Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solomon-121012140059-Phpapp02 146
Uploaded by
Elrey AnatolOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solomon-121012140059-Phpapp02 146
Uploaded by
Elrey AnatolCopyright:
Available Formats
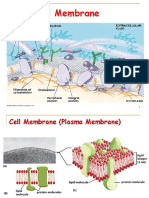
Key Point
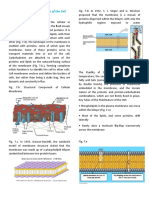
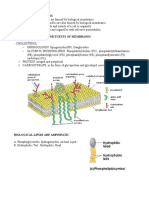
According to the fluid mosaic model, a cell membrane is composed of a fluid bilayer
of phospholipids in which proteins move about like icebergs in a sea.
Carbohydrate
chains
Glycoprotein
Carbohydrate Extracellular fluid
chain Hydrophobic
Hydrophilic
Glycolipid
Cholesterol
α-helix
Hydrophilic Integral
Peripheral proteins
protein
Cytosol
Figure 5-6 Detailed structure of the plasma membrane
Although the lipid bilayer consists mainly of phospholipids, other regions on both sides of the bilayer, connected by a membrane-
lipids, such as cholesterol and glycolipids, are present. Peripheral pro- spanning a-helix. Glycolipids (carbohydrates attached to lipids) and
teins are loosely associated with the bilayer, whereas integral proteins glycoproteins (carbohydrates attached to proteins) are exposed on the
are tightly bound. The integral proteins shown here are transmem- extracellular surface; they play roles in cell recognition and adhesion to
brane proteins that extend through the bilayer. They have hydrophilic other cells.
brane only once, whereas others wind back and forth as many can be easily removed from the membrane without disrupting
as 24 times. The most common kind of transmembrane protein the structure of the bilayer.
is an a-helix (see Chapter 3) with hydrophobic amino acid side
chains projecting out from the helix into the hydrophobic re-
gion of the lipid bilayer. Some proteins span the membrane in Proteins are oriented asymmetrically
the form of rolled-up b-pleated sheets. These protein formations
across the bilayer
are barrel shaped and form pores through which water and other
substances can pass. One of the most remarkable demonstrations that proteins are ac-
Peripheral membrane proteins are not embedded in the tually embedded in the lipid bilayer comes from freeze – fracture
lipid bilayer. They are located on the inner or outer surface of electron microscopy, a technique that splits the membrane into
the plasma membrane, usually bound to exposed regions of in- halves. The researcher can literally see the two halves of the mem-
tegral proteins by noncovalent interactions. Peripheral proteins brane from “inside out.” When cell biologists examine membranes
Biological Membranes 111
You might also like
- Welding CalculatorDocument18 pagesWelding CalculatorKhamdi AfandiNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane (Structure and Function)Document150 pagesCell Membrane (Structure and Function)Dr. Tapan Kr. Dutta100% (1)
- 2 4 Plasma MembraneDocument22 pages2 4 Plasma Membraneıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- The Structural Components of The Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesThe Structural Components of The Cell MembraneJanine CambaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Movement BiochemDocument9 pagesLipid Movement BiochemCrowNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeKimberly C. Javier100% (1)
- FFPMDocument171 pagesFFPMGulyam Maribasappa Rajendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- SOM 201 Cellular MembranesDocument34 pagesSOM 201 Cellular Membraneskxng crockedNo ratings yet
- ISPE Good Practice Guide Compressed Air Specifications - Compressed Air Testing - Trace AnalyticsCompressed Air Testing - Trace AnalyticsDocument2 pagesISPE Good Practice Guide Compressed Air Specifications - Compressed Air Testing - Trace AnalyticsCompressed Air Testing - Trace AnalyticsAnonymous FZs3yBHh7No ratings yet
- 001 Detail Welding Map For Site Project Economizer (PLTU Malinau 2x3 MW)Document22 pages001 Detail Welding Map For Site Project Economizer (PLTU Malinau 2x3 MW)Muhammad Fitransyah Syamsuar Putra100% (2)
- Biogas PDFDocument12 pagesBiogas PDFKhang TrầnNo ratings yet
- Name: Kristine Joy Atos Block: BSN 1-D Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesName: Kristine Joy Atos Block: BSN 1-D Practice ProblemsJenz Hope Segui Novela100% (3)
- Model 10 10fb 11 Carbon HousingsDocument4 pagesModel 10 10fb 11 Carbon HousingsrezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument91 pagesLecture 4 - Membrane Structure and Function202310446No ratings yet
- The Structural Components of The Cell Membrane and Its Functions, With Transport Mechanisms.Document17 pagesThe Structural Components of The Cell Membrane and Its Functions, With Transport Mechanisms.Vieyah Angela VicenteNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure LecDocument11 pagesCell Structure LecMax DelvalleNo ratings yet
