Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 Electric Circuits Practice Test PDF
Uploaded by
skgaddeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8 Electric Circuits Practice Test PDF
Uploaded by
skgaddeCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Circuits Practice Test Name: _______________________
I. VOCABULARY
Date: ___________ Period: _____
If the underlined word is used incorrectly, cross it out and replace it with the correct word.
1. The rate of flow of electric charge is called resistance and it is measured with the unit joule.
2. Current is the electric potential energy per charge. It comes from the wires. The unit is the ohm.
3. Resistors in a circuit increase the flow of charge. This obstruction is called voltage.
4. Resistors dissipate mechanical energy into heat. The rate at which this occurs is called load.
5. In a series circuit each resistor has the same voltage.
II. SERIES AND PARALLEL
6. Two resistors are connected in series. 7. Two resistors are connected in parallel.
9V 𝑉2 10 V
What is: 𝐼1 What is:
(a) 𝐼1 ? ________ (a) 𝐼1 ? ________
𝑉2
𝐼1 2A (b) 𝑉2? ________ 2A (b) 𝑉2? ________
(c) 𝑃? ________ 6A (c) 𝑃? ________
12 V
III. MULTIPLE CHOICE
10 V 2Ω 6Ω 100 V 200 Ω
8. In the circuit shown above, what is the 9. How much power is dissipated by the resistor
current through the 2-ohm resistor? in the circuit shown above?
A 0.2 A C 0.8 A A 25 watts C 50 watts
B 5.0 A D 8.0 A B 100 watts D 800 watts
IV. SOLVING CIRCUITS
10. A 4 Ω and a 6 Ω resistor are connected in series, the current is measured to be 4 A.
(a) Draw a diagram of this circuit. (b) What is the voltage drop (c) What is the voltage drop
across the 4 Ω resistor? across the 6 Ω resistor?
(d) What is the total voltage of (e) What is the total power
the power source? dissipated by the circuit?
Fremont Physics ©Kepple 2013
Electric Circuits – Page#8
Electric Circuits Study Guide 𝑉 = 𝐼𝑅 𝑃 = 𝐼𝑉
Ohm’s Law Joule’s Law
Voltage (𝑽) Current (𝑰) Resistance (𝑹) Power (𝑷)
unit: volt (V) unit: ampere (A) unit: ohm () unit: watt (W)
The electric potential The amount of charge A measure of the The rate at which energy
energy per charge. that passes by a point obstruction to the flow is transformed in an
each second. of electric charge. electric circuit.
SERIES CIRCUIT PARALLEL CIRCUIT
𝑅1
𝑉 𝑅2 𝑉 𝑅1 𝑅2
Resistors are connected on the same path. Resistors are connected across the same points.
There are no breaks in the wire, so each Each R is connected across the same points, so
resistor receives an equal current. each resistor receives an equal voltage.
𝐼 = 𝐼1 = 𝐼2 𝑉 = 𝑉1 = 𝑉2
The electrons have to pass through BOTH The wire branches into separate paths, so the
resistors, so the voltage is split between each. current is split between each path.
𝑉 = 𝑉1 + 𝑉2 𝐼 = 𝐼1 + 𝐼2
Additional resistors increase total resistance. Additional resistors decrease total resistance.
1 1 1
𝑅 = 𝑅1 + 𝑅2 = +
𝑅 𝑅1 𝑅2
SIMPLE CIRCUIT EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE
A circuit with one battery and one resistor. The value of a single resistor which would
replace a combination of multiple resistors.
𝐼
8 8 16
𝑉 𝑅
series combination 𝑅 ↑ and 𝐼 ↓
8
Voltage (𝑉) is provided by the battery. 4
Current (𝐼) flows from the positive to the 8
negative terminal of the battery.
