Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci Skill WKSHT
Uploaded by
sara gademOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sci Skill WKSHT
Uploaded by
sara gademCopyright:
Available Formats
Back Print
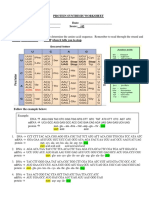
Name Class Date
Skills Worksheet
Protein Synthesis
INTERPRETING TABLES
Use the table below to complete items 1–17.
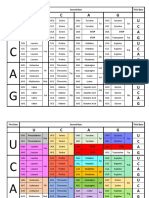
Codons in mRNA
First Second base Third
base U C A G base
UUU UCU UAU UGU U
Phenylalanine Tyrosine Cysteine
UUC UCC Serine UAC UGC C
U
UUA UCA UAA UGA Stop A
Leucine Stop
UUG UCG UAG UGG Tryptophan G
CUU CCU CAU CGU U
Histidine
CUC Leucine CCC CAC CGC Arginine C
C Proline
CUA CCA CAA CGA A
Glutamine
CUG CCG CAG CGG G
AUU ACU AAU AGU U
Asparagine Serine
AUC Isoleucine ACC Threonine AAC AGC C
A AUA ACA AAA AGA A
Lysine Arginine
AUG Start ACG AAG AGG G
GUU GCU GAU Aspartic GGU U
GUC Valine GCC Alanine GAC acid GGC Glycine C
G
GUA GCA GAA Glutamic GGA A
GUG GCG GAG acid GGG G
Complete the table below showing sequences of DNA, mRNA codons, anticodons,
and corresponding amino acids. Use the list of mRNA codons in the table above to
assist you in completing this exercise. Remember that the genetic code is based on
mRNA codons.
Decoding DNA
DNA 1. 2. GAT 3.
mRNA codon 4. 5. 6. UAU
Anticodon 7. UUC 8. 9.
Amino acid Tryptophan 10. 11. 12.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Science: Biology 19 Science Skills Worksheets
Back Print
Name Class Date
Protein Synthesis continued
Determine how the mutations below will affect each amino acid sequence. Use
the mRNA codons in the table on the previous page to complete items 13–16
below. In the space provided, write the names of the amino acids that correspond
to each mRNA sequence and mutation given. An example is provided for you.
Example:
mRNA sequence: UGU-CCG cysteine-proline
mutation sequence: UGC-CGC cysteine-arginine
13. mRNA sequence: GAA-CGU ___________________________
mutation sequence: GAU-CGU ___________________________
14. mRNA sequence: AUC-UGC ___________________________
mutation sequence: AUC-UGG ___________________________
15. mRNA sequence: UGU-CCU-CCU ___________________________
mutation sequence: UGU-UUC-CCU ___________________________
16. mRNA sequence: GGG-UUA-ACC ___________________________
mutation sequence: GGU-UAA ___________________________
17. What kind of mutation occurred to the mRNA sequence in item 16 above?
Explain.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Science: Biology 20 Science Skills Worksheets
Back Print
TEACHER RESOURCE PAGE
DNA Structure Gene Technology
INTERPRETING DIAGRAMS INTERPRETING DIAGRAMS
1. A. phosphate group 1. The structure labeled A is a plasmid.
B. pyrimidine (thymine) It is removed from the bacterial cell
C. hydrogen bond so that the plasmid can be used as a
D. purine (adenine) vector to carry the insulin gene into
E. deoxyribose a bacterial cell.
2. the hydrogen bonds between the 2. Restriction enzymes are used to cut
bases; cytosine and guanine form DNA. DNA molecules cut with restric-
three hydrogen bonds, whereas tion enzymes have sticky ends that
adenine and thymine form only allow different DNA fragments cut
two hydrogen bonds. with the same restriction enzyme to
3. TAA-GGC combine.
3. This is recombinant DNA. (The DNA
with the insulin gene and plasmid
Protein Synthesis DNA are combined).
