Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03.basic Meshing Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDF
Uploaded by
Vaibhav MishraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03.basic Meshing Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDF
Uploaded by
Vaibhav MishraCopyright:
Available Formats
4/15/2020 Basic meshing algorithms — Mesh 9.4.
0 documentation
Basic meshing algorithms
The MESH module contains a set of meshing algorithms, which are used for meshing entities (1D,
2D, 3D sub-shapes) composing geometrical objects.
Note: Algorithms added to the module as plug-ins are described in documentation of the plug-
ins (menu Help / User’s Guide / Mesh module / Plugins).
An algorithm represents either an implementation of a certain meshing technique or an interface to
the whole meshing program generating elements of several dimensions.
For meshing of 1D entities (edges):
Wire Discretization meshing algorithm - splits an edge into a number of mesh
segments following an 1D hypothesis.
Composite Side Discretization algorithm - allows to apply a 1D hypothesis to a whole
side of a geometrical face even if it is composed of several edges provided that they
form C1 curve in all faces of the main shape.
For meshing of 2D entities (faces):
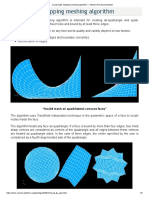
Triangle: Mefisto meshing algorithm - splits faces into triangular elements.
Quadrangle: Mapping meshing algorithm - splits faces into quadrangular elements.
Example of a triangular 2D mesh
Example of a quadrangular 2D mesh
For meshing of 3D entities (solid objects):
https://docs.salome-platform.org/latest/gui/SMESH/basic_meshing_algos.html 1/2
4/15/2020 Basic meshing algorithms — Mesh 9.4.0 documentation
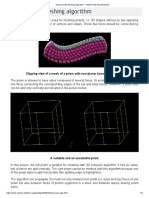
Hexahedron (i,j,k) meshing algorithm - solids are split into hexahedral elements thus
forming a structured 3D mesh. The algorithm requires that 2D mesh generated on a
solid could be considered as a mesh of a box, i.e. there should be eight nodes shared
by three quadrangles and the rest nodes should be shared by four quadrangles.
Structured mesh generated by Hexahedron (i,j,k) on a solid bound by 16 faces
Body Fitting meshing algorithm - solids are split into hexahedral elements forming a
Cartesian grid; polyhedra and other types of elements are generated where the
geometrical boundary intersects Cartesian cells.
Some 3D meshing algorithms, such as Hexahedron(i,j,k) also can generate 3D meshes from
2D meshes, working without geometrical objects.
There is also a number of more specific algorithms:
Extrusion 3D - for meshing prismatic 3D shapes with hexahedra and prisms.
Quadrangle: Medial Axis Projection - for quadrangle meshing of faces with
sinuous borders and rings.
Polygon per Face meshing algorithm - generates one mesh face (either a
triangle, a quadrangle or a polygon) per a geometrical face using all nodes
from the face boundary.
Projection algorithms - for meshing by projection of another mesh.
Import algorithms - for meshing by importing elements from another mesh.
Radial Prism - for meshing 3D geometrical objects with cavities with
hexahedra and prisms.
Radial Quadrangle 1D-2D - for quadrangle meshing of disks and parts of
disks.
Use Faces/Edges to be Created Manually - to create a 1D or a 2D mesh in
a python script.
Segments around Vertex - for defining the length of mesh segments around
certain vertices.
Constructing meshes page describes in detail how to apply meshing algorithms.
