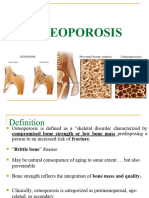
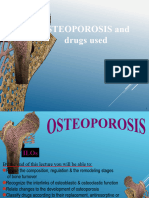
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Management
Uploaded by
Anastasya Gishella RorongOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Management
Uploaded by
Anastasya Gishella RorongCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing management:
- Exercise and promoting independence (to maintain present muscle tone and strength)
- physical safety; (to promote body alignment that will serve to defer further deformity and
complications and to increase her mobility and independence)
- maintaining sufficient oxygen in tissue;
- the ability to hear verbal communications.
- Diet modification; increase calcium and vit D intake, promote reabsorption of calcium
- Encourage the patient to avoid excessive alcohol which can inhibits the formation of the bone
and ability to absorb calcium and may increase fall risk
- Deafness, related to either age or disease might lead to social isolation and patients should
have audiometry and provision of a hearing aid if necessary
Medical management:
- Control weight
- Adequate dietary calcium and vit D supplements
- Pain medication Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
- Bisphosphonate (retard bone resorption such as Fosamax by attaching to bone surface to
inhibit osteoclastic activity)
- Calcium supplements
- Drugs to reduce bone resorption/turnover:
Calcitonin
Cytotoxic antibiotic (mithracin) if severe
- Surgery:
- Orthopedic surgical procedures;
Corrective osteotomy
Fracture fixation
Spinal decompression
Joint arthtoplasty
Tumor resection
You might also like
- Nursing Priorities: 8 Fracture Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document10 pagesNursing Priorities: 8 Fracture Nursing Care Plan (NCP)PagodNo ratings yet
- ABC ACLS Checklist Online CY2020 21Document8 pagesABC ACLS Checklist Online CY2020 21Anastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Sta. Rosa Community Hospital, Sta. Rosa City, Laguna: Actual DeliveryDocument1 pageSta. Rosa Community Hospital, Sta. Rosa City, Laguna: Actual DeliveryAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- A. Pusey Murray (MRS) RN, Cert Psych Nursing & Nursing Admin, BSC (Hons), MPH, Dip. Ed. PHD (C)Document31 pagesA. Pusey Murray (MRS) RN, Cert Psych Nursing & Nursing Admin, BSC (Hons), MPH, Dip. Ed. PHD (C)okaciaNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Done By: Dalal Hussain AlanaziDocument15 pagesOsteoporosis: Done By: Dalal Hussain AlanazidallasNo ratings yet
- Nur 149 p3w3 Fri Part1 Session 22 Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument55 pagesNur 149 p3w3 Fri Part1 Session 22 Musculoskeletal DisordersAlliah Marie CababarosNo ratings yet
- MusculoSensory - TCA #3 - Osteoporosis Osteoarthritis DDDDocument8 pagesMusculoSensory - TCA #3 - Osteoporosis Osteoarthritis DDDapi-3822433No ratings yet
- Bones and DrugsDocument24 pagesBones and DrugsEuro UndisaNo ratings yet
- Sem Osteoporosis (Edit)Document31 pagesSem Osteoporosis (Edit)Rhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Dr. Lubna DwerijDocument26 pagesOsteoporosis: Dr. Lubna DwerijNoor MajaliNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument22 pagesOsteoporosisPrachi DSaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics BoneDisordersDocument20 pagesOrthopedics BoneDisordersannapanna1No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument60 pagesMusculoskeletal Systempetite_chien15No ratings yet
- Four Types of Cells in BoneDocument5 pagesFour Types of Cells in BoneTazrian Islam FarihaNo ratings yet
- Basics: Arthritis, OsteoDocument5 pagesBasics: Arthritis, Osteorahel_ppdunpattiyahoNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis Clinical Case by SlidesgoDocument30 pagesOsteoporosis Clinical Case by SlidesgoHussein Al-jmrawiNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis 1Document4 pagesOsteoporosis 1api-3822433No ratings yet
- Reported by Nacito, Julie Ann T. & Tiongson, Annie Joy MDocument19 pagesReported by Nacito, Julie Ann T. & Tiongson, Annie Joy MTrixie Marie Sabile AbdullaNo ratings yet
- OSTEOPOROSISDocument33 pagesOSTEOPOROSISSelvaraj ChinnasamyNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument9 pagesOsteoporosisRenuka Sivaram71% (7)
