Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AP European History 2020 Course Description-Themes
Uploaded by
kayla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views6 pagesThis document has all the illustrative examples in College Board's AP European History Course Description. I divided it into themes, so that I can distinguish which event led to another.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document has all the illustrative examples in College Board's AP European History Course Description. I divided it into themes, so that I can distinguish which event led to another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views6 pagesAP European History 2020 Course Description-Themes
Uploaded by
kaylaThis document has all the illustrative examples in College Board's AP European History Course Description. I divided it into themes, so that I can distinguish which event led to another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
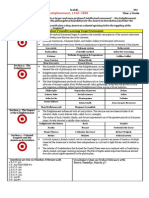
CULTURAL AND INTELLECTUAL Jesuits
DEVELOPMENTS Unit 2.2 Luther and Protestant
Unit 1.2 Italian Renaissance Reformation Unit 4.5 18th century Culture and Arts
Petrarch New Protestant interpretations of Printed materials
Lorenzo Valla christian doctrine and practice Newspapers, periodicals
Marsillo Ficino Priesthood of all believers Books and pamphlets
Pico della Mirandola Primacy of scripture The Encyclopedie
Individuals promoting secular values Predestination Baroque artists and musicians who
Niccolo Machiavelli Salvation by faith alone promoted religion or glorified monarchy
Baldasarre Castiglione Protestants who viewed wealth as a sign Diego Valasquez
Francesco Guicciardini of God’s favour Gian Bernini
Calvinists George Friderich Handel
Individuals promoting revival of JS Bach
Classical texts Unit 2.3 Protestant Reform Continues Artistic movements that reflected
Leonardo Bruni Reformers using press to disseminate commercial society or Enlightenment
Leon Battista Alberti ideas ideals
Niccolo Machiavelli Martin Luther Rembrandt
Painters and architects Vernacular bibles Jan Vermeer
Michelangelo Religious conflicts challenging the Jacques-Louis David
Donatello monarch’s control of religious Pantheon in Paris
Raphael institutions Literature which reflected commercial
Andrea Palladio Huguenots activity and Enlighten.
Leon Batista Alberti Puritans Defoe, Richardson
Filippo Brunelleschi Nobles in Poland Henry Fielding, Austen, Goethe
Unit 2.5 The Catholic Reformation Unit 7.8 19th Century Culture and Arts
Unit 1.3 Northern Renaissance New institutions and doctrines Romantic artists
Artists who employed naturalism St Teresa of Avila Turner, Delacroix
Peiter Breugel the Elder Ursulines Romantic Writers
Rembrand Roman Inquisition Byron, Keats, Shelley, Hugo
Index of Prohibited Books
Andreas Versalius
NAtural philosophers who continued Unit 6.3 Second Wave Industrialization
TECHNOLOGICAL AND SCIENTIFIC to hold traditional views of alchemy and and Its Effects
INNOVATION astrology Factory production
1.4 Printing Paracelsus Manchester, England
Movable printing press by Gutenberg Johannes Kepler The Krupp Family, Essen Germany
1450 Sir Isaac Newton New technologies
Unit 1.6 Technological Advances, the Unit 6.2 The Spread of Industry Bessemer process
Age of Exploration Throughout Europe Mass production
Navigational technology Britain’s leadership Electricity
Compass The Crystal Palace and the Great Chemicals
Sternpost rudder Exhibition of 1851
Portolani Banks Developments in communication and
Quadrant and astrolabe Government financial awards to transportation
Lateen rig inventors Telegraph
Military technology Commercial interest in government Steamship, Railroads
Guns and gunpowder Repeal of the Corn Laws Streetcars or trolley cars
