Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atlas 8620H: Colour Code: Red (Band) - White
Uploaded by
Víctor DominguezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atlas 8620H: Colour Code: Red (Band) - White
Uploaded by
Víctor DominguezCopyright:
Available Formats
Atlas
8620H
Case Hardening Steel Bar 8620H
Colour code: Red (Band) - White
Introduction
Atlas 8620H is a low Nickel Chromium Molybdenum case hardening steel of medium
hardenability used principally for relatively lightly stressed components. Atlas 8620H can
be carburised and subsequently hardened by a quenching and tempering operation. The
“H” designation of 8620H indicates guaranteed hardenability according to the hardenability
diagram on the following page.
Related Specifications
Atlas 8620H complies with AS1444 Grade 8620H and/or ASTM A29 Grade 8620.
Alternatively Atlas 8620H can be supplied as Euronorm grade 20NiCrMo2-2+HH (Material
Number 1.6523/1.6526 under EN 10084).
Chemical Composition Specification values in %
Grade C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo
0.17- 0.10- 0.60- ≤ 0.35- 0.15-
8620H ≤ 0.040 0.35-0.65
0.23 0.35 0.95 0.040 0.75 0.25
0.17- 0.65- ≤ 0.40- 0.15-
1.6523 ≤ 0.40 ≤ 0.035 0.35-0.70
0.23 0.95 0.035 0.70 0.25
Conditions of Supply
Normally supplied in the annealed condition with hardness max 212 HB, with typical
hardness being in the range 170-200 HB. Bars are cold finished (peeled) and supplied to
k12 tolerance for all bar diameters. All bars are ultrasonically inspected (according to
AS1065 level 2 for material procured by Atlas as of 1.12.2003)
Heat Treatments
Treatment Temperature Cooling
Range (°C)
Carburising 880 - 960 Oil (water), hot quench 160-250°C,
Salt bath 580-650°C, Case hardening box, Air*
Intermediate 630 - 650 Air, Furnace
annealing
Core hardening 860 – 900 Oil (water), hot quench 160-250°C*
Case hardening 780 – 820 Oil (water), hot quench 160-250°C*
Tempering 150 - 200 Air
* the choice of cooling medium depends on the desired final properties and geometry of
the section to be case hardened and the effect of the cooling medium, given the
hardenability of the steel.
Revised April 2006 1 of 3
Atlas Specialty Metals
Case Hardening Steel Bar 8620H
After final machining, heat in carburising atmosphere (blank carburise) to 880 to
960°C and hold for sufficient time at temperature to produce the required case depth.
The time at temperature during the blank carburising process determines the depth of
case achieved.
After completion of blank carburisation treatment, re-heat to 860-900°C, hold until
uniform and then quench in oil as rapidly as practical.
A refining treatment is necessary to improve the structure of the case and its
hardness. Heat slowly to 780-820°C, hold until uniform and then quench in oil.
Single quench treatment may also be possible where components are quenched
directly from 820 to 840°C.
Minimum tempering time is 1 hour, but a tempering period of 1 hour per 25mm of
section is recommended. If the steel is to be direct hardened, in general, a carburising
temperature of 950°C should not be exceeded. After case hardening a typical case
hardness of 61 HRC can be achieved.
Mechanical Properties after Case Hardening
The following table shows the typical mechanical properties achievable in the core of a
test section after carburizing, hardening and tempering.
