Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Template) Mini Lesson May 6, 2020
Uploaded by
Alph Brick0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe document provides information about hydrocarbons and their classification. It defines hydrocarbons as organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. Hydrocarbons are classified into three main families based on their structure: alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. Alkanes are saturated and have the general formula CnH2n+2. Alkenes are unsaturated and have at least one double bond with the general formula CnH2n. Alkynes are also unsaturated but have at least one triple bond and the general formula CnH2n-2. Prefixes are used to indicate the number of carbon atoms in each hydrocarbon compound.
Original Description:
Lesson
Original Title
[Template] Mini Lesson May 6, 2020
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information about hydrocarbons and their classification. It defines hydrocarbons as organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. Hydrocarbons are classified into three main families based on their structure: alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. Alkanes are saturated and have the general formula CnH2n+2. Alkenes are unsaturated and have at least one double bond with the general formula CnH2n. Alkynes are also unsaturated but have at least one triple bond and the general formula CnH2n-2. Prefixes are used to indicate the number of carbon atoms in each hydrocarbon compound.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pages(Template) Mini Lesson May 6, 2020
Uploaded by
Alph BrickThe document provides information about hydrocarbons and their classification. It defines hydrocarbons as organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. Hydrocarbons are classified into three main families based on their structure: alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. Alkanes are saturated and have the general formula CnH2n+2. Alkenes are unsaturated and have at least one double bond with the general formula CnH2n. Alkynes are also unsaturated but have at least one triple bond and the general formula CnH2n-2. Prefixes are used to indicate the number of carbon atoms in each hydrocarbon compound.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
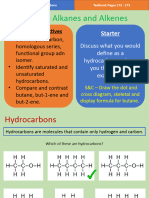
EQ: What are the changes that have occurred in the last 50 years due to the
increased use of carbon-based products? Do the benefits outweigh the
environmental risks?
FQ: What are Hydrocarbons?
LT: I will be able to differentiate the family of hydrocarbons by using the
structural formula
Mini Lesson
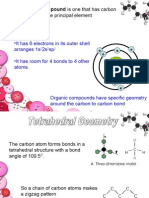
Common Characteristics of Organic Compounds
● Organic compounds are generally nonpolar
● Because they are nonpolar, they are soluble in nonpolar solvents
● Organic compounds are nonelectrolytes
● They have low melting points.
● Reactions are generally slower than inorganic reactions.
● Reactions have high activation energy
Hydrocarbons: are organic compounds that contains only carbon and hydrogen
atoms
Family of Hydrocarbons
Alkane general formula CnH2n + 2
Alkene general formula CnH2n
Alkyne general formula CnH2n-2
1. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbon with general formula CnH2n+2
•The first member of alkane is methane
•All the carbon atoms are connected with single bond
•The name of alkane ends with -ane
•Branching start with four carbon compound
2 Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with general formula CnH2n
•Alkenes has at least one double bond between two carbon atoms.
•The name of alkenes ends with -ene
•The first member of alkene is Ethene
3. Alkyne are unsaturated hydrocarbon with general formula CnH2n-2
•The first member of alkyne is ethyne
•Alkyne has at least one triple bond between two atoms in a compound
•The name of alkyne end with -yne
No of carbon atom Prefix
1 Meth
2 Eth
3 Prop
4 Pent
5 But
6 Hex
7 Hept
8 oct
9 Non
10 Dec
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Lec Review To Organic ChemistryDocument57 pagesLec Review To Organic ChemistryJhan Mark Dri PiocNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Understanding Carbon CompoundDocument20 pagesLearning Objectives: Understanding Carbon Compoundheryana8100% (3)
- Yr12CHEM - M7 Organic Chemistry - Filled - in - NewDocument210 pagesYr12CHEM - M7 Organic Chemistry - Filled - in - Newryan.li20180211No ratings yet
- Organic Chem 2 by HaftomDocument285 pagesOrganic Chem 2 by Haftomdereje dawitNo ratings yet
- Lects. 15,16 (OH) Alkenes & Aromaticity +answersDocument48 pagesLects. 15,16 (OH) Alkenes & Aromaticity +answersvintu pvNo ratings yet
- ALKYNEDocument8 pagesALKYNEallanisaaaacNo ratings yet
- Nota Kimia Carbon Compoun Form 5Document16 pagesNota Kimia Carbon Compoun Form 5akusabrina2012No ratings yet
- G9 - Ch8 - Alkanes-1Document17 pagesG9 - Ch8 - Alkanes-1hamza arroubNo ratings yet
- Santos AlkanealkenesalkynesDocument28 pagesSantos AlkanealkenesalkynesApril JoyNo ratings yet
- Kimia Organik - 3Document52 pagesKimia Organik - 3Gung AriNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxDocument96 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxEgbebessemenow oben ashuNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols - Written Report - SolidumDocument13 pagesHydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols - Written Report - SolidumAva Mae SolidumNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Note Form 5Document9 pagesChemistry Note Form 5SofiyyahOpieNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry CurrentDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry CurrentBierzo JomarNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry CHEM107Document41 pagesOrganic Chemistry CHEM107AhmedAdelIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryDocument40 pagesNomenclature of Organic ChemistrySeema YadavNo ratings yet
- What Are Organic Compounds?Document20 pagesWhat Are Organic Compounds?happymabeeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- SC22a Alkanes and AlkenesDocument10 pagesSC22a Alkanes and AlkenesEmaadB EmaadBNo ratings yet