4. This is a bacterial cell that contains
INTERPRETING TABLES recombined plasmids (plasmids con-
1. ACC taining the insulin gene).
2. TTC 5. CCGG and GGCC
3. ATA 6. pair on the left—GGCC/CCGG; pair on
4. UGG the right—CCGG/GGCC
5. AAG 7. Tetracycline, an antibiotic, destroys
6. CUA bacterial cells. Some bacterial cells,
7. ACC however, contain a gene for tetracy-
8. GAU cline resistance in their plasmid DNA,
9. AUA and they are not harmed by the antibi-
10. lysine otic. These cells are called tetracy-
11. leucine cline-resistant cells. In the diagram,
12. tyrosine the plasmid DNA used in the genetic
13. glutamic acid-arginine to aspartic acid- engineering experiment has the gene
arginine for tetracycline resistance. Only the
14. isoleucine-cysteine to isoleucine- cells that have taken up the plasmid
tryptophan DNA with the gene for tetracycline
15. cysteine-proline-proline to cysteine- resistance survive when tetracycline is
phenylalanine-proline added to the cultures. Only the resist-
16. glycine-leucine-threonine to glycine- ant cells, those that also carry the
stop gene of interest, survive.
17. A frameshift mutation occurred.
One of the G nucleotides and two C
nucleotides have been deleted. The
second codon is a stop codon, which
will cause translation to end prema-
turely. The protein for that gene will
be shortened and incomplete.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Science: Biology 93 Science Skills Worksheets Answer Key
You might also like
- Fast Facts: Les troubles d'oxydation des acides gras à chaîne longue: Comprendre, identifier et aiderFrom EverandFast Facts: Les troubles d'oxydation des acides gras à chaîne longue: Comprendre, identifier et aiderNo ratings yet
- DNA Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesDNA Protein Synthesis WorksheetKate Nicole AndraNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grading Examination-G10 ScienceDocument2 pages3rd Grading Examination-G10 ScienceMaria Conxedes GudesNo ratings yet
- mRNAcodonchart PDFDocument2 pagesmRNAcodonchart PDFFerdinand Fremista JrNo ratings yet
- Signature Assignment 4 Central Dogma 1Document5 pagesSignature Assignment 4 Central Dogma 1api-709276885No ratings yet
- Codon Chart: U C A G UDocument3 pagesCodon Chart: U C A G UyesNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Document6 pagesKami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila Corvalan100% (5)
- The RNA Codons: Arlegui, Ronnel A. MTW-11:30AM-12:30PM Bsn-Ii-F Biochemistry LectureDocument4 pagesThe RNA Codons: Arlegui, Ronnel A. MTW-11:30AM-12:30PM Bsn-Ii-F Biochemistry LecturePaul Orly FerrerNo ratings yet
- Genetics CodesDocument1 pageGenetics CodesNikko AdhitamaNo ratings yet
- Biology Mystery MonstersDocument2 pagesBiology Mystery Monstersapi-540074740No ratings yet
- Activity Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesActivity Protein SynthesissapirasapirasairaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Molecular Biology Control of Gene ExpressionDocument31 pages5.1 Molecular Biology Control of Gene ExpressionGebby TrisaswithaNo ratings yet
- Signature Assignment 4 Central DogmaDocument6 pagesSignature Assignment 4 Central Dogmaapi-724481252No ratings yet
- Cental DogmaDocument1 pageCental DogmaMinggay BragaisNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Tugas Biologi DNA Eugene DarmasaputraDocument1 pageJawaban Tugas Biologi DNA Eugene DarmasaputralouisNo ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument1 pageGenetic CodeCharmae OntingNo ratings yet
- Beta Globulin Gene SequenceDocument5 pagesBeta Globulin Gene SequenceB Riaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- CodonChart 1Document3 pagesCodonChart 1ESCUETA John RobertNo ratings yet
- 15 Gene Expression Translation SDocument6 pages15 Gene Expression Translation SHelp Me Study TutoringNo ratings yet
- Signature Assignment 4 Central DogmaDocument6 pagesSignature Assignment 4 Central Dogmaapi-631586093No ratings yet
- FILE 20230308 111109 Tutor-Genetics-solutionDocument25 pagesFILE 20230308 111109 Tutor-Genetics-solutionthuytrang21032004No ratings yet
- Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Document6 pagesGene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila CorvalanNo ratings yet
