Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.7 Transcription & Translation
Uploaded by
MELANNIE SOFIA ORTIZ CUBIDESCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.7 Transcription & Translation
Uploaded by
MELANNIE SOFIA ORTIZ CUBIDESCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2.
7: TRAnSCRIPTIOn & TRAnSLATIOn
Transcription Types of RNA
Transcription is the synthesis of an RNA sequence from a DNA template Three main types of RNA may be produced:
• This process occurs within the nucleus of a cell • mRNA – Transcript used to make protein
• tRNA – Transfers amino acid to ribosome
Transcription is mediated by the enzyme RNA polymerase, which:
• rRNA – Catalytic component of ribosome
• Separates the DNA strands (breaks H bonds between base pairs)
• Covalently joins free complementary RNA nucleotides together
After transcription, the RNA is released to the cytoplasm (for translation)
and the DNA remains within the nucleus and reforms a double helix mRNA tRNA rRNA
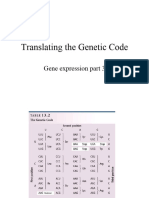
Genetic Code
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in UUU UCU UAU UGU
Phe Tyr Cys
mRNA sequences is converted into a polypeptide sequence UUC UCC
Ser
UAC UGC
UUA UCA UAA STOP UGA STOP
Leu
UUG UCG UAG STOP UGG Trp
Codons: Triplets of bases which correspond to a particular amino acid CUU CCU CAU CGU
His
CUC CCC CAC CGC
Leu Pro Arg
The order of the codons determines the amino acid sequence for a protein CUA CCA CAA CGA
Gln
CUG CCG CAG CGG
• A coding sequence always begins with a start codon (AUG) AUU ACU AAU AGU
Asn Ser
• A coding sequence is terminated with a stop codon AUC Ile ACC AAC AGC
Thr
AUA ACA AAA AGA
Lys Arg
AUG Met ACG AAG AGG
The genetic code has two key features: GUU GCU GAU GGU
Asp
GUC GCC GAC GGC
• Universality – All organisms use the same genetic code Val Ala Gly
GUA GCA GAA GGA
Glu
• Degeneracy – Multiple codons may code for the same amino acid GUG GCG GAG GGG
Translation
Translation is the process of polypeptide synthesis by the ribosome tRNA polypeptide amino acid
• Messenger RNA (mRNA) is transported to the ribosome
• A ribosome reads an mRNA sequence in base triplets called codons
• Each codon codes for a specific amino acid (as per the genetic code)
• Amino acids are transported to ribosomes by transfer RNA (tRNA)
• Each tRNA aligns opposite a codon via a complementary anticodon anticodon codon
• The ribosome moves along the mRNA sequence (5’ → 3’) and joins
amino acids together with peptide bonds (condensation reaction)
• The synthesis of a polypeptide is initiated at a start codon (AUG)
and is completed when the ribosome reaches a STOP codon ribosome
mRNA
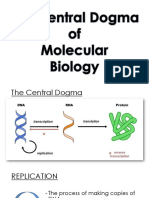
Gene → Protein
A gene is a sequence of DNA which encodes a polypeptide sequence
DNA (gene)
• One gene = one polypeptide (proteins may have multiple polypeptides)
transcription
There are exceptions to this fundamental relationship:
• Genes may be alternatively spliced (one gene = many polypeptides) mRNA
• Genes encoding tRNA or rRNA are transcribed but not translated translation
• Genes may be mutated to alter the original polypeptide product polypeptide
You might also like
- Protein Synthesis and the Genetic Code Overview (39Document15 pagesProtein Synthesis and the Genetic Code Overview (39SeemaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis and The Genetic CodeDocument16 pagesProtein Synthesis and The Genetic CodeDozdiNo ratings yet
- Requirements of Translation & Genetic CodeDocument13 pagesRequirements of Translation & Genetic CodeFenet AdamuNo ratings yet
- BCHS317 SU2.5 - Translation - FMDocument55 pagesBCHS317 SU2.5 - Translation - FMKAGISO BRIAN MOTSHUPHINo ratings yet
- Dna TranslationDocument19 pagesDna Translationandrefc98No ratings yet
- Mekanisme EvolusiDocument25 pagesMekanisme EvolusiSeKarNo ratings yet
- Translation: By: Puspa Julistia Puspita, S.Si, M.Sc. @genetika Dan Biologi MolekulerDocument31 pagesTranslation: By: Puspa Julistia Puspita, S.Si, M.Sc. @genetika Dan Biologi MolekulervinaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Molecular Biology Control of Gene ExpressionDocument31 pages5.1 Molecular Biology Control of Gene ExpressionGebby TrisaswithaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Document6 pagesKami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila Corvalan100% (5)
- Protein Synthesis RevisionDocument22 pagesProtein Synthesis RevisionKrishnendu RoyNo ratings yet
- Mutations With Frank The FrogDocument15 pagesMutations With Frank The FrogCathryn TuttleNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument57 pagesProtein SynthesisMary Joy FalcesoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Building Proteins From RNA 1 PDFDocument3 pagesLab Report Building Proteins From RNA 1 PDFLydia PainterNo ratings yet