See Also a sample TUI Script of a Defining Meshing Algorithms operation.
https://docs.salome-platform.org/latest/gui/SMESH/basic_meshing_algos.html 2/2
You might also like
- LaTeX Mathematical SymbolsDocument4 pagesLaTeX Mathematical Symbolsjfreyre100% (9)
- Trig Problem SetDocument6 pagesTrig Problem Setshreesha mNo ratings yet
- University Math QuizDocument95 pagesUniversity Math QuizJude Martin Ballesteros Grozen100% (1)
- Elena Deza, Michel Marie Deza - Figurate Numbers-World Scientific (2012) PDFDocument469 pagesElena Deza, Michel Marie Deza - Figurate Numbers-World Scientific (2012) PDFAlexis Garcia DuranNo ratings yet
- Cayley Olympiad: Past Papers and Solutions 2003-2009Document40 pagesCayley Olympiad: Past Papers and Solutions 2003-2009Anderson AraújoNo ratings yet
- About 3D ModelingDocument9 pagesAbout 3D ModelingmiltodiavoloNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling: Computer SimulationDocument8 pages3D Modeling: Computer SimulationGuna SeelanNo ratings yet
- Transformation NotesDocument12 pagesTransformation NotespapersculptorNo ratings yet
- Oblique SphericalDocument5 pagesOblique SphericalInriko Rico Castillo100% (1)
- 02.constructing Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument16 pages02.constructing Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 第2章-ANSYS Meshing2013 - v1Document171 pages第2章-ANSYS Meshing2013 - v1stevenNo ratings yet
- IJCI - Volume 8 - Issue 2 - Pages 109-114Document6 pagesIJCI - Volume 8 - Issue 2 - Pages 109-114John RootNo ratings yet
- Mesh Generation and Grid Generation - SoftwareDocument10 pagesMesh Generation and Grid Generation - SoftwareShyam Sundar GodaraNo ratings yet
- DiffuserDocument8 pagesDiffuseranonymous50600No ratings yet
- Intrinsic Shape Signatures: A Shape Descriptor For 3D Object RecognitionDocument9 pagesIntrinsic Shape Signatures: A Shape Descriptor For 3D Object RecognitionBrianChenNo ratings yet
- 3d Image Reconstruction From Point Cloud of 2d ImagesDocument5 pages3d Image Reconstruction From Point Cloud of 2d ImagesAnirudhan AdukkathayarNo ratings yet
- Micromesh ConstructionDocument18 pagesMicromesh ConstructionWitchcraftNo ratings yet
- Benevs2015 - MeshDocument10 pagesBenevs2015 - MeshJose Marcos JrNo ratings yet
- BudMesh2D TreadMesh3Document10 pagesBudMesh2D TreadMesh3Etienne JankovichNo ratings yet
- Wavelet-Based Blind Watermarking of 3D Models: F. Uccheddu M. Corsini M. BarniDocument12 pagesWavelet-Based Blind Watermarking of 3D Models: F. Uccheddu M. Corsini M. BarniWahyu PratiktaNo ratings yet
- Computational Meshing For CFD SimulationsDocument31 pagesComputational Meshing For CFD SimulationsEduardo Antonio Burgos RuidíasNo ratings yet
- Frequency Analysis Using Catia V5Document41 pagesFrequency Analysis Using Catia V5Vasudha Ballarapu100% (1)
- MeshGen PDFDocument50 pagesMeshGen PDFJuanCa Barbosa100% (1)
- Meshing Methods (ANSYS Meshing) - Everyone Is Number OneDocument14 pagesMeshing Methods (ANSYS Meshing) - Everyone Is Number Oneicemage1991No ratings yet
- Lecture1 8 PDFDocument2 pagesLecture1 8 PDFbiruk1No ratings yet
- Materials Today: Proceedings: T.V. Smitha, K.V. NagarajaDocument13 pagesMaterials Today: Proceedings: T.V. Smitha, K.V. NagarajaCarlos Alexis Alvarado SilvaNo ratings yet
- Choy 2019Document9 pagesChoy 2019adsxzNo ratings yet
- Dense 3D Face Decoding Over 2500FPS: Joint Texture & Shape Convolutional Mesh DecodersDocument10 pagesDense 3D Face Decoding Over 2500FPS: Joint Texture & Shape Convolutional Mesh DecoderssahraNo ratings yet
- Learning Boundary Edges For 3d-Mesh Segmentation: (200y), Number Z, Pp. 1-12Document12 pagesLearning Boundary Edges For 3d-Mesh Segmentation: (200y), Number Z, Pp. 1-12Olabanji ShonibareNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: Submitted To Ma'am MominaDocument3 pagesComputer Graphics: Submitted To Ma'am MominaMuhammad TahaNo ratings yet
