Professional Documents
Culture Documents
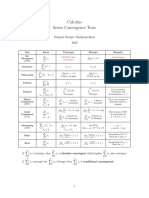
Summary of Convergence and Divergence Tests For Series: 1 N 1 N N !1 N N !1 N
Uploaded by
pal.pallav9457Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Convergence and Divergence Tests For Series: 1 N 1 N N !1 N N !1 N
Uploaded by
pal.pallav9457Copyright:
Available Formats
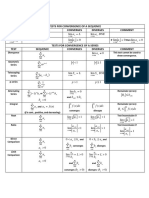
Summary of Convergence and Divergence Tests for Series
Test Series Convergence or Divergence Comments
P
1
Divergence an Diverges if lim an 6= 0 Inconclusive if lim an = 0
n=1 n!1 n!1
Useful for comparison tests
P
1
n a
Geometric ar (1) Converges to S = if |r| < 1; if the nth -term an of a series
n=0 1 r
series (2) Diverges if |r| > 1 is similar to arn .
Useful for comparison tests
P1 1
p-series p
(1) Converges if p > 1; if the nth -term an of a series
n=1 n
1
(2) Diverges if p 6 1 is similar to .
np
The function f obtained
P
1 R1
Integral an (1) Converges if 1 f (x) dx converges; from an = f (n) must be
n=1 R1
an = f (n) (2) Diverges if 1 f (x) dx diverges continuous, positive,
decreasing, and readily
integrable.
P
1
(1) If bn converges and an 6 bn The comparison series
n=1
P
1 P
1
for every n, then an converges; bn is often a geometric
n=1 n=1
P
1 P
1 P
1
Comparison an , bn (2) If bn diverges and an > bn series or a p-series. To find
n=1 n=1 n=1
P1
an > 0, bn > 0 for every n, then an diverges; bn in (3), consider only
n=1
an
(3) If lim > 0 (not 1), then the terms of an that have
n!1 bn
both series converge or both diverge. the greatest e↵ect on the
magnitude.
Inconclusive if L = 1. Useful
an+1
If lim = L (or 1), the series if an involves factorials or
n!1 an
P
1
Ratio an (1) converges (absolutely) if L < 1; nth powers. If an > 0 for
n=1
(2) diverges if L > 1 (or 1) every n, the absolute value
sign may be disregarded.
p Inconclusive if L = 1. Useful
If lim n
|an | = L (or 1), the series if an involves nth powers.
n!1
P
1
Root an (1) converges (absolutely) if L < 1; If an > 0 for every n, the
n=1
(2) diverges if L > 1 (or 1) absolute value sign may be
disregarded.
P
1
Alternating ( 1)n an Converges if ak > ak+1 for every k Applicable only to an
n=1
Series an > 0 and lim an = 0. alternating series.
n!1
You might also like
- MAT 2280 Proving Series Conv - SPR-19Document2 pagesMAT 2280 Proving Series Conv - SPR-19Olivier UwamahoroNo ratings yet
- 1 FormulaDocument2 pages1 FormulaajajaNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Root TestDocument4 pagesRatio and Root TestJose Barrera GaleraNo ratings yet
- MAT 136 CH 5 TheoremDocument3 pagesMAT 136 CH 5 TheoremChilli LeeNo ratings yet
- Summary of Convergence Tests For SeriesDocument1 pageSummary of Convergence Tests For Seriescartoon_nate100% (2)
- Summary of Convergence and Divergence Tests For Infinite SeriesDocument3 pagesSummary of Convergence and Divergence Tests For Infinite Seriesrithu ronaldoNo ratings yet
- Summary - Series and SequencesDocument5 pagesSummary - Series and Sequencesfabian rodeloNo ratings yet
- Series Summary: 1 When Can We Calculate The Sum of A Series?Document3 pagesSeries Summary: 1 When Can We Calculate The Sum of A Series?Justine WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Sequences & Series ToolboxDocument8 pagesSequences & Series ToolboxmoppommtyNo ratings yet
- Absolute convergence ratio root testsDocument12 pagesAbsolute convergence ratio root testsdzikrydsNo ratings yet
- Topic 15 - Infinite Series and Its Convergence (Non-Negative Series)Document12 pagesTopic 15 - Infinite Series and Its Convergence (Non-Negative Series)Moksh YadavNo ratings yet
- Summary Part 2Document3 pagesSummary Part 2Gunnar CalvertNo ratings yet
- Tests For Series: A Summary: Lim 0 Lim 0Document1 pageTests For Series: A Summary: Lim 0 Lim 0Dr. DrawingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Convergence Tests For SeriesDocument2 pagesLecture 14 Convergence Tests For SeriesShresth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Convergence TestsDocument1 pageConvergence TestspgokoolNo ratings yet
- Weber & Arfken Mathematical Methods For Physicists Ch. 5 Selected SolutionsDocument6 pagesWeber & Arfken Mathematical Methods For Physicists Ch. 5 Selected SolutionsJosh Brewer0% (1)
- MA 101 (Mathematics I) : N N N N N N 1 NDocument3 pagesMA 101 (Mathematics I) : N N N N N N 1 NAtul KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28Document45 pagesLecture 28BenedictVillaminPolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5: Series, Power Series, Taylor Series: 0. Then Show That Both The Series ADocument2 pagesAssignment 5: Series, Power Series, Taylor Series: 0. Then Show That Both The Series AvishaldeepNo ratings yet
