Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1) What Is GST? What Are The Various Tax Subsumed Under GST?
Uploaded by
Nethaji BK0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pageseconomics
Original Title
1-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenteconomics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pages1) What Is GST? What Are The Various Tax Subsumed Under GST?
Uploaded by
Nethaji BKeconomics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1) What is GST? What are the various tax subsumed under GST?
GST full form is goods and services tax. The Goods and Service Tax Act was passed
in Parliament on 29th March 2017and the Act came into effect on 1st July 2017. It is a
indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services. It is a comprehensive,
multistage, destination-based tax. Comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all
the indirect taxes except a few state taxes. Multi-staged as it is, the GST is imposed at
every step in the production process, but is meant to be refunded to all parties in the
various stages of production other than the final consumer and as a destination-based
tax, it is collected from point of consumption and not point of origin like previous
taxes.
Various taxes subsumed under GST are:
Central excise duty
Duties of excise (medicinal and toilet preparation)
Additional duties of excise (goods of special importance)
Additional duties of excise (textiles and textile products)
Additional duties of customs
Special additional duty of customs
Service tax
State value added tax
Luxury tax
Entry tax
Entertainment and amusement tax
Taxes on advertisement
Purchase tax
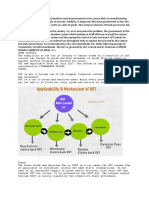
2) What are the various types of GST?
Types of GST are:
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
The Integrated Goods and Services Tax or IGST is a tax under the GST regime
that is applied on the interstate (between 2 states) supply of goods and/or
services as well as on imports and exports. The IGST is governed by the IGST
Act. Under IGST, the body responsible for collecting the taxes is the Central
Government. After the collection of taxes, it is further divided among the
respective states by the Central Government.
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
The State Goods and Services Tax or SGST is a tax under the GST
regime which is applicable on intrastate (within the same state)
transactions. In case of intrastate supply of goods and/or services, both
State GST and Central GST are levied. However, the State GST or
SGST is levied by the state on the goods and/or services that are
purchased or sold within the state. It is governed by the SGST Act. The
revenue earned through SGST is solely claimed by the respective state
government.
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
Just like State GST, the Central Goods and Services Tax of CGST is a
tax under the GST regime which is applicable on intrastate (within the
same state) transactions. The CGST is governed by the CGST Act. The
revenue earned from CGST is collected by the Central Government.
Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST)
The Union Territory Goods and Services Tax or UTGST is the
counterpart of State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) which is levied
on the supply of goods and/or services in the Union Territories (UTs)
of India. The UTGST is applicable on the supply of goods and/or
services in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Daman Diu,
Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Lakshadweep. The UTGST is governed
by the UTGST Act. The revenue earned from UTGST is collected by
the Union Territory government. The UTGST is a replacement for the
SGST in Union Territories. Thus, the UTGST will be levied in
addition to the CGST in Union Territories.
You might also like
- GST Explained: Understanding India's Major Tax ReformDocument8 pagesGST Explained: Understanding India's Major Tax ReformApoorva Chandra100% (1)
- Project 3Document17 pagesProject 3Hemant MandalNo ratings yet
- CGSTDocument7 pagesCGSTstudentNo ratings yet
- Guide To CGST, SGST and IGST: Inter-State Vs Intra-StateDocument6 pagesGuide To CGST, SGST and IGST: Inter-State Vs Intra-StateSuman IndiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - GSTDocument3 pagesChapter 6 - GSTchovvNo ratings yet
- GSTTTTDocument12 pagesGSTTTTstudentNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Good and Service TaxDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Good and Service TaxShubham KuberkarNo ratings yet