- Signature Assignment 4 Central Dogma 1Document5 pagesSignature Assignment 4 Central Dogma 1api-709276885No ratings yet
- 15 Gene Expression Translation SDocument6 pages15 Gene Expression Translation SHelp Me Study TutoringNo ratings yet
- Molecular Gen E6Document31 pagesMolecular Gen E6L fNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Document6 pagesGene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila CorvalanNo ratings yet
- Translation and ModificationDocument49 pagesTranslation and ModificationYasmin BalochNo ratings yet
- Dna and Protein SynthesisDocument37 pagesDna and Protein SynthesisPrabhuNo ratings yet
- 10.translation & Protein StructureDocument29 pages10.translation & Protein StructureRaunak JalanNo ratings yet
- Signature Assignment 4 Central DogmaDocument6 pagesSignature Assignment 4 Central Dogmaapi-724481252No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument57 pagesProtein SynthesisEaron Van JaboliNo ratings yet
- Genetic Material: Prodi Pendidikan Biologi UIN Walisongo Semarang 2019Document40 pagesGenetic Material: Prodi Pendidikan Biologi UIN Walisongo Semarang 2019elina lestariyanti UIN Walisongo SemarangNo ratings yet
- POGIL - Gene - Expression Translation SDocument8 pagesPOGIL - Gene - Expression Translation Sandrew fortneyNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis2Document56 pagesProtein Synthesis2Adegboye Seun100% (1)
- Bacterial Transcriptional Regulation: Transcription Is The First Stage in Gene ExpressionDocument48 pagesBacterial Transcriptional Regulation: Transcription Is The First Stage in Gene ExpressionoctusNo ratings yet
- Biology Mystery MonstersDocument2 pagesBiology Mystery Monstersapi-540074740No ratings yet
- Sci Skill WKSHTDocument3 pagesSci Skill WKSHTsara gademNo ratings yet
- Mod1 PDFDocument84 pagesMod1 PDFPrashant KachhawahaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To GeneticsDocument43 pagesAn Introduction To Geneticsrifatalib4u3504No ratings yet
- 10 Gene Expression LecturesDocument61 pages10 Gene Expression LecturesTererai Lalelani Masikati HoveNo ratings yet
- signature assignment 4 central dogmaDocument6 pagessignature assignment 4 central dogmaapi-631586093No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis - MechanismsDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis - MechanismsKhaled Turk100% (2)
- PM703 Practical Biotechnology (2019) PM703 Practical Biotechnology (2019)Document20 pagesPM703 Practical Biotechnology (2019) PM703 Practical Biotechnology (2019)Hadeer DaifAllahNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma: DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument28 pagesThe Central Dogma: DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationJovit Angelo David100% (1)
- DNA Replication and Transcription Virtual LabDocument6 pagesDNA Replication and Transcription Virtual LabJuan Luis Nevarez MartinezNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument20 pagesTranslationSherilyn MutoNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Codon Tables - WikipediaDocument17 pagesDNA and RNA Codon Tables - WikipediaRam GopalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Solution Chapter 1+2+3Document28 pagesTutorial Solution Chapter 1+2+3Nguyen Minh HoangNo ratings yet
- 05' Protein Synthesis AnimationDocument12 pages05' Protein Synthesis Animationmustafa aliNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document55 pagesUnit 3adithyaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-10-05 at 13.33.13Document17 pagesScreenshot 2021-10-05 at 13.33.13asfsd asdsfasNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis 2Document11 pagesProtein Synthesis 2Avijit MondalNo ratings yet
- Simulating Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesSimulating Protein Synthesis25210580No ratings yet
- Lecture5 - Gene Functions - Proteins and EnzymesDocument25 pagesLecture5 - Gene Functions - Proteins and EnzymesGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis IIDocument57 pagesProtein Synthesis IIJosephine AcioNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 Self-Learning Module 3 Central Dogma of The Transfer of Genetic InformationDocument16 pagesScience: Quarter 3 Self-Learning Module 3 Central Dogma of The Transfer of Genetic InformationKaye ViolaNo ratings yet
- How DNA Codes for Genetic Information in CellsDocument46 pagesHow DNA Codes for Genetic Information in CellsZade DakkakNo ratings yet
- Human β-globin Gene Sequence Reveals Sickle-Cell MutationDocument5 pagesHuman β-globin Gene Sequence Reveals Sickle-Cell MutationB Riaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 - Protein SynthesisDocument45 pagesTopic 12 - Protein SynthesisKaye LapizNo ratings yet
