Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Kenj PereñaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Kenj PereñaCopyright:
Available Formats
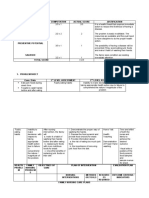
ASSESSMENT NURSING PLANNING NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS INTERVENTION
Subjective Data: Diarrhea related to After 3 days of 1. Observe and 1. Helps differentiate After 3 days of
presence of toxins as Nursing Intervention record stool individual disease nursing intervention
manifested by the patient’s parent/ frequency, and assesses severity the goal was partially
frequent elimination watcher will: characteristics, of episode. met. The patient’s
of mushy stools. amount, and watcher verbalized a
>Report reduction in precipitating factors. mushy stool and less
frequency of stools, frequent of
Objective Data: >return to more 2. Identify foods and 2. Avoiding intestinal defecation.
Increased normal stool cons fluids that precipitate irritants promotes
bowel diarrhea, e.g., raw intestinal rest.
sounds/peristalsis vegetables and fruits,
Frequent, and whole-grain cereals,
often severe, condiments,
mushy stools carbonated drinks,
Changes in milk products
stool color
3. Monitor Intake and 3. Provides
Output. Note number, information about
character, and overall fluid balance,
amount of stools; renal function, and
estimate insensible bowel disease
fluid losses, e.g., control, as well as
diaphoresis. Measure guidelines for fluid
urine specific gravity; replacement.
observe for oliguria.
4. Observe for 4. Indicates excessive
excessively dry skin fluid loss/resultant
and mucous dehydration.
membranes,
decreased skin turgor,
slowed capillary
refill.
5. Monitor laboratory 5. Reduces fluid
studies, e.g., losses from intestines
electrolytes
(especially
potassium,
magnesium) and
ABGs (acid-base
balance).
You might also like
- Health Education HTPDocument4 pagesHealth Education HTPizelelelsNo ratings yet
- Family Structure: Nuclear Family Number of Children: 2Document9 pagesFamily Structure: Nuclear Family Number of Children: 2Nahum Raphael RealNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Care Common Discomforts During PregnancyDocument5 pagesPrenatal Care Common Discomforts During PregnancyKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Cell Ab ActivitiesDocument7 pagesCell Ab ActivitiesJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Standards of Public Health Nursing in The PhilippinesDocument18 pagesStandards of Public Health Nursing in The PhilippinesWilma BeraldeNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan: Learning Objectives Content Rationale MethodologyDocument5 pagesHealth Teaching Plan: Learning Objectives Content Rationale Methodologyjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Google Chrome OSDocument47 pagesGoogle Chrome OSnitin07sharmaNo ratings yet
- Agrarian ReformDocument40 pagesAgrarian ReformYannel Villaber100% (2)
- Rata-Blanca-La Danza Del FuegoDocument14 pagesRata-Blanca-La Danza Del FuegoWalter AcevedoNo ratings yet
- NCM 114: Care of The Older Adult Instructor: Gino Paulo A. Buizon, R.NDocument9 pagesNCM 114: Care of The Older Adult Instructor: Gino Paulo A. Buizon, R.NJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Gordon's Functional Health PatternDocument2 pagesGordon's Functional Health PatternNoriel LacsinaNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction of FNCP 1Document2 pagesIntroduction of FNCP 1Helen QuibuyenNo ratings yet
- Health Deficit: Presence of PediculosisDocument2 pagesHealth Deficit: Presence of PediculosisMariecel GazaNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageFamily Nursing Care PlanBhaby Che AserdnaNo ratings yet
- Health Care Delivery System & COPARDocument52 pagesHealth Care Delivery System & COPARDharylle Cariño100% (1)
- FCP (Gorres)Document3 pagesFCP (Gorres)Kaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities To:: Magnesium SulfateDocument13 pagesNursing Responsibilities To:: Magnesium SulfateabrokenheartedgirlNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Interventions Justification EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Interventions Justification EvaluationPJNo ratings yet
- Proclamation No. 499Document21 pagesProclamation No. 499shaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Making of Homemade Salt and Sugar SolutionDocument2 pagesMaking of Homemade Salt and Sugar SolutionShing Mae MarieNo ratings yet
- Tpo Eo Poa LFDDocument4 pagesTpo Eo Poa LFDEzra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung-Disease Case StudyDocument20 pagesHirschsprung-Disease Case StudyFaith TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesChest Tube Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoNo ratings yet
- NCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFKimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationlaehaaaNo ratings yet
- School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences: St. Paul University Philippines Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Document5 pagesSchool of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences: St. Paul University Philippines Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500CLARENCE REMUDARONo ratings yet
- NCM 108 Healthcare Ethics (Bioethics) Activity 1 MIDTERM: To Withdraw or Not To WithdrawDocument3 pagesNCM 108 Healthcare Ethics (Bioethics) Activity 1 MIDTERM: To Withdraw or Not To WithdrawAndrea Aputen100% (1)
- FNCPDocument5 pagesFNCPCarina QuibinitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanTrisha CayabyabNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Community Health and Public Health NursingDocument1 pageThe Difference Between Community Health and Public Health NursingMelissa Briggs100% (1)
- CHN PTDocument2 pagesCHN PTYzobel Phoebe ParoanNo ratings yet
- Introduction Case StudyDocument10 pagesIntroduction Case StudyJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Rotation II - ObjectivesDocument2 pagesRotation II - ObjectivesPauPauNo ratings yet
- NSO - Adam's Forward Bend TestDocument2 pagesNSO - Adam's Forward Bend TestMaha AmilNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan - Cough and ColdsDocument1 pageFamily Nursing Care Plan - Cough and ColdsArnx QuilonNo ratings yet
- FNCP (Hypertension)Document3 pagesFNCP (Hypertension)Jose Emmanuel Ribaya RuivivarNo ratings yet
- vINA Faulty Eating HabitsDocument2 pagesvINA Faulty Eating HabitsMyrshaida IbrahimNo ratings yet
- FNCP PoorsanitationmarwahDocument3 pagesFNCP PoorsanitationmarwahAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- A. Not My Job!: Ncmp109 Bioethics: Case StudyDocument2 pagesA. Not My Job!: Ncmp109 Bioethics: Case StudyAudrey Ann Acob100% (1)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPYesha Mae MartinNo ratings yet
- Table-10 3Document1 pageTable-10 3Hamil BanagNo ratings yet
- Ablayan Final Family Case StudyDocument12 pagesAblayan Final Family Case StudyKryzza LeizellNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis Physical Assessment Bagtas EstrelitaDocument11 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis Physical Assessment Bagtas EstrelitamarengbibNo ratings yet
- Journal Analysis-BALLON, Karlo CDocument4 pagesJournal Analysis-BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Improper Food HandlingDocument2 pagesImproper Food HandlingampalNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan: Partially AchievedDocument3 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan: Partially AchievedENKELI VALDECANTOSNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Planning For Successful AgingDocument11 pagesPlanning For Successful AgingMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- Family Care Plan of ROSARIO: (1 Level Assessment) (2 Level Assessment) (Specific)Document3 pagesFamily Care Plan of ROSARIO: (1 Level Assessment) (2 Level Assessment) (Specific)Eduard Reyjell MontañoNo ratings yet
- FNCP FinalDocument28 pagesFNCP FinalKristal Jane RuedasNo ratings yet
- 3nu08 - Sesperes - Quiz On Medication Calculation and Iv RegulationDocument4 pages3nu08 - Sesperes - Quiz On Medication Calculation and Iv Regulationbea SesperesNo ratings yet
- Family Case Study-BibliographyDocument1 pageFamily Case Study-BibliographyKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- LevemirDocument2 pagesLevemirViah Angela CaasiNo ratings yet
- Legal Mandates R/T Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument6 pagesLegal Mandates R/T Nutrition and Diet TherapySam Albert RenaciaNo ratings yet
- FNCP Unplanned PregnancyDocument1 pageFNCP Unplanned PregnancyASTRA FAYE QUEENA DELENANo ratings yet
- ROLES RESPONSIBILITIES OF A MC NURSE IN CHALENGEING SITUATIONS Merged Compressed Merged MergedDocument53 pagesROLES RESPONSIBILITIES OF A MC NURSE IN CHALENGEING SITUATIONS Merged Compressed Merged MergedYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- NCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainDocument2 pagesNCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainAubrey RecierdoNo ratings yet
- NCP-Acute Gastroenteritis PediatricDocument11 pagesNCP-Acute Gastroenteritis PediatricJhoevina Dulce Capicio0% (1)