Resistance (𝑅) is determined by the resistor. parallel combination 𝑅 ↓ and 𝐼 ↑
1) current, ampere; 2) voltage, battery, volt; 3) decrease, resistance; 4) electrical, power;
5) series, current; 6) 2 A, 3 V, 24 W; 7) 4 A, 10 V, 60 W;
You might also like
- Short Questions Power System For Competitive Exams Prepared by Venkatesh, Siddhartha Engineering CollegeDocument15 pagesShort Questions Power System For Competitive Exams Prepared by Venkatesh, Siddhartha Engineering Collegevenki249100% (11)
- ElectDocument188 pagesElectMeet Joshi100% (1)
- Typical Questions and AnswersDocument158 pagesTypical Questions and Answersiragire viateurNo ratings yet
- Electricity StructuredDocument10 pagesElectricity StructuredZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DC MachinesDocument2 pagesTutorial DC MachinesSujan ChandNo ratings yet
- RME Supplementary Problem-1Document10 pagesRME Supplementary Problem-1Reneboy LambarteNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations and Finding Speeds from Time ProblemsDocument4 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations and Finding Speeds from Time ProblemsVincent Doroy De Cardo100% (1)
- Vignan's Lara Institute DC Motor AssignmentsDocument6 pagesVignan's Lara Institute DC Motor AssignmentsVenkat ManiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuizDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice QuizMHLS68No ratings yet
- Est Q&a 1Document4 pagesEst Q&a 1Sharmaine CarlosNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Interview Questions and Answers: by ManishDocument107 pagesElectric Circuits Interview Questions and Answers: by ManishSaitejaNo ratings yet
- Resistance Electricity Class X Science Ncert Ncert Questions Science Class 10 Chapter 1 Ncert Notes Electrical ResistivityDocument2 pagesResistance Electricity Class X Science Ncert Ncert Questions Science Class 10 Chapter 1 Ncert Notes Electrical ResistivityPranavMehtaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS: CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONSDocument3 pagesPHYSICS: CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONSHercules ShahNo ratings yet
- Questions On Single Phase Series CircuitsDocument45 pagesQuestions On Single Phase Series Circuitskibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- 10 CPT Model Papers - With AnswersDocument558 pages10 CPT Model Papers - With AnswersRajesh DorbalaNo ratings yet
- EARLY SKY MASTER ELECTRICIAN REVIEW PREBOARD EXAM 1Document6 pagesEARLY SKY MASTER ELECTRICIAN REVIEW PREBOARD EXAM 1Teodoro Jr de Jesus100% (1)
- Questions & Answers On Circuit Elements and Kirchhoff's LawsDocument28 pagesQuestions & Answers On Circuit Elements and Kirchhoff's Lawskibrom atsbha100% (2)
- Electric Circuits Lab ManualDocument33 pagesElectric Circuits Lab Manualsheikmd80% (5)
- Tutorial 5 - DC MachinesDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 - DC MachinesMohdFirdausNo ratings yet
- Voltage-Level Detectors Using Op-AmpDocument7 pagesVoltage-Level Detectors Using Op-AmpMatt Imri0% (1)
- Ohm's Law 1Document5 pagesOhm's Law 1rajesh_patel_007No ratings yet
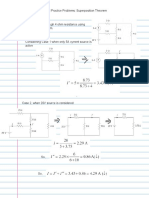
- Solved and Practice Problems: Superposition TheoremDocument3 pagesSolved and Practice Problems: Superposition TheoremmeowkkNo ratings yet
- Circuit QuestionsDocument2 pagesCircuit QuestionsCatherine Dharshini LabrooyNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Philippine Electrical Code PEC Part 5 REE Board ExamDocument19 pagesMCQ in Philippine Electrical Code PEC Part 5 REE Board ExamManuel DizonNo ratings yet
- EE Objectives - 1Document575 pagesEE Objectives - 1Joshua MenesesNo ratings yet
- 1q Induciton MotorDocument14 pages1q Induciton Motorprabhjot singh1100% (2)
- Capacitors & Energy StorageDocument44 pagesCapacitors & Energy StoragearuunrsNo ratings yet
- MCQ Electrical Circuits ECE Board Exam PracticeDocument180 pagesMCQ Electrical Circuits ECE Board Exam Practiceian rafael japsayNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Models and Performance AnalysisDocument36 pagesTransmission Line Models and Performance AnalysisCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Answer KeyDocument2 pagesElectric Circuits Answer KeySabu Lazer50% (2)
- Series & Parallel Capacitor Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesSeries & Parallel Capacitor Practice ProblemsJustin Turner80% (5)
- Rectifier Device Converts AC to DCDocument5 pagesRectifier Device Converts AC to DCpreethiNo ratings yet
- Set B Pec June 18Document7 pagesSet B Pec June 18aeilorv infanteNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions on Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions on Single Phase AC CircuitssanjuNo ratings yet
