Professional Documents
Culture Documents
hw02 PDF
Uploaded by
shum kenneth0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views1 pageOriginal Title
hw02.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views1 pagehw02 PDF
Uploaded by
shum kennethCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
HW #2:
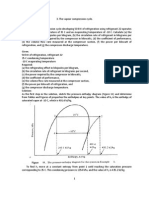
1. An ideal single-stage vapor compression refrigeration cycle
uses R-22 as the working fluid. The condensing temperature is
110 F (43 C) and the evaporating temperature is 40 F (4.5 C).
The system produces 10 tons (35.2 kW) of cooling effect.
Determine the (a) coefficient of performance, (b) refrigerating
efficiency, (c) hp/ton (kW input per kW of refrigeration), (d)
mass flow rate of the refrigerant, (e) theoretical input to the
compressor in hp (kW), and (f) theoretical piston displacement
of the compressor in cfm (m3/s).
2. A vapor compression refrigeration cycle uses R-22 and
follows the theoretical single-stage cycle. The condensing
temperature is 48 C, and the evaporating temperature is -18 C.
The power input to the cycle is 2.5 kW, and the mass flow rate
of refrigerant is 0.05 kg/s. Determine (a) the heat rejected from
the condenser, (b) the coefficient of performance, (c) the
enthalpy at the compressor exit, and (d) the refrigerating
efficiency.
3. Estimate how much money (in HK$) is needed each day if
the seven chillers at HKUST operate continuously for 12 hours
a day. Consider the energy consumption of the chiller only.
(Hints: Assume the refrigeration capacity of each chiller is 3517
kW and COP=3.7).
You might also like
- EME2146 Tutorial 6Document2 pagesEME2146 Tutorial 6iwqb0% (1)
- TutorialX RefrigerationCycleDocument1 pageTutorialX RefrigerationCycleAnurag Kumar0% (1)
- Tutorial 2-Questions (Air-Craft ARC) : Simple Gas Refrigeration CycleDocument3 pagesTutorial 2-Questions (Air-Craft ARC) : Simple Gas Refrigeration CycleRajaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesAssignment 1 Solutions PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- Table 3-3 Psychrometric PropertiesDocument2 pagesTable 3-3 Psychrometric Propertiesshum kennethNo ratings yet
- ME 405 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Question BankDocument6 pagesME 405 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Question BankDeepakNo ratings yet
- Ref Systems - Review ProblemsDocument1 pageRef Systems - Review Problemswaar lockNo ratings yet
- Air Con Past Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesAir Con Past Exam QuestionsSamarth PatelNo ratings yet
- Section-1: Basic and Modified Vapor Compression CyclesDocument2 pagesSection-1: Basic and Modified Vapor Compression CyclesCesar ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesSample QuestionsnakatsuswanNo ratings yet
- RAC AssignmentDocument7 pagesRAC AssignmentSoumikSabyasachi50% (2)
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Pallav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Answers: (A) 0.434, (B) 21.4 KW, (C) 0.478Document2 pagesAnswers: (A) 0.434, (B) 21.4 KW, (C) 0.478Neil BrionesNo ratings yet
- Cap 04Document3 pagesCap 04Jorge PozoNo ratings yet
- Old Question Papers 2006-11-2Document27 pagesOld Question Papers 2006-11-2Sandip GurnuleNo ratings yet
- ME16104 - 1st AssignmentDocument3 pagesME16104 - 1st AssignmentManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper ME 604ADocument11 pagesSample Question Paper ME 604Amumtaz alamNo ratings yet
- The Vapour Compression Cycle (Sample Problems)Document3 pagesThe Vapour Compression Cycle (Sample Problems)allovid33% (3)
- Assignment No 2Document2 pagesAssignment No 2ISHPAL singhNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning (1) - Sheets SolutionDocument25 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning (1) - Sheets SolutionMohamed Maher100% (3)
- RacDocument6 pagesRacYogesh DanekarNo ratings yet
- Share 'Sheet 2 Air ConditioningDocument2 pagesShare 'Sheet 2 Air ConditioningBfhf HdhgNo ratings yet
- Class Test Sets NewDocument7 pagesClass Test Sets NewNSS GBPECNo ratings yet
- Tutorials Refrigiration and Heat Pumps 2024 ThermoDocument2 pagesTutorials Refrigiration and Heat Pumps 2024 Thermosphesihlemchunu40No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Process Tutorial 4 1Document2 pagesThermodynamic Process Tutorial 4 1Boon Khai ChienNo ratings yet
- Carnot CycleDocument2 pagesCarnot CycleJom Ancheta BautistaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper For RACDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper For RACSDvidyaNo ratings yet
- 1418395957089Document3 pages1418395957089MahendraMeenaNo ratings yet
