Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fliuids Mechanics
Fliuids Mechanics
Uploaded by
tua0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Fliuids Mechanics.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesFliuids Mechanics
Fliuids Mechanics
Uploaded by
tuaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
FLUID MECHANICS 963.
Which of the following most
nearly gives the pressure reading at
Properties of Fluid C?
Fluid Density, Unite weight and a. 72.95 kPa b. 72.26 kPa
specific volume c. 71.43 kPa d. 72.61 kPa
Situation 30: A 325 L of carbon Manometry
tetrachloride weighs 500 kg. Situation 32: A piezometer column
958. Which of the following most mercury manometer and a pressure
nearly given its density? gage are connected to a tank of water.
a. 1.850.60 kg/m3 The top of the water is pressured air.
b. 2,010.29 kg/m3 See figure:
c. 1,538.46 kg/m3
d. 1,774.32 kg/m3
959. Which of the following most
nearly gives its specific weight?
a. 19.72 kN/m3 Air
b. 15.09 kN/m3
c. 17.41 kN/m3 Water
d. 18.15 kN/m3 4m
960. Which of the following most A
nearly gives its specific gravity?
a. 1.54 b. 1.77 1m
c. 1.85 d. 2.01
Hydrostatic Pressure
Situation 31: A closed tank with
pressure gages tapped into it at three Mercury
different elevations contains air, oil
and water as shown in the figure 964. If the pressure at A is 85 kPa,
how high will the water rise in the
0.50 m Air piezometer column at the left?
50 kPa
a. 4.00 m b. 6.23 m
A
c. 5.52 m d. 8.66 m
1m
Oil 965. Which of the following nearly
gives the reading in the pressure
58.53 kPa
0.50 m B
gage?
a. 37.72 kPa b. 35.23 kPa
1m c. 45.76 kPa d. 39.24 kPa
Water 966. Which of the following most
nearly gives the mercury in the
C
manometer?
961. Which of the following most a. 0.71 m b. 0.60 m
nearly gives the specific weight of the c. 0.52 m d. 0.45 m
oil? Hydrostatic Force
a. 7.83 kN/m3 Hydrostatic Force on Plane Surface
b. 8.53 kN/m3 Situation 33: A rectangular gate 1.50
c. 6.18 kN/m3 m wide and 4 m high supports oil (S =
d. 9.23 kN/m3 0.80 whose liquid surface is exposed
962. Which of the following most to a constant pressure of -10 kPa as
nearly gives the specific gravity of the shown in the figure. The top of the
oil? gate is hinged and the bottom is kept
a. 0.94 b. 0.63 closed by a stop.
c. 0.87 d. 0.80
971. If the flashboard is pivoted at the
Hinge location determined above and the
water surface is 1 m below M. which of
P = -10 kPa the following most nearly gives the
horizontal reaction at B?
a. 86.25 kN/m b. 77.39 kN/m
c. 62.30 kN/m d. 95.12 kN/m
972. Which of the following most
Oil nearly gives the reaction at N?
4m
a. 15.23 kN/m b. 19.75 kN/m
c. 16.12 kN/m d. 17.59 kN/m
Stop Hydrostatic Force on Curved
Surface
Situation 35: In the figure, surface
967. Which of the following most AB is a quarter arc with radius of 2 m
nearly gives the total hydrostatic and a width of 1 m. The fluid above
pressure acting on the gate? surface AB is water at a depth of 2 m
a. 54.67 kN b. 34.18 kN and above the water is oil of depth 4
c. 43.58 kN d. 57.72 kN m. Atmospheric pressure prevails on
968. Which of the following most the free surface of oil and on the
nearly gives the distance of the total bottom side of surface AB.
hydrostatic pressure measured from
the hinge?
a. 3.84 m b. 2.13 m
c. 2.85 m d. 3.25 m
969. Which of the following most Oil (S = 0.80)
4m
nearly gives the reaction at the stop?
a. 46.25 kN b. 38.61 kN
c. 41.50 kN d. 32.78 kN
Situation 34: In the figure, B
2m
rectangular flashboard MN shown in
cross section (a = 5.40 m) is provided Water
at B.
