Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design For Galvanizing Poster
Uploaded by
harwin ferreiraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design For Galvanizing Poster
Uploaded by
harwin ferreiraCopyright:
Available Formats
Design for Galvanizing
Download from the App Store and Google Play. 03 9654 1266
Search ‘Design Guide for Hot Dip Galvanizing -
best practice for venting and draining’ gaa@gaa.com.au
gaa.com.au
Using Hot-Rolled Sections Using Hollow Sections
Avoiding Distortion – Basic Design Rules
Hanging for Drainage Quality Thick + Thin = Distortion
Leave gaps between 1) Maximise the uniformity of heat transfer into and out 3) Avoid designs that require double dipping.
Cleats and Flanges of the steel. It is preferable to build assemblies and
Zinc drips off causing spikes Thin sheet
sub-assemblies in suitable modules allowing
All Cleats, a. Ensure venting and draining is adequate. This will
Beams Gussets, and a very rough surface allow the article to be immersed in and withdrawn for quick immersion and galvanized in a single
Stiffeners to dip so the entire article can expand and
have corners
from the molten zinc as quickly as possible.
Heavy angle contract uniformly.
sniped b. Minimise section thickness variations wherever
Channels possible in the fabrication. 4) Ensure the structural design of the item is
sufficient to support its own weight at 50%
2) Minimise the effect of stresses while the article is in of the steel’s specified yield strength.
the molten zinc. 5) Avoid using large areas of thin (under 8mm),
Angles
a. Use symmetrically rolled sections in preference to unbraced flat plate.
Natural drain to one point angle or channel frames. I-beams are preferred to 6) Use temporary bracing or reinforcing on
Where possible,
angles or channels. thin-walled and asymmetrical designs.
think 45 degrees!
b. Ensure assembly and welding techniques minimise
End plates to be vented
stresses in components making up the article.
Overlapping Sections
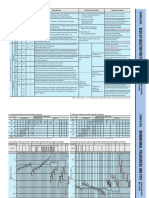
Standard Hole Sizes
CHS/Pipe SHS RHS
B
B
Zinc Trap or Hole Hole size to be a minimum of A
Air Pocket positioned A
close to 25% of the internal diagonal
corner Zinc Trap
NB Outside 1 Hole 2 Holes 4 Holes AxB 1 Hole 2 Holes 4 Holes AxB 1 Hole 2 Holes 4 Holes
Open Ends Preferred A Properly Drained Preferred B Centre Hole Unsatisfactory Diameter Ø (mm) Ø (mm) Ø (mm) (mm) Ø (mm) Ø (mm) Ø (mm) (mm) Ø (mm) Ø (mm) Ø (mm)
Moving Parts – Swinging Gate (mm)
Holes in one
member only
20 26.9 10 10 10 20 x 20 10 10 10 50 x 25 14 10 10
General Rules for Overlapping Surfaces: 25 33.7 10 10 10 25 x 25 10 10 10 65 x 35 18 13 10
a. Overlapping surface areas under 10,000mm2
generally do not require venting. 32 42.4 11 10 10 30 x 30 11 10 10 75 x 25 20 14 10
b. Overlapping surface areas between
Angles
10,000mm2 and 40,000mm2 shall be vented 40 48.3 12 10 10 35 x 35 12 10 10 75 x 50 25 16 11
with a minimum Ø10mm vent hole.
c. Above 40,000mm2 in overlapping surface area,
50 60.3 15 11 10 40 x 40 14 10 10 100 x 50 30 20 14
the vent holes shall be minimum Ø12mm.
d. When the overlapped surface area reaches Channels
250,000mm2, vent holes shall be minimum 65 76.1 19 13 10 50 x 50 18 13 10 125 x 75 40 30 18
Ø20mm and progressively placed every Open Ends Preferred A Opposite Drain Holes Preferred B Centre Hole Unsatisfactory
250,000 mm2. 80 88.9 22 16 11 65 x 65 25 16 11 150 x 50 40 30 20
For designs with intermittent welds the space No special venting or
draining provisions 90 101.6 25 18 13 75 x 75 25 19 13 150 x 100 45 35 25
between overlapping surfaces of two
are required
components shall be at least 2.5mm. IMPORTANT!
