Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 9 PDF
Lecture 9 PDF
Uploaded by
Asad Asad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views17 pagesOriginal Title
Lecture 9.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views17 pagesLecture 9 PDF
Lecture 9 PDF
Uploaded by
Asad AsadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Lecture 9
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١
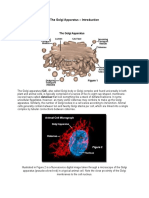
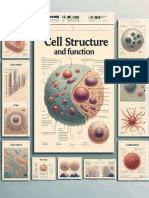
The Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (GA), also called Golgi body or Golgi
complex and found universally in both plant and animal cells
Is typically comprised of a series of five to eight cup-shaped,
membrane-covered sacs called cisternae that look something
like a stack of deflated balloons.
In some unicellular flagellates, however, as many as 60 cisternae
may combine to make up the Golgi apparatus.
Similarly, the number of Golgi bodies in a cell varies according to
its function.
Animal cells generally contain between ten and twenty Golgi
stacks per cell, which are linked into a single complex by tubular
connections between cisternae.
This complex is usually located close to the cell nucleus.
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ٢
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ٣
Golgi Apparatus Structure
The Golgi is composed of membrane-bound stacks
known as cisternae (singular: cisterna).
Between four and eight are usually present; however, in
some protists as many as sixty have been observed.
Each cisterna comprises a flattened membrane disk,
and carries Golgi enzymes to help or to modify cargo
proteins that travel through them.
The cisternae stack has five functional regions: the cis-
Golgi network, cis-Golgi, medial-Golgi, trans-Golgi, and
trans-Golgi network.
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ٤
Golgi Apparatus Structure
Vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum (via the vesicular-tubular
cluster) fuse with the cis-Golgi network and subsequently progress
through the stack to the trans Golgi network, where they are
packaged and sent to the required destination
Each region contains different enzymes which selectively modify the
contents depending on where they reside.
The cisternae also carry structural proteins important for their
maintenance as flattened membranes which stack upon each other.
The trans face of the trans-Golgi network is the face from which
vesicles leave the Golgi.
These vesicles then proceed to later compartments such as the cell
membrane, secretory vesicles or late endosomes
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ٥
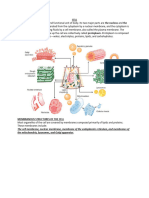
Diagram of secretory process from endoplasmic
reticulum (orange) to Golgi apparatus (pink).
1. Nuclear membrane
2. Nuclear pore
3. Rough endoplasmic
reticulum (rER)
4. Smooth endoplasmic
reticulum (sER)
5. Ribosome attached to
rER 6. Macromolecules
7. Transport vesicles
8. Golgi apparatus
9. Cis face of Golgi
apparatus
10. Trans face of Golgi
apparatus
11. Cisternae of lipids
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ٦
Golgi Apparatus Structure
The modifications to molecules that take place in the Golgi
apparatus occur in an orderly fashion.
Each Golgi stack has two distinct ends, or faces.
The cis face of a Golgi stack is the end of the organelle where
substances enter from the endoplasmic reticulum for processing,
while the trans face is where they exit in the form of smaller
detached vesicles.
Consequently, the cis face is found near the endoplasmic
reticulum, from whence most of the material it receives comes,
and the trans face is positioned near the plasma membrane of
the cell, to where many of the substances it modifies are
shipped.
The chemical make-up of each face is different and the enzymes
contained in the lumens (inner open spaces) of the cisternae
between the faces are distinctive .
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ٧
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ٨
Function
Cells synthesise a large number of different macromolecules.
The Golgi apparatus is integral in modifying, sorting, and packaging these
macromolecules for cell secretion (exocytosis) or use within the cell.
It primarily modifies proteins delivered from the rough endoplasmic
reticulum but is also involved in the transport of lipids around the cell, and
the creation of lysosomes.
In this respect it can be thought of as similar to a post office; it packages
and labels items which it then sends to different parts of the cell.
Enzymes within the cisternae are able to modify substances by the addition
of carbohydrates (glycosylation) and phosphates (phosphorylation).
The Golgi plays an important role in the synthesis of proteoglycans, which
are molecules present in the extracellular matrix of animals.
It is also a major site of carbohydrate synthesis
The Golgi has a putative role in apoptosis
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ٩
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١٠
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an eukaryotic organelle that
forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae
within cells.
The general structure of the endoplasmic reticulum is an extensive
membrane network of cisternae held together by the cytoskeleton.
The phospholipid membrane encloses a space, the cisternal space
(or lumen), from the cytosol, which is continuous with the perinuclear
space.
The functions of the endoplasmic reticulum vary greatly depending
on the exact type of endoplasmic reticulum and the type of cell in
which it resides.