M
A
973. Which of the following most
nearly gives the horizontal component
a B of the total hydrostatic pressure acting
on surface AB?
a. 82.40 kN b. 109.32 kN
c. 78.58 kN d. 98.14 kN
N 974. Which of the following most
nearly gives the vertical component of
the total hydrostatic acting on surface
970. Which of the following most AB?
nearly gives the maximum height f B a. 78.57 kN b. 93.60 kN
above N if the flashboard is on the c. 76.69 kN d. 91.55 kN
verge of tipping when the water 975. Which of the following most
surface rises to M? nearly gives the total hydrostatic
a. 1.80 m b. 1.50 m pressure acting on surface AB?
c. 1.70 m d. 1.60 m a. 120.65 kN b. 133.54 kN
c. 125.72 kN d. 124.70 kN
Buoyancy 980. Which of the following most
Situation 36: An object 75 N when nearly gives the tension T that is
submerged in oil (S = 0.80) and a needed to hold the sphere in place?
force of 100 N is required to hold it a. 1.93 kN b. 3.15 kN
submerged in mercury. c. 2.08 kN d. 2.46 kN
976. Which of the following most 981. Which of the following most
nearly gives the weight of the object? nearly gives the reaction on the pivot?
a. 85.94 N b. 72.13 N a. 1.05 kN b. 1.20 kN
c. 95.06 N d. 64.79 N c. 0.75 kN d. 0.80 kN
977. Which of the following most Hydraulic Dam
nearly gives the volume of the object? Situation 38: The vertical face of a
a. 0.00125 m3 b. 0.00139 m3 trapezoidal concrete dam (S = 2.40)
c. 0.00096 m3 d. 0.00214 m3 supports water to a depth of 16 m.
978. Which of the following most Uplift pressure at the base of the dam
nearly give the specific gravity of the varies from full hydrostatic pressure at
object? the heel to zero at the toe. The total
a. 5.21 b. 6.29 height of the dam is 18 m. Upper base
c. 6.62 d. 7.16 width is 1.50 m, and the bottom base
Situation 37: A solid of diameter 1m width is unknown.
and average mass density of 780 982. Which of the following most
kg/m3 is completely submerged in a nearly gives the minimum safe bottom
tank filled with water. It is held is base of the dam if the factor of safety
place by a string attached to the against overturning is 1.60?
bottom of the tank, as shown. The a. 13.15 m b. 12.03 m
mass distribution inside the sphere is c. 11.06 m d. 10.40 m
non-uniform, so the center of mass 983. Which of the following most
lies at a distance 0.50R from the nearly gives the factor safety against
geometric center. Suppose that the sliding if the coefficient of friction
sphere is attached rigidly to massless between the soil and the base of the
horizontal rod of length 0.75 m and dam is 0.75 using the calculated base
negligible volume oriented along the in the previous question?
line formed by the center of mass and a. 1.15 b. 1.25
the geometric center of the sphere, as c. 1.05 d. 1.00
shown. The rod is attached on the side 984. Which of the following most
of the sphere nearer the center of nearly gives the maximum stress that
mass, and the far end of the rod is is likely to occur at the toe of the
attached to a fixed pivot. dam?
a. 159.90 kPa b. 34.38 kPa
c. 284.60 kPa d. 65.20 kPa
Thin-walled Pressure Vessels
CM Situation 39: An open cylindrical
R
wood stave tank having a a diameter
of 2 m and height of 4 m is full of
0.75 m
water. The upper and lower ends of
T the tank are held by hoops.
985. Which of the following most
979. Which of the following most
nearly gives the tensile force on the
nearly gives the force acting on the
upper end hoop?
sphere?
a. 52.32 kN b. 39.24 kN
a. 6.12 kN b. 5.14 kN
c. 26.16 kN d. 78.48 kN
c. 7.05 kN d. 4.97 kN
986. Which of the following most
nearly gives the tensile force on the
lower end hoop?
a. 52.32 kN b. 39.24 kN 0.80 m from the center of the bottom
c. 26.16 kN d. 78.48 kN of the tank?
987. If the lower end hoop remains a. 7.81 rpm b. 16.82 rpm
on its position, at what distance should c. 74.58 rpm d. 50.94 rpm
the other hoop be placed from the Orifice
upper end of the tank so that both Falling Head
hoops will experience the same Situation 41: The water in a vertical
amount of tensile force? cylindrical tank is lowered by an orifice
a. 2.67 m b. 1.67 m from elevation 3 m to elevation 2.50
c. 1.98 m d. 2.98 m m in 70 seconds. The orifice is located
Relative Equilibrium at the bottom of the tank with
Vertical Translation elevation 0 m.