- Objective Data:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageObjective Data:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSharon T. AumanNo ratings yet
- Age NCPDocument4 pagesAge NCPnj_pink081794No ratings yet
- Scope Project Timeline Resources: System Design, Development, and Customization PhaseDocument10 pagesScope Project Timeline Resources: System Design, Development, and Customization PhaseKenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- NCP PcapDocument2 pagesNCP PcapKenj Pereña100% (1)
- (Miconazole or Fluconazole) : Topical ClotrimazoleDocument2 pages(Miconazole or Fluconazole) : Topical ClotrimazoleKenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- Patient DatabaseDocument25 pagesPatient DatabaseKenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- Health Education ReviewerDocument1 pageHealth Education ReviewerKenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- Scultures:: Pieta Hermes and The Venus de MiloDocument16 pagesScultures:: Pieta Hermes and The Venus de MiloKenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: 15 LearningsDocument17 pagesPharmacology: 15 LearningsKenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and ChildDocument18 pagesMaternal and ChildKenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing: (15 Learnings)Document17 pagesCommunity Health Nursing: (15 Learnings)Kenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 10. Microbial Ecology and Microbial BiotechnologyDocument20 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 10. Microbial Ecology and Microbial BiotechnologyKenj PereñaNo ratings yet
- Orchestral Tools - The Orchestral Grands ManualDocument12 pagesOrchestral Tools - The Orchestral Grands ManualPiotr Weisthor RóżyckiNo ratings yet
- God Whose Will Is Health and Wholeness HymnDocument1 pageGod Whose Will Is Health and Wholeness HymnJonathanNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Words - 20.11Document2 pagesVocabulary Words - 20.11ravindra kumar AhirwarNo ratings yet
- Skylab Our First Space StationDocument184 pagesSkylab Our First Space StationBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1.COMMUNICATION PROCESSES, PRINCIPLES, AND ETHICS - Ver 2Document24 pagesLECTURE 1.COMMUNICATION PROCESSES, PRINCIPLES, AND ETHICS - Ver 2Trixia Nicole De LeonNo ratings yet
- Company Profile RadioDocument8 pagesCompany Profile RadioselviNo ratings yet
- The Civil Mutinies of Romeo and Juliet: Glenn ClarkDocument21 pagesThe Civil Mutinies of Romeo and Juliet: Glenn ClarkmilcahNo ratings yet
- Sauna Studies As An Academic Field: A New Agenda For International ResearchDocument42 pagesSauna Studies As An Academic Field: A New Agenda For International ResearchsedgehammerNo ratings yet
- CA39BDocument2 pagesCA39BWaheed Uddin Mohammed100% (2)
- Lyndhurst OPRA Request FormDocument4 pagesLyndhurst OPRA Request FormThe Citizens CampaignNo ratings yet
- January Payslip 2023.pdf - 1-2Document1 pageJanuary Payslip 2023.pdf - 1-2Arbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Modul9 VPNDocument34 pagesModul9 VPNDadang AbdurochmanNo ratings yet
- Sleep and Dreams PDFDocument16 pagesSleep and Dreams PDFMarina Los100% (1)
- Manual StereoDocument29 pagesManual StereoPeter Mac RedNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Abu Batu Sebagai Subtitusi Agregat Halus DanDocument10 pagesPengaruh Abu Batu Sebagai Subtitusi Agregat Halus Danangela merici rianawatiNo ratings yet
- IKEA AyeshaDocument41 pagesIKEA AyeshaAYESHAREHMAN100No ratings yet
- 7 кмжDocument6 pages7 кмжGulzhaina KhabibovnaNo ratings yet
- Odisha Block Summary - NUAGAONDocument8 pagesOdisha Block Summary - NUAGAONRohith B.NNo ratings yet
- 2U6 S4HANA1909 Set-Up EN XXDocument10 pages2U6 S4HANA1909 Set-Up EN XXGerson Antonio MocelimNo ratings yet
- Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin IIIDocument14 pagesSultan Omar Ali Saifuddin IIISekolah Menengah Rimba100% (3)
- Tim Horton's Case StudyDocument8 pagesTim Horton's Case Studyhiba harizNo ratings yet
- Hoc Volume1Document46 pagesHoc Volume1nordurljosNo ratings yet
- RPS Manajemen Keuangan IIDocument2 pagesRPS Manajemen Keuangan IIaulia endiniNo ratings yet
- Judicial Review of Legislative ActionDocument14 pagesJudicial Review of Legislative ActionAnushka SinghNo ratings yet
- Where Is The Love?-The Black Eyed Peas: NBA National KKK Ku Klux KlanDocument3 pagesWhere Is The Love?-The Black Eyed Peas: NBA National KKK Ku Klux KlanLayane ÉricaNo ratings yet
- Alankit Assignments LTD.: Project Report ONDocument84 pagesAlankit Assignments LTD.: Project Report ONmannuNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Pipe FlowDocument14 pagesAnalysis of Pipe FlowRizwan FaridNo ratings yet