Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Kingdom: These Are Multicellular, Autotrophic, Eukaryotic and Have Cell Wall
Plant Kingdom: These Are Multicellular, Autotrophic, Eukaryotic and Have Cell Wall
Uploaded by
sailuhariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Kingdom: These Are Multicellular, Autotrophic, Eukaryotic and Have Cell Wall
Plant Kingdom: These Are Multicellular, Autotrophic, Eukaryotic and Have Cell Wall
Uploaded by
sailuhariCopyright:
Available Formats
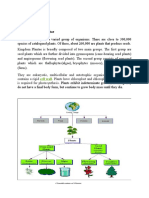
Plant Kingdom: These are multicellular, autotrophic, eukaryotic and have cell wall
composed of cellulose. These organisms can be divided into different divisions based on:
1) Level of differentiation
2) Presence of vascular tissue (xylem and phloem-useful for water and food conduction)
3) Presence of reproductive organs (hidden or exposed)
4) Production of seeds.
The plant kingdom is divided into the following divisions:
Algae: They have undifferentiated body (no root, stem or leaves) i.e, thalloid body and
aquatic organisms. They lack vascular tissue.
They are either unicellular like Chlamydomonas or filamentous like Spirogyra or Ulothrix.
They show both asexual (via fragmentation) and sexual reproduction (fusion of gametes).
Here there are no reproductive organs.
Based on their colour, they are divided into 3 classes: Chlorophyceae (green algae),
Phaeophyceae (Brown algae) and Rhodophyceae (Red algae).
Examples: Chlamydomonas, Ulothrix, Spirogyra, Chara,Sargassum,Fucus,Porphyra,
Gelidium etc.,
Figure 1-Chlamydomonas Figure 2- Ulothrix
Some algae form symbiotic relationship with fungi to form lichens. In them, algae provide
food to the fungi. Lichens are excellent pollution indicators. They do not grow in the
presence of SO2.
You might also like
- General Characters of AlgaeDocument50 pagesGeneral Characters of AlgaeAnilNo ratings yet
- Algae Structure and ReproductionDocument18 pagesAlgae Structure and ReproductionPrasanth Kumar S100% (1)
- General Characters of Algae: Thalloid Plant BodyDocument24 pagesGeneral Characters of Algae: Thalloid Plant Bodyidrees gullNo ratings yet
- 5 Kingdom of LifeDocument12 pages5 Kingdom of LifeDivyanshu AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AlgaeDocument45 pagesIntroduction To AlgaeAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Alage - Bryophyte - Pteridophyte & GymnospermDocument19 pagesBasic Concept of Alage - Bryophyte - Pteridophyte & GymnospermDivyansha Sharma100% (1)
- Characters of Algae: 1. OccurrenceDocument4 pagesCharacters of Algae: 1. Occurrencem umair zahirNo ratings yet
- Characters of Algae: 1. OccurrenceDocument4 pagesCharacters of Algae: 1. Occurrencem umair zahirNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument11 pagesPlant KingdomSuresh SNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument13 pagesPlant KingdomPari ParistanNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument26 pagesPlant Kingdom비KeerthuNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument53 pagesPlant KingdomAashutosh GujareNo ratings yet
- XI-3-Plant KingdomDocument85 pagesXI-3-Plant KingdomEsha (Lekisha)No ratings yet
- Bio AR 2 - Plant & Animal KingdomDocument48 pagesBio AR 2 - Plant & Animal KingdomFazlur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae) :: The Important Characteristics of The Class Phaeophyceae Are Given BelowDocument12 pagesIntroduction of Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae) :: The Important Characteristics of The Class Phaeophyceae Are Given BelowArsalan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Protozoa, Algae, Bacteia NMDocument21 pagesProtozoa, Algae, Bacteia NMOoga ChakaNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. 1st Sem Unit IIDocument8 pagesM.Sc. 1st Sem Unit IIRocky Ray RajNo ratings yet
- Protista Dan FungiDocument17 pagesProtista Dan FungiNur Hasnah PutriNo ratings yet
- MCB 206 Lecture NoteDocument22 pagesMCB 206 Lecture NoteKelly KayodeNo ratings yet
- Sallegue Frances Hailey - Plant KingdomDocument27 pagesSallegue Frances Hailey - Plant KingdomFrances hailey SallegueNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 - Revision NotesDocument34 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 3 - Revision NotesAnubhav MamgainNo ratings yet
- 5 KingdomDocument9 pages5 Kingdomdivine grace mesiasNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument16 pagesPlant Kingdomshriyansh singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Diversity IN Living WorldDocument36 pagesDiversity IN Living WorldAnuradha PorwalNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesDiversity in Living Organismssumendra singhNo ratings yet
- "Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings WhichDocument11 pages"Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings Whichbrm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom NotesDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom NotesVinod MishraNo ratings yet
- Biological Diversity: Unit 10Document29 pagesBiological Diversity: Unit 10rbyq9No ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy BookDocument100 pagesPharmacognosy BookYoussef ElhamamyNo ratings yet
- Week Two Biology SS1Document12 pagesWeek Two Biology SS1Oseni MuibaNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument4 pagesPlant Kingdomaditiyajhaab10No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Biology)Document12 pagesChapter 2 (Biology)MahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument8 pagesKingdom PlantaeSurbhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungia (Fungi Kingdom) : Notes For Gen. Bio 2Document10 pagesKingdom Fungia (Fungi Kingdom) : Notes For Gen. Bio 2Kd123No ratings yet
- Algae Are Protists With Plant-Like Characteristics, That Are Typically Found in Aquatic EnvironmentsDocument3 pagesAlgae Are Protists With Plant-Like Characteristics, That Are Typically Found in Aquatic EnvironmentsShan DyNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument8 pagesKingdom PlantaeDavidNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument20 pagesPlant Kingdombhadri.vihariNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument17 pagesPlant KingdomLyndsayNo ratings yet
- JoannaDocument4 pagesJoannapfaxawaiNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument19 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectRapidtg 1965100% (3)
- Beta Monic Ai-MonicaiDocument6 pagesBeta Monic Ai-MonicaiJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- BSEDSCI 13 (Algea) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Document3 pagesBSEDSCI 13 (Algea) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Christian PatingaNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)Document17 pagesPlant Kingdom Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)shusa harshaNo ratings yet
- 3 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages3 Plant KingdomitzanandNo ratings yet
- Basic Biology 2 Plant Diversity-1Document12 pagesBasic Biology 2 Plant Diversity-1TeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3/Class-XI/Biology: Plant KingdomDocument6 pagesChapter-3/Class-XI/Biology: Plant KingdomraghavNo ratings yet
- Cha Rophy TaDocument4 pagesCha Rophy TaJohnNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity or Biological Diversity STU COPDocument13 pagesBiodiversity or Biological Diversity STU COPcbseiscNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Merged Bio 2023 Class 11 PDFDocument153 pagesChapter 7 Merged Bio 2023 Class 11 PDFamsal200416No ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument38 pagesPlant KingdomAditya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Xi CH 3 Bio-1Document7 pagesXi CH 3 Bio-1Jeet GoraiNo ratings yet
- Algae JupebDocument6 pagesAlgae JupebDavid AsuquoNo ratings yet
- ch-3 Bio Grade 11Document14 pagesch-3 Bio Grade 11shurshtikarande18No ratings yet
- Kebo 103Document14 pagesKebo 103Devanshu JulkaNo ratings yet
- People Environmental BenefitsDocument11 pagesPeople Environmental BenefitsMoyinoluwa AdedotunNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument9 pagesPlant KingdomsanaullahNo ratings yet