988. An unbalanced vertical force of 993. When the water level is initially at
60 lb upward accelerates 1.55 ft3 of elevation 3 m, which of the following
water. If the water is 3 ft deep in a most nearly gives the time required
cylindrical tank, which of the following discharging half of its contents?
most nearly gives the force acting on a. 182.58 sec b. 205.82 sec
the bottom of the tank? c. 215.72 sec d. 235.31 sec
a. 156.72 lb b. 187.27 lb 994. When the water level is initially at
c. 131.04 lb d. 116.33 lb elevation 3 m, which of the following
Horizontal translation most nearly gives the time required to
989. An open tank 30 ft long by 4 ft discharge all the contents?
wide by 4 ft deep is filled with 3.25 ft a. 713.06 sec b. 803.40 sec
of oil (S 0.822). It is accelerated c. 850.72 sec d. 629.60 sec
uniformly from rest to 45 ft/s along its 995. IF the tank is accelerated upward
length. Which of the following most at 12 m/s2, which of the following
nearly gives the shortest time in which most nearly gives the time required to
the tank may be accelerated without discharge all the contents when the
spilling any oil? water level is initially at elevation 3 m?
a. 27.95 sec b. 30.42 sec a. 400.15 sec b. 309.34 sec
c. 23.70 sec d. 25.81 sec c. 440.53 sec d. 538.82 sec
Rotation Weir
Situation 40: A vertical cylindrical Falling head
tank 3 m in diameter and 5 m high Situation 42: A V-notch weir is
is full of water. located at one end of a tank having a
990. Which of the following most horizontal square section 12 m x 12
nearly gives the angle with the vertical m. The intial head of the water is 1.80
that the tank must be titled so that 10 m and it takes 77 seconds to discharge
m3 of water is spilled? 144 m3 of water. The coefficient of
a. 43.320 b. 33.690 discharge is 0.60.
0
c. 46.68 d. 56.310 996. Which of the following most
991. IF the tank is to be rotated about nearly gives the vertex angle of the
its axis, which of the following most weir?
nearly gives the required angular a. 72.390 b. 81.780
0
velocity so that the water profile just c. 77.04 d. 87.800
touches the bottom of the container? 997. Which of the following most
a. 63.05 rpm b. 26.39 rpm nearly gives the initial discharge over
c. 6.60 rpm d. 49.07 rpm the weir?
992. If the tank is to be rotated about a. 5.33 m3/s b. 5.84 m3/s
its axis, which of the following most c. 4.47 m3/s d. 4.90 m3/s
nearly gives the required angular 998. Which of the following most
velocity so that there is no water with nearly gives the instantaneous
discharge after 77 seconds?
a. 0.64 m3/s b. 0.70 m3/s respectively. The diameter of the pipe
c. 0.59 m3/s d. 0.77 m3/s is 60 mm. Assume the flow is laminar.
Pipe Flow 1005. Which of the following most
Major Losses in Pipes nearly gives the head loss along the
Situation 43: Water is pumped pipe segment?
through a 500 mm diameter circular a. 4.90 m b. 3.77 m
pipe which is 800 m long at a velocity c. 6.10 m d. 5.35 m
of 2 m/s. 1006. Which of the following most
999. Which of the following most nearly gives the discharge?
nearly gives the head loss using a. 2.08 m/s b. 2.95 m/s
Darcy-Weisbach equation if f = 0.02? c. 3.37 m/s d. 2.70 m/s
a. 6.25 m b. 5.62 m 1007. Which of the following most
c. 6.52 m d. 5.26 m nearly gives the Reynolds Number?
1000. Which of the following most a. 855 b. 810
nearly gives the head loss using c. 824 d. 1.011
Manning’s formula the n = 0.013? Pipe Networks
a. 8.56 m b. 7.56 m Situation 46: The total head loss from
c. 7.65 m d. 8.65 m A to E in the pipe system shown in the
Reynolds Number figure below is 15 m. Assume f = 0.02
Situation 44: Medium fuel oil having for all pipes. Useful properties of the
an absolute viscosity of 6.55 x 10-5 pipes are given in the following table:
ft2/s flows in a steel pipe 4, 100 ft long 1 2 5
at a maximum rate of 0.210 cfs.