- Ciclos RefrigeracionDocument64 pagesCiclos RefrigeracionSergyNo ratings yet
- Tut 4Document1 pageTut 4me21b105No ratings yet
- Assaingment Rac 1Document6 pagesAssaingment Rac 1Hariom MouryaNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: No of Pages: 2 Course Code: 12M504Document2 pagesInstructions:: No of Pages: 2 Course Code: 12M504CRAZY PIANO PLAYERNo ratings yet
- Ques 1Document6 pagesQues 1ANKIT KUMAR0% (1)
- Set 9Document2 pagesSet 9Carlos Alberto Huamaní GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1Esmail AnasNo ratings yet
- RAC Tutorial Sheet 2Document3 pagesRAC Tutorial Sheet 2Ankur Sachdeva0% (1)
- Assignment 4 - RefrigerationDocument2 pagesAssignment 4 - RefrigerationJade PurezaNo ratings yet
- Rac Gtu SumsDocument8 pagesRac Gtu SumsNainesh SorathiyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (ECE3153)Document1 pageAssignment 5 (ECE3153)Shahul14No ratings yet
- Rac Assignment BvcoeDocument6 pagesRac Assignment BvcoeRAGULNo ratings yet
- HW2 2023Document1 pageHW2 2023Wilfred LeeNo ratings yet
- Ref Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesRef Review ProblemsGiancarlo SantosNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument8 pagesRefrigerationHectorCabz0% (1)
- Old Question Papers 2006-11-2 PDF FreeDocument27 pagesOld Question Papers 2006-11-2 PDF FreeAYUSH SINGHALNo ratings yet
- ATD Module3 Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesATD Module3 Practice ProblemsKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- ME405 RAC Question BankDocument8 pagesME405 RAC Question BankDeepakNo ratings yet
- Thermo Long ProblemDocument2 pagesThermo Long ProblemRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument16 pagesThermoİBRAHİM HAZAR AYTULUNNo ratings yet
- Irs qb1Document4 pagesIrs qb1PachaiyappanRangaNathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment On 'Refrigeration Cycle'Document3 pagesAssignment On 'Refrigeration Cycle'Anonymous GGtvR65MRNo ratings yet
- Etd 2mechDocument2 pagesEtd 2mechgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- Problem Set #2 - ChE 124 - Summer 2018Document3 pagesProblem Set #2 - ChE 124 - Summer 2018SkambalahardarNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument1 pagePDF DocumentMidas Troy VictorNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument11 pagesUntitled DocumentIan Beaver Santos BautistaNo ratings yet
- CT 4 (Rac)Document2 pagesCT 4 (Rac)Swati SachanNo ratings yet
- ATD AssignmentDocument2 pagesATD AssignmentsamarthgkNo ratings yet
- Taller Corte 2Document5 pagesTaller Corte 2Ayder Fabian Rincón RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Maths RefrigerationDocument9 pagesMaths RefrigerationMaherNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 Refrigeration System BDA 3043 - Thermodynamics II Winardi SaniDocument4 pagesTutorial 4 Refrigeration System BDA 3043 - Thermodynamics II Winardi Saniwanpudin0% (1)
- Sample Ideal Refrigeration ProblemsDocument1 pageSample Ideal Refrigeration ProblemsJames AguilarNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 1Document2 pagesProblems Set 1suby0% (1)
- 01 Intro PDFDocument11 pages01 Intro PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering and Society - CIVL1100 - 1 Sept 2016Document55 pagesCivil Engineering and Society - CIVL1100 - 1 Sept 2016shum kennethNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - CIVL1100 - 2016F PDFDocument1 pageCourse Outline - CIVL1100 - 2016F PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - CIVL1100 - 2016F PDFDocument1 pageCourse Outline - CIVL1100 - 2016F PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- 04 Moist Air Properties & PDFDocument70 pages04 Moist Air Properties & PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro PDFDocument11 pages01 Intro PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- hw06 PDFDocument2 pageshw06 PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- hw02 SolutionDocument2 pageshw02 Solutionshum kennethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 0114Document15 pagesChapter 3 0114Cyduck Guevarra100% (2)
- hw02 SolutionDocument2 pageshw02 Solutionshum kennethNo ratings yet
- HW01 Refanswer PDFDocument2 pagesHW01 Refanswer PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- hw08 PDFDocument2 pageshw08 PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- hw03 PDFDocument1 pagehw03 PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- hw06 PDFDocument2 pageshw06 PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- hw05 PDFDocument1 pagehw05 PDFshum kennethNo ratings yet
- MECH4340 hw01Document1 pageMECH4340 hw01Andi LiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 Solutionsshum kennethNo ratings yet