100 114.4 30 20 14 89 x 89 35 22 16 200 x 100 60 40 30
External inspection
hole required to
check internal venting 125 139.7 35 25 17 90 x 90 35 25 16 250 x 150 75 55 40
Large Overlapping Areas Snipe Guide (min Ø10mm)
Nominal Snipe Size 150 165.1 45 30 22 100 x 100 35 25 18 300 x 200 90 65 45
Example: Section (mm)
Radial
Crane Beams Open Mitred Clearance 168.3 45 30 22 125 x 125 45 35 22 350 x 250 110 80 55
PFC Completely sealed Joints
150 to 250 25x25 fabrications cannot
above 250 30x30 be galvanized 219.1 55 40 30 150 x 150 55 40 30 400 x 200 115 80 60
Open Ends Recommended minimum radial clearance
Angle before galvanizing
100 to 150 25x25 273.1 70 50 35 200 x 200 75 50 35 400 x 300 125 90 65
above 150 30x30 Shaft or spindle size Minimum radial
(mm) clearance 323.9 85 60 40 250 x 250 90 65 45 Note: ‘1 hole’, ‘2 holes’ and
UB
up to 250 25x25 Purpose of Venting and Draining (mm) ‘4 holes’ means the number
above 250 30x30 < Ø10 1.0 355.6 90 65 45 300 x 300 110 75 55 of holes in each otherwise
unopen end.
UC ≥ Ø10 to ≤ Ø30 2.0 406.4 105 75 55 350 x 350 125 90 65
Progressive vent up to 200 25x25
holes required. above 200 30x30 > Ø30 2.5
Hole size to be equal 457 115 85 60 400 x 400 145 100 75
or greater than steel Note: Some fettling may be required after galvanizing to
(For the smaller sections, a enable parts to be free moving.
thickness, with a
hole is the more preferred 508 130 90 65
minimum Ø10mm
option for venting)
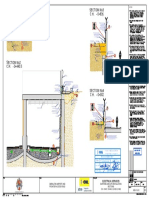
Identification Markings Handrail Hole Positions
Permanent identification Sealed Unit One Hole Two Holes
Recommended methods are: Super heated stream inside Will vent steam but unit Allows unit to vent and drain Designs which will provide the highest quality Designs which will need special consideration to
012 • Heavily embossed markings leads to explosions will float and to be galvanized inside Vent and drain
holes in rails HDG finish are: provide the highest quality HDG finish are:
• Punched markings and out
and stanchions • Modules within a single plane (straight sections). • Handrails with multiple planes (corner or bent
• Welded markings
• Modular designs that can be bolted together sections) so that some parts of the handrail vent
Hole Position Hole Size and drain slower than others parts within the
Temporary identification on-site.
• Holes should be placed as • Holes should be orientated • Minimum hole size is same handrail. This can affect available hanging
Before and after galvanizing: recommend • Large vent and drain holes in the hollow sections
use of heavily embossed metal tags, close to corners and/or in the same plane as the ø10mm angles due to both vent and drain designs and
which will allow the zinc to flow freely and air to
generally attached to the article via wire. connections as practical. fabrication. • Hole diameters should be bath size restrictions which could reduce
escape from inside the article.
• Holes must be located as • Holes should not be located at least the same size as coating quality.
Only before galvanizing: recommend • Internal venting of all rail portions inside a
water-based paints/marking pens. close to the high and low in the centre of end plates the steel thickness. • Vent and drain holes that are internal will need
stanchion is required if the rail runs continuously
points of hollow sections as and connections. • Having bigger holes (where to be verified through the use of external
Identification methods not acceptable: through the stanchion.
possible to prevent air locks, • Holes should be diagonally feasible) is always better for inspection holes.
• Oil-based paints/marking pens entrapment of pre-treatment opposed where possible. the galvanizing outcome.
Do Not Use OIL
PAINTS • Stickers chemicals and zinc puddling.
