Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
Uploaded by
Maryam FadahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
Uploaded by
Maryam FadahCopyright:
Available Formats
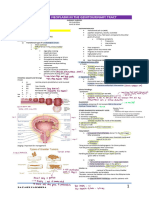
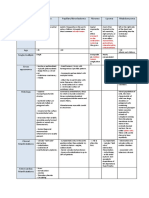
Main player in
Pancreatitis Etiology Gross morphology Microscopic morphology Dx
pathogenesis
1) Typical
clinical
symptom
- Hemorrhagic 2) High se
parenchyma & amylase a
scattered yellow- 1.Interstitial edema. lipase leve
st white chalky areas of 2.Fat necrosis. greater th
1 : Gallstones. Trypsinogen
Acute fat necrosis. 3.Acute inflammation. three tim
2nd: Alcohol. activation.
- Peritoneal serous 4.Pancreatic parenchymal destruction. upper lim
slightly turbid or 5.Blood vessels destruction normal
brownish fluid
contains fat globules. 3) Imagin
showing
pancreati
inflamma
CT is the b
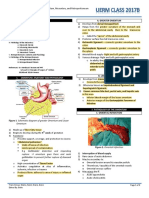
Clinical
symptom
1. Pancrea
1. Parenchymal fibrosis. calcificatio
2. ↓number/size of acini with relative
sparing of islets of Langerhans. 2. Ductal
Stellate cells Hard, dilated ducts,
Chronic* Alcohol Abuse. 3. Pancreatic ducts dilatation with dilatation
activation. Visible calcifications.
luminal protein plugs.
4. Chronic inflammation around lobules 3. Parench
& ducts atrophy a
focal
inflamma
masses.
*PRSS1 or SPINK1 gene mutation
You might also like
- Med Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Document7 pagesMed Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Maxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Kidney Part 1Document5 pagesKidney Part 1sarguss14No ratings yet
- Patho Ospe 1Document16 pagesPatho Ospe 1PomNo ratings yet
- UC & Crohn's DiseaseDocument3 pagesUC & Crohn's DiseaseYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- Aiims NOV 2010: SolutionsDocument25 pagesAiims NOV 2010: SolutionsPranav DevaniNo ratings yet
- GIT OSPE Pathology - Final-2 PDFDocument29 pagesGIT OSPE Pathology - Final-2 PDFafaq alismailiNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument7 pagesPancreasMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Head & Neck TumorsDocument4 pagesHead & Neck TumorsDez RayosNo ratings yet
- Cancer BulletsDocument3 pagesCancer Bulletsraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Staging Laparotomy For Malignant Lymphoma: Description ProcedureDocument3 pagesStaging Laparotomy For Malignant Lymphoma: Description Procedureandres restrepoNo ratings yet
- AIJ1Document19 pagesAIJ1Sandra Arely Rodriguez EscobarNo ratings yet
- Surgery PancreasDocument11 pagesSurgery PancreasMATTHEW EARL MALUMAYNo ratings yet
- URO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractDocument8 pagesURO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractHa Jae kyeongNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument3 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeRona PieNo ratings yet
- Surgery 2.01.3 Omentum, Mesentery and Retroperitoneum - Dr. MendozaDocument8 pagesSurgery 2.01.3 Omentum, Mesentery and Retroperitoneum - Dr. MendozaJorge De VeraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer DiseaseJhade RelletaNo ratings yet
- Patologã - A AnorectalDocument38 pagesPatologã - A AnorectalGARDY LIZETT GONZALES PINTONo ratings yet
- CancerDocument4 pagesCancerPaul AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument5 pagesDiarrheamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Micro para OSCE For YL6 BacteriaDocument2 pagesMicro para OSCE For YL6 Bacteriagzldiwa100% (1)
- Ocr 439989329 Practice Questions For Dermatology Specialty Examinati 2Document50 pagesOcr 439989329 Practice Questions For Dermatology Specialty Examinati 2Andrés WunderwaldNo ratings yet
- Section 3-7 Slides + CommentsDocument9 pagesSection 3-7 Slides + CommentsNkgivgNo ratings yet
- Thematic Plan of Clinical Surgery LecturesDocument5 pagesThematic Plan of Clinical Surgery Lecturesareebasarfraz786No ratings yet
- High Ent YielDocument15 pagesHigh Ent YielJana AldourNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Renal Masses and Congenital AnomaliesDocument9 pages5.2 Renal Masses and Congenital AnomaliesMaria roxanne HernandezNo ratings yet
- Acute Chronic PancreatitisDocument17 pagesAcute Chronic Pancreatitisjimjose antonyNo ratings yet