- 3D Fabrication of 2D Mechanisms: EUROGRAPHICS 2015 / O. Sorkine-Hornung and M. Wimmer (Guest Editors) (2015), Number 2Document10 pages3D Fabrication of 2D Mechanisms: EUROGRAPHICS 2015 / O. Sorkine-Hornung and M. Wimmer (Guest Editors) (2015), Number 2tostes_brNo ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional Object RepresentationsDocument7 pagesThree-Dimensional Object RepresentationsRishab Mehta83% (6)
- Mesh - Encoding and Decoding: D. Srinivasa Reddy Dr. M. V. Subba Reddy and Dr. B. Jaya Rami ReddyDocument11 pagesMesh - Encoding and Decoding: D. Srinivasa Reddy Dr. M. V. Subba Reddy and Dr. B. Jaya Rami ReddyRakeshconclaveNo ratings yet
- MESH2D - Automatic 2D Mesh GenerationDocument5 pagesMESH2D - Automatic 2D Mesh GenerationIgor GjorgjievNo ratings yet
- Milenko Vic 2019Document10 pagesMilenko Vic 2019SHAIK MOHAMMED SOHAIL SHAIK MOHAMMED SOHAILNo ratings yet
- FPGA Implementation of A Simple 3D Graphics PipelineDocument9 pagesFPGA Implementation of A Simple 3D Graphics PipelineBharat NarumanchiNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphic ReportDocument8 pagesComputer Graphic ReportAliNo ratings yet
- Glasses Frame Detection With 3D Hough TransformDocument4 pagesGlasses Frame Detection With 3D Hough TransformhaawmaawNo ratings yet
- CAD Import, Partitioning & Meshing: J.Cugnoni LMAF / EPFL 2009Document21 pagesCAD Import, Partitioning & Meshing: J.Cugnoni LMAF / EPFL 2009Xuan ThuNo ratings yet
- CAD MeshingDocument21 pagesCAD Meshingipman99No ratings yet
- SOM A Computer Vision Technique For Face Sketch Featured DatabaseDocument5 pagesSOM A Computer Vision Technique For Face Sketch Featured DatabaseEditor IJRITCC100% (1)
- Meshing Methods (ANSYS Meshing) - Everyone Is Number OneDocument14 pagesMeshing Methods (ANSYS Meshing) - Everyone Is Number OneLK AnhDungNo ratings yet
- 3D Grid GenerationDocument5 pages3D Grid Generationsiva_ksrNo ratings yet
- Visual KnitDocument13 pagesVisual KnitMohamed TamerNo ratings yet
- Fulltext09 (071 140)Document70 pagesFulltext09 (071 140)Maria JoseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document23 pagesLecture 1Hermain KarimNo ratings yet
- ANSYS WorkbenchDocument7 pagesANSYS WorkbenchpramodassNo ratings yet
- MeshNet - Mesh Neural Network For 3D Shape RepresentationDocument9 pagesMeshNet - Mesh Neural Network For 3D Shape Representationalt.s2-8hnmzegNo ratings yet
- Learning Efficient Point Cloud Generation For Dense 3D Object ReconstructionDocument8 pagesLearning Efficient Point Cloud Generation For Dense 3D Object ReconstructionArmandoNo ratings yet
- 3D Point Cloud Segmentationa SurveyDocument7 pages3D Point Cloud Segmentationa Survey陳傳生No ratings yet
- Grasshopper Add-On - Spider WebDocument12 pagesGrasshopper Add-On - Spider WebAnca HorvathNo ratings yet
- An Autonomous Mobile Robot With A 3D Laser Range Finder For 3D Exploration and Digitalization of Indoor EnvironmentsDocument18 pagesAn Autonomous Mobile Robot With A 3D Laser Range Finder For 3D Exploration and Digitalization of Indoor EnvironmentsCocias AdrianNo ratings yet
- Diff ShaderDocument12 pagesDiff Shaderds0313No ratings yet
- Rev Ques AnswerDocument23 pagesRev Ques AnswerKamarul NizamNo ratings yet
- SketchingReality TOG PDFDocument21 pagesSketchingReality TOG PDFSunny RajNo ratings yet
- Spectral Mesh Processing: SIGGRAPH Asia 2009 Course 32Document47 pagesSpectral Mesh Processing: SIGGRAPH Asia 2009 Course 32Wilson Javier ForeroNo ratings yet
- Mat Raft BentleyDocument3 pagesMat Raft BentleyParameswaran GanesanNo ratings yet
- 3Dmfv: 3D Point Cloud Classification in Real-Time Using Convolutional Neural NetworksDocument8 pages3Dmfv: 3D Point Cloud Classification in Real-Time Using Convolutional Neural NetworksNina MouhoubNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Semantic Slam With DCNN-based Feature Point Detection, Matching and Dense Point Cloud AggregationDocument6 pagesReal-Time Semantic Slam With DCNN-based Feature Point Detection, Matching and Dense Point Cloud AggregationJUAN CAMILO TORRES MUNOZNo ratings yet
