: Physical PropertiesBernard ShamNo ratings yet
- LESER-Safety-Relief-Valve-High Performance Catalog en 07 2016Document102 pagesLESER-Safety-Relief-Valve-High Performance Catalog en 07 2016Mukiara LuffyNo ratings yet
- HACCP TemplateDocument28 pagesHACCP Templateraphael damanikNo ratings yet
- Flow Past Semicircular CylinderDocument8 pagesFlow Past Semicircular CylinderMohamad FaruqNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument22 pagesChemistryGuruKPO100% (1)
- NS1-18PAB-M-JEE-1002 R1 Erection Procedure For CW Piping InstallationDocument106 pagesNS1-18PAB-M-JEE-1002 R1 Erection Procedure For CW Piping Installationnamdq-1No ratings yet
- Fascia and AcupunctureDocument6 pagesFascia and AcupunctureRichard FosterNo ratings yet
- Coplastix Brochure 2006Document4 pagesCoplastix Brochure 2006bmpNo ratings yet
- Steel Water Tank Failure CalsDocument11 pagesSteel Water Tank Failure Calsriyazkader100% (1)
- Heat Equation in One - and Two-Dimensional Systems - Utkstair OrgDocument26 pagesHeat Equation in One - and Two-Dimensional Systems - Utkstair Orgar_frankNo ratings yet
- Aspen OLI V8 - 8 Readme PDFDocument2 pagesAspen OLI V8 - 8 Readme PDFVu TranNo ratings yet
- All in One SCIENCE - 10 - Activity - CH 1Document5 pagesAll in One SCIENCE - 10 - Activity - CH 1ShanthoshNo ratings yet
- Product Specification Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument64 pagesProduct Specification Dimensioning and TolerancingilroscioNo ratings yet
- Large-Scale Path LossDocument28 pagesLarge-Scale Path LossMoHsin KhNo ratings yet
- Astm F949Document11 pagesAstm F949Juan Carlos MendezNo ratings yet
- Rr410805 Process Modelling SimulationDocument8 pagesRr410805 Process Modelling SimulationSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Expamet ConstructionDocument95 pagesExpamet Constructionanele_amisNo ratings yet
- DNA Packaging by Enamul HaqueDocument27 pagesDNA Packaging by Enamul HaqueEnamul Haque100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Sieve AnalysisDocument20 pagesLesson 3 Sieve AnalysisjrNo ratings yet
- Low Zafin Jiki Nukiliya Makamashi: Sanyi Fusion, Kyauta Ikon Karya Kimiyya? (Taƙaitaccen A Harshen Hausa) / Cold Fusion: Free Energy Pseudo Science?Document498 pagesLow Zafin Jiki Nukiliya Makamashi: Sanyi Fusion, Kyauta Ikon Karya Kimiyya? (Taƙaitaccen A Harshen Hausa) / Cold Fusion: Free Energy Pseudo Science?Ben RusuisiakNo ratings yet
- Principle of UV SpectrosDocument2 pagesPrinciple of UV SpectrosJohn BobNo ratings yet
- Time 120Document3 pagesTime 120ardhra pNo ratings yet