The three varieties are called rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth
endoplasmic reticulum and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
The quantity of RER and SER in a cell can quickly interchange from
one type to the other, depending on changing metabolic needs
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١١
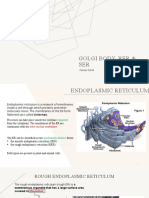
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
The surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is studded
with protein-manufacturing ribosomes giving it a "rough" appearance
(hence its name).
However, the ribosomes bound to the RER at any one time are not a
stable part of this organelle's structure as ribosomes are constantly
being bound and released from the membrane
A ribosome only binds to the ER once it begins to synthesize a
protein destined for the secretory pathway.
Here, a ribosome in the cytosol begins synthesizing a protein until a
signal recognition particle recognizes the pre-piece of 5-15
hydrophobic amino acids preceded by a positively charged amino
acid
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١٢
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
This signal sequence allows the recognition particle to bind to the
ribosome, causing the ribosome to bind to the RER and pass the
new protein through the ER membrane.
The pre-piece is then cleaved off within the lumen of the ER and the
ribosome released back into the cytosol.
The membrane of the RER is continuous with the outer layer of the
nuclear envelope
Although there is no continuous membrane between the RER and
the Golgi apparatus, membrane-bound vesicles shuttle proteins
between these two compartments.
Vesicles are surrounded by coating proteins called COPI and COPII.
COPII targets vesicles to the golgi and COPI marks them to be
brought back to the RER.
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١٣
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) has functions in
several metabolic processes, including synthesis of lipids and
steroids, metabolism of carbohydrates, regulation of calcium
concentration, drug detoxification, attachment of receptors on
cell membrane proteins, and steroid metabolism.
It is connected to the nuclear envelope.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is found in a variety of cell types
(both animal and plant) and it serves different functions in each.
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١٤
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
The Smooth ER also contains the enzyme glucose-6-
phosphatase which converts glucose-6-phosphate to
glucose, a step in gluconeogenesis
The SER consists of tubules and vesicles that branch
forming a network.
In some cells there are dilated areas like the sacs of
RER.
The network of SER allows increased surface area for
the action or storage of key enzymes and the products of
these enzymes.
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١٥
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١٦
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), from the Greek sarx, "flesh", is a
special type of smooth ER found in smooth and striated muscle.
The only structural difference between this organelle and the SER is
the medley of proteins they have, both bound to their membranes
and drifting within the confines of their lumens.
This fundamental difference is indicative of their functions: the SER
synthesizes molecules while the SR stores and pumps calcium ions.
The SR contains large stores of calcium, which it sequesters and
then releases when the muscle cell is stimulated.
The SR's release of calcium upon electrical stimulation of the cell
plays a major role in excitation-contraction coupling.
cell Biology ٢٢٢ ١٧
You might also like
- Introduction To Botany PDFDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Botany PDFElujulo Oyinkansola0% (1)
- SGOTDocument2 pagesSGOTDinesh Sreedharan0% (1)
- Chapter 6Document4 pagesChapter 6Astrii LyNo ratings yet
- Golgi Body, Rer & SerDocument8 pagesGolgi Body, Rer & SerZainab ZahidNo ratings yet
- Endomembrane System SummaryDocument17 pagesEndomembrane System Summaryʟᴏғɪ.No ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Function Lectrue 3Document19 pagesCellular Structure and Function Lectrue 3madhav biyaniNo ratings yet
- Golgi Apparatus - WikipediaDocument17 pagesGolgi Apparatus - WikipediaPrakashananda ThakurNo ratings yet
- GolgiDocument32 pagesGolgiramNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 5Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 5jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument8 pagesPlant CellIrish Nicole PacionNo ratings yet
- Cell 2Document26 pagesCell 2Rashul ChutaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Structure & FunctionDocument27 pagesBasic Cell Structure & FunctionJawaad AsifNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaDocument6 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaJosett RomanoNo ratings yet
- PL4 Cell CompartmentsDocument11 pagesPL4 Cell CompartmentsJake GopitaNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument4 pagesEndoplasmic Reticulumnikki_fuentes_1100% (1)
- Golgi Bodies.Document7 pagesGolgi Bodies.Ambreen RehmanNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument8 pagesCell OrganellesMuqadas khanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Document8 pagesStructure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Ishita KumariNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument3 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumHanumat SinghNo ratings yet