- Mutations With Frank The FrogDocument15 pagesMutations With Frank The FrogCathryn TuttleNo ratings yet
- 20 Amino Acids in Human ProteinDocument2 pages20 Amino Acids in Human Proteinpanomo nasabyNo ratings yet
- BCHS317 SU2.5 - Translation - FMDocument55 pagesBCHS317 SU2.5 - Translation - FMKAGISO BRIAN MOTSHUPHINo ratings yet
- Kirk Polka - Genetic Code WorksheetsDocument3 pagesKirk Polka - Genetic Code WorksheetsKirk PolkaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation WorksheetDocument3 pagesTranscription and Translation Worksheetjessica100% (2)
- DNA and RNA Codon Tables - WikipediaDocument17 pagesDNA and RNA Codon Tables - WikipediaRam GopalNo ratings yet
- Row 3 Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesRow 3 Protein Synthesis WorksheetRyanNo ratings yet
- Translation and ModificationDocument49 pagesTranslation and ModificationYasmin BalochNo ratings yet
- Trace The Code ObjectiveDocument3 pagesTrace The Code Objectiverommel rentoria100% (1)
- Dna TranslationDocument19 pagesDna Translationandrefc98No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis - MechanismsDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis - MechanismsKhaled Turk100% (2)
- Amino Acid and Codon TableDocument1 pageAmino Acid and Codon TableAsher Manangan100% (1)
- Lab Report Building Proteins From RNA 1 PDFDocument3 pagesLab Report Building Proteins From RNA 1 PDFLydia PainterNo ratings yet
- POGIL - Gene - Expression Translation SDocument8 pagesPOGIL - Gene - Expression Translation Sandrew fortneyNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument15 pagesDNA SequencingVINCENT ANGELO LINGANo ratings yet
- Activity About Central Dogma Science 10Document2 pagesActivity About Central Dogma Science 10cathlyn ranarioNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma Review KEYDocument8 pagesCentral Dogma Review KEYeula faith miracle andam0% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: DNA Base Pairing WorksheetDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: DNA Base Pairing Worksheetphil tolentinoNo ratings yet
- g10 Protein Synthesis 2023Document1 pageg10 Protein Synthesis 2023Lyn GomezNo ratings yet
- Activity Protein SythesisDocument5 pagesActivity Protein SythesisQueencess Ara Torres0% (1)
- Eac - Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesEac - Protein Synthesis WorksheetKyla DuenaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 BioDocument2 pagesActivity 2 BioTrafelgar DNo ratings yet
- Practicals in GeneticsDocument112 pagesPracticals in GeneticscarlosaeserranoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetEderlyn Zate100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidDocument33 pagesNucleic AcidchennielafleurNo ratings yet
- Camacho, Kate Frances G. / MEB 22 Lecture 5 Central Dogma: 5' Uuaaccggaugccguaaauuaaacg 3'Document1 pageCamacho, Kate Frances G. / MEB 22 Lecture 5 Central Dogma: 5' Uuaaccggaugccguaaauuaaacg 3'Kate CamachoNo ratings yet
- Requirements of Translation & Genetic CodeDocument13 pagesRequirements of Translation & Genetic CodeFenet AdamuNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Transcription & TranslationDocument1 page2.7 Transcription & TranslationMELANNIE SOFIA ORTIZ CUBIDESNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN SYNTHESIS - DELLAVA, James BDocument6 pagesPROTEIN SYNTHESIS - DELLAVA, James BJamesBuensalidoDellavaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following:: 9. What Are The Stop Codons? (Use Your mRNA Chart) UAA UAG UGADocument7 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following:: 9. What Are The Stop Codons? (Use Your mRNA Chart) UAA UAG UGAJamesBuensalidoDellava100% (1)
- Balauro Worksheet Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesBalauro Worksheet Protein SynthesisHami BalauroNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis and The Genetic CodeDocument16 pagesProtein Synthesis and The Genetic CodeDozdiNo ratings yet
- PR Report BoiiiiiDocument4 pagesPR Report BoiiiiibalucanjnNo ratings yet
- PCR ExtrategyDocument4 pagesPCR ExtrategyLeire HerbosoNo ratings yet
- Amino PotaDocument2 pagesAmino PotaArianaNo ratings yet