- Oncomelania Quadrasi (Tiny Snail)Document7 pagesOncomelania Quadrasi (Tiny Snail)JoshuaNo ratings yet
- GI Internal Medicine PDFDocument9 pagesGI Internal Medicine PDFArianneJulienaCervaniaAndradaNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Calcification : Friedreich"Document7 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Calcification : Friedreich"putriNo ratings yet
- Postpartum ComplicationsDocument7 pagesPostpartum ComplicationsCarlo BerzNo ratings yet
- Z Revision PracticalDocument124 pagesZ Revision PracticalsamNo ratings yet
- L1-IM-Colonic Polyps and Polyposis Syndrome (Feb1122)Document9 pagesL1-IM-Colonic Polyps and Polyposis Syndrome (Feb1122)patriciaatan1497No ratings yet
- 15 Rectal Prolapse - Libre PathologyDocument3 pages15 Rectal Prolapse - Libre PathologyfadoNo ratings yet
- TID Dr. Lu 2014Document4 pagesTID Dr. Lu 2014MACATANGAY, GAELLE LISETTENo ratings yet
- Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Chronic Gastritis in Two Related Persian CatsDocument5 pagesGastric Adenocarcinoma and Chronic Gastritis in Two Related Persian CatsOa JebeNo ratings yet
- Git Radiology and ImagingDocument4 pagesGit Radiology and Imagingoddone_outNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology Trans No 7. The LIVER DR ROXAS by MCD Recoverd 1Document14 pagesSurgical Pathology Trans No 7. The LIVER DR ROXAS by MCD Recoverd 1miguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pageAcute GlomerulonephritisAyrheen FornolesNo ratings yet
- CT Evaluation of Inflammatory Conditions of The ColonDocument45 pagesCT Evaluation of Inflammatory Conditions of The ColondedyjossNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis and Intraabdominal AbscessDocument10 pagesPeritonitis and Intraabdominal AbscessArluk WanthaphisutNo ratings yet
- CA 2 CDN Review Notes 2Document21 pagesCA 2 CDN Review Notes 2Andrew Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Panniculitis 2021Document45 pagesPanniculitis 2021karimahihdaNo ratings yet
- Surgery Block - T&T ClubDocument2 pagesSurgery Block - T&T ClubJocel CastilloNo ratings yet
- SurgeryDocument14 pagesSurgeryVinit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- M3.2 Pancreas and Islets of Langerhans (CC2-LEC)Document5 pagesM3.2 Pancreas and Islets of Langerhans (CC2-LEC)Hannah Elizabeth CastroNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Peptic Ulcer Disease: 55 Y/o Female)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Peptic Ulcer Disease: 55 Y/o Female)kristian markus delos santos100% (1)
- PR Liver Panc GBLDR 05LDocument14 pagesPR Liver Panc GBLDR 05LAditya MuchayatsyahNo ratings yet
- Pancreas RobbinsDocument13 pagesPancreas RobbinsAndrea PescosolidoNo ratings yet
- GI - Surgical Aspects of The EsophagusDocument3 pagesGI - Surgical Aspects of The Esophagusjalexander1006No ratings yet
- GIT - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFDocument47 pagesGIT - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFMohammedNo ratings yet
- Digital Notebook CompilationDocument44 pagesDigital Notebook CompilationReese Alessandra GandulfoNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous Necrotizing Sialometaplasia of The Submandibular Salivary Gland in A Beagle DogDocument4 pagesSpontaneous Necrotizing Sialometaplasia of The Submandibular Salivary Gland in A Beagle Dogandrianiputri916No ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome 1Document3 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome 1Rona PieNo ratings yet
- Platelts and CoaglatinDocument7 pagesPlatelts and CoaglatinManila MedNo ratings yet
- Coins Pathology PDFDocument7 pagesCoins Pathology PDFAthena BorjaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Compiled NotesDocument21 pagesCommunicable Disease Compiled NotesJoanne PaulineNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Concept MapDocument1 pagePneumonia Concept MapsekwetNo ratings yet
- Radiology Notes For OSCEDocument6 pagesRadiology Notes For OSCEChristine NaNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Pathophysiologic Effects of Cancer and Treatment ModalitiesDocument2 pagesMod 1 Pathophysiologic Effects of Cancer and Treatment ModalitiesJorese Hannah VictorinoNo ratings yet