- CTP AssignmentDocument10 pagesCTP AssignmentANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Indirect TaxesDocument1 pageIndirect TaxesPrerna PatnaikNo ratings yet
- GST Definition, Objective, Framework, Action Plan & Scope: Historical Background of GSTDocument6 pagesGST Definition, Objective, Framework, Action Plan & Scope: Historical Background of GSTRamapriyaiyengarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GST: 1. What Is GST? When Is GST Expected To Be Implemented?Document1 pageIntroduction To GST: 1. What Is GST? When Is GST Expected To Be Implemented?JItNo ratings yet
- A Study On Impact of GST On Indian Economy: Chirag RanaDocument4 pagesA Study On Impact of GST On Indian Economy: Chirag RanaPratyasha SarkarNo ratings yet
- GST in IndiaDocument12 pagesGST in IndiaRahul ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Dual GST (Goods and Services Tax) in IndiaDocument1 pageDual GST (Goods and Services Tax) in IndiaWelcome 1995No ratings yet
- What Is SGST CGST & IGST?Document2 pagesWhat Is SGST CGST & IGST?Filing BuddyNo ratings yet
- GST AssignmentDocument16 pagesGST AssignmentDroupathyNo ratings yet
- Goods and Service Tax: India Government of IndiaDocument2 pagesGoods and Service Tax: India Government of Indiaabhishek ganeshNo ratings yet
- INCOME TAX AND GST. JURAZ-Module 3Document11 pagesINCOME TAX AND GST. JURAZ-Module 3hisanashanutty2004100% (1)
- GST - IiDocument12 pagesGST - IiGaurav vaidya0% (1)
- GST Unit 1-5Document21 pagesGST Unit 1-5Joshua StarkNo ratings yet
- Gap Analysis.: Meaning and Purpose of GSTDocument9 pagesGap Analysis.: Meaning and Purpose of GSTsatya narayanNo ratings yet
- GST NotesDocument22 pagesGST NotesSARATH BABU.YNo ratings yet
- Cycle 3 Notes-3 Class 11 GSTDocument6 pagesCycle 3 Notes-3 Class 11 GSTtmoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument16 pagesUnit 1 NotesThanuja BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Earlier The Constitution Empowered The Central Government To Levy Excise Duty On Manufacturing and Service Taxes On The Supply of ServicesDocument3 pagesEarlier The Constitution Empowered The Central Government To Levy Excise Duty On Manufacturing and Service Taxes On The Supply of ServicesIshu SinghNo ratings yet
- GST Questions & Answers PDF | Latest Banking AwarenessDocument6 pagesGST Questions & Answers PDF | Latest Banking AwarenessAnkita GhogaleNo ratings yet
- An Ultimate Guide To Goods and Service Tax (GST)Document6 pagesAn Ultimate Guide To Goods and Service Tax (GST)bfinservNo ratings yet
- Ashish TaxDocument20 pagesAshish TaxAshish RajNo ratings yet
- GST AssgmntDocument16 pagesGST AssgmntMuhammed Samil MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Guru Nanak International Public School: Conomics Project OnDocument42 pagesGuru Nanak International Public School: Conomics Project OnRohit NagarNo ratings yet
- Components of GSTDocument2 pagesComponents of GSTDevil DemonNo ratings yet
- Impact of Implementation GST On Common Man & Indian Economy: Positive or NegativeDocument5 pagesImpact of Implementation GST On Common Man & Indian Economy: Positive or Negativekatejagruti3No ratings yet
- Constitutional Basis of GSTDocument10 pagesConstitutional Basis of GSTNANDINI RAJ N RNo ratings yet
- Impact of Gst on Hotel Industry - Vedanti PedamkarDocument71 pagesImpact of Gst on Hotel Industry - Vedanti Pedamkargoswamiharish666No ratings yet
- How to Handle Goods and Service Tax (GST)From EverandHow to Handle Goods and Service Tax (GST)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Ankit GSTDocument10 pagesAnkit GSTManuj PareekNo ratings yet
- GST IntroductionDocument103 pagesGST IntroductionAnonymous MhCdtwxQINo ratings yet
- Types of Taxes Under GSTDocument4 pagesTypes of Taxes Under GSTDiya SharmaNo ratings yet
- GST Fast Track Notes PDFDocument69 pagesGST Fast Track Notes PDFJayadeepNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GSTDocument16 pagesIntroduction To GSTkomil bogharaNo ratings yet
- GST or Goods and Services Tax Can Be Rightfully Called The Largest IndirectDocument26 pagesGST or Goods and Services Tax Can Be Rightfully Called The Largest IndirectDevesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Types of GST: Presented BY Kowsalya.SDocument8 pagesTypes of GST: Presented BY Kowsalya.SKowsiNo ratings yet
- Taxguru - In-Dual GST Model GST Structure in IndiaDocument9 pagesTaxguru - In-Dual GST Model GST Structure in IndiahumanNo ratings yet
- Key Features of GST ExplainedDocument2 pagesKey Features of GST Explainedtina tanwarNo ratings yet
