Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Cavity - Inferior and Anterior Walls (Including Clinical Significance)
Uploaded by
Andra BauerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oral Cavity - Inferior and Anterior Walls (Including Clinical Significance)
Uploaded by
Andra BauerCopyright:
Available Formats
26.
Oral cavity – Inferior and anterior walls (including clinical significance)
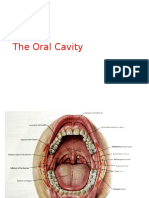
INFERIOR WALL
- It’s not the tongue.
- It is a small u-shaped region situated beneath the moveable
tongue and above the diaphragm formed by mylohyoid
muscle.
- Mylohyoid together with anterior belly of digastric will also
support in opening of the jaw.
- Mylohyoid = innervated by the nerve to mylohyoid (from
mandibular)
- Anterior belly of the digastric = innervated by the facial
nerve (post. belly) and by the nerve to mylohyoid (ant. belly)
- They also elevate the hyoid bone and move it forward
during swallowing.
FLOOR OF THE ORAL CAVITY
- On floor of the oral cavity we can find the sublingual papilla/caruncle or Wharton duct,
where the ducts of the sublingual gland and submandibular gland open into.
- The frenulum of the tongue is continuous with the mucosa of the oral floor.
- The floor of the mouth is highly vascularized, lingual veins and arteries can be distinguished.
- #C.S. Some drugs can be rapidly absorbed through the thin mucosa of the floor of the
mouth, also alcohol.
- Medial to the vein the lingual artery - supplies genioglossus.
- In the same region the hypoglossal nerve and lingual nerve.
ANTERIOR WALL
- Anteriorly, the oral cavity = bounded by the lips and the oral
orifice.
- The orbicularis oris forms their bulk.
- They upper and lowers lips meet each other at the angle of the
mouth.
- Each of the lips is attached at its midpoint to the gingiva by the
frenulum.
- The upper frenulum is more prominent than lower.
- The transition between the facial skin and the oral mucous membrane occurs in the
vermilion border.
The lip consists of labial glands that helps in moisturizing the oral mucosa, these can be
distinguished by rolling your tongue along the lips and you will feel small “round shapes”.
These glands do not support the external lip at “vermillion border” and that’s why we have
to “lick our lips”.
The oral mucosa is stratified squamous epithelium just like vocal cords and part of
epiglottis.
The oral mucosa is thicker than the skin in order to maintain protection, but also because
the skin has other compounds such as sweat glands and hair follicles.
Salivary gland, Sublingual and Submandibular glands, provide ducts to inferior wall of
oral cavity.
Sublingual gland- mucosa producing gland.
Submandibular gland – Serous and mucosa producing gland
You might also like
- Mouth & Oral CavityDocument28 pagesMouth & Oral CavityButool FatimaNo ratings yet
- Teeth, Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument12 pagesTeeth, Tongue and Salivary GlandsGideon WillieNo ratings yet
- Vascular Supply and Innervation - The Cheeks Receives Its Arterial Blood SuppluDocument5 pagesVascular Supply and Innervation - The Cheeks Receives Its Arterial Blood SuppluSimina TanaseNo ratings yet
- L. 10 The Oral CavityDocument79 pagesL. 10 The Oral CavityAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- Mulut, Faring, LaringDocument76 pagesMulut, Faring, LaringNiddy Rohim FebriadiNo ratings yet
- RT Basics Digestive SystemDocument88 pagesRT Basics Digestive Systemmaricar paracadNo ratings yet
- The MouthDocument16 pagesThe MouthNiño GarciaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument177 pagesDigestive Systemarham.yousafzaiNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument44 pagesTongueSidhartha BordoloiNo ratings yet
- The TongueDocument7 pagesThe Tonguemanojchouhan2014No ratings yet
- Histologi Saluran CernaDocument57 pagesHistologi Saluran CernaAdinda TobingNo ratings yet
- Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco: División Académica Multidisciplinaria de ComalcalcoDocument10 pagesUniversidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco: División Académica Multidisciplinaria de ComalcalcoMayra Elizabeth LiñaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Oral CavityDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity28 manan patelNo ratings yet
- SplanchoDocument77 pagesSplanchoDr Ankit yadavNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument98 pagesOral CavitynicewanNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument19 pagesOral CavityProy DCNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Histology of The Oral Cavity2 3Document31 pagesAnatomy Histology of The Oral Cavity2 3drsondosNo ratings yet
- W2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFDocument69 pagesW2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFSAHIL AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Oral MucosaDocument36 pagesOral MucosaSiphiwe MayindiNo ratings yet