- 2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceDocument71 pages2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults AafpDocument2 pagesObesity in Adults AafpMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Addison Disease Early Detection and TreatmentDocument6 pagesAddison Disease Early Detection and TreatmentNajib Al FatinNo ratings yet
- Iron Defeciency AnemiaDocument7 pagesIron Defeciency AnemiaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D DefeciencyDocument6 pagesVitamin D DefeciencyMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D ScreeningDocument7 pagesVitamin D ScreeningMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- 2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceDocument71 pages2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument108 pagesAcute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- AAFP Cushing's Disease - Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Evaluation - American Family PhysicianDocument9 pagesAAFP Cushing's Disease - Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Evaluation - American Family PhysicianMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Ugib Esophagitis: Candida, Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Human ImmunodeficiencyDocument1 pageUgib Esophagitis: Candida, Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Human ImmunodeficiencyMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Presentation - DysuriaDocument17 pagesFamily Medicine Presentation - DysuriaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Acute COPD ExacerbationDocument65 pagesAcute COPD ExacerbationMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Efast: Name Position Normal US Pic Abnormal US Pic SubcostalDocument4 pagesEfast: Name Position Normal US Pic Abnormal US Pic SubcostalMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station ChecklistDocument5 pagesCardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station ChecklistMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- ND NDDocument1 pageND NDMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- E FastDocument4 pagesE FastMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Chronic DiarrheaDocument1 pageChronic DiarrheaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis SummaryDocument1 pageVasculitis SummaryMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Demand Ischemia: Not A Total Occlusion, So If YouDocument1 pageDemand Ischemia: Not A Total Occlusion, So If YouMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- The Right Clinical Information, Right Where It's Needed: Last Updated: Sep 12, 2019Document92 pagesThe Right Clinical Information, Right Where It's Needed: Last Updated: Sep 12, 2019Maryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Malignancy/ Papillary Thyroid CarcinomaDocument2 pagesThyroid Malignancy/ Papillary Thyroid CarcinomaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Centriacinar Panacinar Paraseptal Irregular Emphysema Bullous EmphysemaDocument1 pageCentriacinar Panacinar Paraseptal Irregular Emphysema Bullous EmphysemaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Stimulating NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageStimulating NeurotransmittersMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Hypotension DrugsDocument1 pageHypotension DrugsMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Release Is Stimulated Whenever Nutrients Reach Down Into The Distal BowelDocument1 pageRelease Is Stimulated Whenever Nutrients Reach Down Into The Distal BowelMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Red Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenDocument3 pagesRed Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Intrahepatic Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument1 pageIntrahepatic Biliary Tract DiseaseMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Primary Cardiac Tumors SummaryDocument2 pagesPrimary Cardiac Tumors SummaryMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Stanolol From The Name Stanly (Male)Document2 pagesStanolol From The Name Stanly (Male)Maryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Stimulating NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageStimulating NeurotransmittersMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Superficial Parotidectomy TRZDocument20 pagesSuperficial Parotidectomy TRZdokteraan100% (3)