- Calcproject 2010Document5 pagesCalcproject 2010helenxwhoNo ratings yet
- 4.3.1. The P-Series. The Following Series Is Called P-SeriesDocument3 pages4.3.1. The P-Series. The Following Series Is Called P-SeriesisaackNo ratings yet
- 12 - Series Tests SummaryDocument1 page12 - Series Tests SummaryscottNo ratings yet
- Rearrangements of numerical series: An in-depth analysisDocument18 pagesRearrangements of numerical series: An in-depth analysisMaria Jose de las mercedes Costa AzulNo ratings yet
- Lecturen 2Document6 pagesLecturen 2S.m. ChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- Series Summary CompleteDocument3 pagesSeries Summary CompleteFrantz ClermontNo ratings yet
- Series Strategies and Tests For Convergence: Test Name When To Use DetailsDocument3 pagesSeries Strategies and Tests For Convergence: Test Name When To Use Detailssharmanator99No ratings yet
- Series TheoremsDocument4 pagesSeries TheoremsIsmail Medhat SalahNo ratings yet
- II Series-1Document15 pagesII Series-1IduncareNo ratings yet
- Math 142 Series NotesDocument2 pagesMath 142 Series NotestibarionNo ratings yet
- 4.1. Convergence of SeriesDocument31 pages4.1. Convergence of SeriesPrat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesMaths SyllabusNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- MAT136 Week 11Document7 pagesMAT136 Week 11Nasim SharifNo ratings yet
- Random Series Functions Exercises Weeks 1-2Document2 pagesRandom Series Functions Exercises Weeks 1-2Dor ShmoishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Test For Cord NOTESDocument1 pageChapter 9 Test For Cord NOTESeperlaNo ratings yet
- 11.6 Absolute Convergence and The Ratio and Root TestsDocument3 pages11.6 Absolute Convergence and The Ratio and Root TestsAustin RedmonNo ratings yet
- HL Series Summary Page TableDocument1 pageHL Series Summary Page TableAndrianna TsakiridouNo ratings yet
- Sign Changing Series ExplainedDocument119 pagesSign Changing Series ExplainedTùng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 4.4.1. The Ratio TestDocument2 pages4.4.1. The Ratio TestisaackNo ratings yet
- IIT Guwahati Math Tutorial Sheet 4Document1 pageIIT Guwahati Math Tutorial Sheet 4Nitish MeenaNo ratings yet
- Binomial MomentsDocument27 pagesBinomial MomentscocoyetacocoNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series ReviewDocument9 pagesSequences and Series Reviewcartoon_nate100% (4)
- Lecture GDocument9 pagesLecture Gabraham gkNo ratings yet
- I2-Tests For Absolute ConvergenceDocument29 pagesI2-Tests For Absolute ConvergenceJapheth Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Tests For VergencesDocument1 pageTests For VergencesPrashanth SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Absolute ConvergenceDocument2 pagesAbsolute ConvergenceUninvited GuestNo ratings yet
- Series Reference GuideDocument4 pagesSeries Reference GuideShivani SinhaNo ratings yet
- Cal 2 FormulasDocument4 pagesCal 2 FormulasAustin MirandaNo ratings yet
- Sarvajanik College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument23 pagesSarvajanik College of Engineering and TechnologylalaNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Tests For Convergence of A Sequence Test Sequence Converges Diverges CommentDocument2 pagesA A A A A: Tests For Convergence of A Sequence Test Sequence Converges Diverges CommentRashmi PalankarNo ratings yet
- Hints For Ex. Sheet 6Document5 pagesHints For Ex. Sheet 6Akshat MittalNo ratings yet
- A Aplicação de Softwares Matemáticos Nos Ensinos Básico e SuperiorDocument37 pagesA Aplicação de Softwares Matemáticos Nos Ensinos Básico e Superioraye pyoneNo ratings yet
- Fix GordonDocument20 pagesFix GordonVijaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Series Convergence Tests BlackpenredpenDocument1 pageSeries Convergence Tests BlackpenredpenKarolina Padilla ValdezNo ratings yet
- Problem 11Document2 pagesProblem 11modidNo ratings yet
- IIT Guwahati Mathematics Course Covers Series of Real NumbersDocument11 pagesIIT Guwahati Mathematics Course Covers Series of Real NumbersAdarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis Test SeriesDocument48 pagesReal Analysis Test Series21mma019 Anmol PatialNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Practical Guide - Series of Real NumbersDocument3 pages0.1 Practical Guide - Series of Real NumbersEmilNo ratings yet
- 11.6 Part2 Abs ConvergenceDocument3 pages11.6 Part2 Abs ConvergenceAk GamingNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)From EverandHarmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)No ratings yet
- Random Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101From EverandRandom Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101No ratings yet