1001. Which of the following most
nearly gives the head loss using
Hazen-Williams formula if C = 110?
a. 7.34 m b. 7.43 m 3 4
c. 6.34 m d. 6.43 m Pipe Length (m) Diameter (m)
1002. Which of the following most 1 450 600
nearly gives the minimum diameter of 2 600 500
the pipe required to keep the flow in 3 360 450
laminar condition? 4 480 450
a. 1.95 ft b. 2.03 ft 5 540 600
c. 1.88 ft d. 2.16 ft
1003. Using the diameter obtained in 1008. Which of the following most
the previous problem, which of the nearly gives the discharge in pipe 1?
following most nearly gives the friction a. 0.677 m3/s b. 0.608 m3/s
factor of the pipe? 3
c. 0.896 m /s d. 0.485 m3/s
a. 0.032 b. 0.042 1009. Which of the following most
c. 0.051 d. 0.059 nearly gives the discharge in pipe 2?
1004. Which of the following most a. 0.561 m3/s b. 0.301 m3/s
nearly gives the head loss in the pipe? 3
c. 0.411 m s d. 0.553 m3/s
a. 0.0025 ft b. 0.0047 ft 1010. Which of the following most
c. 0.0036 ft d. 0.0050 ft nearly gives the discharge in pipe 3?
Laminar And Turbulent Flow in a. 0.335 m3/s d. 0.267 m3/s
Pipes 3
c. 0.125 m /s d. 0.486 m3/s
Situation 45: An oil with = 900 Pumps and Turbines
kg/m3 and v = 0.0002 m2/s flows Situation 47: Water is pumped at the
upward through a 10 m long pipe rate of 20 m3/s from the reservoir and
segment inclined at 400 with the out through the steel pipe, which has a
horizontal. The pressures at the constant diameter of 1.50 m. Hazen-
upstream and downstream end of the Williams constant is 100.
pipe are 350 kPa and 250 kPa
1011. which of the following most 1015. Which of the following most
nearly gives the total head loss? nearly gives the required length of
a. 22.57 m b. 42.10 m pipeline 1?
c. 35.62 m d. 48.74 m a. 3,933.16 m b. 6,108.72 m
El. 140 m c. 3,762.09 m d. 4,985.22 m
El. 100 m 300 m 1016. Which of the following most
nearly gives the elevation of water
P surface in reservoir B?
El. 95 m
a. 15.47 m b. 14.76 m
5 m suction line c. 16.35 m d. 18.20 m
Three Reservoir Problems
1012. Which of the following most Situation 49: The design of a city
nearly gives the power that must be water supply system is shown in the
supplied to the water? figure. Reservoir A needs to supply
a. 22,701.86 hp 0.0938 m3/s to lower reservoir B and
b. 13,556.18 hp C. Pipe 1 is 300 m diameter and 900
c. 18,171.83 hp m long, pipe 2 is 200 mm diameter
d. 16,935.59 hp and 387 m long, and pipe 3 is 200 mm
1013. Which of the following most diameter and 700 m long. The
nearly gives the pressure at the roughness coefficient for all pipes is
suction line? 0.011.
a. -18.68 kPa b. -19.35 kPa A
c. -17.51 kPa d. -16.75 kPa El. 150 m
Reservoir Problems B
Two Reservoir Problems 1 2
Situation 48: The total flow from El. 140 m
reservoir A in the figure is 0.394 m3/s 3
and the discharge from pipe 4 is 0.254 C
m3/s. 1017. Which of the following most
El. 43 m nearly gives the flow rate in pipe 2?
a. 0.0684 m3/s b. 0.0500 m3/s
A c. 0.0391 m3/s d. 0.0566 m3/s
1018. Which of the following most
1 El. B nearly gives the flow rate in pipe 3?
2 3 a. 0.0254 m3/s b. 0.0438 m3/s
c. 0.0547 m3/s d. 0.0372 m3/s
1019. Which of the following most
4 nearly gives the elevation of water
El. 14 m
surface in reservoir A to supply the
needed flow rate?