- Mrs - Jagadeeswari.J M.SC NursingDocument13 pagesMrs - Jagadeeswari.J M.SC NursingBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan: Age Group: Middle and Late ChildhoodDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan: Age Group: Middle and Late ChildhoodHeinna Alyssa Garcia100% (1)
- Pearson's Correlation Coefficient: BMJ (Online) July 2012Document3 pagesPearson's Correlation Coefficient: BMJ (Online) July 2012Randy Rafael Asencio AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Guideline Perkeni 2019Document29 pagesGuideline Perkeni 2019Tiens MonisaNo ratings yet
- Paleco Safety PlanDocument17 pagesPaleco Safety PlanBobomo PoNo ratings yet
- Tourist Attractions in TaiwanDocument2 pagesTourist Attractions in TaiwanKASHMEER SHANE CAYATNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition Concepts & Nutrition Indicators: Training Manual For Project Management Unit MembersDocument45 pagesBasic Nutrition Concepts & Nutrition Indicators: Training Manual For Project Management Unit MembersireneNo ratings yet
- TRF Mapeh 8Document8 pagesTRF Mapeh 8Dhen Velez LargoNo ratings yet
- Z-TRACK-METHOD ChecklistDocument5 pagesZ-TRACK-METHOD ChecklistDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Blueprint 4 Student Book Answer KeyDocument18 pagesBlueprint 4 Student Book Answer Keykyawzayar phyoNo ratings yet
- Sushrut Dental Clinic: Dr. Bhagyashree Ramesh Khedkar BDS (Reg No. A-45644)Document1 pageSushrut Dental Clinic: Dr. Bhagyashree Ramesh Khedkar BDS (Reg No. A-45644)Ganesh ganiNo ratings yet
- Erikson's Psycho-Social Theory of DevelopmentDocument10 pagesErikson's Psycho-Social Theory of DevelopmentCielo DasalNo ratings yet
- Is 9473 2002 PDFDocument34 pagesIs 9473 2002 PDFvijayaNo ratings yet
- ST Bernard GuideDocument12 pagesST Bernard GuidesuzypienaarNo ratings yet
- Received::::: Name Lab No. Gender: Collected Female Mrs. Shampa KarmakarDocument2 pagesReceived::::: Name Lab No. Gender: Collected Female Mrs. Shampa KarmakarakanshaNo ratings yet
- Incident Reporting Process VisioDocument1 pageIncident Reporting Process Visiopjtx100No ratings yet
- Energetic Rejuvenation Newsletter III-7.262130934Document16 pagesEnergetic Rejuvenation Newsletter III-7.262130934Catalin MeiuNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Hallux Valgus Preopertive Criteria and Surgical OutcomesDocument108 pages2015 - Hallux Valgus Preopertive Criteria and Surgical OutcomesMiguel Angel Palacios Flores100% (1)
- Ssri Research PaperDocument10 pagesSsri Research Papergqsrcuplg100% (1)
- LF2F Parental Consent and Waiver FormDocument6 pagesLF2F Parental Consent and Waiver FormDreSznNo ratings yet
- Medical School Pediatric Department Chairs, Inc.: Notes From The Association ofDocument4 pagesMedical School Pediatric Department Chairs, Inc.: Notes From The Association ofChristian NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Tibial Shaft Fractures in Adults - UpToDateDocument37 pagesTibial Shaft Fractures in Adults - UpToDateLyka MahrNo ratings yet
- Indonesia-Korea Medical Roadshow 2023 (Seminar Program With Speaker Info)Document2 pagesIndonesia-Korea Medical Roadshow 2023 (Seminar Program With Speaker Info)Eko BudiarsoNo ratings yet
- lastCleanException 20221129215815Document2 pageslastCleanException 20221129215815poisoxnedNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing IntensiveDocument75 pagesOncology Nursing IntensiveVinsuiCzar BaylonNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Carrot JuiceDocument7 pagesHealth Benefits of Carrot JuiceSana KhanNo ratings yet
- DHA Assessment and Exam Exemption Policy: Definitions / Key TermsDocument31 pagesDHA Assessment and Exam Exemption Policy: Definitions / Key TermsHammad Mustafa50% (2)
- Macrobiotic DietDocument2 pagesMacrobiotic DietMarcio AurélioNo ratings yet
- The Body of The Analyst and The Analytic Setting Reflections On The Embodied Setting and The Symbiotic Transference - Alessandra LemmaDocument20 pagesThe Body of The Analyst and The Analytic Setting Reflections On The Embodied Setting and The Symbiotic Transference - Alessandra LemmaPaulina EstradaNo ratings yet