Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Handout 10
Uploaded by
SahabCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Handout 10
Uploaded by
SahabCopyright:
Available Formats
Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro
Department of Telecommunication Engineering
Applied Physics (1st Semester, 1st Year)
______________________________________________________________________________
Name: ______________________________________________ Roll Number: _____________
Score: _____________ Signature: ________________________Date:____________________
LAB HANDOUT # 10
INTRODUCTION TO THE OSCILLOSCOPE AND FUNCTION GENERATOR
OBJECTIVE:
To understand the basic functionality of Function/Signal Generator and Digital Storage
Oscilloscope.
Basic signal generation from function generator and observation at Digital Storage
Oscilloscope.
THEORY:
i) Function Generator
The front panel of your function generator is shown in Figure 1. This instrument outputs a time-
varying periodic voltage signal (the OUTPUT connector, do not use the sync connector. By
pushing the appropriate buttons on the front panel, the user can specify various characteristics of
the signal.
Figure 1: Front panel of a conventional function/signal generator
The main characteristics that you will be concerned with in this class are:
• Shape: sine, square, or triangle waves.
• Frequency: inverse of the period of the signal; units are cycles per second (Hz)
• Vpp: peak to peak Voltage value of the signal
• DC Offset: constant voltage added to the signal to increase or decrease its mean or average
level. In a schematic, this would be a DC voltage source in series with the oscillating voltage
source.
Figure 2 demonstrates few of the above stated parameters.
Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro
Department of Telecommunication Engineering
Applied Physics (1st Semester, 1st Year)
______________________________________________________________________________
Figure 2: Basic parameters of a function/signal generator
You must specify the characteristics of the signal you need. For example, to set the frequency of
the signal:
Enable the frequency modify mode by pressing the Freq button.
Enter the value of the desired frequency by operating of the corresponding button with rotary
knob and two cursor buttons < > or with the decadic range buttons ÷10 and ×10.
The parameter to be changed is selected by operating the corresponding button in the
PARAMETER field (OFFSET, AMPL, PULSE WIDTH, FREQ). the button is illuminated,
when the parameter can be changed. By operating the rotary knob the value of the digit
underlined by the cursor is modified. If the cursor underlines a blank position, it is considered as
0 and can be changed by turning the rotary knob to the desired value. The cursor is shifted to
another position with two cursor buttons < >. Turning the rotary knob increments or decrements
the value depending on the direction the knob is turned.
ii) Digital Storage Oscilloscope (DSO):
What is an oscilloscope? An oscilloscope is basically a graph-displaying device – it draws the
graph of an electrical signal. In most applications, the graph shows how signals change over
time: the vertical (Y) axis represents voltage and the horizontal (X) axis represents time. The
intensity or brightness of the signal is sometimes called the Z axis. This can be shown in Fig 3.
Figure 3: X, Y and Z components of a waveform
Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro
Department of Telecommunication Engineering
Applied Physics (1st Semester, 1st Year)
______________________________________________________________________________
This simple graph can tell you many things about a signal such as:
• The time and voltage values of a signal
• The frequency of an oscillating signal
• Whether or not a malfunctioning component is distorting the signal
• How much of a signal is direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC)
BNC inputs:
The channel 1 and 2 BNC inputs receive electrical signals for display.
You can measure different characteristics of a waveform with an oscilloscope – amplitude,
frequency, DC offset and phase.
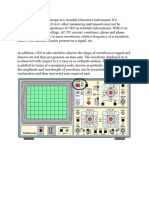
Figure 4: Digital Storage Oscilloscope
Your oscilloscope consists of four main systems – the vertical system, the horizontal system, the
main function and the trigger system. The different systems are described below.
The Vertical System:
You select the channel you want by pressing CH1 or CH2. You can use the Volts/Div to
adjust the vertical scale. The position knobs move the waveform up or down on the
scope screen.
The Horizontal System:
An oscilloscope’s horizontal system is most closely associated with its acquisition of an
input signal. Horizontal controls are used to position and scale the waveform horizontally
Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro
Department of Telecommunication Engineering
Applied Physics (1st Semester, 1st Year)
______________________________________________________________________________
Figure 5: Vertical and Horizontal Systems
The Main Function
The main function keys are: Acquire key, Display key, Utility key, Hard copy key, Program key,
Cursor key, Measure key, Help key, Save/Recall key, Auto set key, Run/Stop key.
To measure the amplitude/volts and frequency/time period, press the cursor button and follows
the steps:
1. Press the F1, for selecting the channel.
2. To select the cursor to be activated, press F2 (Horizontal cursor) and F3(Vertical cursor).
3. To move the cursor, use the vertical knob.
4. The bottom right corner of the display shows the position of two cursors (T1 and T2), their
time difference (Δ), and the frequency (f).
Even the most advanced instrument can only be as precise as the data that goes into it. A probe
functions in conjunction with an oscilloscope as part of the measurement system. Hence we talk
about the probes you use with your oscilloscope. Figure 6 shows a picture of your scope probe.
Figure 6: Scope probes
Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro
Department of Telecommunication Engineering
Applied Physics (1st Semester, 1st Year)
______________________________________________________________________________
QUESTIONS:
i) What is the use of volts/div and time/div? And what happen with the signal by
altering these parameters of the Oscilloscope?
ii) Which connector is used in the probes of oscilloscope?
iii) What is the difference between cursor and measure option?
iv) What is function of Function Generator? List the waves which be generated via
Function Generator.
v) Differentiate Function Generator and Digital Storage Oscilloscope.
vi) Generate arbitrary waveforms from the Signal Generator and observe the signal at the
oscilloscope. Record the readings
FINAL CHECK LIST
1. Return all equipment and material to their proper storage area
2. Submit your answers to questions, and results before the next laboratory
You might also like
- Experiment 1: Familiarization With Laboratory Test Equipment and InstrumentsDocument7 pagesExperiment 1: Familiarization With Laboratory Test Equipment and InstrumentsHenry Theodore DaquinagNo ratings yet
- Machinery Diagnostic PlotsDocument16 pagesMachinery Diagnostic Plotsfazzlie100% (1)
- Lab 1 (Introduction To Test and Measurement Equipment)Document9 pagesLab 1 (Introduction To Test and Measurement Equipment)afaq ahmad khanNo ratings yet
- Solid State Devices and Circuits (EET-201) : Practical Lab FileDocument10 pagesSolid State Devices and Circuits (EET-201) : Practical Lab FileRajarshi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Familiarization With Laboratory Instruments: Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter, and DC Power SupplyDocument7 pagesExperiment 1 Familiarization With Laboratory Instruments: Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter, and DC Power Supplypappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Electronics Lab 1Document18 pagesElectronics Lab 1Sheraz HassanNo ratings yet
- EEE102 Exp1Document7 pagesEEE102 Exp1Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Study of Different Electronics InstrumentsDocument9 pagesExp 2 Study of Different Electronics Instrumentsabhinav tuplondheNo ratings yet
- Lab 4A Jun 2018 Introduction of Oscilloscope and Signal GeneratorDocument10 pagesLab 4A Jun 2018 Introduction of Oscilloscope and Signal GeneratorAugustine JR RobertNo ratings yet
- Lab1-Introduction To DSO ND FGDocument11 pagesLab1-Introduction To DSO ND FGHamza AliNo ratings yet
- The OscilloscopeDocument5 pagesThe OscilloscopeSadiq IdrisNo ratings yet
- enme350-LabManual Spring 11-2Document54 pagesenme350-LabManual Spring 11-2Aaron OlszewskiNo ratings yet
- Micro-Scope (Microcontrolle R Oscilloscope) : Thebeast Inc. Philippines User ManualDocument10 pagesMicro-Scope (Microcontrolle R Oscilloscope) : Thebeast Inc. Philippines User ManualRina EllaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Familiarization With Laboratory Instruments: Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter, and DC Power SupplyDocument12 pagesExperiment No. 1 Familiarization With Laboratory Instruments: Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter, and DC Power SupplyMukul ChandraNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 06 A: Title: Cathode Ray Oscilloscope: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 06 A: Title: Cathode Ray Oscilloscope: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimStar LordNo ratings yet
- Use of The Oscilloscope-UMDDocument25 pagesUse of The Oscilloscope-UMDAngela Majaba0% (1)
- CroDocument4 pagesCroRajan SharmaNo ratings yet
- TaraNG UserManual GECA-1Document42 pagesTaraNG UserManual GECA-1Durgesh DhoreNo ratings yet
- EMI Lab Manual2Document27 pagesEMI Lab Manual2charuNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Electric Motors and Drivers - Module 1Document7 pages2022 - Electric Motors and Drivers - Module 1Rafi AkbarNo ratings yet
- 403 Lab1 Intro To Spectral Analysis 092006Document16 pages403 Lab1 Intro To Spectral Analysis 092006Dehri BrahimNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Oscilloscope and Waveform GeneratorDocument9 pagesExp 2 Oscilloscope and Waveform GeneratorusmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Measuring Instruments and Power/Signal Sources: 1-Digital MultimeterDocument8 pagesLecture 4: Measuring Instruments and Power/Signal Sources: 1-Digital MultimeterHuzaifa RehanNo ratings yet
- Bee Exp 3Document17 pagesBee Exp 3Kashish JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Oscilloscope Function Generator)Document12 pagesChapter 3 (Oscilloscope Function Generator)che syakirNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Analogue and Digital Communication LabDocument14 pagesLaboratory Manual: Analogue and Digital Communication LabZain HaiderNo ratings yet
- P-P Volts DivisionDocument12 pagesP-P Volts DivisionG.Srinivasa sagarNo ratings yet
- The Oscilloscope and Function GeneratorDocument9 pagesThe Oscilloscope and Function GeneratorMohamed KamilNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document45 pagesUnit 4apakkiNo ratings yet
- Escom Electronica AnalogicaDocument9 pagesEscom Electronica AnalogicaEduardo Zamarron MuñozNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis and Condition MonitoringDocument5 pagesModal Analysis and Condition Monitoringbidyutkr30100% (2)
- Unit 5 MergedDocument71 pagesUnit 5 MergedSakshiNo ratings yet
- Emi Lab Manual PDFDocument39 pagesEmi Lab Manual PDFMadhusudhanan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab ManualDocument100 pagesBasic Electronics Lab ManualMitchell Cifuentes100% (4)
- Activity 2Document3 pagesActivity 2Jameson EstanderNo ratings yet
- ECE 311 Measurement & Instrumentation-1Document25 pagesECE 311 Measurement & Instrumentation-1SamuelNo ratings yet
- Voltage Dip SimulationDocument5 pagesVoltage Dip Simulationrjk941No ratings yet
- Lab 3Document17 pagesLab 3asdqNo ratings yet
- ESC 201A ExpDocument9 pagesESC 201A Expanshikamittal2626No ratings yet
- Instrumentation EngineeringDocument126 pagesInstrumentation EngineeringGaurav UpaNo ratings yet
- تجربة 1Document17 pagesتجربة 1Moaid BinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document16 pagesExperiment 3Ashish patelNo ratings yet
- A Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDocument2 pagesA Cathode Ray OscilloscopeZUBAIRNo ratings yet
- Eca Ii Lab 1Document14 pagesEca Ii Lab 1Tausif MinhasNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical EngineeringDocument100 pagesBasics of Electrical Engineeringdeep voraNo ratings yet
- PM540WCDocument6 pagesPM540WCMiron ShikulaNo ratings yet
- Apparatus:: AIM: Acquire The Knowledge of Output Devices Like CRO and DSO For Observing OutputDocument5 pagesApparatus:: AIM: Acquire The Knowledge of Output Devices Like CRO and DSO For Observing OutputAdwait BorikarNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document8 pagesExp 4Elisbeth MurugasNo ratings yet
- Be Lab ManualDocument96 pagesBe Lab ManualBhargav garlapatiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Measurement and InstrumentationDocument29 pagesLab Manual Measurement and Instrumentationkkp0650No ratings yet
- Transverse Vibration8thDocument4 pagesTransverse Vibration8thAbhishek KudalNo ratings yet
- Microscopic View of Flank Wear AreaDocument4 pagesMicroscopic View of Flank Wear Areajacobian1810No ratings yet
- Interpretation of ResultsDocument3 pagesInterpretation of ResultsJulian CaminaNo ratings yet
- Waveform MeasurementsDocument17 pagesWaveform MeasurementsrobertNo ratings yet
- Input Interface Using Fingertip Pressure (Nonaka)Document5 pagesInput Interface Using Fingertip Pressure (Nonaka)Oscar Alejandro Cruz ArguelloNo ratings yet
- DCS Original (2) FinalDocument46 pagesDCS Original (2) FinalRaji RNo ratings yet
- Arduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsFrom EverandArduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Stem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V11From EverandStem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V11No ratings yet
- Stem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles V11From EverandStem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles V11No ratings yet
- Lab Handout 3 PDFDocument3 pagesLab Handout 3 PDFSahabNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout 11 PDFDocument3 pagesLab Handout 11 PDFSahabNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout 3 PDFDocument3 pagesLab Handout 3 PDFSahabNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout 11 PDFDocument3 pagesLab Handout 11 PDFSahabNo ratings yet
- Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro Department of Telecommunication EngineeringDocument3 pagesMehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro Department of Telecommunication EngineeringSahabNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1SahabNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout 9Document3 pagesLab Handout 9SahabNo ratings yet
- Itp Lab 9Document6 pagesItp Lab 9SahabNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout 8Document3 pagesLab Handout 8SahabNo ratings yet
- Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro Department of Telecommunication EngineeringDocument3 pagesMehran University of Engineering and Technology, Jamshoro Department of Telecommunication EngineeringSahabNo ratings yet
- Name: - Roll No: - Score: - Signature of The Lab Tutor: - Date: - /01/2018Document8 pagesName: - Roll No: - Score: - Signature of The Lab Tutor: - Date: - /01/2018SahabNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1SahabNo ratings yet
- Itp Lab 13-14Document10 pagesItp Lab 13-14SahabNo ratings yet
- Name: - Roll No: - Score: - Signature of The Lab Tutor: - DateDocument8 pagesName: - Roll No: - Score: - Signature of The Lab Tutor: - DateSahabNo ratings yet
- Itp Lab 10Document10 pagesItp Lab 10SahabNo ratings yet
- ITP Lab 3Document11 pagesITP Lab 3SahabNo ratings yet
- Name: - Roll No: - Score: - Signature of The Lab Tutor: - Date: - /01/2018Document8 pagesName: - Roll No: - Score: - Signature of The Lab Tutor: - Date: - /01/2018SahabNo ratings yet
- ITP Lab 2Document7 pagesITP Lab 2SahabNo ratings yet
- Itp Lab 9Document6 pagesItp Lab 9SahabNo ratings yet
- ITP Lab 3Document11 pagesITP Lab 3SahabNo ratings yet
- ITP Lab 2Document7 pagesITP Lab 2SahabNo ratings yet
- Circular For Enrolment Card 17CEDocument1 pageCircular For Enrolment Card 17CESahabNo ratings yet
- Requirement of Protection Systems Engineering: Knowledge Management SystemDocument27 pagesRequirement of Protection Systems Engineering: Knowledge Management SystemSamNo ratings yet
- HA16129FPJ: Single Watchdog TimerDocument24 pagesHA16129FPJ: Single Watchdog TimerMichael PorterNo ratings yet
- Ch29 StudentDocument12 pagesCh29 StudentJA55EENo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Potentiometer Model QY9010A1014: GeneralDocument4 pagesAuxiliary Potentiometer Model QY9010A1014: Generalvubac11No ratings yet
- Kirchhoff Laws and Network TheoremDocument12 pagesKirchhoff Laws and Network TheoremDeepak KumbharNo ratings yet
- T-DM-008-D Alpha Prius VDocument30 pagesT-DM-008-D Alpha Prius VHameed BangishNo ratings yet
- Magnetizing CurrentDocument4 pagesMagnetizing CurrentSureshraja9977No ratings yet
- 115/13.8kV TRANSFORMER (T601) PROTN. SET-1 PANEL-1 +TRPA.11Document1 page115/13.8kV TRANSFORMER (T601) PROTN. SET-1 PANEL-1 +TRPA.11Anonymous BZQOJwWIh6No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Gaurav Sharma: Professional ExperienceDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae Gaurav Sharma: Professional Experiencegaurav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesDatasheet PDFEka Hikmah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Micromaster 420: 0.12 KW - 11 KWDocument190 pagesMicromaster 420: 0.12 KW - 11 KWCristian SilvaNo ratings yet
- Box Fan ®Document5 pagesBox Fan ®pukymottoNo ratings yet
- F 124098384Document66 pagesF 124098384Costin AngelescuNo ratings yet
- 1vap428601-Db SCVDocument4 pages1vap428601-Db SCVSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Digital HD Videocassette RecorderDocument78 pagesService Manual: Digital HD Videocassette RecorderthewarapperumaiuNo ratings yet
- The Science of Photobiology - 2nd EdDocument428 pagesThe Science of Photobiology - 2nd EdFede ZannierNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Battery Specifications: DIN Number 72310 1988Document5 pagesUnderstanding The Battery Specifications: DIN Number 72310 1988asifzaman3180No ratings yet
- Part 5 - Electroacoustic Devices - HandoutDocument17 pagesPart 5 - Electroacoustic Devices - HandoutJade Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- TLZJ23022844586Document13 pagesTLZJ23022844586alonsoNo ratings yet
- L1 L2 GPS GLONASS Active AntennaDocument1 pageL1 L2 GPS GLONASS Active AntennaMaxtenaNo ratings yet
- Tda8359 PDFDocument20 pagesTda8359 PDFsiliboyNo ratings yet
- EFR-25RM7Q: Product DatasheetDocument2 pagesEFR-25RM7Q: Product DatasheetRio AribowoNo ratings yet
- Zxdu68 B201 DC PDFDocument42 pagesZxdu68 B201 DC PDFronnymareNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor Using TriacDocument3 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor Using Triackummarai saileelaNo ratings yet
- Manual M100T Series 50 60Document18 pagesManual M100T Series 50 60Samir KhanNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram 3 General Notes & Specification 1 Legend & Symbol 4Document1 pageSingle Line Diagram 3 General Notes & Specification 1 Legend & Symbol 4Abnar KumplishaNo ratings yet
- E12686-1601-YC21-11-04 Low Voltage Distribution Overview PDFDocument1 pageE12686-1601-YC21-11-04 Low Voltage Distribution Overview PDFthanhNo ratings yet
- TV Sony Kv-21t5kDocument6 pagesTV Sony Kv-21t5keduardskNo ratings yet
- VillamorDocument80 pagesVillamorJeremiash ForondaNo ratings yet
- Lecture4. DC Generators - 1.ppt - 0Document52 pagesLecture4. DC Generators - 1.ppt - 0abd rahim bin a.samatNo ratings yet