Pipe Length Diameter Friction a. 160.00 m b. 145.40 m
(m) (mm) Factor c. 155.96 m d. 147.11 m
1 430 0.020 Open Channel Flow
2 3,500 450 0.020 Manning’s Formula
3 4,600 400 0.018 Situation 50: A trapezoidal channel
4 4,500 500 0.019 with uniform flow has a normal depth
of 2 m. The base width is 5 m and the
1014. Which of the following most sides slope at 2H:1V. Manning’s n can
nearly gives the velocity of flow along be taken as 0.015 and the bed slope is
pipe 2? 0.001.
a. 1.34 m/s b. 1.81 m/s 1
3 10 m 2.50 m 4m
c. 4.89 m/s d. 3.62 m/s 10 m 1
2 5m
1020. Which of the following most 1026. Which of the following most
nearly gives the velocity? nearly gives the slope if the flow rate
a. 2.50 m/s b. 3.15 m/s is 663 cfs?
c. 3.73 m/s d. 2.75 m/s a. 0.0006 b. 0.0004
1021. Which of the following most c. 0.0005 d. 0.0003
nearly gives the discharge? 1027. Which of the following most
a. 44.99 m/s b. 55.29 m/s nearly gives the critical depth?
c. 67.65 m/s d. 36.07 m/s a. 4.57 ft b. 5.32 ft
1022. If the channel in the above c. 6.09 ft d. 2.65 ft
problem were to be designed for 1028. Which of the following most
flooding it may have a section as nearly gives the critical velocity?
shown in the figure. When the flow a. 5.98 ft/s b. 8.01 ft/s
goes over the top of the trapezoidal c. 7.49 ft/s d. 9.58 ft/s
channel it moves to the “flood plains” Efficient Sections
so the section allows for a lot more Situation 53: water flows in a
discharge to be carried. IF the flood trapezoidal channel whose bottom
channels are 10 m wide, have side width is 2.50 m. One side of the
slopes of 3:1, and Manning’s n of channel is vertical and the other is
0.035, calculate the discharge for a inclined at 450. The slope of the
flood level of 4 m. channel is 0.002 and n = 0.011.
a. 243.76 m3/s b. 114.50 m3/s 1029. Which of the following most
c. 267.21 m3/s d. 160.36 m3/s nearly gives the depth of flow for most
Non Uniform Flow efficient section?
Situation 51: A rectangular flume of a. 1.576 m b. 1.768 m
planed timber (n = 0.012) is 5 ft wide c. 1.845 m d. 1.621 m
and carries 60 cfs of water. The bed 1030. Using the depth obtained in the
slope is 0.0006. At a certain section previous problem, which of the
the depth is 3 ft and at another section following most nearly gives the value
the depth is 2.50 ft. of the hydraulic radius?
1023. Which of the following most a. 0.884 m b. 0.811 m
nearly gives the slope of the energy c. 0.923 m d. 0.788 m
line between the two sections? 1031. Which of the following most
a. 0.00088 b. 0.00065 nearly gives the rate of flow?
c. 0.00033 d. 0.00042 a. 17.97 m3/s b. 18.97 m3/s
1024. Which of the following most c. 24.33 m3/s d. 22.40 m3/s
nearly gives the distance between the Hydraulic Jump
two sections? Situation 54: A hydraulic jump occurs
a. 1,376.43 ft b. 1,542.16 ft in an efficient triangular channel
c. 1,400.70 ft d. 1,321.70 ft carrying 8 m3/s on a slope of 0.006.
1025. Which of the following most The depth after the jump is 2.96 m.
nearly gives the head loss between the 1032. Which of the following most
two sections? nearly gives the depth before the
a. 1.06 ft b. 0.89 ft jump?
c. 1.18 ft d. 1.23 ft a. 0.952 m b. 0.843 m
Alternate Depths of Flow in Open c. 0.654 m d. 0.732 m
Channels 1033. Which of the following most
Critical Flow nearly give the loss of energy in the
Situation 52: Water flows at a depth jump?
of 6ft in a trapezoidal concrete-lined a. 3.17 m b. 5.40 m
channel having a side slope of 2:1 and c. 4.31 m d. 2.56 m
base width of 6 ft. Use n = 0.012. 1034. Which of the following most
nearly gives the loss of the power in
the jump?