- Computerised AccountingDocument10 pagesComputerised Accountingshagun sharmaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Impact of GST On The Prices in Odisha: Samira PatraDocument14 pagesA Study On Impact of GST On The Prices in Odisha: Samira PatraBiplab SwainNo ratings yet
- GST Explained: Understanding India's Major Tax ReformDocument6 pagesGST Explained: Understanding India's Major Tax ReformUma MaheshNo ratings yet
- GST Economics ProjectDocument11 pagesGST Economics ProjectAbeer ChawlaNo ratings yet
- The Goods and Services Tax and Its Likely Impact On Indian EconomyDocument8 pagesThe Goods and Services Tax and Its Likely Impact On Indian Economyaryaa_statNo ratings yet
- GST and Indirect TaxesDocument84 pagesGST and Indirect TaxesSreepada KameswariNo ratings yet
- GST(Sayantan Kundu)Document17 pagesGST(Sayantan Kundu)Sayantan KunduNo ratings yet
- 7. IGST & UTGSTDocument8 pages7. IGST & UTGSTVarun AgarwalNo ratings yet
- GST Simplifies India's Complex Tax SystemDocument26 pagesGST Simplifies India's Complex Tax SystemIlma FatimaNo ratings yet
- GST in 40Document7 pagesGST in 40KeertiNo ratings yet
- BE Assignment 1Document20 pagesBE Assignment 1AdityaPalNo ratings yet
- Suraj TybmsDocument6 pagesSuraj Tybmsdrawback979No ratings yet
- DraftDocument36 pagesDraftAbhinand SadhanandanNo ratings yet
- GST-1Document26 pagesGST-1pranaynagrale876No ratings yet
- Introduction to GST in India - CGST, SGST, IGST and UTGST TypesDocument2 pagesIntroduction to GST in India - CGST, SGST, IGST and UTGST Types777priyankaNo ratings yet
- GST - Concept & Status - May, 2016: For Departmental Officers OnlyDocument6 pagesGST - Concept & Status - May, 2016: For Departmental Officers Onlydroy21No ratings yet
- Ethics in Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument3 pagesEthics in Electrical and Computer EngineeringNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Ethics in EE & CEDocument4 pagesEthics in EE & CENethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Electrical and Computer Engineering: Lecture #11Document2 pagesEthics in Electrical and Computer Engineering: Lecture #11Nethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Construction Economics and Finances Assignment-3Document8 pagesConstruction Economics and Finances Assignment-3Nethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Causes and Consequences of the Highland Towers CollapseDocument24 pagesCauses and Consequences of the Highland Towers CollapseNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Civil Engg 2005 PDFDocument28 pagesCivil Engg 2005 PDFSowjanyaReddyNo ratings yet
- Types of Inflation Basis of CausesDocument12 pagesTypes of Inflation Basis of CausesNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Electrical and Computer Engineering: Sexual Harassment: Sexual Harassment Is A Display of Power andDocument2 pagesEthics in Electrical and Computer Engineering: Sexual Harassment: Sexual Harassment Is A Display of Power andNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- CE 1997 Unsolved PDFDocument8 pagesCE 1997 Unsolved PDFNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- A 4Document9 pagesA 4Nethaji BKNo ratings yet
- CE 1997 Unsolved PDFDocument8 pagesCE 1997 Unsolved PDFNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- 1energy Management and Audit - 18.06.2017Document75 pages1energy Management and Audit - 18.06.2017Nethaji BKNo ratings yet
- ProfessionalismDocument1 pageProfessionalismNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- 1) How Inflation Can Be Prevented and Controlled? Is Inflation Good or Bad? Inflation Can Be Controlled byDocument3 pages1) How Inflation Can Be Prevented and Controlled? Is Inflation Good or Bad? Inflation Can Be Controlled byNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryMirzaadnanbeigNo ratings yet
- Ethical BlindnessDocument1 pageEthical BlindnessNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Organizational DisobedianceDocument3 pagesOrganizational DisobedianceNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Full Notes Construction Management-1Document47 pagesFull Notes Construction Management-1Nethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Unit3 - Electrical SystemDocument57 pagesUnit3 - Electrical SystemNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Engineering EthicsDocument1 pageEngineering EthicsNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CodesDocument42 pagesLecture 2 CodesSrinivas GopalNo ratings yet