- 02 BJTs & BJT Amplifiers-ProblemsDocument4 pages02 BJTs & BJT Amplifiers-ProblemsntldvlaiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Submitted ToDocument7 pagesLab Report: Submitted ToMd. Al Amin 201-15-34790% (1)
- Close Exam 7Document4 pagesClose Exam 7sieged_rj3165No ratings yet
- Rigid Conduit Locknut Bushing GuideDocument4 pagesRigid Conduit Locknut Bushing Guidesieged_rj3165No ratings yet
- Power Elex Finals PDFDocument5 pagesPower Elex Finals PDFDanilo PerezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BJT DevicesDocument22 pagesChapter 3 BJT DevicesDaNieL RuPErTONo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Electrical Measurement and InstrumentationDocument24 pagesLecture 5 Electrical Measurement and InstrumentationAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- AMPLIFIERSDocument4 pagesAMPLIFIERStinNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoffs Law Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesKirchhoffs Law Problems and SolutionsSpencer HayesNo ratings yet
- 04AP Physics C - Capacitance and DielectricsDocument16 pages04AP Physics C - Capacitance and DielectricsJs ChongNo ratings yet
- 109-TOP-AC Objectives PDFDocument11 pages109-TOP-AC Objectives PDFVea ValcorzaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Ohm's Law WorksheetDocument2 pages5 - Ohm's Law WorksheetNaveed Ahmed100% (1)
- Ee 6604 Design of Electrical Machines Question BankDocument12 pagesEe 6604 Design of Electrical Machines Question BankAlex Neo XanderNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4Document13 pagesLab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4api-439639600No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Questions-3Document1 pageElectrical Engineering Questions-3tutulkarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky ISBN 0132622262 9780132622264Document31 pagesSolution Manual For Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky ISBN 0132622262 9780132622264lauraNo ratings yet
- DC BIASING - BJTs: Key ConceptsDocument44 pagesDC BIASING - BJTs: Key ConceptsUgeswran ThamalinggamNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik BJTDocument35 pagesKarakteristik BJTKrisna Adji SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Lec 14 - Electric CircuitsDocument37 pagesLec 14 - Electric CircuitsNikky SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Electricity ConceptsDocument4 pagesElectricity ConceptsKaustubh FFNo ratings yet
- Q3 - STE - Week 2 - Electric Current and Ohms LawDocument38 pagesQ3 - STE - Week 2 - Electric Current and Ohms LawVinz RegenciaNo ratings yet
- Circuits Packet 1Document8 pagesCircuits Packet 1Jyannejm MaylasNo ratings yet
- Complete DC Circuit NotesDocument59 pagesComplete DC Circuit NotesIsha chandravanshiNo ratings yet
- Resistors in Series and ParallelDocument27 pagesResistors in Series and ParallelRaymund EspinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To e Commerce PDFDocument209 pagesIntroduction To e Commerce PDFZayNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Formulae: White PaperDocument9 pagesEarned Value Formulae: White PaperWaqaar Ali VirkNo ratings yet
- Study On The Competitiveness of The Toy Industryecsip - enDocument96 pagesStudy On The Competitiveness of The Toy Industryecsip - enAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stock Market Investment StrategiesDocument62 pagesAnalysis of Stock Market Investment Strategieschetanbaviskar0_6175No ratings yet
- Introduction To e Commerce PDFDocument209 pagesIntroduction To e Commerce PDFZayNo ratings yet
- Stocksinal PDFDocument62 pagesStocksinal PDFskgaddeNo ratings yet
- Oil Analysis Handbook-6.5x9 2017 Web SinglesDocument120 pagesOil Analysis Handbook-6.5x9 2017 Web Singlesjuanmanuel_4615958No ratings yet
- Itdf PDFDocument2 pagesItdf PDFskgaddeNo ratings yet
- Itdf PDFDocument2 pagesItdf PDFskgaddeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To e Commerce PDFDocument209 pagesIntroduction To e Commerce PDFZayNo ratings yet
- QNX Technical PresentationDocument57 pagesQNX Technical PresentationskgaddeNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Main12 PDFDocument52 pagesMain12 PDFskgaddeNo ratings yet
- Neet PG Book FinalDocument88 pagesNeet PG Book FinalkdkoshalNo ratings yet
- VXLB Ki 5 S APk CDocument234 pagesVXLB Ki 5 S APk CskgaddeNo ratings yet
- 2011 04 05 Safety and Reliability PatternsDocument16 pages2011 04 05 Safety and Reliability PatternsskgaddeNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump Defrost Control Book - 34-4101-07Document38 pagesHeat Pump Defrost Control Book - 34-4101-07skgadde100% (1)
