Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SOUND&lens
Uploaded by
Leo LiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SOUND&lens
Uploaded by
Leo LiCopyright:
Available Formats
SOUND
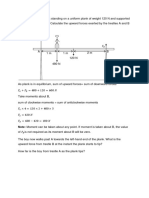
1 (a) Boy A and boy B are 150 m and 350 m respectively from a high wall. Boy A gives a clap
and boy B hears two claps 2 s apart. Calculate the speed of sound in air.
(b) A boy stands between two high walls. He claps his hands once and hears two echoes, one
after 0.5 s and the other 0.3 s after the first. Calculate the distance between the two walls given
that the speed of sound in air is 330 m/s.
LENSES
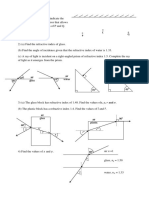
1) (a) A student is asked to measure the focal length f of a convex lens. A quick method is used
first to obtain a rough estimate for f. This is followed by a more accurate experiment.
For the quick estimate, the student forms a focused image of the Sun on a piece of card.
(i) Sketch a labelled diagram to show how f can be measured.
(ii) The student repeats the experiment in (a) using a window 4m away instead of the
Sun. State how this will affect the measurement obtained for f.
(b) A small object is placed 6 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm By means of a
ray diagram drawn to scale, find the nature, position and linear magnification of the image.
(c) A convex lens of focal length 30 cm is used to form a real image on a screen 90 cm from the
lens. By a ray diagram drawn to scale, find the object distance from the lens and the
magnification.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- X2 NotesDocument2 pagesX2 NotesLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- TST 2Document1 pageTST 2Leo LiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Extended PDFDocument1 pageExtended PDFLeo LiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Moment 2020Document1 pageMoment 2020Leo LiNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Diamondtir PDFDocument1 pageDiamondtir PDFLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- TransfDocument2 pagesTransfLeo LiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- 2 Ndterm 2015 TESTDocument3 pages2 Ndterm 2015 TESTLeo LiNo ratings yet
- SetprobDocument1 pageSetprobLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Report NE PDFDocument1 pageReport NE PDFLeo LiNo ratings yet
- LOCI in 2 DimensionsDocument2 pagesLOCI in 2 DimensionsLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- TST 2Document1 pageTST 2Leo LiNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- FrictDocument1 pageFrictLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- PrismDocument1 pagePrismLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- GravDocument2 pagesGravLeo LiNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Light ExerDocument1 pageLight ExerLeo LiNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- G 9 CicuitsDocument1 pageG 9 CicuitsLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Irregular PDFDocument1 pageMeasurement of Irregular PDFLeo LiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Measu ALLLLDocument5 pagesMeasu ALLLLLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Tape RecordingDocument2 pagesTape RecordingLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Exercises WS2019Document1 pageExercises WS2019Leo LiNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Moleg 3Document1 pageMoleg 3Leo LiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- G10 2020Document1 pageG10 2020Leo LiNo ratings yet
- Stecroixg 7Document2 pagesStecroixg 7Leo LiNo ratings yet
- Applicants Details: Mauritius Housing Company LTDDocument2 pagesApplicants Details: Mauritius Housing Company LTDLeo LiNo ratings yet
- WS PartIVDocument16 pagesWS PartIVLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Leh PointDocument1 pageLeh PointLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Farata SDocument2 pagesFarata SLeo LiNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Tuitiong 8Document1 pageTuitiong 8Leo LiNo ratings yet
- PIC X CT Us MriDocument1 pagePIC X CT Us MriLeo LiNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)