Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Present Simple Gramatica
Uploaded by
Kelly Johana Díaz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesThe document discusses the simple present tense in Spanish. It explains that the simple present is used to express habits, general facts, repeated actions, permanent situations, emotions, and permanent desires. It is also used for giving instructions or indications. Additionally, it discusses how to form the simple present tense in affirmative, interrogative, and negative forms. It provides notes on conjugating verbs in the third person singular and examples of verbs conjugated in the simple present tense.
Original Description:
Original Title
PRESENT SIMPLE GRAMATICA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the simple present tense in Spanish. It explains that the simple present is used to express habits, general facts, repeated actions, permanent situations, emotions, and permanent desires. It is also used for giving instructions or indications. Additionally, it discusses how to form the simple present tense in affirmative, interrogative, and negative forms. It provides notes on conjugating verbs in the third person singular and examples of verbs conjugated in the simple present tense.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesPresent Simple Gramatica
Uploaded by
Kelly Johana DíazThe document discusses the simple present tense in Spanish. It explains that the simple present is used to express habits, general facts, repeated actions, permanent situations, emotions, and permanent desires. It is also used for giving instructions or indications. Additionally, it discusses how to form the simple present tense in affirmative, interrogative, and negative forms. It provides notes on conjugating verbs in the third person singular and examples of verbs conjugated in the simple present tense.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
EL "SIMPLE PRESENT" SE UTILIZA:
Para expresar hábitos y rutinas, hechos generales, acciones repetidas o
situaciones, emociones y deseos permanentes:
I smoke (hábito); I work in London (permanencia)
Para dar instrucciones o indicaciones:
You walk for two hundred meters, then you turn left.
Para hablar de eventos programados, presentes o futuros:
Your exam starts at 09.00.
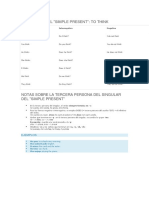
FORMACIÓN DEL "SIMPLE PRESENT": TO THINK
Afirmativa Interrogativa Negativa
I think Do I think? I do not think
You think Do you think? You do not think
He thinks Does he think? He does not think
She thinks Does she think? She does not think
It thinks Does it think? It does not think
We think Do we think? We do not think.
They think Do they think? They do not think.
NOTAS SOBRE LA TERCERA PERSONA DEL
SINGULAR DEL "SIMPLE PRESENT"
En la tercera persona del singular, el verbo siempre termina en -s:
he wants, she needs, he gives, she thinks.
Verbos que terminan en consonante y “-y “: en la tercera persona del
singular, se cambia la -y por -ies:
fly --> flies, cry --> cries
Cuando en un verbo una vocal precede a la -y:
play --> plays, pray --> prays
Añadimos -es a los verbos que terminan en:-ss, -x, -sh, -ch:
he passes, she catches, he fixes, it pushes
Contractions en oraciones negativas (does not: doesn’t) cuando hablamos
de (She, he, it), (do not: don’t) cuando hablamos de I, You, We, They
EJEMPLOS
He goes to school every morning.
She understands English.
It mixes the sand and the water.
He tries very hard.
She enjoys playing the piano.