- BC368 Biochemistry of The Cell II: Biological MembranesDocument41 pagesBC368 Biochemistry of The Cell II: Biological Membranesparik kakaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane ZDocument79 pagesCell Membrane ZhediyeNo ratings yet
- ch10 Biomembrane structure-LODISHDocument79 pagesch10 Biomembrane structure-LODISHHurmat AmnaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Cell Biology and Its Application BI-1202: 2009, RRE/AB, SITH ITBDocument20 pagesCell Membrane Cell Biology and Its Application BI-1202: 2009, RRE/AB, SITH ITBFachrudin HanafiNo ratings yet
- 2A Cell BiologyDocument53 pages2A Cell Biologyfimig11681No ratings yet
- Biologi CHP 6 Sem 1Document81 pagesBiologi CHP 6 Sem 1Aliaa AkbarNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Organization Part1Document7 pagesCellular-Organization Part1Nina IlaganNo ratings yet
- Structure of PhospholipidsDocument8 pagesStructure of Phospholipidsnevio.wirtgenNo ratings yet
- Membrana EstuDocument81 pagesMembrana Estuemmanuel.diaz17No ratings yet
- A407433177 - 23745 - 23 - 2019 - Plasma Membrane - Compressed PDFDocument111 pagesA407433177 - 23745 - 23 - 2019 - Plasma Membrane - Compressed PDFDiotima BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 4 BiomembranesDocument43 pages4 Biomembranesc3rberussNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument15 pagesCell MembraneAbaz BabicNo ratings yet
- 2.B.1 Cell Membranes: Cell Membranes Are Selectively Permeable Due To Their StructureDocument24 pages2.B.1 Cell Membranes: Cell Membranes Are Selectively Permeable Due To Their Structureapi-373344212No ratings yet
- K Struktur Dan Fungsi Membran SelDocument34 pagesK Struktur Dan Fungsi Membran SelYusardi R PradanaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Genomes MacromoleculesDocument10 pagesCells and Genomes MacromoleculesAkmad SugodNo ratings yet
- What Is A MembraneDocument16 pagesWhat Is A MembranesameerNo ratings yet
- 2022 Cell MembraneDocument49 pages2022 Cell MembraneAwais RehmanNo ratings yet
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditDocument13 pagesq1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditInele Ellia AgReNo ratings yet
- SDL AssignmentDocument6 pagesSDL Assignmentmandaliya.krishna26No ratings yet
- Cell Membranes - TheoryDocument3 pagesCell Membranes - TheoryBrooke MorganNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 6Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 6JewelNo ratings yet
- Tissue BiochemistryDocument3 pagesTissue BiochemistryNeelam MehtabNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Membranes StructureDocument43 pages1.3 Membranes StructuregvreevrevNo ratings yet
- BTY117 L1aDocument7 pagesBTY117 L1aRuchikaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesCell Membrane Structure and FunctionkyleeebooggNo ratings yet
- CBS Lipids and Membrane Structure KEATS 22 - 23Document22 pagesCBS Lipids and Membrane Structure KEATS 22 - 23Arm UdomratNo ratings yet
- Structure of Cell Membrane: Surabhi Roll No. - 39Document24 pagesStructure of Cell Membrane: Surabhi Roll No. - 39Kumar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- CSIR Life Science Sample Cell BiologyDocument17 pagesCSIR Life Science Sample Cell Biologygamer zoneNo ratings yet
- The Cell MembraneDocument36 pagesThe Cell Membraneanulorance98No ratings yet
- Structure of Cell Membrane & Cellular Junctions: Pradeep Singh M.Sc. Medical Biochemistry Himsr, Jamia HamdardDocument37 pagesStructure of Cell Membrane & Cellular Junctions: Pradeep Singh M.Sc. Medical Biochemistry Himsr, Jamia HamdardFarhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 03 - The Structure of M. PlasmaDocument26 pages03 - The Structure of M. PlasmaZANUBA ULYA’ HAURA CELLIN 1No ratings yet
- 2 Cell Membrane 20210908Document83 pages2 Cell Membrane 20210908Sayan KonarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Jnu Biomembranes-1 - 複本Document48 pagesChapter 4-Jnu Biomembranes-1 - 複本Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Lect 1 Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument67 pagesLect 1 Membrane Structure and FunctionIzukanji kayoraNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2Document4 pagesGenbio 2Mhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Cell Components 2015Document114 pagesCell Components 2015Jacob MasikaNo ratings yet
- Biological MembranesDocument31 pagesBiological MembranesHimani Jha100% (1)
- BIO 315. NotesDocument42 pagesBIO 315. NotesKevin KipropNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of C.MDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of C.MFahad NaeemNo ratings yet
- 01.5 Bio Lec TransDocument8 pages01.5 Bio Lec TransKyleNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument72 pagesCell MembraneDonisha Janah DonaireNo ratings yet
- CMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadDocument24 pagesCMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument60 pagesMembrane Structure and FunctionRawanNo ratings yet