States seeking access to luxury goods Government support of industrialization Telephones
Spanish in the New World Canals Internal combustion engine
Portuguese in the Indian Ocean Railroads Airplane
Dutch in the East Indies/Asia Trade agreements Radio
Mercantilist policies employed by the Geographical factors in eastern and New efficient methods of transportation
state southern Europe and other innovations
Jean-Baptiste Colbert Lack of resources Refrigerated rail cars
Religion and exploration Lack of adepquate transportation Ice boxes
Jesuit activities Primitive agricultural practices and New industries
Unit 4.2 The Scientific Revolution famines Chemical industry
Additional physicians who challenged The Hunger 40s Electricity and utilities
Galen Irish Potato famine Automobile
Paracelcus Russian serfdom
Leisure travel Edict of Nantes The Catalan Revolts in Spain
Professional and leisure sport Commercial and professional groups Competition between minority and
Unit 6.3 Second Wave continued that gained power najtional groups
Mass marketing Merchants and financiers in Celtic regions of Scotland, Ireland
Advertising Renaissance Italy and and France
Department stores northern Europe Dutch resistance in the Spanish
Catalogs Nobels of the robe in France Netherlands
Industrialization in Prussia Secular political theorists Czech identity in the Holy Roman
Zollverein Jean Bodin Empire/Jan Hus/ Defenestration
Investment in transportation Hugo Grotius Unit 4.6 Enlightened and Other
network Niccolo Machiavelli Approaches to Power
Adoption of improved methods of Unit 2.4 Wars of Religion Enlightened monarchs
manufacturing French Wars of religion Frederick II of Prussia
Friedrich List’s National System Catherine de Medici Joseph II of Austria
St Bartholomew’s Day Massacre Prussian and Habsburg rulers
STATES AND OTHER INSTITUTIONS OF War of the Three Henrys Marie Theresa of Austria
POWER Habsburg ruler Frederick William I of Prussia
Unit 1.5 New Monarchies Charles V Frederick II of Prussia
State actions to control religion and State exploitation of conflict
morality Spain and England Unit 3.2 English Civil War and the
Spanish Inquisition France, Sweden and Denmark in Glorious Revolution
Concordat of Bologna the Thirty Years War Competitors for power in the English
Book of Common Prayer States allowing religious pluralism Civil War
Peace of Augsburg Poland James I
Monarchical control The Netherlands Charles I
Ferdinand and Isabella Unit 3.1 Contextualizing State Building Oliver Cromwell
Star Chamber Competition between monarchs and Quadrant and astrolabe
Concordat of Bologna nobles Outcomes of the English Civil War and
Peace of Augsburg Louis XIII and Cardinal Richelieu the Glorious Revolution
The Fronde in France English Bill of Rights
Parliamentary Sovereignty
Unit 5.6 Napoleon’s Rise, Dominance,
Unit 3.6 Balance of Power Unit 5.4 The French Revolution and Defeat
Louis XIVs nearly continuous wars Causes of the French Revolution Reforms under Napoleon
Dutch War Peasant and bourgeois grievances Careers open to talent
Nine Years’ War Bread shortages Educational system
War of the Spanish succession French involvement in the Centralised bureaucracy
States that benefited from the military American Revolution Civil Code
revolution Actions taken during the moderate Concordat of 1801
Spain under the Habsburgs phase of the revolution Curtailment of rights under Napoleon
Sweden under Gustavus Adolphus Declaration of the Rights of Man Secret police
France and Citizen Censorship
Civil Constitution of the Clergy Limitation of women’s rights
Unit 3.7 Absolutist Approaches to Constitution of 1791 Nationalist responses to Napoleon
Power Abolition of provinces and division Student protest in German states
Absolute monarchs of France into departments Guerilla war in Spain