You might also like
- Songwriting for Geniuses: 25 Tips for the Genius in EveryoneFrom EverandSongwriting for Geniuses: 25 Tips for the Genius in EveryoneRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Communicative English 2016 BestDocument58 pagesCommunicative English 2016 BestYusuf HussenNo ratings yet
- Word Order in Questions Present SimpleDocument15 pagesWord Order in Questions Present SimpleesmerNo ratings yet
- 16 TensesDocument18 pages16 TensesAnonymous eCws3ENo ratings yet
- Name: - DateDocument3 pagesName: - DateKelly Johana Díaz100% (1)
- 1 Present Simple TenseDocument13 pages1 Present Simple TenseClaudia BalasNo ratings yet
- El "Simple Present" Se UtilizaDocument2 pagesEl "Simple Present" Se UtilizaKelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet
- El "Simple Present" Se Utiliza:: EjemplosDocument2 pagesEl "Simple Present" Se Utiliza:: EjemplosCarlitos MartínezNo ratings yet
- O "Simple Present" É Utilizado:: As Soon As, UntilDocument2 pagesO "Simple Present" É Utilizado:: As Soon As, UntilSara SilvaNo ratings yet
- El "Simple Present" Se Utiliza:: EjemplosDocument2 pagesEl "Simple Present" Se Utiliza:: EjemplosGardith SadeniaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple&Present Continous Grammar ExplanationDocument3 pagesPresent Simple&Present Continous Grammar ExplanationHéctor León SaavedraNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present Tense Is UsedDocument6 pagesThe Simple Present Tense Is UsedMade AnomaharsiNo ratings yet
- Formación Del "Simple Present": To Think: Afirmativa Interrogativa NegativaDocument1 pageFormación Del "Simple Present": To Think: Afirmativa Interrogativa Negativaouyeah1984No ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument31 pagesSimple PresentJuni DzibNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present Tense Се КористиDocument2 pagesThe Simple Present Tense Се КористиLjupcho PetreskiNo ratings yet
- I-The Form Forming The Simple Present Tense: To ThinkDocument3 pagesI-The Form Forming The Simple Present Tense: To ThinkZineb BouzaidNo ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument26 pagesSimple PresentLuis Alberto Sanchez SubiaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense PDFDocument4 pagesSimple Present Tense PDFAnthony ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Present Simple PDFDocument5 pagesPresent Simple PDFPaula A ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Universidad Tecnologica Del Suroeste de Guanajuato: Obed Armando Cabrera YbarraDocument17 pagesUniversidad Tecnologica Del Suroeste de Guanajuato: Obed Armando Cabrera YbarraObed Armando Cabrera YbarraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Excepție: Dacă - y e Precedat de o Vocală, Atunci Schimbarea Nu Mai Are Loc Și Forma deDocument2 pagesPresent Simple: Excepție: Dacă - y e Precedat de o Vocală, Atunci Schimbarea Nu Mai Are Loc Și Forma deCristina SNo ratings yet
- Present Simple (Presente Simple) : Afirmativa Interrogativa NegativaDocument1 pagePresent Simple (Presente Simple) : Afirmativa Interrogativa NegativaLiza7478No ratings yet
- After, When, Before, As Soon As, UntilDocument6 pagesAfter, When, Before, As Soon As, UntilJuan DavidNo ratings yet
- I-Simple Present and Present ContinuousDocument6 pagesI-Simple Present and Present ContinuousIvon SalemNo ratings yet
- Present Tense Simple: Does She Eat Bread For Breakfast Every Morning? (Daily Routine)Document2 pagesPresent Tense Simple: Does She Eat Bread For Breakfast Every Morning? (Daily Routine)awakening20121No ratings yet
- Present Simple e ContinuousDocument5 pagesPresent Simple e ContinuousMarta ZaccagniNo ratings yet
- Present: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectDocument7 pagesPresent: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectWaad AlteeNo ratings yet
- Manual Ingles IV 2024 - Parcial 1Document26 pagesManual Ingles IV 2024 - Parcial 1diegoandreordazlazaroNo ratings yet
- Deberes de InglesDocument8 pagesDeberes de Inglesanon_767047614No ratings yet
- Present Simple: Affirmative NegativeDocument15 pagesPresent Simple: Affirmative NegativeJosé Miguel SerraNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense AbdoDocument7 pagesSimple Present Tense AbdoAbdelhadi Ait AllalNo ratings yet
- Simple Present VerbsDocument3 pagesSimple Present VerbsSofía RamirezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple PresentationDocument13 pagesPresent Simple PresentationClaudia BalasNo ratings yet
