Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DUCK
Uploaded by
Maria CeciliaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DUCK
Uploaded by
Maria CeciliaCopyright:
Available Formats
DUCK
PRODUCTION
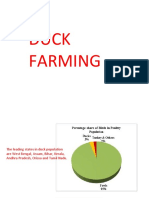
Duck raising is a lucrative livestock industry in the Philippines because
of its egg. Its most important product, the “balut” (boiled incubated duck’s
egg), is sold daily throughout the archipelago for its delicious flavor and
nutritive value.
What is production?
Production is the method of turning raw materials or inputs into
finished goods or products in a manufacturing process.
The raw materials used in production process are also known as
resources or factors of production.
What is DUCK?
a water bird with a broad bill, short legs, webbed feet, and a waddling
gait.
a pure white thin-shelled bivalve mollusk found off the Atlantic of America.
Lifespan: MALLA
Clutch size: MALLARD 8-13 years
Phylum: CHORDATA
Wingspan: MALLARD 81-98 cm
Mass: MALLARD 0.72-1.6 kg, CANVASBACK: 1.2 kg, MARBLED DUCK: 480g and etc.
Length: MALLARD 50-65 cm, CANVASBACK: 48-56cm
BROODING AND REARING DUCKS
Ducklings can be successfully brooded in any brooder house and under any
type of brooder used for chickens.
Brooder house- design the brooder house so that it is well ventilated but excludes the
draughts that cause chills. Wall openings 1.2 m from the floor provide good ventilation.
Brooder- Irrespective of the type of brooder — gas, electricity, hot water or hot air — it
should provide enough constant heat and ventilation, and ample space to avoid
overcrowding. As a general rule, the number of ducklings that can be brooded is half the
stated chick capacity of a brooder.
WATERERS AND FEEDERS
Ducklings must have a permanent supply of good clean drinking water.
4.5 L drinking for first few days.
To avoid damp litter, place drinkers on a wire grid over the concrete floor.
Ducklings can die if they are without water for even short periods.
can die if they are without water for even short periods. Staggering and convulsions are typical
symptoms of lack of water.
Should the water supply fail, give ducklings a drink of warm milk before providing them
with water — this will help avoid intestinal cramp and staggers.
Place feeders on an elevated platform to prevent them from becoming contaminated with
droppings.
For each duckling up to 3 weeks of age, provide 1.5 cm of drinking space and 4 cm of
feeding space.
Rearing
- After brooding, ducklings may be placed in intensive or semi-intensive rearing sheds
or in wire colony cages.
Ground rearing -In intensive housing, allow 1250 cm2 of floor space per bird for
growing ducks up to 8 weeks of age. Those housed semi-intensively need the same
space allocation (i.e. 8 birds/m2).
Carrying and handling
Ducks can be carried:
• by the top of the neck;
• by grasping both wings in one hand;
• by holding them under one’s arm with the duck’s head facing the rear; or
• by holding one wing and the leg from the same side.
You might also like
- Leghorn Fowls - Exhibition and Utility - Their Varieties, Breeding and ManagementFrom EverandLeghorn Fowls - Exhibition and Utility - Their Varieties, Breeding and ManagementNo ratings yet
- The Illustrated Guide to Ducks and Geese and Other Domestic Fowl: How To Choose Them - How To Keep ThemFrom EverandThe Illustrated Guide to Ducks and Geese and Other Domestic Fowl: How To Choose Them - How To Keep ThemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Duck Farming GuideDocument13 pagesDuck Farming Guideamitdhote100% (1)
- How to breed ducks: beginner's guide with everything you need to know, with many images for maximum compression.From EverandHow to breed ducks: beginner's guide with everything you need to know, with many images for maximum compression.No ratings yet
- Duck Breeding - A Collection of Articles on Selection, Crossing, Feeding and Other Aspects of Breeding DucksFrom EverandDuck Breeding - A Collection of Articles on Selection, Crossing, Feeding and Other Aspects of Breeding DucksNo ratings yet
- A - Mallard DuckDocument24 pagesA - Mallard DuckcmembreveNo ratings yet
- Starting a Duck Farm - A Collection of Articles on Stock Selection, Rearing, Economics and Other Aspects of Duck FarmingFrom EverandStarting a Duck Farm - A Collection of Articles on Stock Selection, Rearing, Economics and Other Aspects of Duck FarmingNo ratings yet