Diameter Yield Strength Tensile Strength Elongation Impact Value
(mm) (MPa) (MPa) (A%) DVM (J)
11 785 min 980 – 1270 9 min 41 min
30 590 min 780 – 1080 10 min 41 min
63 490 min 690 – 930 11 min --
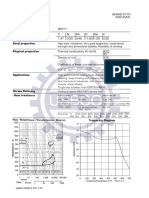
Hardenability Diagram
Hardness limits for Jominy test Hardness limits for Jominy test
EN 10084 specification for 20NiCrMo2-2+HH (1.6523) AS 1444 requirement for 8620H
50 50
45 45
Rockwell hardness (HRC)
Rockwell hardness (HRC)
40 40
max
35 min 35 max
min
30 30
25 25
20 20
15 15
0 1.5 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 20 25 30 35 40 0 1.5 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 20 25 30 35 40
distance from quenched end (mm) distance from quenched end (mm)
Revised April 2006 2 of 3
Atlas Specialty Metals
Case Hardening Steel Bar 8620H
Welding
Pre-heat welding area to 250-450°C and maintain this temperature while welding with
a low hydrogen electrode. Cool at a maximum rate of 100°C per hour. Weld before
carburising.
Applications
Small diameter gear parts exposed to low-medium stress. Typical components include
gears, planet wheels, drive pinions, shafts.
Disclaimer
Whilst every effort has been made to ensure accuracy of the information in this Datasheet, Atlas Specialty
Metals accepts no liability for damages arising from its use.
Revised April 2006 3 of 3
You might also like
- Database Management Systems: Understanding and Applying Database TechnologyFrom EverandDatabase Management Systems: Understanding and Applying Database TechnologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Low-Alloy SteelsFrom EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Low-Alloy SteelsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Case Hardening Alloy Steel Bar 6587Document3 pagesCase Hardening Alloy Steel Bar 6587CelsoNo ratings yet
- Quenched and Tempered Alloyed Engineering Steel DINDocument2 pagesQuenched and Tempered Alloyed Engineering Steel DINkazdoelahNo ratings yet
- SA/AS1548 - 7 - 460R: XlerplateDocument3 pagesSA/AS1548 - 7 - 460R: XlerplatenavNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog AluminiuDocument32 pagesProduct Catalog AluminiusnoofsnoofNo ratings yet
- Quenched and Tempered Alloyed Engineering Steel DINDocument2 pagesQuenched and Tempered Alloyed Engineering Steel DINkazdoelahNo ratings yet
- Cosmos Alminium-Technical - Specifications PDFDocument2 pagesCosmos Alminium-Technical - Specifications PDFmindsopenNo ratings yet
- Tempering Conditions For 30CrNiMo8Document2 pagesTempering Conditions For 30CrNiMo8madyeNo ratings yet
- Steel Grade: Material Data SheetDocument5 pagesSteel Grade: Material Data Sheetdan howsNo ratings yet
- Aisi 4140Document8 pagesAisi 4140ViruzTrisnaNo ratings yet
- 30crnimo8: Steel GradeDocument2 pages30crnimo8: Steel GradewemersonsrNo ratings yet
- DS Mold 4140Document3 pagesDS Mold 4140reza prasetiaNo ratings yet
- 42 CR Mo 4Document4 pages42 CR Mo 4eduardomanar1224No ratings yet
- 8620 Case Hardening Steel - Interlloy - Engineering Steels + AlloysDocument4 pages8620 Case Hardening Steel - Interlloy - Engineering Steels + Alloysankit7588No ratings yet
- 42 CR Mo 4Document4 pages42 CR Mo 4Alin ChehadeNo ratings yet
- 41 CR 4Document3 pages41 CR 4AHMED FATHINo ratings yet
- Passivate Stainless Steel SafelyDocument2 pagesPassivate Stainless Steel Safelymbe joseph100% (1)
- Datasheet Sandvik Saf 2205 en PDFDocument12 pagesDatasheet Sandvik Saf 2205 en PDFYuriy NesterovNo ratings yet
- 1.7225 en PDFDocument2 pages1.7225 en PDFTheodoros AtheridisNo ratings yet
- 20 MN CR 5Document7 pages20 MN CR 5AHMED FATHINo ratings yet