- Notas Sobre La Tercera Persona Del Singular Del "Simple Present"Document9 pagesNotas Sobre La Tercera Persona Del Singular Del "Simple Present"Anonymous thHFCANo ratings yet
- Tempos VerbaisDocument22 pagesTempos VerbaisGUILHERME OLIVEIRA PATTERSONNo ratings yet
- Secion 6 InglesDocument12 pagesSecion 6 InglesWalter Atao SalazarNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TeoriaDocument3 pagesSimple Present TeoriaKaty GallagherNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - VerbsDocument81 pagesEnglish Grammar - VerbsAisy AstarinaNo ratings yet
- Of Your Favourite Food You Saw in The VideoDocument6 pagesOf Your Favourite Food You Saw in The VideoLisette Cifuentes RiañoNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Tense Grammar PresentationDocument14 pagesPresent Continuous Tense Grammar PresentationRiski Norita SariNo ratings yet
- Libro Ingles DaniDocument153 pagesLibro Ingles DaniIsmant PCNo ratings yet
- Deberes de InglesDocument9 pagesDeberes de Inglesgemy loorNo ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument3 pagesSimple PresentsandianavarroNo ratings yet
- Communicative English 2016 BestDocument57 pagesCommunicative English 2016 BestyusufNo ratings yet
- Portfolio of EvidenceDocument28 pagesPortfolio of EvidenceEduardo RamosNo ratings yet
- Present Simple - Continuous Lesson - 220109 - 213225Document6 pagesPresent Simple - Continuous Lesson - 220109 - 213225wafaaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present - Summary: Affirmative NegativeDocument3 pagesSimple Present - Summary: Affirmative NegativeJ.Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 17the Present TensesDocument5 pages17the Present TensesazizNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument67 pagesEnglish Tensesdonisparta5No ratings yet
- MAteri Kelas 7 - Present TenseDocument3 pagesMAteri Kelas 7 - Present TenseOneKuta febryNo ratings yet
- Present: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectDocument10 pagesPresent: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectIoana TrîmbițașNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent ContinuousAizack WiverNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: He Wants, She Needs, He Gives, She ThinksDocument10 pagesSimple Present: He Wants, She Needs, He Gives, She ThinksAisyah RasdiNo ratings yet
- SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE v2Document6 pagesSIMPLE PRESENT TENSE v2heruNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent ContinuousDavid SilvaNo ratings yet
- 3ro InglesDocument14 pages3ro InglesEfrain JenryNo ratings yet
- 7.-Resumen 7.2 Inglés ESODocument21 pages7.-Resumen 7.2 Inglés ESOInmaculadaNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous TenseDocument30 pagesPresent Continuous TenseSania KhanNo ratings yet
- Verbe Dinamice: 2.3. Verbele Dinamice Si StaticeDocument9 pagesVerbe Dinamice: 2.3. Verbele Dinamice Si StaticenameNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense IDM 1Document3 pagesSimple Present Tense IDM 1Mabel Condori QuispeNo ratings yet
- My Class Schedule: Hour Monday Tuesday Wednesda Y Thursday FridayDocument4 pagesMy Class Schedule: Hour Monday Tuesday Wednesda Y Thursday FridayKelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet
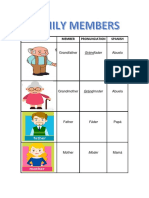
- Picture Member Pronunciation Spanish: Grandfather AbueloDocument3 pagesPicture Member Pronunciation Spanish: Grandfather AbueloKelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet
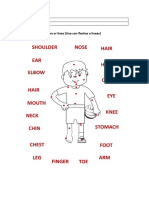
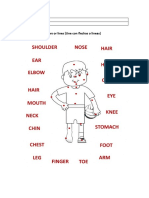
- Body PartsDocument2 pagesBody PartsKelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet
- Daily RoutineDocument1 pageDaily RoutineKelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet
- Join With Arrows or Lines (Une Con Flechas o Líneas) : Name DateDocument2 pagesJoin With Arrows or Lines (Une Con Flechas o Líneas) : Name DateKelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet
- Taller WH QuestionsDocument1 pageTaller WH QuestionsKelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet
- Write in The Correct Form These Sentences (Escribe en El Orden Correcto Las Siguientes Oraciones) : For ExampleDocument1 pageWrite in The Correct Form These Sentences (Escribe en El Orden Correcto Las Siguientes Oraciones) : For ExampleKelly Johana Díaz100% (1)
- Name: - DateDocument1 pageName: - DateKelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 1Document3 pagesLearning Activity 1Kelly Johana DíazNo ratings yet