0% found this document useful (0 votes)
577 views11 pagesWireless Power Transfer Overview
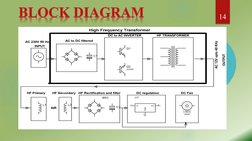
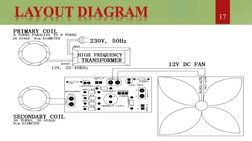
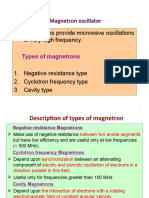
This document discusses wireless power transfer through electromagnetic induction. It summarizes that wireless power transmission involves transferring electrical energy from a power source to an electrical load without wires by using electromagnetic fields. Specifically, the document discusses Nikola Tesla's pioneering experiments with wireless electricity in 1894 using resonant inductive coupling. It then provides details about the experimental setup, which uses a high frequency transformer to wirelessly power a small DC fan over short distances of up to 3 cm through near-field inductive coupling and magnetic resonance between coils.
Uploaded by
Erole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
577 views11 pagesWireless Power Transfer Overview
This document discusses wireless power transfer through electromagnetic induction. It summarizes that wireless power transmission involves transferring electrical energy from a power source to an electrical load without wires by using electromagnetic fields. Specifically, the document discusses Nikola Tesla's pioneering experiments with wireless electricity in 1894 using resonant inductive coupling. It then provides details about the experimental setup, which uses a high frequency transformer to wirelessly power a small DC fan over short distances of up to 3 cm through near-field inductive coupling and magnetic resonance between coils.
Uploaded by
Erole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Wireless Power Transfer Introduction
- What is Wireless Electricity?
- History of Development
- Basic Principle
- Experimental Set-Up
- Components
- HF Transformer
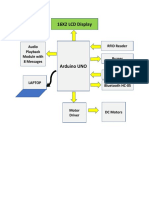
- Block Diagram
- Layout Diagram
- Operation
- Conclusion Slide