- NAS 660 Heat-Resistant Stainless Steel PropertiesDocument4 pagesNAS 660 Heat-Resistant Stainless Steel Propertiessafat parNo ratings yet
- 90 MN CR V8Document1 page90 MN CR V8arunajay724No ratings yet
- Data Sheet Cronidur 30 2009Document4 pagesData Sheet Cronidur 30 2009sgwilliamsNo ratings yet
- 34crnimo6: Steel GradeDocument6 pages34crnimo6: Steel GradeBiju KNo ratings yet
- 25crmo4: Steel GradeDocument3 pages25crmo4: Steel GradeCristian Stiven Martinez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- EN24 and EN24T SteelDocument3 pagesEN24 and EN24T Steelpatrik710No ratings yet
- 50CRMO4_50CrMo4-Nr.1.7228-ENGDocument2 pages50CRMO4_50CrMo4-Nr.1.7228-ENGLuiz Antonio dos AnjosNo ratings yet
- 20Mncr5: Steel GradeDocument4 pages20Mncr5: Steel GradeAhmad ShujaNo ratings yet
- SIHARD K770 high wear resistance tool steel with nitriding potentialDocument1 pageSIHARD K770 high wear resistance tool steel with nitriding potentialaadhavan rNo ratings yet
- 42 CR Mo 4Document3 pages42 CR Mo 4lucasNo ratings yet
- 42crmo4: Steel GradeDocument5 pages42crmo4: Steel GradeMahmoud KchaouNo ratings yet
- 56 Si 7Document2 pages56 Si 7Bhuvanesh ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- 42crmo6 : Steel GradeDocument2 pages42crmo6 : Steel GradeYonas Dwiananta YuwonoNo ratings yet
- CDA 84400 phosphor bronze alloy propertiesDocument4 pagesCDA 84400 phosphor bronze alloy propertiesShariq KhanNo ratings yet
- 20Mnv6 Hollow Bar: Iso Stocked Sizesiso ChartDocument3 pages20Mnv6 Hollow Bar: Iso Stocked Sizesiso ChartretrogradesNo ratings yet
- Dual Phase Steels Voestalpine EN 28092018Document4 pagesDual Phase Steels Voestalpine EN 28092018Silverio AcuñaNo ratings yet
- (17CrNiMo6) 4317 Case Hardening SteelDocument3 pages(17CrNiMo6) 4317 Case Hardening Steelazhar mohammedNo ratings yet
- A N D High-Cycle Fatigue Properties of Various Steels Specified in Jis For Machine Structural USEDocument12 pagesA N D High-Cycle Fatigue Properties of Various Steels Specified in Jis For Machine Structural USEKadek Santiari DewiNo ratings yet
- ASTM A335 Pipe Specification1Document8 pagesASTM A335 Pipe Specification1Rupam BaruahNo ratings yet
- ASTM A335 Pipe Specification1 PDFDocument8 pagesASTM A335 Pipe Specification1 PDFRoberto EliasNo ratings yet
- 1.8550 34cralni7 Ni50: Chemical CompositionDocument2 pages1.8550 34cralni7 Ni50: Chemical CompositionMichel PortalNo ratings yet
- Interlloy Grade 8620 Case Hardening SteelDocument3 pagesInterlloy Grade 8620 Case Hardening Steelajitchavan2150No ratings yet
- 304 (Allegheny Ludlum, Figures Scan)Document2 pages304 (Allegheny Ludlum, Figures Scan)P DNo ratings yet
- 42 CR Mo 4Document2 pages42 CR Mo 4ElMacheteDelHuesoNo ratings yet
- Annealed Engineering Steel C45E / 1042 (ASTMDocument2 pagesAnnealed Engineering Steel C45E / 1042 (ASTMkazdoelahNo ratings yet
- S235JR Sau OL 37Document1 pageS235JR Sau OL 37Pișta GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mild Steels Voestalpine EN 09082019Document5 pagesMild Steels Voestalpine EN 09082019Alma Aliza VillaberNo ratings yet
- Voestalpine Heavy Plate Datasheet Durostat en 20170904Document3 pagesVoestalpine Heavy Plate Datasheet Durostat en 20170904Kristy HillNo ratings yet
- 52crmov4: Steel GradeDocument3 pages52crmov4: Steel GradeemregnesNo ratings yet
- Macsteel VRN - Wear Abrasion Steels - Creusabro 8000Document4 pagesMacsteel VRN - Wear Abrasion Steels - Creusabro 8000jonodo89No ratings yet
- 41Cr4 steel data sheetDocument2 pages41Cr4 steel data sheetDewi Lanjarsari Purnama SastriNo ratings yet