- The C Puzzle BookDocument93 pagesThe C Puzzle Bookabhijeetnayak67% (3)
- Testing PrimerDocument43 pagesTesting PrimerAndrei CiobanuNo ratings yet
- RTOSDocument259 pagesRTOSskgaddeNo ratings yet
- Apt 0406Document6 pagesApt 0406skgaddeNo ratings yet
- Hitech C ManualDocument364 pagesHitech C ManualKailash KumarNo ratings yet
- India Solar Power Plant VPCDocument35 pagesIndia Solar Power Plant VPCShashwat YadavNo ratings yet
- 32 PDP Code ImpDocument37 pages32 PDP Code ImpskgaddeNo ratings yet
- Cold Weld Cracking of HSLA SteelDocument3 pagesCold Weld Cracking of HSLA Steelarjun prajapatiNo ratings yet
- CPP-Solution of Triangle SMC NEWDocument2 pagesCPP-Solution of Triangle SMC NEWtechnical yogeshNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Characterization - F&aDocument580 pagesReservoir Characterization - F&aОлег КупчинськийNo ratings yet
- Ac Generator TheoryDocument3 pagesAc Generator TheoryKrizelle ManaloNo ratings yet
- NEW BENNI - Manual de ServicioDocument678 pagesNEW BENNI - Manual de ServicioSantiago CosNo ratings yet
- Astm-e855 Изгиб МеталлаDocument8 pagesAstm-e855 Изгиб МеталлаАлесь БуяковNo ratings yet
- FOR Approval Specification: 32.0" Wxga TFT LCD TitleDocument42 pagesFOR Approval Specification: 32.0" Wxga TFT LCD TitleJulio Alberto Cabrera RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Conductor Ampacity Based On The 2017 National Electrical Code®Document1 pageConductor Ampacity Based On The 2017 National Electrical Code®Ira Jane LosañezNo ratings yet
- Small Wheel Loader, 924K, 930K and 938K, 926M, 930M and 938M Hydraulic System, 478-9871-01 PDFDocument16 pagesSmall Wheel Loader, 924K, 930K and 938K, 926M, 930M and 938M Hydraulic System, 478-9871-01 PDFMuhammad Zeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- Volume 2 Highways Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special StructuresDocument86 pagesVolume 2 Highways Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special Structuresgeorge santiagoNo ratings yet
- Notes For Paper 6Document25 pagesNotes For Paper 6RamY El NahasNo ratings yet
- Catalogue C-Pac Asia W Mee15k019 RevDocument30 pagesCatalogue C-Pac Asia W Mee15k019 RevNguyễn Xuân Điệp100% (1)
- Crystal Field Stabilisation Energies of Octahedral Complexes (CFSEsDocument2 pagesCrystal Field Stabilisation Energies of Octahedral Complexes (CFSEsAyushi JoshyaNo ratings yet
- Bending Moment CoefficientsDocument2 pagesBending Moment CoefficientssabishanuNo ratings yet
- Percubaan 2 Matematik SPM 09Document6 pagesPercubaan 2 Matematik SPM 09khai_83No ratings yet
- Tank Nozzle Loads - CalcstressDocument11 pagesTank Nozzle Loads - CalcstressDam VoNo ratings yet
- Appendix 02 - Ground Survey Report of The Surrounding AreaDocument165 pagesAppendix 02 - Ground Survey Report of The Surrounding AreaMai_hung_trungNo ratings yet
- JKSSB Je Me 2015 103 A Series 470e8f91Document17 pagesJKSSB Je Me 2015 103 A Series 470e8f91ZAFFAR GANINo ratings yet
- Powder Properties Test Method Alm Pa 650: Nylon 12 Laser Sintering MaterialDocument1 pagePowder Properties Test Method Alm Pa 650: Nylon 12 Laser Sintering MaterialLuiskar MedinaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium (8 Mark Questions)Document6 pagesIonic Equilibrium (8 Mark Questions)Nagesh NangiNo ratings yet
- Study Habits Guide: Effective vs Ineffective TechniquesDocument30 pagesStudy Habits Guide: Effective vs Ineffective TechniquesJustin Dave TiozonNo ratings yet
- L-BL2 User ManualDocument40 pagesL-BL2 User ManualrubiodegoNo ratings yet
- Ritz Carlton-Residential Curtain Wall F19 - Calculation Note - Rev 01Document102 pagesRitz Carlton-Residential Curtain Wall F19 - Calculation Note - Rev 01hisambergNo ratings yet
- Quadrant+SystemDocument34 pagesQuadrant+SystemVM ViKasNo ratings yet
- Chem2exam2 PDFDocument6 pagesChem2exam2 PDFLouis ParrNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument34 pagesSolving Quadratic EquationsJaninne Villa Del Rey100% (1)
- Atom Percent Fission in Uranium and Plutonium Fuel (Neodymium-148 Method)Document9 pagesAtom Percent Fission in Uranium and Plutonium Fuel (Neodymium-148 Method)astewayb_964354182No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: 10. Perturbation TheoryDocument46 pagesPhysical Chemistry: 10. Perturbation TheoryToujours BlackroseNo ratings yet
- Preformulation and Product Development: Bishnu Prasad KoiralaDocument59 pagesPreformulation and Product Development: Bishnu Prasad Koiralasaloni patelNo ratings yet
- Design of Beam Slide ShareDocument26 pagesDesign of Beam Slide ShareVRKVRK10No ratings yet