a. 243.06 kW b. 196.38 kW
c. 424.29 kW d. 338.37 kW
You might also like
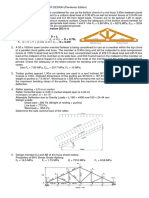
- Feu Hydraulics PreboardDocument2 pagesFeu Hydraulics PreboardEla Macabante100% (1)
- 115Document10 pages115Memo LyNo ratings yet
- Eview Nnovations May 2022 Ce Board Exam RENDON 6 (Hydraulics)Document3 pagesEview Nnovations May 2022 Ce Board Exam RENDON 6 (Hydraulics)Kian InductivoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech May 2021Document5 pagesFluid Mech May 2021Naigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Timber Design (Pandemic Edition)Document2 pagesFinal Exam Timber Design (Pandemic Edition)darlene zaraNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Document4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Yoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- Refresher Course Module - Structural Engineering: Hakuna Matata"Document1 pageRefresher Course Module - Structural Engineering: Hakuna Matata"Mohammad Hussein Masiu BacaramanNo ratings yet
- Refresher STEEL 4 Nov 2022Document2 pagesRefresher STEEL 4 Nov 2022emielyn lafortezaNo ratings yet
- Steel 3Document3 pagesSteel 3Mayya Bona100% (1)
- Structural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)Document4 pagesStructural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)ELMERNo ratings yet
- Review Module 45-RCD 5 - Part 1 & 2Document2 pagesReview Module 45-RCD 5 - Part 1 & 2Arlyn ConsumeNo ratings yet
- Quiz 6Document1 pageQuiz 6Nikki Marie G OclaritNo ratings yet
- 4 Flexural Members PDFDocument9 pages4 Flexural Members PDFCristan RetuermaNo ratings yet
- Review Module: - Strength of Materials 1 Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module: - Strength of Materials 1 Part 1John andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- Hydro Geo Online Preboard Questionnaire PDFDocument6 pagesHydro Geo Online Preboard Questionnaire PDFCarl Justin AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Tos 2Document4 pagesTos 2Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodiesdonald escalanteNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDocument1 pageRefresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsMadelyn OronosNo ratings yet
- Psad - 16Document2 pagesPsad - 16SamNo ratings yet
- Geotech 8Document18 pagesGeotech 8Bemzar SamsonNo ratings yet
- Sec - PS1Document2 pagesSec - PS1Monica Amor AbengozaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledRojane FloraNo ratings yet
- November 2023 - PSAD 1Document2 pagesNovember 2023 - PSAD 1Viele Antonette NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Geo ProbsDocument2 pagesGeo Probsadonis bibatNo ratings yet
- RC 3Document4 pagesRC 3Jade David FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam Geo Nov 2021Document10 pagesEvaluation Exam Geo Nov 2021Yedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- Design 1qsy1718 QuestionsDocument9 pagesDesign 1qsy1718 QuestionsRachel Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Refresher GEO Part1Document2 pagesRefresher GEO Part1Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Design and Const2Document101 pagesDesign and Const2Sigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- Inhinyero Review CenterDocument2 pagesInhinyero Review CenterVincent NavaNo ratings yet
- Topics Problem Set 9 - Structural Theory (Final) 1ST Term 2020-2021Document1 pageTopics Problem Set 9 - Structural Theory (Final) 1ST Term 2020-2021Levi John Corpin AmadorNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 3: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 3: Eview NnovationsKian InductivoNo ratings yet
- Sec - Forces and Principles of Equilibrium Module 00Document6 pagesSec - Forces and Principles of Equilibrium Module 00jovar jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 5 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesPolicarpio 5 - Refresher SECMigaea100% (1)
- Review Module 44 Part 2 (PCD - WSD)Document1 pageReview Module 44 Part 2 (PCD - WSD)Juan Miguel PinedaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Strema Part 3Document3 pagesPractice Problems - Strema Part 3Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- File 1582710448 PDFDocument5 pagesFile 1582710448 PDFNatasha Marie MallareNo ratings yet