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysFrom EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- CSSYB Insert B1698 PDFDocument8 pagesCSSYB Insert B1698 PDFVinit ShahNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Yellow Belt Presentation PDFDocument143 pagesSix Sigma Yellow Belt Presentation PDFDeeds VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Thermal DeburringDocument20 pagesThermal DeburringVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Free GD T Wall Chart PDFDocument1 pageFree GD T Wall Chart PDFAnonymous tGFxtqNNo ratings yet
- Minfc1963 Astm A575 Grade m1017Document3 pagesMinfc1963 Astm A575 Grade m1017Víctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- DLC Coating CamsDocument5 pagesDLC Coating CamsVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Mike Forster PresentationDocument29 pagesMike Forster PresentationVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Toyota Mirai FCV Posters LR Tcm-11-564265Document10 pagesToyota Mirai FCV Posters LR Tcm-11-564265Barbu MihailNo ratings yet
- How Can OEMs Win The Power Play in Tomorrow's Radically Changed Automotive EcosystemDocument16 pagesHow Can OEMs Win The Power Play in Tomorrow's Radically Changed Automotive EcosystemVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Automotive: Innovative Tooling Solutions For Front Suspension & Rear Differential ComponentsDocument23 pagesAutomotive: Innovative Tooling Solutions For Front Suspension & Rear Differential ComponentsVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Technical Molded Parts: Close To The Customer Around The WorldDocument10 pagesTechnical Molded Parts: Close To The Customer Around The WorldVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- H F C E V: Ydrogen UEL ELL Lectric EhiclesDocument20 pagesH F C E V: Ydrogen UEL ELL Lectric EhiclesVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Full Cell GMDocument71 pagesHydrogen Full Cell GMVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Graphene-Supported Platinum Catalyst-Based Membrane Electrode Assembly For PEM Fuel CellDocument9 pagesGraphene-Supported Platinum Catalyst-Based Membrane Electrode Assembly For PEM Fuel CellVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- EN 500-14 SSF-Ductile IronDocument34 pagesEN 500-14 SSF-Ductile IronVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- GKN Powder Metal BrochureDocument12 pagesGKN Powder Metal BrochureVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- 1 LeoTorresDocument49 pages1 LeoTorresVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Linfografric Hidrogeno GKNDocument1 pageLinfografric Hidrogeno GKNVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- PSA FCA Proposed Merger Presentation Dec 18 19Document27 pagesPSA FCA Proposed Merger Presentation Dec 18 19Fiat500USA0% (1)
- FLOWCast BrochureDocument2 pagesFLOWCast BrochureVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- Material Capabilities: Sintered Materials Other MaterialsDocument1 pageMaterial Capabilities: Sintered Materials Other MaterialsVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- 1 LeoTorres PDFDocument21 pages1 LeoTorres PDFVíctor DominguezNo ratings yet
- De Fasteners CompleteDocument44 pagesDe Fasteners CompleteantblyNo ratings yet
- AISI 1035 cs46Document2 pagesAISI 1035 cs46Russell ShacklefordNo ratings yet
- ADI WordDocument8 pagesADI WordAshutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- ASTM F2282 - 03 Steel RequirementsDocument15 pagesASTM F2282 - 03 Steel RequirementsFernado RinconNo ratings yet