James I of England Radical Jacobin leaders and institutions Russian scorched earth policy
Peter the Great of Russia Georges Danton
Philip II, II and IV of Spain Jean-Paul Marat NATIONAL AND EUROPEAN IDENTITY
Extended power of the state Committee of Public Safety 7.2 Nationalism
Intendants Mass conscription Nationalists:
Modernized, state-controlled Levee en masse Fichte
military Female involvement in the revolution Grimm brothers
Russian westernization October March on Versailles Pan-slavists
Russian Academy of Sciences Olympe de Gouges Anti-semitism:
Education Society of Republican Dreyfus affair
Western fashion Revolutionary Women Christian Social Party in Germany
Expanded military Opponents of the Revolution Luegger, mayor of Vienna
Edmund Burke Zionists:
Theodor Hertzel SOCIAL ORGANIZATION AND
Communication and transportation DEVELOPMENT
7.3 National Unification and Diplomatic Technologies: Unit 2.6 16th c. Society and Pollitics
Tensions Steamships Continued social hierarchies
Bismark’s alliances: Telegraph Prestige of land ownership
Three Emperor’s League Photography Aristocratic privileges of taxes,
Triple alliance Advances in Medicine fees for services and
Reinsurance treaty Pasteur’s germ theory of disease legal protection
Nationalist tensions in the Balkans Public Health projects Political exclusion of women
Congress of Berlin in 1878 7.7 Imperialism’s Global Effects Debates about women’s roles
Growing influence of Serbia Diplomatic tensions Women’s intellect and education
Bosnia-Herzegovina annexation Berlin conference (1884-85) Women as preachers
crisis Fashoda crisis (1898) Le Querelle des Femmes
First Balkan War Morroccan crises (1905 and 1911) Regulating public morals
Participants in the imperialism debates New secular laws
INTERACTION OF EUROPE AND THE Pan-German League Codes on begging and prostitution
WORLD Hobson Abolishing carnival
Unit 1.9 The Slave Trade Congo Reform Association Witchcraft
Middle Passage Responses to European Imperialism: Unit 4.3 The Enlightenment
Planter society Indian Congress Party Works applying scientific principles to
7.6 New Imperialism: Motivations and Zulu Resistance society
Methods India’s Sepoy Mutiny Montesquieu’s The Spriti of the
Ideas of cultural and racial superiority: China’s Boxer Rebellion Laws
The White Man’s Burden Japan’s Meji restoration Cesare Beccaria’s On Crimes and
Mission civilsatrice Punishments
Social darwinism
Advanced weaponary: Individuals who challenged Rousseau’s
Minie ball (bullet) position on women
Breech-loading rifle Mary Wollstonecraft
Machine gun Marquis de Concorcet
Institutions that broadened the Unit 6.4 Social Effects of
audience for new ideas Industrialization
Coffeehouses Laws restricting the labor of children
Academies and women
Lending libraries Factory Mines Act 1833
Masonic lodges Mines Act 1842
Proponents of new economic ideas Ten Hours Act 1847
Physiocrats Leisure time activities and spaces
Francois Quesney Parks
Anne Robert Jacques Turgot Sports clubs and arenas
Intellectuals Beaches
David Hume Department stores
Baron d’Holbach Museums
Religious developments Theatres
Revival of German Pietism Opera Houses
Unit 4.4 18th century Society and
Demographics
Inoculation and disease control
Lady Mary Wortley Montagu
Increased emphasis on childhood
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Education in Napoleonic France
and Austria
Patinting and portraiture
You might also like
- Western ArchitectureDocument388 pagesWestern ArchitectureFran Hrzic100% (9)
- Friends and Enemies: The Underground War Between Great Britain and France, 1793-1802Document143 pagesFriends and Enemies: The Underground War Between Great Britain and France, 1793-1802Christopher Gibbs100% (1)
- Haliczer - Sexuality in The Confessional. A Sacrament ProfanedDocument276 pagesHaliczer - Sexuality in The Confessional. A Sacrament ProfanedMariana ZinniNo ratings yet