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 7 - Soil Testing, Foundations, Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Document6 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 7 - Soil Testing, Foundations, Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Steel PDFDocument3 pagesSteel PDFCj Delos Reyes Macanas100% (1)
- Hyd - 7Document2 pagesHyd - 7SamNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document3 pagesQuiz 4Nikki Marie G OclaritNo ratings yet
- Q P A Q 1600 4 (4) Q 100 Kpa: SolutionDocument8 pagesQ P A Q 1600 4 (4) Q 100 Kpa: SolutionFrancis John BuacNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: Soil CDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam: Soil CKathlyn Mae BeberinoNo ratings yet
- Colloids: B. 3529 A.4393 LB D. 1471Document3 pagesColloids: B. 3529 A.4393 LB D. 1471Jason RamosNo ratings yet
- April 2024 - PSAD 2Document2 pagesApril 2024 - PSAD 2rando12345No ratings yet
- PSAD 1 May 2 2023Document21 pagesPSAD 1 May 2 2023Renne Jude RollorataNo ratings yet
- Foundationxpart 1Document3 pagesFoundationxpart 1Haydeesheen SisonNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center: 2 Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, ManilaDocument2 pagesF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center: 2 Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, ManilaBluezed14No ratings yet
- Quiz No 1Document2 pagesQuiz No 1Tris ZackNo ratings yet
- 2023april Psad UnlockedDocument6 pages2023april Psad UnlockedKristelle V. TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringDocument1 pageRefresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringMadelyn Oronos100% (1)
- Topic 3 - Allowable StressesDocument20 pagesTopic 3 - Allowable StressesMohammad Taha PumbayaNo ratings yet
- CE527 Correlation Course Structural Engi PDFDocument2 pagesCE527 Correlation Course Structural Engi PDFjunNo ratings yet
- Eval 2 FinalDocument4 pagesEval 2 FinalGreg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- Stdl02e Final ExamDocument6 pagesStdl02e Final ExamPaulo ValderamaNo ratings yet
- WORK OUT 4b - Bolted, Riveted & Welded Connections PDFDocument1 pageWORK OUT 4b - Bolted, Riveted & Welded Connections PDFJeyvie Cabrera OdiameNo ratings yet
- 603 CompreDocument15 pages603 CompreCj SuarezNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingFrancis Philippe CariñoNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Activity No. 1Document6 pagesIrrigation Activity No. 1Jeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Economics VITDocument201 pagesEconomics VITCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Chuck Used On Turret Lathe Is A. Collet Chuck B. Four Jaw Self Centering Chuck C. Magnetic Chuck D. Three Jaw Independent ChuckDocument183 pagesChuck Used On Turret Lathe Is A. Collet Chuck B. Four Jaw Self Centering Chuck C. Magnetic Chuck D. Three Jaw Independent ChuckCaro Kan Lopez100% (1)
- Deophantine 6Document169 pagesDeophantine 6Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Deophantine 3 ProblemsDocument104 pagesDeophantine 3 ProblemsCaro Kan Lopez0% (1)
- Deophantine 5 ProblemsDocument60 pagesDeophantine 5 ProblemsCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Simple Mechanical Machine With The Ability To Increase An Applied Force?Document105 pagesWhich of The Following Simple Mechanical Machine With The Ability To Increase An Applied Force?Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Deophantine 5Document86 pagesDeophantine 5Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Deophantine 1 ProblemsDocument69 pagesDeophantine 1 ProblemsCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Deophantine 6 ProblemsDocument231 pagesDeophantine 6 ProblemsCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- MDSPDocument33 pagesMDSPCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Steam ProblemsDocument10 pagesSteam ProblemsCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- MDSP 5Document215 pagesMDSP 5Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Plane - Solid GeometryDocument16 pagesPlane - Solid GeometryCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Deophantine 1Document134 pagesDeophantine 1Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Machine Designs Problems/ElementsDocument263 pagesMachine Designs Problems/ElementsCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Machine Designs Problems/ElementsDocument263 pagesMachine Designs Problems/ElementsCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Set 