- 12c-Genetic CodeDocument19 pages12c-Genetic CodeGlen John Tamayo AmbolNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code HMDocument30 pagesGenetic Code HMdrhmpatel100% (2)
- PCR ExtrategyDocument4 pagesPCR ExtrategyLeire HerbosoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingKent100% (2)
- Genetic Material Chromosomes DNA ReplicationDocument25 pagesGenetic Material Chromosomes DNA ReplicationYudi Santoso0% (1)
- Protein Synthesis2Document56 pagesProtein Synthesis2Naila NurrobbaniNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma Review KEYDocument8 pagesCentral Dogma Review KEYeula faith miracle andam0% (1)
- COVID-19 Information: Ncbi S Kip To Main Content S Kip To Navigation Resources How To A Bout NCBI AccesskeysDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Information: Ncbi S Kip To Main Content S Kip To Navigation Resources How To A Bout NCBI AccesskeyscatheirneNo ratings yet
- Inactivates .: Insulin, Secreted by The Pancreas When Blood Glucose Is High, Stimulates PP-1, WhichDocument5 pagesInactivates .: Insulin, Secreted by The Pancreas When Blood Glucose Is High, Stimulates PP-1, Whichratih puspasariNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure & Sequence Model-Remote Learning VersionDocument2 pagesDNA Structure & Sequence Model-Remote Learning VersionstellaNo ratings yet
- Elmer J Sabalilag Stem 1: Mitosis MeiosisDocument1 pageElmer J Sabalilag Stem 1: Mitosis MeiosisAria NichiNo ratings yet
- World of Corn 2005Document10 pagesWorld of Corn 2005National Corn Growers AssociationNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Certificate (Mummy)Document1 pageVaccine Certificate (Mummy)Aàdesh SámudreNo ratings yet
- FHSC1234 Tutorial 9S 202210Document5 pagesFHSC1234 Tutorial 9S 202210Zhi YongNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Business Possibilities and ProspectsDocument106 pagesBiotechnology Business Possibilities and ProspectsPramod MalikNo ratings yet
- NSF-ITR: EIA-0086015: Structural DNA NanotechnologyDocument93 pagesNSF-ITR: EIA-0086015: Structural DNA NanotechnologyShashank GargNo ratings yet
- Paul Rabinow - Making PCR - A Story of Biotechnology (1996) PDFDocument98 pagesPaul Rabinow - Making PCR - A Story of Biotechnology (1996) PDFWagner AlvesNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - (Group 1.2) Els Reporting Module 24 Genetic EngineeringDocument61 pagesPart 1 - (Group 1.2) Els Reporting Module 24 Genetic EngineeringJerico CastilloNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Applications of Biotechnology in AgricultureDocument18 pagesQuarter 4 Applications of Biotechnology in AgriculturegabriellouiemadriagaNo ratings yet
- Diagrama en BlancoDocument1 pageDiagrama en BlancoDIEGO ANDRES GIRALDO UTRIANo ratings yet
- 01 Hiv Taqman48Document37 pages01 Hiv Taqman48Sp PpvNo ratings yet
- CTAB ExtractionDocument3 pagesCTAB ExtractionJanikaa Singaravel MuruganNo ratings yet
- AP Biology: Student Interactive Learning GuideDocument20 pagesAP Biology: Student Interactive Learning GuideA ForeverNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalDocument71 pagesBiochemistry FinalJanie-Vi Gorospe100% (2)
- Intro To Med. ChemDocument30 pagesIntro To Med. ChemF ParikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Food Safety Hazards: This Page Is Part of The Guidance Document Repository (GDR)Document20 pagesChapter 4: Food Safety Hazards: This Page Is Part of The Guidance Document Repository (GDR)Rajam SankarNo ratings yet
- Complement Fixation Test Detects AntibodiesDocument9 pagesComplement Fixation Test Detects AntibodiesMunir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Ligation ReactionDocument4 pagesTroubleshooting Ligation ReactionSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Klebsiella Pneumoniae: A Major Worldwide Source: and Shuttle For Antibiotic ResistanceDocument24 pagesKlebsiella Pneumoniae: A Major Worldwide Source: and Shuttle For Antibiotic ResistancerehanaNo ratings yet
- I. A New Diet: Table 1.the Biological Effects of InsulinDocument9 pagesI. A New Diet: Table 1.the Biological Effects of InsulinmelisaNo ratings yet
- MS-MS Analysis Programs - 2012 SlidesDocument14 pagesMS-MS Analysis Programs - 2012 SlidesJovanderson JacksonNo ratings yet
- Microbial Toxins PDFDocument11 pagesMicrobial Toxins PDFAnonymous OPix6Tyk5INo ratings yet
- DNA RAN Prot Syn Web PracticeDocument11 pagesDNA RAN Prot Syn Web PracticeTimothy MacdonaldNo ratings yet
- Milliplex - Analyte QuarterlyDocument40 pagesMilliplex - Analyte QuarterlyFrancisco SiirNo ratings yet
- Southern Blotting TechniqueDocument5 pagesSouthern Blotting TechniqueVĩnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Drug DesignDocument38 pagesDrug DesignPhArMaCyGrAdUaTeSNo ratings yet
- FREE CV - Resume SampleDocument2 pagesFREE CV - Resume Samplesadiamushtaq822No ratings yet