- EssaysDocument176 pagesEssaysppdzssx7ghNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Part 1Document38 pagesDigestive System Part 1mozajamil777No ratings yet
- Amirhossein Vaezi MS121 Oral CavityDocument27 pagesAmirhossein Vaezi MS121 Oral Cavityamirhossein vaeziNo ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- Assignment Structure of Oral CavityDocument4 pagesAssignment Structure of Oral CavityNarjis BatoolNo ratings yet
- Oral Anatomy NotesDocument20 pagesOral Anatomy NotesMyrian V. Legaspi100% (1)
- Digestive System at Head and NeckDocument8 pagesDigestive System at Head and NeckArinaNo ratings yet
- Dentistry Section From Slatter - Textbook of Small Animal SurgeryDocument80 pagesDentistry Section From Slatter - Textbook of Small Animal Surgerymmatthew74No ratings yet
- Tongue I LastDocument30 pagesTongue I LastEmuyeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemchipsNo ratings yet
- Digestive Tract: Esophagus, Stomach, Small and Large Intestines, Rectum, and Anus and ItsDocument10 pagesDigestive Tract: Esophagus, Stomach, Small and Large Intestines, Rectum, and Anus and Itsحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (18)
- Histologi Saluran CernaDocument57 pagesHistologi Saluran CernaAdinda TobingNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFshagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- Oral Physiology and OcclusionDocument64 pagesOral Physiology and OcclusionFrances SyNo ratings yet
- ASSESSING MOUTH, THROAT, NOSE and SINUSESDocument13 pagesASSESSING MOUTH, THROAT, NOSE and SINUSESKenneth Andre Batuyog TecsonNo ratings yet
- TONGUEDocument63 pagesTONGUEAthulya LakshmananNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument79 pagesOral CavityueumanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document7 pagesLecture 12rahaf alshoumaryNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of The Nose and MouthDocument68 pagesParts and Function of The Nose and MouthMireya Ysadel O. DulayNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument162 pagesTongueDevendra ChhonkarNo ratings yet
- Mammalian System-01 (Digestive System)Document35 pagesMammalian System-01 (Digestive System)Saumya99No ratings yet
- 01 Oral Cavity Anatomy DR Sharmistha RoyDocument100 pages01 Oral Cavity Anatomy DR Sharmistha RoyOshydh PojnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (Oral Cavity) DR DoaaDocument40 pagesLecture 1 (Oral Cavity) DR DoaakhaledNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Anatomy I Splanchnology 1Document17 pagesModule 5 Anatomy I Splanchnology 1neannaNo ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- AzmizDocument174 pagesAzmizEthio Dangote TubeNo ratings yet
- Intraoral Soft Tissue Anatomy: Morphology 115Document57 pagesIntraoral Soft Tissue Anatomy: Morphology 115Asrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- L1) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueDocument39 pagesL1) Oral Cavity, Palate and Tongue3amroooni.a.aNo ratings yet
- 2-Oral Clinical ExaminationDocument13 pages2-Oral Clinical Examinationyahia salahNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (Final)Document164 pagesDigestive System (Final)aubrey alcantaraNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument106 pagesDigestive SystemUnboxthings 9No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument67 pagesDigestive SystemShacquille Suelto Bautista0% (1)
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- 14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalDocument50 pages14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalSudeep DhakalNo ratings yet
- ORAL CAVITY (Mouth Cavity) : MR Kukiriza JohnDocument54 pagesORAL CAVITY (Mouth Cavity) : MR Kukiriza JohnTrevor Ishmael SiakambaNo ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument37 pages14-Oral CavitySajid AliNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Bowel OcclusionDocument4 pagesBowel OcclusionAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Gastric PathologyDocument11 pagesGastric PathologyAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Venous Thromboembolic DiseaseDocument27 pagesVenous Thromboembolic DiseaseAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- TUBERCULOSISDocument9 pagesTUBERCULOSISAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- 1 HematopoiesisDocument8 pages1 HematopoiesisAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Esophageal PathologyDocument8 pagesEsophageal PathologyAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- 342 Hematology Physiology Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationDocument3 pages342 Hematology Physiology Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument19 pagesAsthmaAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Ninja Nerd AnemiaDocument13 pagesNinja Nerd AnemiaAndra Bauer100% (3)