- Duck 2019Document52 pagesDuck 2019Adrian BAGAYANNo ratings yet
- Duck 2019Document52 pagesDuck 2019Adrian BAGAYANNo ratings yet
- Poultry RaisingDocument41 pagesPoultry RaisingCharie C. OrbocNo ratings yet
- Commonpoultryfarmtools 141230005911 Conversion Gate02Document23 pagesCommonpoultryfarmtools 141230005911 Conversion Gate02lynie rose mesajonNo ratings yet
- DuckDocument20 pagesDuckgemma salomonNo ratings yet
- Pigeon Husbandry: General InformationDocument6 pagesPigeon Husbandry: General InformationshachoujosephNo ratings yet
- Modern Duck Farming PracticesDocument7 pagesModern Duck Farming Practicessurajdevverma1516No ratings yet
- Duck PointersDocument17 pagesDuck Pointersalvin_348100% (1)
- Backyard Duck Raising For Meat and Eggs: Home LivestockDocument3 pagesBackyard Duck Raising For Meat and Eggs: Home LivestockJassy Abril100% (1)
- Common Poultry Tools Poultry ProductionDocument17 pagesCommon Poultry Tools Poultry ProductionApril Joy Sumagit Hidalgo100% (1)
- Lallo. Broiler Duck Production ManualDocument82 pagesLallo. Broiler Duck Production ManualJTheron5850% (2)
- Animal ProductionDocument84 pagesAnimal ProductionJOEL QUITONNo ratings yet
- How To Raise Ducks For Food and Project - Asian Rural Development FoundationDocument40 pagesHow To Raise Ducks For Food and Project - Asian Rural Development Foundationdcollot8026No ratings yet
- Ducks, Geese and Turkeys - A Collection of Articles on the Methods and Equipment of Poultry KeepingFrom EverandDucks, Geese and Turkeys - A Collection of Articles on the Methods and Equipment of Poultry KeepingNo ratings yet
- Raising Commercial Ducks As A 4-H or FFA Project: The Origin of DucksDocument9 pagesRaising Commercial Ducks As A 4-H or FFA Project: The Origin of DucksMark Jovin RomNo ratings yet
- Pekin Duck: Half A Century of Progress in Breeding and Management of Ducks in The Philippines (2004)Document9 pagesPekin Duck: Half A Century of Progress in Breeding and Management of Ducks in The Philippines (2004)Joanalyn LataNo ratings yet
- DuckDocument10 pagesDuckHereComesTheBitchNo ratings yet
- Guide To Quail Raising - Ag PDFDocument22 pagesGuide To Quail Raising - Ag PDFcurlycarlNo ratings yet
- Duck RaisingDocument14 pagesDuck RaisingJoraxNo ratings yet
- A Small-Scale Agriculture Alternative - Poultry - VirginiaAg 2902-1099 (2009)Document6 pagesA Small-Scale Agriculture Alternative - Poultry - VirginiaAg 2902-1099 (2009)fodoNo ratings yet
- A Beginner’s Guide to Keeping Ducks: Keeping Ducks in Your BackyardFrom EverandA Beginner’s Guide to Keeping Ducks: Keeping Ducks in Your BackyardRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Ducks for Starters: A Practical Guide to Backyard Duck KeepingFrom EverandDucks for Starters: A Practical Guide to Backyard Duck KeepingNo ratings yet
- Quail Farming: Dr. Ghulam Abbas Hashmi PHD Poultry Science MSC (Hons) Poultry Science MSC (Hons) Molecular GeneticsDocument51 pagesQuail Farming: Dr. Ghulam Abbas Hashmi PHD Poultry Science MSC (Hons) Poultry Science MSC (Hons) Molecular GeneticsMuhammad HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Duck ProductionDocument23 pagesDuck Productionokodi andrewNo ratings yet
- Selecting, Brooding & Rearing Small Numbers of Chicks LPM-00840Document2 pagesSelecting, Brooding & Rearing Small Numbers of Chicks LPM-00840Plantain frankyNo ratings yet
- Producing Broilers and Fryers - An Instructional Article on Raising ChickensFrom EverandProducing Broilers and Fryers - An Instructional Article on Raising ChickensNo ratings yet
- Animal Production Group 2 (Autosaved)Document49 pagesAnimal Production Group 2 (Autosaved)Roxanne Jane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Duck FarmingDocument10 pagesAdvantages of Duck FarmingMartin S. NoblezadaNo ratings yet
- Basics For Raising Backyard Chickens: David D. FrameDocument5 pagesBasics For Raising Backyard Chickens: David D. FrameZaki PratomoNo ratings yet
- Alpaca Animals Guidebook: Keeping Alpacas Simple Guide For BeginnersFrom EverandAlpaca Animals Guidebook: Keeping Alpacas Simple Guide For BeginnersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Poultry Keeping On A Small ScaleDocument7 pagesPoultry Keeping On A Small Scaleronalit malintadNo ratings yet
- Improved Management of The Native ChickenDocument3 pagesImproved Management of The Native ChickenShakira Miki L. CutamoraNo ratings yet