- Exam1practicesolutions PDFDocument4 pagesExam1practicesolutions PDFAyah Al-AnaniNo ratings yet
- 2 Series: 2.1 Some Typical ExamplesDocument12 pages2 Series: 2.1 Some Typical Examplespal.pallav9457No ratings yet
- Iesc 109Document17 pagesIesc 109Kaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Physics Class 7 ICSE Solutions - SoundDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Physics Class 7 ICSE Solutions - Soundpal.pallav9457100% (1)
- Closer Guitar TabsDocument8 pagesCloser Guitar Tabspal.pallav9457No ratings yet
- Abdxghsl PDFDocument1 pageAbdxghsl PDFpal.pallav9457No ratings yet
- Bifurcation matrix second derivativeDocument1 pageBifurcation matrix second derivativepal.pallav9457No ratings yet
- Bifurcation11 PDFDocument1 pageBifurcation11 PDFpal.pallav9457No ratings yet
- Bifurc1ation11 PDFDocument1 pageBifurc1ation11 PDFpal.pallav9457No ratings yet
- Syllabus for B.A./B.Sc. (Honours) in MathematicsDocument37 pagesSyllabus for B.A./B.Sc. (Honours) in MathematicsSam DasNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 Positive Term SeriesDocument27 pagesUnit-6 Positive Term SeriesChandradeep Reddy TeegalaNo ratings yet
- 2 Series: 2.1 Some Typical ExamplesDocument12 pages2 Series: 2.1 Some Typical Examplespal.pallav9457No ratings yet
- Review: Chapter 11: 11.1: SequencesDocument4 pagesReview: Chapter 11: 11.1: SequencesRahul NayakNo ratings yet
- Taylor and Maclaurin Series ExplainedDocument14 pagesTaylor and Maclaurin Series ExplainedalyssaNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: Key ExamplesDocument35 pagesSequences and Series: Key ExamplesJarl SolitudeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - I (MATH F111) : BITS PilaniDocument70 pagesMathematics - I (MATH F111) : BITS PilaniAkash KolliNo ratings yet
- L3 D'Alembert's TestDocument23 pagesL3 D'Alembert's TestArnav Dasaur100% (3)
- ASSIGNMENT-1 Mathematics I MA101 Odd Sem 2018-2019-2Document2 pagesASSIGNMENT-1 Mathematics I MA101 Odd Sem 2018-2019-2Harsh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Infinite Series TestsDocument16 pagesInfinite Series TestsArnav Dasaur100% (1)
- Infinite Geometric SeriesDocument4 pagesInfinite Geometric SeriesMorvaridYiNo ratings yet
- Convergence or Divergence Tests for SeriesDocument10 pagesConvergence or Divergence Tests for SeriesRajdeep ChopdekarNo ratings yet
- Series 01Document39 pagesSeries 01jackNo ratings yet
- Maths Assignment DTUDocument2 pagesMaths Assignment DTUKaran0% (1)
- Chapter 8. Infinite Series: Le Cong NhanDocument71 pagesChapter 8. Infinite Series: Le Cong NhanKoasa NishikiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Series Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument22 pagesNumerical Series Chapter 1 SolutionsMarian LupulescuNo ratings yet
- Power SeriesDocument55 pagesPower SeriesFaizNo ratings yet
- Lista 2 SeriesDocument3 pagesLista 2 SeriesSamuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Fourier Series: X X X F X NX N NX N NDocument2 pagesUnit 1: Fourier Series: X X X F X NX N NX N NHarish ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Infinte Series NotesDocument5 pagesInfinte Series Notesabd_93No ratings yet
- BS Grewal.Document77 pagesBS Grewal.Debmalya PariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MAT455 PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 1 MAT455 PDFaleeyakamalNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Physics - I Review - : SeriesDocument26 pagesMathematical Physics - I Review - : SeriesPrastiawanNo ratings yet
- Sequences (Ch.11)Document20 pagesSequences (Ch.11)wiswisnuNo ratings yet
- Formulae of Sequence and SeriesDocument3 pagesFormulae of Sequence and SeriesMayank Kumar BhagatNo ratings yet
- E e X X X N!: Abdulrazzaq - 23Document4 pagesE e X X X N!: Abdulrazzaq - 23William G'nrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Power SeriesDocument55 pagesChapter 4 Power SeriesThalagawali RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Power Series Solutions Taylor SeriesDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Power Series Solutions Taylor SeriesJosamy MartinezNo ratings yet
- Geometric Series & Telescoping Series: Calculus IIDocument20 pagesGeometric Series & Telescoping Series: Calculus IInou channarithNo ratings yet
- Math 10 - Lesson 3 - Geometric Sequences Series and MeansDocument65 pagesMath 10 - Lesson 3 - Geometric Sequences Series and MeansCleopatraNo ratings yet
- Exam Progression-Jawapan PDFDocument3 pagesExam Progression-Jawapan PDFKhairul WarsNo ratings yet
- Home Work Ke 2Document7 pagesHome Work Ke 2Dira LutfiyaNo ratings yet
- Series Convergence TestDocument6 pagesSeries Convergence Testsan_kumar@ymail.commNo ratings yet