- Skeletal System Vanitys PartDocument6 pagesSkeletal System Vanitys PartJM ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting On Osteoporosis #3Document14 pagesDrugs Affecting On Osteoporosis #3Aryan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Pharma Agasbsn2-ADocument4 pagesAssignment in Pharma Agasbsn2-AMahdiyah AgasNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Bone MetabolismDocument15 pagesDrugs For Bone MetabolismkwennybiangNo ratings yet
- Osteitis DeformansDocument4 pagesOsteitis Deformansmhuggnetoh19No ratings yet
- ORTHOPAEDICSDocument135 pagesORTHOPAEDICSJimmy MainaNo ratings yet
- 2023 MSSDocument34 pages2023 MSSmerga wekwayaNo ratings yet
- Paget's Disease of The BoneDocument9 pagesPaget's Disease of The BonePam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting On Osteoporosis: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, Pharmd International Medical UniversityDocument25 pagesDrugs Effecting On Osteoporosis: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, Pharmd International Medical UniversityRtxGaming Zone 73No ratings yet
- Penyakit DegeneratifDocument108 pagesPenyakit DegeneratifYauffa Hanna Elt MisykahNo ratings yet
- 3 OsteoporosisDocument6 pages3 Osteoporosisiraqeana100100No ratings yet
- Strength of Osteoporotic Bone Is Impaired By:: Name: Johne Vincent V. Sarian Year/Section/Group: BSN 4-6 Group 4Document9 pagesStrength of Osteoporotic Bone Is Impaired By:: Name: Johne Vincent V. Sarian Year/Section/Group: BSN 4-6 Group 4Dodong GalitNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument35 pagesOsteoporosisFarida Abo ElmagdNo ratings yet
- Name of Disorder: Osteoporosis Description: Osteoporosis Is A Bone Disease That Occurs When The Body Loses Too MuchDocument2 pagesName of Disorder: Osteoporosis Description: Osteoporosis Is A Bone Disease That Occurs When The Body Loses Too MuchAnjelika Noelle SilvaNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument33 pagesOsteoporosisNadya LiemNo ratings yet
- Masculoskeletal Disorders PharmacotherapyDocument101 pagesMasculoskeletal Disorders PharmacotherapyWaaqoo Guutuu Waaqoo GuutuuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document13 pagesChapter 9Zaky DavidiaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatologic Disorders: OsteoporosisDocument7 pagesRheumatologic Disorders: Osteoporosisمحمد رحمان محمد الدليميNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocument5 pagesOsteoporosis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsEmeka JusticeNo ratings yet
- Metabolic and Endocrine DisordersDocument76 pagesMetabolic and Endocrine DisordersMika Kresna100% (1)
- OsteoporosisDocument13 pagesOsteoporosisRuaa MalekNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument33 pagesOsteoporosisCiptadi Permana Wijaya100% (1)
- Clubfoot TreatmentDocument2 pagesClubfoot Treatmenthellven11No ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument201 pagesOrthopedic NursingMitch Hellgirl Almonte100% (2)
- Osteoarthritis ATI: PG 461Document20 pagesOsteoarthritis ATI: PG 461mp1757No ratings yet
- Kelompok 6 OsteoporosisDocument10 pagesKelompok 6 OsteoporosisNur Indah FitrianaDewiNo ratings yet
- OP ملونة كاملةDocument27 pagesOP ملونة كاملةArcangela QuaintrelleNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument24 pagesOsteoporosisMousa SuhailNo ratings yet
- Mus Culo SkeletalDocument26 pagesMus Culo SkeletalCristy Ellain EsparteroNo ratings yet
- In The Name of GodDocument46 pagesIn The Name of GodGalaxyNo ratings yet
- A Bone FractureDocument2 pagesA Bone FractureMarkimz AligaenNo ratings yet
- SR 2Document33 pagesSR 2hussein alnasryNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis Edited 100201092008 Phpapp02Document32 pagesOsteoporosis Edited 100201092008 Phpapp02Maya SwariNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis v1Document24 pagesOsteoporosis v1Abegail Bautista DoriaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in OsteoporosisDocument30 pagesDrugs Used in Osteoporosissigit_riyantonoNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec 6Document2 pagesANAPHY Lec 6Mary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PhysiologyDocument25 pagesSkeletal System PhysiologyJonathan Young XDNo ratings yet