- Golgi Apparatus: Macromolecules Proteins LipidsDocument2 pagesGolgi Apparatus: Macromolecules Proteins LipidsIs SianNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument8 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumShahab Saqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesEukaryotic CellsBhavanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Last-Cell Organelles.Document3 pagesLecture Last-Cell Organelles.OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- Golgi Apparatus Structure and Function RelationshipDocument3 pagesGolgi Apparatus Structure and Function RelationshipHaroldNo ratings yet
- Golgi ApparatusDocument6 pagesGolgi Apparatusrksuripeddi517No ratings yet
- Cells InfoDocument4 pagesCells InfoLyza PacibeNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic RecticulumDocument5 pagesEndoplasmic RecticulumNora ZarahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 8 Cell The Unit of Lifeaatishsubash9b35832No ratings yet
- Zoo Sem2 Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument7 pagesZoo Sem2 Endoplasmic ReticulumAnadi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cell HandoutsDocument25 pagesCell Handoutsgameaus00No ratings yet
- The Golgi ApparatusDocument10 pagesThe Golgi ApparatusRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SISTEMA ENDOMEMBRANAR ConcluidoDocument20 pagesSISTEMA ENDOMEMBRANAR ConcluidojacintomateuscandaNo ratings yet
- B0302 - OrganellStruct and Funct (Inside The Cell) (2012)Document51 pagesB0302 - OrganellStruct and Funct (Inside The Cell) (2012)Prishneesha KalatharanNo ratings yet
- Internal Organization: Eukaryotic Cells Have They Performs Specific Functions For The CellDocument12 pagesInternal Organization: Eukaryotic Cells Have They Performs Specific Functions For The CellHACKER MANNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0Document14 pagesBiology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0gana63693No ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument30 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumMuhammad Junaid Iqbal100% (1)
- The Cytoplasm: CytosolDocument5 pagesThe Cytoplasm: CytosolHariniNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Standard 1EDocument15 pagesCell Biology Standard 1EveeramaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture 1Document17 pagesCell Biology Lecture 1NIMRAHNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic Reticulum ILLL PDFDocument23 pagesEndoplasmic Reticulum ILLL PDFTIMOTHY JAMESONNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document12 pagesLec 2HACKER MANNo ratings yet
- C1 - Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument70 pagesC1 - Cell Structure and OrganisationPaula MorisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Tour of The CellDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Tour of The CellAstrii LyNo ratings yet
- Physiology02 Cell PhysiologyDocument63 pagesPhysiology02 Cell PhysiologysmpoojasubashNo ratings yet
- Scrapy Group 3Document7 pagesScrapy Group 3Andrea Ericka CanawayNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Cell Structure and Function of OrganellesDocument66 pages2.1. Cell Structure and Function of OrganellesNama Saya100% (1)
- Cell BiologyDocument17 pagesCell BiologyVidit DixitNo ratings yet
- Diagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteDocument4 pagesDiagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteAdriana Santiago RoaNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 L5 NIADocument31 pagesBio 103 L5 NIAsubrotoghosh2001No ratings yet
- Unit-7-8-Cell Structure and Function (Chapter 4)Document47 pagesUnit-7-8-Cell Structure and Function (Chapter 4)DrMufaddal RampurwalaNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasmicmembranesystemschap8 130329081745 Phpapp01Document36 pagesCytoplasmicmembranesystemschap8 130329081745 Phpapp01IzarreNo ratings yet
- Er, Structure & Its FunctionsDocument20 pagesEr, Structure & Its FunctionsTalha AfzalNo ratings yet
- Golgi Complex: Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesGolgi Complex: Structure and FunctionjanapriyaNo ratings yet
- Partoza - JB, Concept Article - Endomembranesystem - DocxDocument4 pagesPartoza - JB, Concept Article - Endomembranesystem - DocxJenny PartozaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellvjaNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: Presented by Abhay AryaDocument17 pagesEndoplasmic Reticulum: Presented by Abhay AryaAbhay AryaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument45 pagesCellsapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Cell Structures & Organelles FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Structures & Organelles Functionsnasimzand78100% (1)
- Cell AnalogyDocument17 pagesCell AnalogyJianne CabildoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure and FunctionHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Marquez 3d CellDocument5 pagesMarquez 3d CellSatori TendōNo ratings yet