- Brooding and Rearing Baby ChicksDocument10 pagesBrooding and Rearing Baby Chicksronalit malintadNo ratings yet
- Duck ProductionDocument10 pagesDuck ProductionSamuel Ivan Ngan100% (1)
- Poultryequipmentandfacilities 151109052032 Lva1 App6892Document45 pagesPoultryequipmentandfacilities 151109052032 Lva1 App6892Jessica EscañoNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Million Dollars With Ducks: The Ultimate Guide To Profitable Duck FarmingFrom EverandHow To Make A Million Dollars With Ducks: The Ultimate Guide To Profitable Duck FarmingNo ratings yet
- Domestic Geese And Ducks - A Complete And Authentic Handbook And Guide For Breeders, Growers And Admirers Of Domestic Geese And DucksFrom EverandDomestic Geese And Ducks - A Complete And Authentic Handbook And Guide For Breeders, Growers And Admirers Of Domestic Geese And DucksNo ratings yet
- The Health of Ducks on the Farm - A Collection of Articles on Diseases and Their TreatmentFrom EverandThe Health of Ducks on the Farm - A Collection of Articles on Diseases and Their TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Caring For KookaburrasDocument4 pagesCaring For KookaburrasDbalt100% (1)
- Name: Eugene D. Emperua Quail ProductionDocument3 pagesName: Eugene D. Emperua Quail Productioneugene emperuaNo ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Raising Perfect Healthy Chickens in 7 Days: Volume 1From EverandBeginners Guide To Raising Perfect Healthy Chickens in 7 Days: Volume 1No ratings yet
- Resume Template 3Document4 pagesResume Template 3Lucky PradhanNo ratings yet
- Daniel GolemanDocument4 pagesDaniel GolemanMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Mayla GabatoDocument31 pagesMayla GabatoMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- PPR 218 Key Steps To Retirement Income PlanningDocument9 pagesPPR 218 Key Steps To Retirement Income PlanningMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- PPR 215Document1 pagePPR 215Maria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- 80'S Attire Vs Millennial AttireDocument2 pages80'S Attire Vs Millennial AttireMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Employment History: Nigel H. ArthurDocument2 pagesEmployment History: Nigel H. ArthurShweta MishraNo ratings yet
- APPROACHES Written RepoortDocument3 pagesAPPROACHES Written RepoortMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Charlie and The FrogDocument16 pagesCharlie and The FrogMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- The Milkmaid and Her PailDocument5 pagesThe Milkmaid and Her PailMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Cecil PT2Document4 pagesCecil PT2Maria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- How To Motivate Children To Have A Healthy SelfDocument2 pagesHow To Motivate Children To Have A Healthy SelfMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- ShierrreeyDocument3 pagesShierrreeyMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Bread&pastry SummaryDocument5 pagesBread&pastry SummaryMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Jeya Dress (Reflection)Document3 pagesJeya Dress (Reflection)Maria Cecilia100% (1)
- DUCKDocument2 pagesDUCKMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Swine ProductionDocument2 pagesSwine ProductionMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- DUCKDocument2 pagesDUCKMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- How To Motivate Children To Have A Healthy SelfDocument2 pagesHow To Motivate Children To Have A Healthy SelfMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Angelica Rose CDocument1 pageAngelica Rose CMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Swine ProductionDocument2 pagesSwine ProductionMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Title: Fill The Bucket Water Game Indication: For Physical Development InstructionsDocument4 pagesTitle: Fill The Bucket Water Game Indication: For Physical Development InstructionsMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Title: Fill The Bucket Water Game Indication: For Physical Development InstructionsDocument4 pagesTitle: Fill The Bucket Water Game Indication: For Physical Development InstructionsMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Title: Fill The Bucket Water Game Indication: For Physical Development InstructionsDocument4 pagesTitle: Fill The Bucket Water Game Indication: For Physical