You might also like
- Corrosion prevention through hot dip galvanizingDocument1 pageCorrosion prevention through hot dip galvanizingEng-Ahmed AllamNo ratings yet
- CFSB3 - Permanent Restraint - Bracing of Chords & Web MembersDocument2 pagesCFSB3 - Permanent Restraint - Bracing of Chords & Web MembersTodd HenryNo ratings yet
- Structural GilbaneDocument11 pagesStructural Gilbanejh50000No ratings yet
- Structual Plan 2-Storey ResidentialDocument9 pagesStructual Plan 2-Storey ResidentialMark Christian EsguerraNo ratings yet
- StrucDocument3 pagesStrucAlvin DeliroNo ratings yet
- SKF Double Direction Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings For Screw DrivesDocument12 pagesSKF Double Direction Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings For Screw DrivesSusmit patelNo ratings yet
- PlanDocument8 pagesPlanMark Christian EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Acuv Stage 5-PlansDocument1 pageAcuv Stage 5-PlansMonde Tidimalo Lunathi MbaluNo ratings yet
- Bd57a 22x34Document1 pageBd57a 22x34jayson egeniasNo ratings yet
- Ewan Engineering Consultancy: Engineered/Contractor To Verify and Submit Calculation For The Approval of EngineersDocument1 pageEwan Engineering Consultancy: Engineered/Contractor To Verify and Submit Calculation For The Approval of EngineersAbid AyubNo ratings yet
- Mait hr130 BrochureDocument2 pagesMait hr130 BrochuregeethsanNo ratings yet
- 32 Gfc-P2c3-Tu02-Crp-Dr-Btn-73106-01-ADocument1 page32 Gfc-P2c3-Tu02-Crp-Dr-Btn-73106-01-ASUBHASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Shipping container living wall planDocument1 pageShipping container living wall planفاطمة السبيعيNo ratings yet
- WSp110 112Document3 pagesWSp110 112Marie DoloresNo ratings yet
- Gambar Concrete PoleDocument1 pageGambar Concrete PolerifkynetNo ratings yet
- Design and construction details for attaching span wires and ground wires to concrete and strain polesDocument1 pageDesign and construction details for attaching span wires and ground wires to concrete and strain polesrifkynetNo ratings yet
- Castillejos WELL DataDocument3 pagesCastillejos WELL DataJohn Christopher BaquingNo ratings yet
- Type "E" Bearings: General NotesDocument1 pageType "E" Bearings: General NotesMiguel Angel Montaña PeñaNo ratings yet
- CNC 104 Rim Vent: DatasheetDocument1 pageCNC 104 Rim Vent: DatasheetAs'adNo ratings yet
- MAG'Impact: The High-Performance Impactor: Cubicity and SimplicityDocument5 pagesMAG'Impact: The High-Performance Impactor: Cubicity and SimplicityPrekelNo ratings yet
- General Structural Notes:: Typ. Det. For Beam or Slab Change Soffit Typ. Det. For Sleeves Thru RC BeamDocument1 pageGeneral Structural Notes:: Typ. Det. For Beam or Slab Change Soffit Typ. Det. For Sleeves Thru RC BeamJan Lawrence AlbertoNo ratings yet
- General: Schedule of CHB & Ceramic Block ReinforcementDocument1 pageGeneral: Schedule of CHB & Ceramic Block Reinforcementbobmarley20161934No ratings yet
- Installation Guide Fabrications, Safety & Lighting SolutionsDocument1 pageInstallation Guide Fabrications, Safety & Lighting SolutionsAThaddeusAntonioNo ratings yet
- Da 950092 001Document1 pageDa 950092 001munnaNo ratings yet
- Uci Mce Stru D S-20.6Document1 pageUci Mce Stru D S-20.6Thanh Đạt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Resultant Consulting Enginers: Top ViewDocument1 pageResultant Consulting Enginers: Top ViewEnrique RafaelNo ratings yet
- Ficha J2zzpv4tt5818pxf4ohmm8312xuihlDocument15 pagesFicha J2zzpv4tt5818pxf4ohmm8312xuihlJulio Cruzado SolanoNo ratings yet
- TXDOT Traffic Signal Pole FoundationDocument1 pageTXDOT Traffic Signal Pole FoundationfiercecatNo ratings yet
- C.H. - 0+465.5 Section No5Document1 pageC.H. - 0+465.5 Section No5Fran LuqueNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet BD?Document2 pagesCheat Sheet BD?Book SutthisriNo ratings yet
