Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SEO-Optimized Title for Electrical Components Document
Uploaded by
Johan ChaconOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SEO-Optimized Title for Electrical Components Document
Uploaded by
Johan ChaconCopyright:
Available Formats
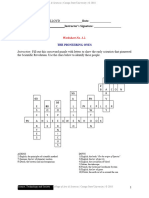
4 O 1 T
P R
1 R E S I S T A N C E
N 9 N
C G 4 S W I T C H
6 D I O D E F 2 6 3
R 9 N O A C 7 A M P
C E R T O T 5
U R 3 M U L T I M E T E R C
I A E E M R L
9 V O L T T R N U A O
O U T 5 C O N D E N S E R
8 B A T T E R Y A A T E
T D I D
O O O C
1
R R N I
0
C R
8 A C
T B U
7 U L I
1
C U R R E N T
0
O B
I I
D E L 2 N
E
HORIZONTAL
1. Opposition that finds the current as it passes through a
closed electric circuit, attenuating or slowing the free flow
of circulation of electric charges or electrons.
2. Diode composed of the superposition of several layers of
semiconductor material which emits light at one or more
wavelengths (colors) when properly biased.
3. Portable electric instrument for directly measuring
electrical quantities.
4. A device or element which is used to mechanically open or
close a circuit.
5. Element formed by metal plates alternating with others of
insulating material, said plates will be able to accumulate
tension.
6. Semiconductor element that only lets current flow in one
direction.
7. Unit of measurement of the intensity of electric current.
8. Voltage source that converts chemical energy into DC power
9. It is the unit of force that drives the electric charges so
that they can move to Through a driver.
10. Movement of electricity by a conductor.
VERTICAL
1. Device used to raise or lower the voltage. It is formed by
two coils magnetically coupled to each other.
2. Electrical device that dampens or diminishes the value of the
magnitudes that are provided.
3. Mutual force that originates between two magnetic bodies
linked by a magnetic flux.
4. Path interrupted by which an electric current could not
circulate.
5. Electric circuit that constitutes a complete step for the
circulation of current without existing in the no
interruption.
6. Apparatus that is used to change the flow of current from one
circuit to another.
7. Winding of a conductor wire around a solid or hollow
cylinder.
8. Rotary machine with the ability to convert the kinetic energy
of a fluid into mechanical energy. Its basic elements are
rotor with blades, propellers, blades, etc.
9. Electromechanical device used to convert mechanical energy
into electrical energy by means of electromagnetic induction.
10. Conductor formed by a set of strands, whether braided or
twisted.
You might also like
- Experiment 8 Transformer Equivalent CircuitDocument9 pagesExperiment 8 Transformer Equivalent CircuitBrett GallNo ratings yet
- Bonafide CertificateDocument3 pagesBonafide CertificateIIT HelpNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument1 pageThe Nervous SystemmichelleNo ratings yet
- CROSSWORDDocument2 pagesCROSSWORDJohan ChaconNo ratings yet
- Formulaire Passeport CiDocument1 pageFormulaire Passeport CiAmara KouroumaNo ratings yet
- Formulaire Passeport DiasporaDocument1 pageFormulaire Passeport Diasporacedrickoki10No ratings yet
- Short Quiz in Practical Research 2Document1 pageShort Quiz in Practical Research 2kelvinNo ratings yet
- Computer Terminology 3be6b 6162f72bDocument1 pageComputer Terminology 3be6b 6162f72bZindy TorinoNo ratings yet
- Crossword Electricity Answers 1Document1 pageCrossword Electricity Answers 1Ralph brian VillarNo ratings yet
- Crossword About JobsDocument2 pagesCrossword About JobsDovydasLTUNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle Form 3 AnswersDocument6 pagesCrossword Puzzle Form 3 AnswersNur Irdhina AkhtariNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 5Document9 pagesEvidencia 5Angel ThomasNo ratings yet
- Across HorizontalDocument2 pagesAcross HorizontalRucutundo PancracioNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary-Electricity and Electronic Crossword: Presented To InstructorDocument5 pagesVocabulary-Electricity and Electronic Crossword: Presented To Instructorfranklin osorioNo ratings yet
- Answers Key Crosswords 3.8Document1 pageAnswers Key Crosswords 3.8XDMissShayXD -No ratings yet
- 3.1 Money and Finance: © Brian Titley 2012: This May Be Reproduced For Class Use Solely For The Purchaser's InstituteDocument1 page3.1 Money and Finance: © Brian Titley 2012: This May Be Reproduced For Class Use Solely For The Purchaser's InstituteNadine ZalfaNo ratings yet