- Account and Finance 2.Document49 pagesAccount and Finance 2.Nethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - Electric MotorsDocument61 pagesUnit2 - Electric MotorsNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Engineering Moral ValuesDocument2 pagesEngineering Moral ValuesNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- aCCOUNTS AND FINANACEDocument49 pagesaCCOUNTS AND FINANACENethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Engineering EthicsDocument1 pageEngineering EthicsNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Parinita Mam Case HV PDFDocument5 pagesParinita Mam Case HV PDFNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Satyendra DubeyDocument1 pageSatyendra DubeyNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Amaysim Australia LimitedDocument9 pagesAmaysim Australia LimitedMahnoor NooriNo ratings yet
- Kotak Securities Payslip for August 2020Document1 pageKotak Securities Payslip for August 2020Aakash PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- RR 21-2020 (Digest)Document4 pagesRR 21-2020 (Digest)Joel SyNo ratings yet
- SSGC Duplicate Bill20210323 132303Document1 pageSSGC Duplicate Bill20210323 132303toseef ul islamNo ratings yet
- CIR Vs Baier-Nickel and NDC Vs CIRDocument3 pagesCIR Vs Baier-Nickel and NDC Vs CIRKath LeenNo ratings yet
- 180 January LickNailDocument1 page180 January LickNailRam kunwar KumawatNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - Overview of Malaysian TaxationDocument22 pagesChap 1 - Overview of Malaysian TaxationrajarajeswryNo ratings yet
- TAXATION 2 Chapter 5 Estate Tax Payable PDFDocument5 pagesTAXATION 2 Chapter 5 Estate Tax Payable PDFKim Cristian MaañoNo ratings yet
- Filling, Penalties and RemediesDocument14 pagesFilling, Penalties and RemediesMichael Brian TorresNo ratings yet
- Tax Alert Mining Royalty Income Tax TreatmentDocument6 pagesTax Alert Mining Royalty Income Tax Treatmentivan vivanoNo ratings yet
- Malaysia tax planning guideDocument32 pagesMalaysia tax planning guideHairani ArisNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Billed To: Invoice DetailsDocument1 pageTax Invoice: Billed To: Invoice DetailsVINAY BANSAL100% (1)
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited: Telephone Bill Name and Address of The CustomerDocument1 pageBharat Sanchar Nigam Limited: Telephone Bill Name and Address of The CustomerVijaya ChandNo ratings yet
- PensionersDocument2 pagesPensionersJanardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Transfer and Business Tax 2014 Ballada PDFDocument26 pagesTransfer and Business Tax 2014 Ballada PDFCamzwell Kleinne HalyieNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax Return: Part I - Taxpayer InformationDocument3 pagesEstate Tax Return: Part I - Taxpayer InformationHartel BuyuccanNo ratings yet
- HI6028 Taxation Theory, Practice & Law: Student Name: Student NumberDocument12 pagesHI6028 Taxation Theory, Practice & Law: Student Name: Student NumberMah Noor FastNUNo ratings yet
- As 94Document7 pagesAs 94Kinga MochockaNo ratings yet
- Kratos - Quotation For - Website1Document1 pageKratos - Quotation For - Website1fapebiNo ratings yet
- Howe Engineering Projects India PVT LTD: Earnings Amount Deductions Amount Perks/Other income/Exempton/RebatesDocument1 pageHowe Engineering Projects India PVT LTD: Earnings Amount Deductions Amount Perks/Other income/Exempton/RebatesSumantrra ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- CIR authority to enforce tax laws during WWIIDocument1 pageCIR authority to enforce tax laws during WWIIAlan GultiaNo ratings yet
- Bharatbhai Tax Bill Godown No-7Document1 pageBharatbhai Tax Bill Godown No-7VaghasiyaBipinNo ratings yet
- Abid AliDocument1 pageAbid AliXen cdh818No ratings yet
- Tax Calculator by Tax GurujiDocument4 pagesTax Calculator by Tax GurujiSunitKumarChauhanNo ratings yet
- Moving Expenses: Before You BeginDocument4 pagesMoving Expenses: Before You BeginEloy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- QB - Indirect Tax - Mcom Sem 4Document5 pagesQB - Indirect Tax - Mcom Sem 4Prathmesh KadamNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Unit 2Document15 pagesMCQ - Unit 2Niraj PandeyNo ratings yet
- CH10 Alternative Means of Government Finance 2015 (Compatibility Mode) PDFDocument20 pagesCH10 Alternative Means of Government Finance 2015 (Compatibility Mode) PDFHendra PoltakNo ratings yet
- Government Pay SlipDocument1 pageGovernment Pay SlipBidhya DahalNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Purani Bazar Jamui-811307 (Bihar) GSTIN/UIN: 10AIIPB8433E1ZV State Name: Bihar, Code: 10Document1 pageTax Invoice: Purani Bazar Jamui-811307 (Bihar) GSTIN/UIN: 10AIIPB8433E1ZV State Name: Bihar, Code: 10Randhir SinghNo ratings yet