- Manual Geologico Con GocadDocument56 pagesManual Geologico Con GocadDarwin HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Large-Scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation With Superpoint GraphsDocument13 pagesLarge-Scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation With Superpoint GraphsbarosyoungNo ratings yet
- AN4132Document16 pagesAN4132dibekayaNo ratings yet
- Imensionin: Automatic Understanding of Engineering DrawingsDocument12 pagesImensionin: Automatic Understanding of Engineering DrawingsSrinath SaiNo ratings yet
- 02 SalomeDocument21 pages02 SalomeAmar AlicheNo ratings yet
- Finite Elements Using Maxima: Theory and Routines for Rods and BeamsFrom EverandFinite Elements Using Maxima: Theory and Routines for Rods and BeamsNo ratings yet
- 88.element Diameter 3D - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument2 pages88.element Diameter 3D - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 37.moving Nodes - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument3 pages37.moving Nodes - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 26.adding Nodes and Elements - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument13 pages26.adding Nodes and Elements - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 36.merging Elements - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument3 pages36.merging Elements - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 30.rotation - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument3 pages30.rotation - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 100.point Marker - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument2 pages100.point Marker - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- Me Gate 2022 Fore Noon Solution UpdateDocument29 pagesMe Gate 2022 Fore Noon Solution UpdateVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 100.point Marker - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument2 pages100.point Marker - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 21.importing and Exporting Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFDocument3 pages21.importing and Exporting Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 17.max Element Volume Hypothesis - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument1 page17.max Element Volume Hypothesis - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 20.editing Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFDocument2 pages20.editing Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 13.segments Around Vertex - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument1 page13.segments Around Vertex - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 20.editing Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFDocument2 pages20.editing Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 09.import Elements From Another Mesh Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFDocument2 pages09.import Elements From Another Mesh Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 14.about Hypotheses - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument2 pages14.about Hypotheses - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 09.import Elements From Another Mesh Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFDocument2 pages09.import Elements From Another Mesh Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 06.extrusion 3D Meshing Algorithm - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument3 pages06.extrusion 3D Meshing Algorithm - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 05.body Fitting 3D Meshing Algorithm - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument4 pages05.body Fitting 3D Meshing Algorithm - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 03.basic Meshing Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument2 pages03.basic Meshing Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 12.use Edges - Faces To Be Created Manually - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument1 page12.use Edges - Faces To Be Created Manually - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 09.import Elements From Another