- 20 Standard Amino AcidsDocument3 pages20 Standard Amino AcidsAim Eden RamosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Central Dogma: 5' Uuaaccggaugccguaaauuaaacg 3'Document1 pageLecture 5 Central Dogma: 5' Uuaaccggaugccguaaauuaaacg 3'Kate CamachoNo ratings yet
- DMLS Vs SLM 3D Printing For Metal ManufacturingDocument1 pageDMLS Vs SLM 3D Printing For Metal Manufacturing曹大伟No ratings yet
- Pass Trinity Now 12 - Teacher BookDocument47 pagesPass Trinity Now 12 - Teacher BookMarina Mora GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of The Neurotoxin Domoic Acid in A Bloom-Forming DiatomDocument4 pagesBiosynthesis of The Neurotoxin Domoic Acid in A Bloom-Forming DiatomHamidun BunawanNo ratings yet
- DRDRA Assessment - Part46Document1 pageDRDRA Assessment - Part46azereth bartonNo ratings yet
- 6640 MSDSDocument4 pages6640 MSDSShaikhRizwanNo ratings yet
- Ch-12 Surface TensionDocument21 pagesCh-12 Surface Tensionpandya.mamta1981No ratings yet
- FEM - Solid - Mechanics - 2022-2023Document52 pagesFEM - Solid - Mechanics - 2022-2023houda houbanNo ratings yet
- Merged TL Feedback PDFDocument295 pagesMerged TL Feedback PDFThembisa NobethaNo ratings yet
- The Language of Psychology: APA Style As EpistemologyDocument9 pagesThe Language of Psychology: APA Style As EpistemologyMafalda Lourenço SantosNo ratings yet
- اساسيات هندسة انتاج النفط والغاز-محول (051-075)Document25 pagesاساسيات هندسة انتاج النفط والغاز-محول (051-075)روان الباشاNo ratings yet
- Spec. For InsulationDocument45 pagesSpec. For InsulationVivek ShettyNo ratings yet
- Marks and Spencer Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesMarks and Spencer Literature Reviewc5p0cd99100% (1)
- Wind System in The WorldDocument4 pagesWind System in The WorldFarrel LeroyNo ratings yet
- A Motivational View of Learning Performance and Behavior ModificationDocument15 pagesA Motivational View of Learning Performance and Behavior ModificationAndrewsNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: TA-FE230/FE330R/FE530RDocument23 pagesService Manual: TA-FE230/FE330R/FE530RDame1612No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document47 pagesChapter 3yasinNo ratings yet
- FE Imp QuestionsDocument8 pagesFE Imp QuestionsYeswanth PaluriNo ratings yet
- 0450 - Volume V.4Document47 pages0450 - Volume V.4Billy MakoyNo ratings yet
- To All Stock Exchanges Bse Limited National Stock Exchange of India Limited New York Stock ExchangeDocument314 pagesTo All Stock Exchanges Bse Limited National Stock Exchange of India Limited New York Stock ExchangeMohammad Faizan MansooriNo ratings yet
- How To Write Case Comment - Simple GuideDocument3 pagesHow To Write Case Comment - Simple GuidepranjalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Geometry 7esDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Geometry 7esGrizz P100% (3)
- #2-Crash Course World History The Indus Valley CivilizationDocument2 pages#2-Crash Course World History The Indus Valley CivilizationBrian RappNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Tank Survey (MFL) and RepairDocument14 pagesMethod Statement For Tank Survey (MFL) and RepairMG67% (3)
- Addis Ababa Science & Technology University: College of Electrical & Mechanical EngineeringDocument91 pagesAddis Ababa Science & Technology University: College of Electrical & Mechanical Engineeringliyou eshetuNo ratings yet
- The Si-Traceable Calibration of Shunted Reference Solar Cells Via Differential Spectral Responsivity MeasurementsDocument3 pagesThe Si-Traceable Calibration of Shunted Reference Solar Cells Via Differential Spectral Responsivity MeasurementsShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Result BrickhallDocument2 pagesResult BrickhallmrpankeyksrulesNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam Syllabus Class IVDocument3 pagesAnnual Exam Syllabus Class IVMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- In PlantsDocument23 pagesIn PlantsRobert Darwin GabrielNo ratings yet
- Homework #4 MEMS6460: (30 Points)Document7 pagesHomework #4 MEMS6460: (30 Points)vidhukiran100% (1)
- A Report of The Aspen Institute's Dialogue On Sustainable Water Infrastructure in The USDocument43 pagesA Report of The Aspen Institute's Dialogue On Sustainable Water Infrastructure in The USapi-25924194100% (2)