18 3Document19 pagesSet 18 3Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous & Recent Board Problems: Set 18-Miscellaneous & Part 5-Structural Steel DesignDocument2 pagesMiscellaneous & Recent Board Problems: Set 18-Miscellaneous & Part 5-Structural Steel DesignCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Set 19 3Document6 pagesSet 19 3Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Set 19 6Document6 pagesSet 19 6Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus ExamDocument6 pagesDifferential Calculus ExamCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- CE522 Problem Manual 1-1 PDFDocument2 pagesCE522 Problem Manual 1-1 PDFMarc Martiniano Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Powertech ™ 6068afm85 Diesel Engine: Marine Generator Drive Engine SpecificationsDocument2 pagesPowertech ™ 6068afm85 Diesel Engine: Marine Generator Drive Engine SpecificationsElton FloresNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Construction, Repair & Modification Mock Board Exam 10Document5 pagesAircraft Construction, Repair & Modification Mock Board Exam 10July TadeNo ratings yet
- 9883511790ENUWADocument8 pages9883511790ENUWAhalexNo ratings yet
- Ansys FENSAP-ICE Tutorial Guide 2022 R2Document692 pagesAnsys FENSAP-ICE Tutorial Guide 2022 R2ajkNo ratings yet
- Friction Factor For Turbulent Pipe Flow: January 2006Document17 pagesFriction Factor For Turbulent Pipe Flow: January 2006John AnthoniNo ratings yet
- Fiber Metal LaminatesDocument224 pagesFiber Metal Laminatesyaswanth1992100% (1)
- Elastic Deformations Basic Knowledge - English PDFDocument1 pageElastic Deformations Basic Knowledge - English PDFMuhammad Naseem Ishaq /ME Lab EngineerNo ratings yet
- V2500 & CFM56 Difference PDFDocument5 pagesV2500 & CFM56 Difference PDFBahador100% (3)
- Operation and Maintenance Manual PDFDocument102 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual PDFdjpolhn1750% (2)
- Cat 3516E: Diesel Generator SetsDocument4 pagesCat 3516E: Diesel Generator Setsavinash_1229No ratings yet
- AIChE Wilhelm April 08 Process SafetyDocument16 pagesAIChE Wilhelm April 08 Process Safetymostafa_1000No ratings yet
- Pre Order Contract Review /enquiry No.: Infused Systems PVT LTDDocument3 pagesPre Order Contract Review /enquiry No.: Infused Systems PVT LTDSales Infused SystemsNo ratings yet
- STP 559-1974Document319 pagesSTP 559-1974Tim SchouwNo ratings yet
- ABS Ship SFA Guide - e Dec07Document46 pagesABS Ship SFA Guide - e Dec07Advan ZuidplasNo ratings yet
- Lloyd S Register Energy Guidance Notes For Risk Based Ana PDFDocument22 pagesLloyd S Register Energy Guidance Notes For Risk Based Ana PDFankitalalwaniNo ratings yet
- PVC-PP-PVDF Swing Check Valve SpecificationsDocument4 pagesPVC-PP-PVDF Swing Check Valve SpecificationsthangNo ratings yet
- Gek - 84745d Manual Servicio Motor de Traccion DCDocument246 pagesGek - 84745d Manual Servicio Motor de Traccion DCEdinhoBelloRamos100% (3)
- General Tolerances For MN: MAN Nutzfahrzeuge AG Works Standard Accuracy of ShapeDocument3 pagesGeneral Tolerances For MN: MAN Nutzfahrzeuge AG Works Standard Accuracy of ShapeAkmal Nizametdinov100% (1)
- A Practical Method For Statistical Analysis of Strain-Life Fatigue DataDocument10 pagesA Practical Method For Statistical Analysis of Strain-Life Fatigue DatabloomdidoNo ratings yet
- Irmra Report BilalDocument47 pagesIrmra Report BilalAhmar KhanNo ratings yet
- нтн бомбіровані з фланцем PDFDocument45 pagesнтн бомбіровані з фланцем PDFVolodymyrNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar 3300hp Marine EngineDocument3 pagesCaterpillar 3300hp Marine Enginejinxy5779No ratings yet
- Turbo CompoundDocument29 pagesTurbo CompoundDIONYBLINKNo ratings yet
- Suction Specific SpeedDocument11 pagesSuction Specific Speeddhanu_aqua100% (1)
- Power Calculations: Design ParametersDocument4 pagesPower Calculations: Design ParametersDhirender KapoorNo ratings yet
- Audi Self Study ProgramDocument76 pagesAudi Self Study ProgramJorge Gonzalez Perez100% (1)
- Edbase Dhanmondi: Edx Olp Worksheet 1 - Motion and Graphs: (1 Mark) (1 Mark)Document8 pagesEdbase Dhanmondi: Edx Olp Worksheet 1 - Motion and Graphs: (1 Mark) (1 Mark)Munavi Bin Zaman Mbz100% (1)
- Tractor 75 HPDocument329 pagesTractor 75 HPVipul100% (1)
- 0400-0004-092013 Mini-VentDocument1 page0400-0004-092013 Mini-VentFrancisco Aldunate AllegroNo ratings yet