- GST201-Study Session 7Document16 pagesGST201-Study Session 7Elujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2019 Chapter Wise Question Bank: Carboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives - QuestionsDocument4 pagesJEE Mains 2019 Chapter Wise Question Bank: Carboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives - QuestionsElujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- GST201-Study Session 4Document16 pagesGST201-Study Session 4Elujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- The Golgi Apparatus: An Organelle With Multiple Complex FunctionsDocument9 pagesThe Golgi Apparatus: An Organelle With Multiple Complex FunctionsElujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- GST201-Study Session 9Document18 pagesGST201-Study Session 9Elujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- Study Session 1 Cultures and Societies in Africa 1.1Document12 pagesStudy Session 1 Cultures and Societies in Africa 1.1Elujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- GST201-Study Session 6Document13 pagesGST201-Study Session 6Elujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- SimpleDocument1 pageSimpleNehal KumarNo ratings yet
- Quiz and Exam Solutions in Organic Chemistry: June 2013Document2 pagesQuiz and Exam Solutions in Organic Chemistry: June 2013Elujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Lipids and Fats: October 2017Document8 pagesDifference Between Lipids and Fats: October 2017Elujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2019 Chapter Wise Question Bank: Carboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives - QuestionsDocument4 pagesJEE Mains 2019 Chapter Wise Question Bank: Carboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives - QuestionsElujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- Jorgensen Laboratories, Inc.: J-326B Lactophenol Cotton Blue Stain (For Fungi)Document1 pageJorgensen Laboratories, Inc.: J-326B Lactophenol Cotton Blue Stain (For Fungi)Elujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: MLT 415 - Fundamentals of MicrobiologyDocument12 pagesObjectives:: MLT 415 - Fundamentals of MicrobiologyElujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions - S: Discussion Section Problems SolutionsDocument3 pagesLecture 3: Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions - S: Discussion Section Problems SolutionsElujulo OyinkansolaNo ratings yet
- Dna Interactive ActivityDocument3 pagesDna Interactive Activityapi-195601294No ratings yet
- Case Study - Plasma MembraneDocument5 pagesCase Study - Plasma MembranejajajaredredNo ratings yet
- Chap 15Document40 pagesChap 15Koby100% (4)
- Ijmm 31 6 1375 PDFDocument6 pagesIjmm 31 6 1375 PDFAlex RogobeteNo ratings yet
- Production of L-Lysine Corynebacterium GlutamicumDocument8 pagesProduction of L-Lysine Corynebacterium GlutamicumUMNA NIZAMI BSBSNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Introduction To Peptide SynthesisDocument17 pagesNIH Public Access: Introduction To Peptide SynthesisStella AguirreNo ratings yet
- Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesBiomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: SciencedirectEyex97No ratings yet
- Lec 7 VirologyDocument35 pagesLec 7 VirologyQuezon, Michaella BSN1No ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- Biohacking LiteDocument25 pagesBiohacking Litetxboxi23No ratings yet
- Digestion 2 MCQDocument6 pagesDigestion 2 MCQgopod60% (5)
- Therapeutic Applications of Citicoline and Piracetam As Fixed Dose CombinationDocument6 pagesTherapeutic Applications of Citicoline and Piracetam As Fixed Dose CombinationFerdinando BaehaNo ratings yet
- Detection of Carbohydrates, Proteins and Fats (Animation) : Class 11: BiologyDocument2 pagesDetection of Carbohydrates, Proteins and Fats (Animation) : Class 11: BiologyAbigail ShantiaNo ratings yet
- Lec-Aeo-11-Biochem 2018Document4 pagesLec-Aeo-11-Biochem 2018mimrahmi7No ratings yet
- Student Book 2Document101 pagesStudent Book 2helena coelho odaNo ratings yet
- History of BiochemistryDocument3 pagesHistory of BiochemistryAmisha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Proteins Overview Part 1Document16 pagesAmino Acids and Proteins Overview Part 1Loulou ApolloNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Shows Part of One Strand of A DNA MoleculeDocument12 pagesFigure 1 Shows Part of One Strand of A DNA MoleculeAmal GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microbial Diagnostic Techniques in PeriodonticsDocument38 pagesAdvanced Microbial Diagnostic Techniques in PeriodonticsPiyusha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pro DrugsDocument25 pagesPro DrugsMankaran Singh100% (1)
- Dna ReportDocument21 pagesDna Report168-Shivank DwivediNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument90 pagesCell StructureYashwinni VijayasekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Cellular Respiration: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - Cellular Respiration: Multiple ChoiceMike MurdockNo ratings yet
- Energy and Life: Lesson QuizDocument3 pagesEnergy and Life: Lesson QuizMarko DesnicaNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Stress - Molecular Mechanisms and Biological EffectsDocument374 pagesOxidative Stress - Molecular Mechanisms and Biological EffectsEML100% (2)
- 9700 w08 QP 1Document20 pages9700 w08 QP 1Jason LeeNo ratings yet
- Histamine: A Mediator of Inflammation: Donald Macglashan, JR, MD, PHD Baltimore, MDDocument7 pagesHistamine: A Mediator of Inflammation: Donald Macglashan, JR, MD, PHD Baltimore, MDVo Xuan QuangNo ratings yet
- Responses of Lactic Acid Bacteria To OxygenDocument12 pagesResponses of Lactic Acid Bacteria To OxygenKerstin BernNo ratings yet
- Zivak Organic Acid LC-MS-MS UrineDocument2 pagesZivak Organic Acid LC-MS-MS UrineYousra ZeidanNo ratings yet