Mesh Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFDocument2 pages09.import Elements From Another Mesh Algorithms - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 07.medial Axis Projection Quadrangle Meshing Algorithm - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFDocument2 pages07.medial Axis Projection Quadrangle Meshing Algorithm - Mesh 9.4.0 Documentation PDFVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 04.quadrangle - Mapping Meshing Algorithm - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument2 pages04.quadrangle - Mapping Meshing Algorithm - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- Extended Surfaces FinsDocument14 pagesExtended Surfaces FinsVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: by Vaibhav M. Enroll No. 171E021 May 10, 2020Document3 pagesAssignment-3 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: by Vaibhav M. Enroll No. 171E021 May 10, 2020Vaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- 01.about Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationDocument2 pages01.about Meshes - Mesh 9.4.0 DocumentationVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- Assignment Advance Manufacturing Processes: by Vaibhav M. Enroll No. 171E021 May 8, 2020Document11 pagesAssignment Advance Manufacturing Processes: by Vaibhav M. Enroll No. 171E021 May 8, 2020Vaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- Doomsday Mathematical Olympiad: 2 Set of Sample ProblemsDocument13 pagesDoomsday Mathematical Olympiad: 2 Set of Sample ProblemsRwitabrata MallickNo ratings yet
- Crystal HandoutsDocument23 pagesCrystal HandoutsArup DasNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 7Document6 pagesMaths Grade 7Anonymous 3E1GVENo ratings yet
- Mathematics 6 LAS Q4.PDF RemovedDocument10 pagesMathematics 6 LAS Q4.PDF RemovedShefa CapurasNo ratings yet
- Tri QuikDocument2 pagesTri QuikJoseCastilhoNo ratings yet
- Precalculus-Grade 11-Quarter 1-Week 3 FinalDocument9 pagesPrecalculus-Grade 11-Quarter 1-Week 3 FinalLuvie Jhun GahiNo ratings yet
- Pe 2 TrigonometryDocument10 pagesPe 2 TrigonometryJosuelle MadulaNo ratings yet
- Geometric QuestionsDocument64 pagesGeometric QuestionsshoumikNo ratings yet
- Trigo PDFDocument5 pagesTrigo PDFSachin ShreyNo ratings yet
- Math LiteracyDocument1 pageMath LiteracyGenesis NGNo ratings yet
- Iemh 110Document20 pagesIemh 110Avais KhanNo ratings yet
- Model Paper - Grade-V - MathsDocument8 pagesModel Paper - Grade-V - Mathsmaqbool ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- Final-Exam MathDocument8 pagesFinal-Exam MathJeybi SedilloNo ratings yet
- Perimeter and Area Question PaperDocument2 pagesPerimeter and Area Question Papersclad91No ratings yet
- Geometry Theorem and CorollariesDocument9 pagesGeometry Theorem and CorollariesNicole LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper For Class 9 Maths Sa2 PDFDocument5 pagesCbse Sample Paper For Class 9 Maths Sa2 PDFShweta GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesMaths Class Ix Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 02riyas babuNo ratings yet
- 4MA1 1HR January2021Document28 pages4MA1 1HR January2021redbrickfireballNo ratings yet
- Finding Interior Angles 1Document2 pagesFinding Interior Angles 1mattNo ratings yet
- Pre-Algebra Ch. 8 Quiz 2Document2 pagesPre-Algebra Ch. 8 Quiz 2KaitlynNo ratings yet
- Multi-Grade Lesson Plan in Teaching MathematicsDocument18 pagesMulti-Grade Lesson Plan in Teaching MathematicsKimberly Ann M. AbalosNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya Maths MATCH MATRIX Type Question BANKkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkDocument25 pagesSri Chaitanya Maths MATCH MATRIX Type Question BANKkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkSai GokulNo ratings yet
- IB-07Direction Ratios and Direction Cosines (29-35)Document4 pagesIB-07Direction Ratios and Direction Cosines (29-35)eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Non Euclidean CompanionDocument53 pagesNon Euclidean CompanionMiloš KovačevićNo ratings yet