- Alkenes GroupDocument8 pagesAlkenes GroupHanna GalatiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and AlkenesDocument73 pagesAlkanes and AlkenesRosemaryTanNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds - NotesDocument18 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds - NotesFitfulNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument10 pagesHydrocarbonsjoeNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument48 pagesCarbon CompoundIlakiya Sharvinee KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon and PetroleumDocument38 pagesHydrocarbon and PetroleumVincentius Matthew YonathanNo ratings yet
- Carbon & Its CompoundsDocument64 pagesCarbon & Its Compoundssiya89308No ratings yet
- Organic Chem 10 SL2023Document111 pagesOrganic Chem 10 SL2023Fadilatu Abdoul ZakouNo ratings yet
- Lecture #9 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesLecture #9 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Organic ChemistryG8 ODL Mary Angeline M. GalmanNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONSDocument15 pagesHYDROCARBONSJaxene Breanna AbuanNo ratings yet
- Dienes & Aromatic Compounds, FNDocument60 pagesDienes & Aromatic Compounds, FNMuzahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - 103 - Lecture 1Document41 pagesOrganic Chemistry - 103 - Lecture 1Abdus SubhanNo ratings yet
- Key Notes On Organic KemistreeDocument2 pagesKey Notes On Organic Kemistreedamilareagunbiade7No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - HydrocarbonsDocument58 pagesChapter 3 - HydrocarbonsMarielle RumbaoaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes Lecture 2Document33 pagesAlkenes Lecture 2Дана ЧилибаеваNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Organic PathwaysDocument43 pagesChapter 10 - Organic Pathwaysmanthan212No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument45 pagesOrganic ChemistryShiv PriyamNo ratings yet
- By: Michael B. Logue: AliphaticDocument1 pageBy: Michael B. Logue: AliphaticCLester MadShadowNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Alkanes & Alkense (Organic)Document17 pagesIntroduction, Alkanes & Alkense (Organic)Aaditya MKNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFjacobNo ratings yet
- Lecture-10 (Organic Chemistry and Hidrocarbon) - 1Document75 pagesLecture-10 (Organic Chemistry and Hidrocarbon) - 1Permadi BagasNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Alkanes Alkanes & & Alkanes Alkanes & & Cycloalkanes CycloalkanesDocument61 pagesOrganic Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Alkanes Alkanes & & Alkanes Alkanes & & Cycloalkanes CycloalkanesRSLNo ratings yet
- AlkenesAlkynes-nomenclature-and-properties-for - College-Bio StudentsDocument23 pagesAlkenesAlkynes-nomenclature-and-properties-for - College-Bio Studentshixevab276No ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument4 pagesAlkanesjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument61 pagesOrganic ChemistryfuturainfermieraregistrataNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument76 pagesOrganic Chemistryapi-3738901100% (2)
- Aromatic Compounds: © 2006 Thomson Higher EducationDocument103 pagesAromatic Compounds: © 2006 Thomson Higher Educationbrigittanwp putriNo ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesDocument7 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesMuhammad Hasnain AliNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Rajendra01Document49 pagesOrganic Chemistry Rajendra01ecotechconsultantsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 CHEM 102 2023 Alkanes and NomenclatureDocument24 pagesLecture 3 CHEM 102 2023 Alkanes and Nomenclaturegray mollowakgotlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Saturated HydrocarbonsDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Saturated HydrocarbonsChristian Guimmayen ArizoNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Tr. BDocument47 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Tr. BChishala IsaacNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Organic CompoundsDocument56 pagesWeek 2 - Organic CompoundsMorissette GarciaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes PDFDocument24 pagesAlkanes PDFSarah SarahNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NoteDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notemensahdelali73No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons 1Document32 pagesHydrocarbons 1Jocelyn MatigaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument37 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsRoopa KhenedNo ratings yet
- Advance Chem Report 1Document31 pagesAdvance Chem Report 1Keziah TaycoNo ratings yet
- Decision May Lead To Consequences: ForeshadowDocument3 pagesDecision May Lead To Consequences: ForeshadowAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- George Westinghouse High School: Student Class Schedule Effective March 23, 2020 Period TimeDocument1 pageGeorge Westinghouse High School: Student Class Schedule Effective March 23, 2020 Period TimeAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- SPEECHDocument2 pagesSPEECHAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Regents PracticeDocument5 pagesChemical Equilibrium Regents PracticeAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- HW - Energy Diagram Worksheet: 1. Using The Energy Curve Below The Label and Answer The Following QuestionsDocument3 pagesHW - Energy Diagram Worksheet: 1. Using The Energy Curve Below The Label and Answer The Following QuestionsAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Conductors and Insulators: InsulatorDocument2 pagesConductors and Insulators: InsulatorAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- ALPHDOEUVE CEUS - U8L2 Student Work QUESTION 2 Edited PDFDocument1 pageALPHDOEUVE CEUS - U8L2 Student Work QUESTION 2 Edited PDFAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument4 pagesElectrochemical CellsAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- PBT Graphic Organizer LongDocument6 pagesPBT Graphic Organizer LongAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Oxidation NumberDocument2 pagesOxidation NumberAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Determining Percent Composition: Sample ProblemDocument3 pagesDetermining Percent Composition: Sample ProblemAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Assignment #9 What Were The Causes of The Russian Revolution?Document5 pagesAssignment #9 What Were The Causes of The Russian Revolution?Alph BrickNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction End of Unit Test ReviewDocument4 pagesOxidation Reduction End of Unit Test ReviewAlph BrickNo ratings yet