- 868 - THE - AGE - OF - CAPITALISM - 6 - Vladimir MossDocument403 pages868 - THE - AGE - OF - CAPITALISM - 6 - Vladimir MossIgnacioPérezBurgaréNo ratings yet
- Chapter Renaissance and ReformationDocument41 pagesChapter Renaissance and Reformationmbr91853285100% (2)
- Chapter 12-Renaissance and ReformationDocument27 pagesChapter 12-Renaissance and ReformationJonathan Daniel KeckNo ratings yet
- Censored Chapters of 200 Years TogetherDocument329 pagesCensored Chapters of 200 Years TogetherJustyouzerneimNo ratings yet
- The Exile Issue 22 (2004)Document24 pagesThe Exile Issue 22 (2004)Sophie Mavzalevskaya100% (1)
- Questions and Answers about: World HistoryFrom EverandQuestions and Answers about: World HistoryRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Renaissance Part 1Document97 pagesRenaissance Part 1Joeima SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Yuen-Gen Liang (Editor), Jarbel Rodriguez (Editor) - Authority and Spectacle in Medieval and Early Modern Europe - Essays in Honor of Teofilo F. Ruiz-Routledge (2017)Document272 pagesYuen-Gen Liang (Editor), Jarbel Rodriguez (Editor) - Authority and Spectacle in Medieval and Early Modern Europe - Essays in Honor of Teofilo F. Ruiz-Routledge (2017)Mario GrañaNo ratings yet
- The Congress of Vienna PowerDocument445 pagesThe Congress of Vienna Powercolotelo100% (2)
- Renaissance - NotesDocument4 pagesRenaissance - NotesMok Lak0% (1)
- Stanley Kubrick Napoleon - Movie ScriptDocument155 pagesStanley Kubrick Napoleon - Movie Scriptkoskinou100% (2)
- (Renaissance Society of America Texts and Studies Series Vol 11) Hilaire Kallendorf - A Companion To The Spanish Renaissance-Brill (2018)Document699 pages(Renaissance Society of America Texts and Studies Series Vol 11) Hilaire Kallendorf - A Companion To The Spanish Renaissance-Brill (2018)Juan100% (1)
- HALICZER, Stephen. Inquisition and Society in The Kingdom of Valencia PDFDocument456 pagesHALICZER, Stephen. Inquisition and Society in The Kingdom of Valencia PDFAlisson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Napoleon Bonaparte PDFDocument2 pagesNapoleon Bonaparte PDFJeffrey75% (4)
- Stone, Harold Samuel - Vico's Cultural HistoryDocument351 pagesStone, Harold Samuel - Vico's Cultural HistoryMaurizio80100% (1)
- Gerd Rainer Horn The Spirit of Vatican II Western European Progressive Catholicism in The Long Sixties PDFDocument275 pagesGerd Rainer Horn The Spirit of Vatican II Western European Progressive Catholicism in The Long Sixties PDFDaniel FernandesNo ratings yet
- Knoetel Napoleonic Uniforms Vol 4 German States 1814 15Document20 pagesKnoetel Napoleonic Uniforms Vol 4 German States 1814 15Todd Duckett100% (1)
- Saxon List1Document2 pagesSaxon List1misfirekkNo ratings yet
- INT GCSE History-Specification PDFDocument62 pagesINT GCSE History-Specification PDFilovefettuccineNo ratings yet
- Essential Vocabulary From The AP European History Key ConceptsDocument8 pagesEssential Vocabulary From The AP European History Key Conceptsise eggfNo ratings yet
- 7 Question BankDocument7 pages7 Question BankSamir ParmarNo ratings yet
- Theme - 7: Changing Cultural TraditionsDocument5 pagesTheme - 7: Changing Cultural TraditionsAnjali PrasadNo ratings yet
- LT ExcelDocument28 pagesLT Excelapi-553438116No ratings yet
- Unit VI Study Guide - UpdatedDocument2 pagesUnit VI Study Guide - UpdatedSidney DoreyNo ratings yet
- Changing Cultural Tradition QuestionsDocument4 pagesChanging Cultural Tradition Questionsdwivedikanaklata24No ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Revolution and Enlightenment, 1550-1800: World History Pre-AP - Duez NAME - PDDocument2 pagesChapter 17: Revolution and Enlightenment, 1550-1800: World History Pre-AP - Duez NAME - PDDavid Duez100% (1)