- S-241 - ARCH - 04.05.2022-ModelDocument1 pageS-241 - ARCH - 04.05.2022-ModelSuhail AhamedNo ratings yet
- 150mm thick reinforced concrete block wall structural notesDocument1 page150mm thick reinforced concrete block wall structural notesAnthonio MaraghNo ratings yet
- Bearing Elements: Series LEL, With Ground RacewaysDocument12 pagesBearing Elements: Series LEL, With Ground RacewaysJezB1234No ratings yet
- Power Tap SwitchesDocument2 pagesPower Tap Switchesmikepower007No ratings yet
- Reinforced Walls Design ManualDocument17 pagesReinforced Walls Design ManualNANA ADDONo ratings yet
- H型钢规格表Document1 pageH型钢规格表luke luckyNo ratings yet
- Notes:: Surf. TreatmentDocument1 pageNotes:: Surf. Treatmentberliani navitasNo ratings yet
- Parent: Customer Name: Project Name: 9281D4ASSEM 09281 D4 Certified: Approved For Construction Assy. WTDocument9 pagesParent: Customer Name: Project Name: 9281D4ASSEM 09281 D4 Certified: Approved For Construction Assy. WTmoneyphotocopyshopNo ratings yet
- 7 Details Passive House PDFDocument1 page7 Details Passive House PDFEvin LawlorNo ratings yet
- Screened Backshell Product FinderDocument1 pageScreened Backshell Product Finderpaula09No ratings yet
- Steel Contractor Notes and Grating SpecificationsDocument1 pageSteel Contractor Notes and Grating SpecificationssivagnanamNo ratings yet
- Water Supply DetailsDocument1 pageWater Supply DetailsUsha CastagneNo ratings yet
- Fitting Which Requires Large Force For Assembly/disassembly A Key or Other Device Is Required For High-Torque Transmission Purposes.Document1 pageFitting Which Requires Large Force For Assembly/disassembly A Key or Other Device Is Required For High-Torque Transmission Purposes.Eli BoscanNo ratings yet
- C.H. - 0+407 Section No1 C.H. - 0+835 Section No3Document1 pageC.H. - 0+407 Section No1 C.H. - 0+835 Section No3Fran LuqueNo ratings yet
- Pavement Design Parameters and Catch Basin DimensionsDocument1 pagePavement Design Parameters and Catch Basin DimensionsrickNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart: Floor Slab DesignDocument8 pagesFlow Chart: Floor Slab Designtecon ploiestiNo ratings yet
- General notes and steelwork specificationsDocument1 pageGeneral notes and steelwork specificationsKeise AliNo ratings yet
- Direct Chill Aluminum Casting Without Homogenization Using HT-EMS TechnologyDocument4 pagesDirect Chill Aluminum Casting Without Homogenization Using HT-EMS TechnologyRaj Kumar GiriNo ratings yet
- Ajv DPW 10 525 CL DWG 0695 03 R03Document1 pageAjv DPW 10 525 CL DWG 0695 03 R03sivagnanamNo ratings yet
- Ramothibe T - Stage 4-Acuv300Document2 pagesRamothibe T - Stage 4-Acuv300Monde Tidimalo Lunathi MbaluNo ratings yet
- Specification for soakaway and gas boiler replacementDocument1 pageSpecification for soakaway and gas boiler replacementLaurentiu NaeNo ratings yet
- 8mm roof insulation with aluminum foil radiant barrierDocument1 page8mm roof insulation with aluminum foil radiant barrierglen raymundoNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Concrete Masonry Fences Built On Reinforced Concrete Strip FootingsDocument10 pagesData Sheet: Concrete Masonry Fences Built On Reinforced Concrete Strip FootingsTeodoro Miguel Carlos IsraelNo ratings yet
- BSD-C Plain: Manual Push Up OperatedDocument1 pageBSD-C Plain: Manual Push Up OperatedLordM00nNo ratings yet
- NakshaDocument1 pageNakshaRavinder Deep Singh BrarNo ratings yet
- Truss - 1 Details Truss Diagram T-2: 4Th Flr. Framg. PlanDocument1 pageTruss - 1 Details Truss Diagram T-2: 4Th Flr. Framg. Planmark gumamelaNo ratings yet
- Typical Drainage DetailsDocument1 pageTypical Drainage DetailssuhailNo ratings yet
- CE038 Rev1Document1 pageCE038 Rev1Jonas MwatangeNo ratings yet
- IE2600A-15-FF: 1.5" (F) NPT X 1.5" (F) NPT (BR) Adjustable Regulating Valve InformationDocument1 pageIE2600A-15-FF: 1.5" (F) NPT X 1.5" (F) NPT (BR) Adjustable Regulating Valve Informationharwin ferreiraNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Catalogue PDFDocument10 pagesFire Protection Catalogue PDFharwin ferreiraNo ratings yet