- Salivary Gland PathologyDocument11 pagesSalivary Gland PathologyAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- II.36. Hand Topography - Central Palmar RegionDocument3 pagesII.36. Hand Topography - Central Palmar RegionAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- II.12.serratus AnteriorDocument1 pageII.12.serratus AnteriorAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Tongue (Including Clinical Significance)Document3 pagesTongue (Including Clinical Significance)Andra Bauer100% (1)
- Orbit and EyeballDocument3 pagesOrbit and EyeballAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Pneumo Tot MergedDocument103 pagesPneumo Tot MergedAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Exterior and Middle EarDocument26 pagesExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- II - 51. The Parotid Salivary GlandDocument5 pagesII - 51. The Parotid Salivary GlandAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- I - 37. Heart Tube - Segments, Looping, EvolutionDocument1 pageI - 37. Heart Tube - Segments, Looping, EvolutionAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Research Paper: Valentines DayDocument1 pageResearch Paper: Valentines DayRuth EllerNo ratings yet
- Putting It All TogetherDocument3 pagesPutting It All Togetherapi-337078278No ratings yet
- LZW Fundamentals: Lempel Ziv 1977 1978 Terry Welch's 1978 Algorithm 1984Document9 pagesLZW Fundamentals: Lempel Ziv 1977 1978 Terry Welch's 1978 Algorithm 1984Vishal PatilNo ratings yet
- CHATSUMI - Score and PartsDocument2 pagesCHATSUMI - Score and PartsisadockNo ratings yet
- Translation Strategies For Pun in William Shakespeare's "King Lear"Document5 pagesTranslation Strategies For Pun in William Shakespeare's "King Lear"Academic JournalNo ratings yet
- Pasyon and RevolutionDocument8 pagesPasyon and RevolutionKurt ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Materials EvaluationDocument10 pagesMaterials EvaluationkariyetNo ratings yet
- Bowman, Egypt After The Pharaohs PDFDocument272 pagesBowman, Egypt After The Pharaohs PDFEvelyn Ciocan67% (3)
- Delhi Public School, Gomti Nagar Extn., Lucknow SESSION 2021-22 P.A. - I Syllabus Grade - Viii Sno. Subject Syllabus LiteratureDocument2 pagesDelhi Public School, Gomti Nagar Extn., Lucknow SESSION 2021-22 P.A. - I Syllabus Grade - Viii Sno. Subject Syllabus LiteratureVasu RathoreNo ratings yet
- Listening Practice - Future of Libraries PDFDocument20 pagesListening Practice - Future of Libraries PDFSanjay SahooNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument8 pagesSummaryAkashNo ratings yet
- Lect1 Intro To JavaDocument58 pagesLect1 Intro To JavaLương Tiến Dũng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- DLL English Q3 Week1Document6 pagesDLL English Q3 Week1Ma. Catherine MendozaNo ratings yet
- Drilling Q XII - Week 8.1Document6 pagesDrilling Q XII - Week 8.1a malikaNo ratings yet
- Traveller Elementary - Test 2Document2 pagesTraveller Elementary - Test 2mppetra15No ratings yet
- Mairs The Archaeology of The Hellenistic Far East: A Survey. Update 1 2013.Document24 pagesMairs The Archaeology of The Hellenistic Far East: A Survey. Update 1 2013.hcarn2016No ratings yet
- Complete The Dialogue BelowDocument2 pagesComplete The Dialogue BelowNajib Habibi100% (1)
- Joe Paulo B. Batoto: TertiaryDocument2 pagesJoe Paulo B. Batoto: TertiaryDavid Renz Pila BonifacioNo ratings yet
- First City Providential College: Bgy. Narra, Francisco Homes Subd., City of San Jose Del Monte BulacanDocument6 pagesFirst City Providential College: Bgy. Narra, Francisco Homes Subd., City of San Jose Del Monte BulacanMarilyn TamboonNo ratings yet
- Class 1 18 19 Unit 2Document17 pagesClass 1 18 19 Unit 2Saakshay JainNo ratings yet
- Malla Curricular 2018Document1 pageMalla Curricular 2018158526No ratings yet
- Word BuildingDocument2 pagesWord BuildingRaluca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Tu Elt Conference Program 2017 May 15Document3 pagesTu Elt Conference Program 2017 May 15api-285624898No ratings yet
- Howard Holzer:: Lincoln at Cooper Union: The Speech That Made Abraham Lincoln PresidentDocument8 pagesHoward Holzer:: Lincoln at Cooper Union: The Speech That Made Abraham Lincoln PresidentJohn LukezicNo ratings yet
- Electronic Medical RecordsDocument4 pagesElectronic Medical Recordsdew23No ratings yet
- Reviewer Grade 9Document2 pagesReviewer Grade 9Nelson PiconesNo ratings yet
- Soal PTS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8Document4 pagesSoal PTS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8Muhammad HaikalNo ratings yet
- PANTE - The History of English in Ten MinutesDocument3 pagesPANTE - The History of English in Ten MinutesMelissa PanteNo ratings yet
- Grammar Unit 41Document21 pagesGrammar Unit 41api-3826199100% (1)
- EtymologyDocument6 pagesEtymologyShiree ChanNo ratings yet