- HumanismDocument39 pagesHumanismpaula martinezNo ratings yet
- Ren and Ref09Document25 pagesRen and Ref09Ms. ShulerNo ratings yet
- Art and Reform in The Late Renaissance: After TrentDocument12 pagesArt and Reform in The Late Renaissance: After TrentJasmina S. CiricNo ratings yet
- Hist.102 Midterm Exam Study GuideDocument4 pagesHist.102 Midterm Exam Study GuideTomás DiasNo ratings yet
- Notes 3rd QuarterDocument7 pagesNotes 3rd QuarterHector Gloria IIINo ratings yet
- Age of RationalismDocument2 pagesAge of RationalismDenise CuizonNo ratings yet
- Renaissance and Reformation Study GuideDocument5 pagesRenaissance and Reformation Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldNo ratings yet
- Renaissance The Renaissance Was A Fervent Period of European CulturalDocument23 pagesRenaissance The Renaissance Was A Fervent Period of European CulturalMARY A.No ratings yet
- Culture and Art of The Revolutionary PeriodDocument2 pagesCulture and Art of The Revolutionary PeriodJosé Andrés SantanaNo ratings yet
- Middle Ages or The Medieval Times: Science Technology and SocietyDocument9 pagesMiddle Ages or The Medieval Times: Science Technology and SocietySANTOS, CHARISH ANNNo ratings yet
- Ch. 12 Renaissance Reformation P. 396Document12 pagesCh. 12 Renaissance Reformation P. 396api-268644570No ratings yet
- CH 10 RenaissanceDocument4 pagesCH 10 RenaissanceSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Renaissance With ArtDocument46 pagesRenaissance With Artapi-662060477No ratings yet
- AP Euro NotesDocument11 pagesAP Euro NotesJeffrey LeeNo ratings yet
- APEC Chapter 12 Study GuideDocument3 pagesAPEC Chapter 12 Study GuideSteven ChenNo ratings yet
- The Renaissance and ReformationDocument6 pagesThe Renaissance and ReformationslepzyysznNo ratings yet
- European 16 - 17 Century: TH THDocument10 pagesEuropean 16 - 17 Century: TH THUsoph Two PiecesNo ratings yet
- Contemporary History of Europe Prelim Module 1Document11 pagesContemporary History of Europe Prelim Module 1Mhebzky DizonNo ratings yet
- The Transformation of The West, 1450Document23 pagesThe Transformation of The West, 1450Shakil Ahmad AligNo ratings yet
- HISTORY 6 - Self-TransformationsDocument52 pagesHISTORY 6 - Self-Transformationsrajeev_khanna_15No ratings yet
- Anna Middleton - 2004Document347 pagesAnna Middleton - 2004marcosdabataNo ratings yet
- Renaissance: Renaissance of The 12th Century Renaissance (Disambiguation)Document27 pagesRenaissance: Renaissance of The 12th Century Renaissance (Disambiguation)ekkexxeNo ratings yet
- History Notes Class IX (Rennaissance)Document4 pagesHistory Notes Class IX (Rennaissance)Sutanu PatiNo ratings yet
- Age of Enlightenment - WikipediaDocument14 pagesAge of Enlightenment - WikipediaMaria Emilia del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Vanilla Planifolia, The First Mesoamerican Orchid: Illustrated, and Notes On The de La Cruz-Badiano CodexDocument8 pagesVanilla Planifolia, The First Mesoamerican Orchid: Illustrated, and Notes On The de La Cruz-Badiano CodexTania CastilloNo ratings yet
- Renaissance: Nothing Is True, Everything Is PermittedDocument19 pagesRenaissance: Nothing Is True, Everything Is PermittedSuffer with MeNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Unit 6 The Birth of The Modern AgesDocument5 pagesApuntes Unit 6 The Birth of The Modern AgesSilvania SánchezNo ratings yet
- Modern World - The Age of ReasonDocument21 pagesModern World - The Age of ReasonMahendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Media04 Baroque PDFDocument48 pagesMedia04 Baroque PDFIrma OsmanovićNo ratings yet
- World History (2022)Document10 pagesWorld History (2022)Mouli MajumdarNo ratings yet
- DeLaRosaLorente 2017Document333 pagesDeLaRosaLorente 2017Fábio Bezerra de BritoNo ratings yet