Development InstructionsMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- ShirereretttDocument1 pageShirereretttMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Angelica Rose CDocument1 pageAngelica Rose CMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Angelica Rose CDocument1 pageAngelica Rose CMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- How To Motivate Children To Have A Healthy SelfDocument2 pagesHow To Motivate Children To Have A Healthy SelfMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Bread&pastry SummaryDocument5 pagesBread&pastry SummaryMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives PracticeDocument4 pagesComparatives and Superlatives Practiceangie julieth cetina caroNo ratings yet
- 1934 Reading Comprehension TextsDocument4 pages1934 Reading Comprehension TextsYijun PengNo ratings yet
- Why Does My Dog Still Have A Puppy Face - Google SearchDocument1 pageWhy Does My Dog Still Have A Puppy Face - Google SearchIsabelle O'NeillNo ratings yet
- Research ReportDocument13 pagesResearch ReportAllza AllNo ratings yet
- Exercise - I: Levels of OrganizationDocument23 pagesExercise - I: Levels of OrganizationMayuri chatpalliwar100% (1)
- The Internal Organs of The Human BodyDocument2 pagesThe Internal Organs of The Human BodyIulian Mircea NicaNo ratings yet
- The Peregrine Fund Annual 2005Document40 pagesThe Peregrine Fund Annual 2005Israel100% (1)
- Mhaturi - Kesrawan Sapi PerahDocument8 pagesMhaturi - Kesrawan Sapi PerahMhaturi Sitti RaoNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Veterinary Internal MedicineDocument2 pagesHandbook - Veterinary Internal MedicineAsyo Lexis100% (1)
- Artificial Insemination in Humans and AnimalsDocument5 pagesArtificial Insemination in Humans and Animalsnoneivy anonymousNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell ModificationsDocument62 pages1 Cell ModificationsJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Artificial SelectionDocument25 pagesArtificial SelectionElizabeth ThomasNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in AnimalsDocument11 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in AnimalsVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Classification of 00 BlacDocument104 pagesClassification of 00 BlacRajuNo ratings yet
- Business Plan MaziwaDocument32 pagesBusiness Plan Maziwagilbert kifundaNo ratings yet
- Eat Your Heart Out - Choice and Handling of Novel Toxic Prey by Predatory Water RatsDocument6 pagesEat Your Heart Out - Choice and Handling of Novel Toxic Prey by Predatory Water RatsJean Carlos MirandaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Eagle: A. Ways On How We Can Help in Saving The Critically Endangered Animals in The Philippines. (30 Points)Document4 pagesPhilippine Eagle: A. Ways On How We Can Help in Saving The Critically Endangered Animals in The Philippines. (30 Points)Fiona SuzenneNo ratings yet
- Science Relationships hw123Document3 pagesScience Relationships hw123api-250941636No ratings yet
- Lungs and Gas Exchange - Lesson 1 - Grade 8Document13 pagesLungs and Gas Exchange - Lesson 1 - Grade 8SAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- Newsletter Nov/Dec 2016Document6 pagesNewsletter Nov/Dec 2016cheryl morganNo ratings yet
- Dairy Bull - 551BS01439 - Kulp-Gen Can Decide ETDocument1 pageDairy Bull - 551BS01439 - Kulp-Gen Can Decide ETJonasNo ratings yet
- 1734.do Alligators Eat DucksDocument4 pages1734.do Alligators Eat DuckstvrNo ratings yet
- Gruber-Clay - 2016 - Pan ComparisonDocument14 pagesGruber-Clay - 2016 - Pan ComparisonCarlos González LeónNo ratings yet
- Friendly AnimalsDocument80 pagesFriendly AnimalsantcaraNo ratings yet
- Animal DiversityDocument3 pagesAnimal DiversityChristian Dave Sanchez0% (1)
- Biology Mammal Review SheetDocument4 pagesBiology Mammal Review Sheetdanny belenNo ratings yet
- The Phylum Mollusca: A. AmphineuraDocument16 pagesThe Phylum Mollusca: A. AmphineuraCindy RahmahNo ratings yet
- A Stinky SituationDocument2 pagesA Stinky SituationSOFIA USECHE MANRIQUENo ratings yet
- Justice For Oxen: Protect Them From Slaughtering in India - Abhishek KadyanDocument318 pagesJustice For Oxen: Protect Them From Slaughtering in India - Abhishek KadyanNaresh KadyanNo ratings yet
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 1Document13 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 1sakshiNo ratings yet