- Entry Ticket Energy Resources Answer KeyDocument1 pageEntry Ticket Energy Resources Answer KeyVictor OnasNo ratings yet
- Phenomena of Life Radio Electric TheoryDocument390 pagesPhenomena of Life Radio Electric TheoryCorey WasicekNo ratings yet
- Renal and Urinary System Crossword Answers GR 4Document1 pageRenal and Urinary System Crossword Answers GR 4Raymond EdgeNo ratings yet
- Crucigrama YuriDocument1 pageCrucigrama YuriMercibel VasquezNo ratings yet
- Workshop Translation and GuidelinesDocument10 pagesWorkshop Translation and GuidelinesOscar BaccaNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle and Hidden WordsDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle and Hidden WordsElizabeth C. PajaNo ratings yet
- Crucigrama202505 1Document3 pagesCrucigrama202505 1dadueas72No ratings yet
- Crossword SNDocument6 pagesCrossword SNsuzawadiNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Crossword Puzzle Answer Key 40238 6162ed83Document1 pageCell Organelle Crossword Puzzle Answer Key 40238 6162ed83B0% (1)
- Physical Science Chapter 4 Crossword Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPhysical Science Chapter 4 Crossword Answer KeyRenolsa EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Equilibrium ExplainedDocument5 pagesConsumer Equilibrium ExplainedRekha MarlechaNo ratings yet
- Crossword EvaluationDocument2 pagesCrossword EvaluationJASTINE ORILLANo ratings yet
- Rotated 61000-4-11 Immunity To Ac Supply Dips Dropouts InterruptionsDocument13 pagesRotated 61000-4-11 Immunity To Ac Supply Dips Dropouts InterruptionsShawn DeolNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures Answer KeyDocument1 pageSeparating Mixtures Answer KeyNtando Nkunzimanikina XimbaNo ratings yet
- Jugar CrucigramaDocument2 pagesJugar CrucigramaNixon F. SandovalNo ratings yet
- "Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)Document1 page"Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)SusanAngDíaz0% (2)
- Find The Words and The Mystery Message:Let'S AllDocument2 pagesFind The Words and The Mystery Message:Let'S AllveroNo ratings yet
- 07HEAT - WS 03: Solve The Crossword On "Heat" Within 10 MinutesDocument2 pages07HEAT - WS 03: Solve The Crossword On "Heat" Within 10 MinutesSHUBHAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument3 pagesActivityEtsi TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesUrinary SystemShania SarciaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy Answer KeyDocument1 pageNuclear Energy Answer KeyMagdalainaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Module 3 Task 4 - Model AnswerDocument3 pagesMicrosoft Module 3 Task 4 - Model AnswerAshutosh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Econ Words CrosswordWords Crossword - WordMint AnswerDocument2 pagesEcon Words CrosswordWords Crossword - WordMint AnswerSandy SaddlerNo ratings yet
- M Set TheoryDocument1 pageM Set TheoryMarriel Palle TahilNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom - Worksheet 1Document1 pageAnimal Kingdom - Worksheet 1ultbngNo ratings yet
- Workshop Getting Started As A Translator: GuidelinesDocument7 pagesWorkshop Getting Started As A Translator: GuidelinesYami GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 870 Evaluation BoardDocument8 pages870 Evaluation BoardLeonel GalliNo ratings yet
- Hidden Words Science Year 2 ElectricalDocument1 pageHidden Words Science Year 2 ElectricalGUANG AK AMBA MoeNo ratings yet
- Sts CanonoDocument1 pageSts CanonoJOHN POL MAGLASANGNo ratings yet
- 74358bos60276-cp2Document1 page74358bos60276-cp2Radhika GargNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesActivity 2 - Crossword PuzzleHailla GuiralNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 5 BilinguismoDocument8 pagesEvidencia 5 BilinguismoValentina JimenezNo ratings yet
- Earthquake and Faults QuizDocument1 pageEarthquake and Faults QuizMARISTELA MACARANASNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary - Unit 4 termsDocument2 pagesVocabulary - Unit 4 termsFelícia LimaNo ratings yet
- Our Little Friends (Pets) : Fill in The Crossword and Find The Hidden WordsDocument2 pagesOur Little Friends (Pets) : Fill in The Crossword and Find The Hidden WordseciNo ratings yet
- T.L.E 7 and 8 Week 5Document15 pagesT.L.E 7 and 8 Week 5Eleonor DistrajoNo ratings yet
- Workshop: Getting Started As A TranslatorDocument8 pagesWorkshop: Getting Started As A TranslatorTatiana Garrido SuarrezNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Politics: Across DownDocument2 pagesKnowledge and Politics: Across Downdanishaqil711No ratings yet