- Ill - Episodes in The Life of The Early Modern Learned Book - Dec.2020Document439 pagesIll - Episodes in The Life of The Early Modern Learned Book - Dec.2020Vaan HoolNo ratings yet
- BFM - 978 94 017 2280 3/1Document17 pagesBFM - 978 94 017 2280 3/1Bruno LloretNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Review: Global History & Geography 9 Grade - 24 February 2013Document9 pagesChapter 12 Review: Global History & Geography 9 Grade - 24 February 2013dontblameda1No ratings yet
- Reading MaterialDocument5 pagesReading MaterialPriyanka GhaiNo ratings yet
- Eliana Josephine HernandezPages 500Document4 pagesEliana Josephine HernandezPages 500Eliana Josephine Gemelos-HernandezNo ratings yet
- RenancebDocument6 pagesRenancebDABBUNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 The RenaissanceDocument13 pagesUnit 2 The RenaissanceRongila MeyeNo ratings yet
- Napoléon BonaparteDocument4 pagesNapoléon BonapartevidhuNo ratings yet
- Liebertwolkwitz 131014Document4 pagesLiebertwolkwitz 131014jhawkesNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Life Span Development 5th Edition Santrock Test BankDocument35 pagesEssentials of Life Span Development 5th Edition Santrock Test Bankbayedaidancerkobn8100% (15)
- The Life of Napoleon BonaparteVol. I. (Of IV.) by Sloane, William Milligan, 1850-1928Document191 pagesThe Life of Napoleon BonaparteVol. I. (Of IV.) by Sloane, William Milligan, 1850-1928Gutenberg.org100% (2)
- ENDGAME Script and Timecodes For SubtitlingDocument99 pagesENDGAME Script and Timecodes For SubtitlingVelocitorNo ratings yet
- French Revolution 2017 NotesDocument25 pagesFrench Revolution 2017 Notesreut sabriNo ratings yet
- I. F. Clarke - Voices Prophesying War. Future Wars, 1763-3749-Oxford University Press (1992)Document292 pagesI. F. Clarke - Voices Prophesying War. Future Wars, 1763-3749-Oxford University Press (1992)Ramon SouzaNo ratings yet
- The Congress of Vienna LLJ Metternich's Era LJ The Congress System and The Concert of EuropeDocument4 pagesThe Congress of Vienna LLJ Metternich's Era LJ The Congress System and The Concert of EuropeNouman MaharNo ratings yet
- Honors French Revolution PBL AssignmentDocument27 pagesHonors French Revolution PBL Assignmentapi-553438116No ratings yet
- The Art of Strategy Napoleon's Maxims of WarDocument166 pagesThe Art of Strategy Napoleon's Maxims of WarJohn MarshallNo ratings yet
- Bentley5 TB ch28Document12 pagesBentley5 TB ch28balsamicmyvinNo ratings yet
- Otumfuo's Speech at UPSA Leadership LectureDocument19 pagesOtumfuo's Speech at UPSA Leadership Lecturemyjoyonline.com67% (3)
- Beethoven - Wellington's Victory or The Battle of Vittoria (Wellingtons Sieg), Op 91 - I - Battle PDFDocument43 pagesBeethoven - Wellington's Victory or The Battle of Vittoria (Wellingtons Sieg), Op 91 - I - Battle PDFOleksii TernoviiNo ratings yet
- Cat Forklift t225 t250 t300 Spare Parts ManualDocument22 pagesCat Forklift t225 t250 t300 Spare Parts Manualshannonnichols110597biy100% (26)
- History Notes NapoleonDocument2 pagesHistory Notes NapoleonKatarzynaNo ratings yet
- Merlo Treemme Mm280b Service Maintenance Manual Parts Manual Hydraulic Electrical Diagram deDocument22 pagesMerlo Treemme Mm280b Service Maintenance Manual Parts Manual Hydraulic Electrical Diagram demichellejackson130187gcq100% (114)
- Bill and Ted'S: Excellent Musical AdventureDocument58 pagesBill and Ted'S: Excellent Musical AdventureNathanNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument12 pagesFrench Revolutionshaileshawasthi100% (1)
- Practicum Lesson Plan - NapoleonDocument6 pagesPracticum Lesson Plan - Napoleonapi-372578521No ratings yet
- LynchDocument31 pagesLynchluvistrosNo ratings yet
- Napoleons Memoirs Reading and QuestionsDocument4 pagesNapoleons Memoirs Reading and QuestionsL AgostoNo ratings yet