- Study Exercise Biology 10-12 97.03Document7 pagesStudy Exercise Biology 10-12 97.03Fabiola Vania FeliciaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Membrane StructureDocument2 pages2.4 Membrane StructurelaranbazziiNo ratings yet
- Bio - 3 3 - Student EditionDocument4 pagesBio - 3 3 - Student EditionjoodNo ratings yet
- Module: 3 Food Lipids Lesson M.III.10Document4 pagesModule: 3 Food Lipids Lesson M.III.10Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Genbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerEleah MelchorNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism 1Document15 pagesTransport Mechanism 1tlmargullanoNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument16 pagesCell Membraneeishawajid75No ratings yet
- Figure 5-7 Membrane Proteins: AnimatedDocument1 pageFigure 5-7 Membrane Proteins: AnimatedElrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-8 Composite Diagram of An Animal Cell: AnimatedDocument1 pageFigure 4-8 Composite Diagram of An Animal Cell: AnimatedElrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-7 Composite Diagram of A Plant Cell: AnimatedDocument1 pageFigure 4-7 Composite Diagram of A Plant Cell: AnimatedElrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Solomon-121012140059-Phpapp02 130Document1 pageSolomon-121012140059-Phpapp02 130Elrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-1 Biological Size and Cell Diversity: MeasurementsDocument1 pageFigure 4-1 Biological Size and Cell Diversity: MeasurementsElrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Solomon-121012140059-Phpapp02 45Document1 pageSolomon-121012140059-Phpapp02 45Elrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Three Domains:: Eukarya Bacteria ArchaeaDocument1 pageThree Domains:: Eukarya Bacteria ArchaeaElrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Organism: Figure 1-6 The Hierarchy of Biological OrganizationDocument1 pageOrganism: Figure 1-6 The Hierarchy of Biological OrganizationElrey Anatol0% (1)
- Solomon-121012140059-Phpapp02 264Document1 pageSolomon-121012140059-Phpapp02 264Elrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Meterbox SpecificationsDocument1 pageMeterbox Specifications4ctechNo ratings yet
- Potassium Iodide - Wikipedia PDFDocument92 pagesPotassium Iodide - Wikipedia PDFAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- PH-2102 SR L-1 Furan Chemistry 13Document3 pagesPH-2102 SR L-1 Furan Chemistry 13Mahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Biological Roles of Water - Why Is Water Necessary For Life - Science in The NewsDocument17 pagesBiological Roles of Water - Why Is Water Necessary For Life - Science in The NewsJoel SteveNo ratings yet
- Adopting Multifunctional Material SystemsDocument197 pagesAdopting Multifunctional Material Systems_AniMuS__No ratings yet
- Chem01 - Matter Concept MapDocument1 pageChem01 - Matter Concept MapKerzona Harriet CababasadaNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilisation Using Flyash: Civil EngineeringDocument28 pagesSoil Stabilisation Using Flyash: Civil EngineeringNeeraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4HSAB TheoryDocument15 pagesChapter 4HSAB TheoryAnurag NihalNo ratings yet
- BenzaldehydeDocument9 pagesBenzaldehydeMichelle AngelaNo ratings yet
- EAMCET-QR-Chemistry-Jr Chem-2.Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument13 pagesEAMCET-QR-Chemistry-Jr Chem-2.Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiespvnchem100% (1)
- CH 7Document30 pagesCH 7Eman AlbastawyNo ratings yet
- GPH-BUET Test ReportDocument24 pagesGPH-BUET Test ReportAtikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chap03 TemperatureNHeatDocument24 pagesChap03 TemperatureNHeatsamtomNo ratings yet
- Fluidum R11Document2 pagesFluidum R11عبدالعزيز مقيطوفNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysical Science ReviewerMary Angeline L. BatacNo ratings yet
- CHE 029 - Exercise No 1Document3 pagesCHE 029 - Exercise No 1ronduexNo ratings yet
- Blunt Et Al, 2011Document73 pagesBlunt Et Al, 2011Elena LópezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Problems 1,, Straightforward, IntermediateDocument12 pagesChapter 22 Problems 1,, Straightforward, Intermediatecobalt boronNo ratings yet
- LAB 1 Growth of E. ColiDocument24 pagesLAB 1 Growth of E. ColiYusof SundangNo ratings yet
- Z Energy Limited: Safety Data SheetDocument11 pagesZ Energy Limited: Safety Data SheetRajeshNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument14 pagesPresentationshu-sunanNo ratings yet
- A Procedure To Obtain The Effective Nuclear Charge From The Atomic Spectrum of SodiumDocument3 pagesA Procedure To Obtain The Effective Nuclear Charge From The Atomic Spectrum of SodiumBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- Piccs 2012 PDFDocument1,614 pagesPiccs 2012 PDFAnnabelle GuilingNo ratings yet