- List of Etchant For MetallographyDocument3 pagesList of Etchant For Metallographyniraj_hwbNo ratings yet
- A 897 - A 897M - 02 Qtg5ny9bodk3ts1sruqDocument11 pagesA 897 - A 897M - 02 Qtg5ny9bodk3ts1sruqrolando cuadro blancoNo ratings yet
- Specifying Harmonized Standard Grade Compositions For Wrought Stainless SteelsDocument7 pagesSpecifying Harmonized Standard Grade Compositions For Wrought Stainless SteelsJosé Ramón GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Matmatch Com Learn Material Carbon SteelDocument7 pagesMatmatch Com Learn Material Carbon Steeldennis adamsNo ratings yet
- 12345-Elements of Physical MetallurgyDocument546 pages12345-Elements of Physical MetallurgyEkant Sharma100% (3)
- F136Document4 pagesF136Gustavo SuarezNo ratings yet
- Non Ferrous PyrometallurgyDocument34 pagesNon Ferrous PyrometallurgyKundayi ChagwederaNo ratings yet
- Tungsten Extractive Metallurgy - A Review of Processes and Their Challenges For SustainabilityDocument14 pagesTungsten Extractive Metallurgy - A Review of Processes and Their Challenges For SustainabilityJuan Diego Lopez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 1994 HERMAN Computer Assisted Modelling of Metallurgical Aspects of Hot Deformation and Transformation of SteelsDocument150 pages1994 HERMAN Computer Assisted Modelling of Metallurgical Aspects of Hot Deformation and Transformation of SteelsElliot AmadiNo ratings yet
- Alloy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesAlloy - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- The Treasure of Gold and Silver Artifacts From The Royal Tombs of Sipan - Peru PDFDocument30 pagesThe Treasure of Gold and Silver Artifacts From The Royal Tombs of Sipan - Peru PDFBernardDelorNo ratings yet
- CFA Guidance Note - Fixings and CorrosionDocument4 pagesCFA Guidance Note - Fixings and CorrosionkanekuenenNo ratings yet
- Laraib Sarfraz Khanzada's ProfileDocument3 pagesLaraib Sarfraz Khanzada's ProfileTanveerNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Metals Production ProcessesDocument31 pagesFerrous Metals Production Processessabasaktir4142No ratings yet
- Continuously Hot-Dip Coated Steel Flat Products - Technical Delivery ConditionsDocument40 pagesContinuously Hot-Dip Coated Steel Flat Products - Technical Delivery ConditionsReginaldo SantosNo ratings yet
- Option 02Document62 pagesOption 02suitup100No ratings yet
- Presentation Heat Treatment-Induction HardeningDocument37 pagesPresentation Heat Treatment-Induction HardeningRizwanNo ratings yet
- ASTM, SAE AND ISO GRADE MARKINGS FOR STEEL FASTENERSDocument6 pagesASTM, SAE AND ISO GRADE MARKINGS FOR STEEL FASTENERShoannhuNo ratings yet
- ASM Cross Reference For NonferrousDocument17 pagesASM Cross Reference For Nonferrousfedaqui100% (2)
- Josiah Resume Compressed PDFDocument1 pageJosiah Resume Compressed PDFJosiah PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 (Iron-Iron Carbide Diagram)Document20 pagesLec 8 (Iron-Iron Carbide Diagram)HdjdNo ratings yet
- Surface Corrosion Protection MethodsDocument10 pagesSurface Corrosion Protection MethodsmotiNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Pickling and Passivation Process of Stainless SteelDocument5 pagesThe Difference Between Pickling and Passivation Process of Stainless SteelRakibul IslamNo ratings yet
- Alloy286 - ASTM A453 660 DatasheetDocument2 pagesAlloy286 - ASTM A453 660 Datasheetn1ghtfallNo ratings yet
- AISI 4340 Alloy Steel Properties and UsesDocument4 pagesAISI 4340 Alloy Steel Properties and UsesFazry NurokhmanNo ratings yet
- Steelgrades 2Document6 pagesSteelgrades 2dexterisNo ratings yet