0% found this document useful (0 votes)
331 views2 pagesRain Sensor Circuit Design Guide
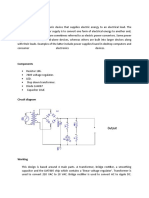
A rain sensor is a device that detects rainfall and has two main uses: 1) to shut down automatic irrigation systems when rain is detected, and 2) to activate car windshield wipers and protect the interior from rain. The rain sensor circuit uses an LM358 operational amplifier as a voltage comparator to detect changes in voltage from the rain sensor. When rain is detected, the sensor voltage increases above the threshold set by resistor voltage divider, triggering the comparator output to turn on an LED and buzzer.
Uploaded by
Erole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
331 views2 pagesRain Sensor Circuit Design Guide
A rain sensor is a device that detects rainfall and has two main uses: 1) to shut down automatic irrigation systems when rain is detected, and 2) to activate car windshield wipers and protect the interior from rain. The rain sensor circuit uses an LM358 operational amplifier as a voltage comparator to detect changes in voltage from the rain sensor. When rain is detected, the sensor voltage increases above the threshold set by resistor voltage divider, triggering the comparator output to turn on an LED and buzzer.
Uploaded by
Erole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
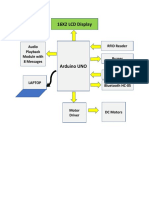
- Components: Lists the primary components necessary for the rain sensor circuit, including the rain sensor and various microelectronics.
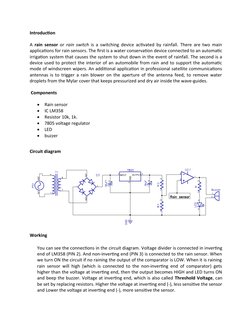
- Circuit Diagram: Illustrates and describes the circuit diagram used in the rain sensor setup.
- Introduction: Provides an overview of a device activated by rainfall, explaining its applications and types of rain sensors and CCDs.
- Working: Explains the functionality and operation of the rain sensor circuit, including LED indicator behavior in response to rain detection.
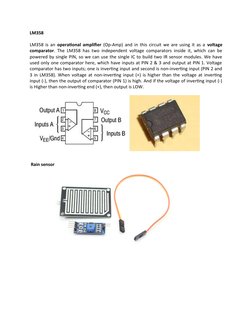
- Rain Sensor: Provides an image of the rain sensor and its connection to the LM358 to demonstrate its integration within the system.
- LM358: Describes the LM358 operational amplifier used in the circuit, including its purpose, configuration, and application in the rain sensor.