- Biologic and Biophysical Technologies. FINALDocument28 pagesBiologic and Biophysical Technologies. FINALRafael Miguel MallillinNo ratings yet
- NCMB316 OsteoporosisDocument11 pagesNCMB316 Osteoporosis3-B-4 NAVIA, Kyle Bless V.No ratings yet
- Paget'S Disease: Presented By-Riya Kumari Basic BSC 2 Year College of NursingDocument20 pagesPaget'S Disease: Presented By-Riya Kumari Basic BSC 2 Year College of NursingRashi SinghNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis WorkDocument5 pagesOsteoporosis WorkMostafa Al AtwehNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Threats in The Twenty-First Century: Strengthening The Global ResponseDocument12 pagesInfectious Disease Threats in The Twenty-First Century: Strengthening The Global ResponseAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- CHITSDocument17 pagesCHITSJane RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A Bird's-Eye ViewDocument13 pagesPathophysiology of Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A Bird's-Eye ViewMa Christine TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Adventist University of The Philippines: Academic Year 2020-2021Document2 pagesAdventist University of The Philippines: Academic Year 2020-2021Anastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- 02 Student Speech 2Document2 pages02 Student Speech 2Sam C HelloNo ratings yet
- Encoding-Guide NDocument11 pagesEncoding-Guide NAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Document 2 PDFDocument1 pageDocument 2 PDFAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- (1875855X - Asian Biomedicine) Successful Weaning of Adult Patients With Respiratory Failure From Mechanical Ventilators Using An L-PieceDocument8 pages(1875855X - Asian Biomedicine) Successful Weaning of Adult Patients With Respiratory Failure From Mechanical Ventilators Using An L-PieceAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- 02 Student Speech 2Document2 pages02 Student Speech 2Sam C HelloNo ratings yet
- NCP (1) - SyudetDocument2 pagesNCP (1) - SyudetAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Drill 7 CAPN 411.online - Activity.for - September 28.2020Document4 pagesDrill 7 CAPN 411.online - Activity.for - September 28.2020Anastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- CD RationalizationDocument19 pagesCD RationalizationAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- MSOFFICE2013 - Exercesis INFN230Document78 pagesMSOFFICE2013 - Exercesis INFN230Anastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Subjective Nervous SystemDocument1 pageSubjective Nervous SystemAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- PresentationnnDocument46 pagesPresentationnnAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Quiz For Rabies and IshDocument11 pagesQuiz For Rabies and IshAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Quiz For Rabies and IshDocument11 pagesQuiz For Rabies and IshAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Research Priorities For The Future: Recommendations From An International SurveyDocument6 pagesNursing Informatics Research Priorities For The Future: Recommendations From An International SurveyAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- MSOFFICE2013 - Exercesis INFN230Document78 pagesMSOFFICE2013 - Exercesis INFN230Anastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- PresentationnnDocument46 pagesPresentationnnAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Inguinal Hernia Repair TasyaDocument6 pagesInguinal Hernia Repair TasyaAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Nikki M. Id 2Document4 pagesNikki M. Id 2Anastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- What Is Hypertension? 6 Ways To Prevent HypertensionDocument3 pagesWhat Is Hypertension? 6 Ways To Prevent HypertensionAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Health HistoryDocument28 pagesHealth HistoryAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Gross Monthly Income of The Head of The Family Gross Income NoDocument6 pagesGross Monthly Income of The Head of The Family Gross Income NoAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Oral Hygiene For Kids: Tips To Keep Your Kids' Teeth HealthyDocument2 pagesOral Hygiene For Kids: Tips To Keep Your Kids' Teeth HealthyAnastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet