0% found this document useful (0 votes)
476 views3 pagesComprehensive Guide to Staining Techniques
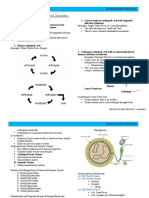
This document describes 31 different stains used for various tissue staining purposes. Some key stains mentioned are Van Gieson stain for connective tissues, Acridine Orange for distinguishing living and dead cells, Alcian Blue for acid mucopolysaccharides, Methylene Blue as a basic nuclear stain, Toluidine Blue as a substitute for thionine in fresh frozen sections, Giemsa Stain for staining blood cells, Orcein for elastic fibers, and Picric Acid as a contrast stain with acid fuchsin for connective tissue staining. The stains described are used to stain a variety of cellular structures and components for microscopic examination.
Uploaded by
Mdrrmo MaconaconCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
476 views3 pagesComprehensive Guide to Staining Techniques
This document describes 31 different stains used for various tissue staining purposes. Some key stains mentioned are Van Gieson stain for connective tissues, Acridine Orange for distinguishing living and dead cells, Alcian Blue for acid mucopolysaccharides, Methylene Blue as a basic nuclear stain, Toluidine Blue as a substitute for thionine in fresh frozen sections, Giemsa Stain for staining blood cells, Orcein for elastic fibers, and Picric Acid as a contrast stain with acid fuchsin for connective tissue staining. The stains described are used to stain a variety of cellular structures and components for microscopic examination.
Uploaded by
Mdrrmo MaconaconCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Celestine Blue: Serves as a substitute in hematoxylin staining procedures.
- Toluidine Blue: Used in microanatomical and circulation system studies.
- Acriflavine: Used for demonstrating phosphate activities in cells.
- Van Gieson stain (Acid Fuchsin-Picric Acid): Describes the use of Van Gieson stain for demonstrating connective tissues.
- Acridine Orange: Explains use for genetic material fluorescence and monitoring cellular processes.
- Congo Red: Stain used particularly for cylinders in nephrology research.
- Alcian Blue: Highlights acid mucopolysaccharides in biological samples.
- Basic Fuchsin: Used in fast staining of mycobacteria and fungus.
- Bismarck Brown: Serves as a background stain for counterstaining processes.
- Iodine: Common stain for starch in histological applications.
- Benzidine Brown: Used for staining cellulose in plant structures.
- Victoria Blue: Stains neuroglia in frozen sections and chromosomes.
- Coomassie Blue: Commonly used in protein band visualization after electrophoresis.
- Giemsa Stain: Used for differential staining in hematology, primarily for blood smears.
- Carmine: A traditional stain for identifying glycogen deposits.
- Mayer's Carmalum: Alternative to carmine for staining glycogen with trichrome protocols.
- Gold Sublimate: Used in histology for intricate tissue detail techniques.
- Janus Green B: Serves in demonstrating mitochondria visually in cells.
- Orcein: Highlights elastic fibers in dermatological sections.
- Osmium Tetroxide: Primarily a fixative for lipid components within cells, stains fat black.
- Lead Hematoxylin: Used for nuclear details in advanced tissue preparations.
- Silver Nitrate: 0.1% aqueous solution used for biological stain preparations.
- Picric Acid: Used for contrast in acid fuchsin methodologies.