- Lit1011a ML 800 Install Manual PDFDocument44 pagesLit1011a ML 800 Install Manual PDFDmytro UvarovNo ratings yet
- Elements Word Search Group ExperimentDocument1 pageElements Word Search Group ExperimentAloysius Brent GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Pioneer SX-3900Document47 pagesPioneer SX-3900Reciclando ChatarraNo ratings yet
- By Rina Machaca Justo.: Complete The Crossword Puzzle BelowDocument1 pageBy Rina Machaca Justo.: Complete The Crossword Puzzle Belowjanet condori chipanaNo ratings yet
- 5309 Resource 5eb9b25aafb58485582232-1Document4 pages5309 Resource 5eb9b25aafb58485582232-19z97kt9f7dNo ratings yet
- List ContactsDocument9 pagesList ContactsrobertthomaswhiteNo ratings yet
- OCR GCE Physics B G496 Coursework (Research Report)Document19 pagesOCR GCE Physics B G496 Coursework (Research Report)Maurice YapNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: ER500 ER506Document2 pagesData Sheet: ER500 ER506Thành nguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- The Art of Electronics Solutions Chapter 1Document20 pagesThe Art of Electronics Solutions Chapter 1James BanandoNo ratings yet
- WBCHSE Physics Sample PaperDocument62 pagesWBCHSE Physics Sample PaperRiju GhoshNo ratings yet
- Filonenko-Borodich - Theory of ElastictyDocument407 pagesFilonenko-Borodich - Theory of ElastictyAvanish KumarNo ratings yet
- Measuring Force: A GuideDocument26 pagesMeasuring Force: A GuideAbdi samad MohamedNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL1ed Model PDFDocument1 pageELECTRICAL1ed Model PDFLuzbella GandezaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Sag and Mitigation Using Dynamic Voltage Restorer DVR System For Power Quality ImprovementDocument8 pagesVoltage Sag and Mitigation Using Dynamic Voltage Restorer DVR System For Power Quality ImprovementInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Exp # 10 Analysis of Band-Pass Filters (Using Multisim Electronics Workbench)Document10 pagesExp # 10 Analysis of Band-Pass Filters (Using Multisim Electronics Workbench)Irfan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Tuto2 (S) 2016 30102016204804033Document5 pagesTuto2 (S) 2016 30102016204804033Chandini ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument12 pagesTransmission Linesacestrider1023No ratings yet
- Test 1 Unit 1 Physics Sem 1 2017Document10 pagesTest 1 Unit 1 Physics Sem 1 2017SongNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Electrical Machines Used in Two-Frequency Indirect Temperature Rise TestsDocument5 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Electrical Machines Used in Two-Frequency Indirect Temperature Rise TestsErhan TekeliNo ratings yet
- Dielectric properties of pressboard in oil and esterDocument1 pageDielectric properties of pressboard in oil and esterFari PratomosiwiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16, Concept Question PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 16, Concept Question PDFAnderson Eiji KanawaNo ratings yet
- Free Body Diagrams GuidelinesDocument3 pagesFree Body Diagrams GuidelinesMichael Mays0% (1)
- Demagnetization Curves For EllipsoidsDocument7 pagesDemagnetization Curves For EllipsoidsShubham YadavNo ratings yet
- Himel Residential PDFDocument12 pagesHimel Residential PDFAlbertNo ratings yet
- How To Remember (Doppler Effect)Document3 pagesHow To Remember (Doppler Effect)fuzing_2012No ratings yet
- E74h IbmDocument37 pagesE74h IbmJose BerrospiNo ratings yet
- Practice Test-1: Resonance Eduventures LimitedDocument67 pagesPractice Test-1: Resonance Eduventures LimitedagNo ratings yet
- Extensive Review On Laminated Bus Bar For Low and High Power ApplDocument7 pagesExtensive Review On Laminated Bus Bar For Low and High Power ApplMANGAL KUMAR MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- PDF PPT 3Document71 pagesPDF PPT 3RafiaNo ratings yet
- Solution#1Document5 pagesSolution#1Exel Dua CincinNo ratings yet
- Operador PanasonicDocument96 pagesOperador PanasonicVilla Robert RamoaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Transformadores DONGAN USADocument108 pagesCatalogo Transformadores DONGAN USAjpousada100% (1)
- Statics ProjectDocument15 pagesStatics Projectapi-570030183No ratings yet
- Course Folder FormatDocument39 pagesCourse Folder FormatIshfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Antenna 2008Document18 pagesFinal Exam Antenna 2008abdulwahab12100% (2)