- IPS Electric UnicycleDocument6 pagesIPS Electric UnicycleyoungmaxenNo ratings yet
- N 90 FS PRV Installation Operation InstructionsDocument12 pagesN 90 FS PRV Installation Operation Instructionsharwin ferreiraNo ratings yet
- Self-Cleaning Nanocoatings Inspired by NatureDocument41 pagesSelf-Cleaning Nanocoatings Inspired by NatureAshwin Vijaysai100% (1)
- 16 Outotec Physical SeparationDocument12 pages16 Outotec Physical SeparationirfanNo ratings yet
- 3 Interfacial PhenomenaDocument8 pages3 Interfacial PhenomenaJames DayritNo ratings yet
- Oluseyi Presentation SoilmechanicsDocument186 pagesOluseyi Presentation SoilmechanicsOluseyi AbegundeNo ratings yet
- HSD Bio Diesel and SoapDocument35 pagesHSD Bio Diesel and SoapkdkrkdkrkdkrNo ratings yet
- WeldingDocument27 pagesWeldingJean PierreNo ratings yet
- Spofa Catalogue en 2013 2014Document59 pagesSpofa Catalogue en 2013 2014sorcNo ratings yet
- Saeco Incanto Deluxe Parts DiagramDocument5 pagesSaeco Incanto Deluxe Parts DiagramAlain HOAREAU100% (1)
- Elcometer 130 Scm400 Salt Contamination Meter Data SheetDocument1 pageElcometer 130 Scm400 Salt Contamination Meter Data SheetRinush SinagaNo ratings yet
- TDS MasterRoc MP 800Document2 pagesTDS MasterRoc MP 800RogerNo ratings yet
- Part 18 - Prestressed ConcreteDocument8 pagesPart 18 - Prestressed Concretetkram1981No ratings yet
- 3 - The Role of Oxygen-Permeable Ionomer For Polymer Electrolyte Fuel CellsDocument9 pages3 - The Role of Oxygen-Permeable Ionomer For Polymer Electrolyte Fuel CellsFaseeh KKNo ratings yet
- ZP11 MCE3 AUS DTC排故手册 20180419 PDFDocument723 pagesZP11 MCE3 AUS DTC排故手册 20180419 PDFtallerr.360No ratings yet
- Sunon Dp203at 2122LBT - GN.155 (A12003480g-00) - 1Document9 pagesSunon Dp203at 2122LBT - GN.155 (A12003480g-00) - 1German DANo ratings yet
- Is 1367 13 1983Document7 pagesIs 1367 13 1983Dharmendra TomarNo ratings yet
- Providing and laying bituminous concreteDocument2 pagesProviding and laying bituminous concreteHPSIDC MehatpurNo ratings yet
- 2.syllabus EME-504 HMTDocument1 page2.syllabus EME-504 HMTdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Transition Elements - Model Questions PDFDocument6 pagesTransition Elements - Model Questions PDFSubhasish Sau100% (1)
- Module 1 - Introduction To ChemistryDocument10 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To ChemistryJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Radiography Test & Liquid Penetrant Test ProcedureDocument7 pagesRadiography Test & Liquid Penetrant Test ProcedurePrashant MalveNo ratings yet
- Sesion 5Document35 pagesSesion 5Martin Y. KouNo ratings yet
- Oxarol CaoDocument1 pageOxarol CaoMohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Zhou - 2023 - LCA of Polycarbonate ProductionDocument10 pagesZhou - 2023 - LCA of Polycarbonate Productionayemyattheint kyawNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellen0% (1)
- STC FittingDocument32 pagesSTC Fittingdj22500No ratings yet
- Computational AI Models For Investigating The Radiation Shielding Potential of High-Density ConcreteDocument19 pagesComputational AI Models For Investigating The Radiation Shielding Potential of High-Density ConcreteNat NewNo ratings yet
- ID 4083 PresentationDocument17 pagesID 4083 PresentationNgIa MaStaNo ratings yet
- Assessment: Directions: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answers On A Separate Sheet of PaperDocument5 pagesAssessment: Directions: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answers On A Separate Sheet of Paperkim aaron marcelinoNo ratings yet
- L01 Dead and Live Loads Sample ProblemDocument10 pagesL01 Dead and Live Loads Sample ProblemN GraceNo ratings yet
- MaterialExam1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesMaterialExam1 SolutionslarasmoyoNo ratings yet